What does alpinia look like and how to grow it?
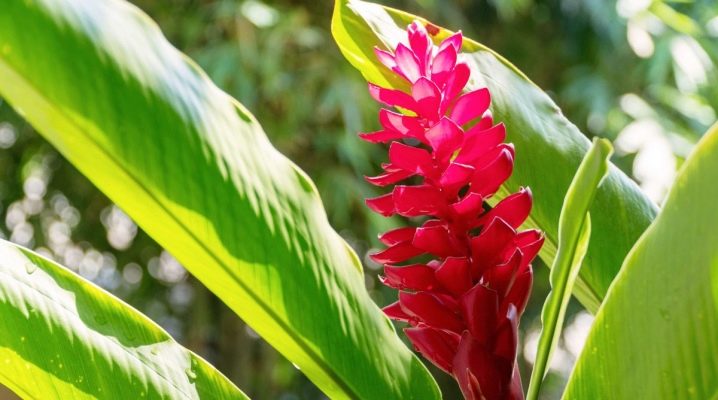

A bright representative of the ginger family, alpinia variegated and galanga, medicinal and cerumbet, purple and other species, is successfully cultivated as a houseplant. Caring for her at home is not particularly difficult, even a novice florist can handle it. Having studied the description of the existing varieties, the features of their reproduction and cultivation, you can easily provide optimal conditions for the alpinia on the indoor windowsill.

Description
The alpinia plant, traditional for Asian countries, belongs to the ginger family. This genus of herbaceous wild crops needs appropriate growing conditions, similar to the climate of subtropical and tropical zones. In total, it includes about 240 plant species.
All alpines are characterized by the following features:
-
the root is long, strongly branched, up to 1 m;
-
the central shoot is strong, reddish;
-
stems are flexible, bearing leaves and flowers, 60 to 300 cm long;
-
fruits of a box with seeds inside;
-
inflorescence-spikelet of red, yellow or white shade;
-
purple and red berries.
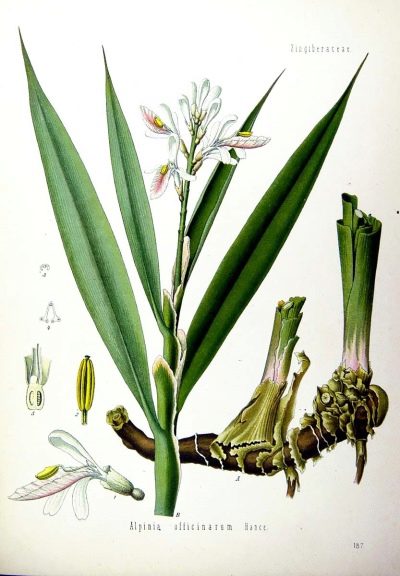
All parts of the plant are considered medicinal, rich in essential oils. Rhizomes used as spices or raw materials in pharmaceuticals are especially highly valued. Fresh leaf plates on a fracture give a pleasant aroma. In a crushed and dried form, the root is put in fish and meat dishes. The external resemblance to ginger in alpinia is not accidental, these plants are direct relatives with many common features.
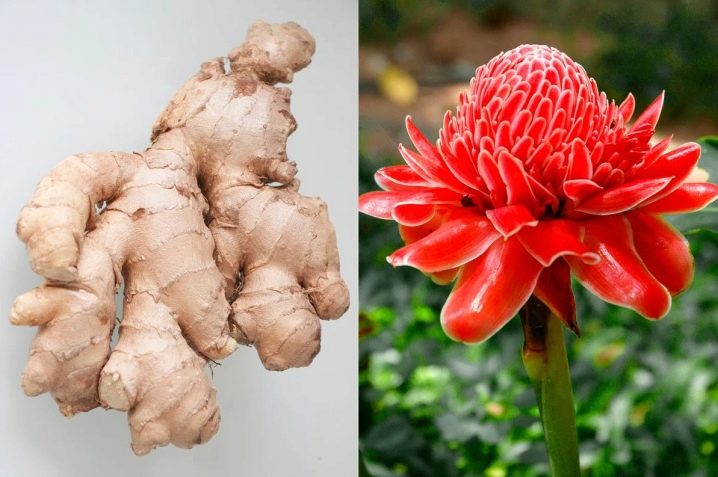

Types and varieties
Species diversity is one of the main advantages of this plant. It is not found in the wild in Russia, but it is successfully grown in a pot culture, in greenhouses and simply on window sills. Here are the most common types.
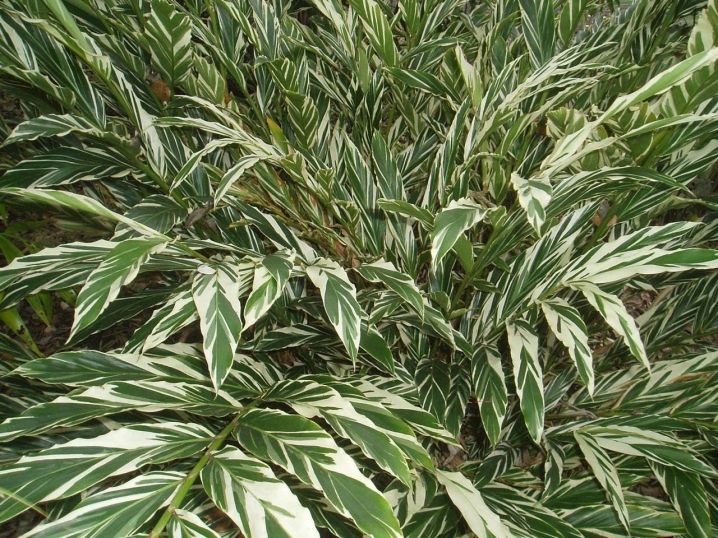
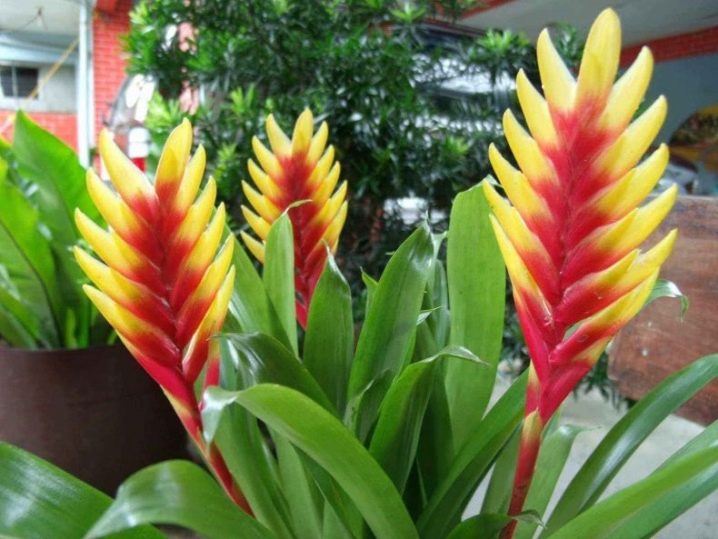
- Variegated. A rather compact variety of alpinia, even in nature it does not reach a height of more than 2 m. The plant has wide lanceolate leaves covered with yellow diagonal stripes radiating from the cutting. It is a popular indoor culture with lush foliage and high decorative appearance.
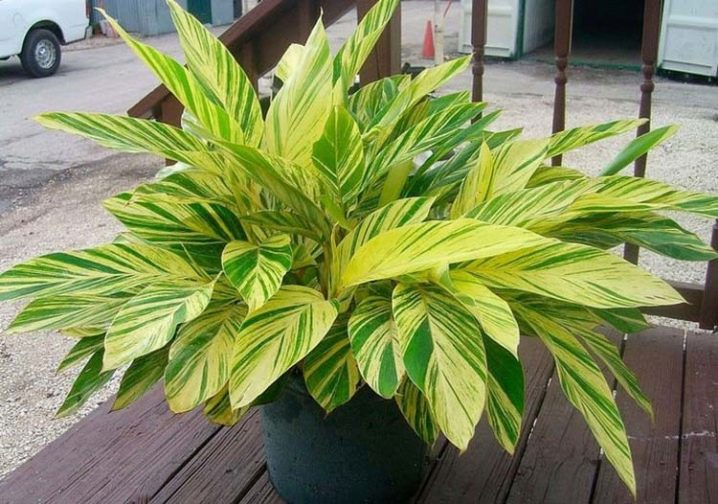

- Variegated. The most compact indoor alpine. The leaves on the bush are oval, rather large, they look spectacular and bright. During the flowering period, the petals in the spikelets have a white background color and a yellow border. The brushes themselves are long, very decorative

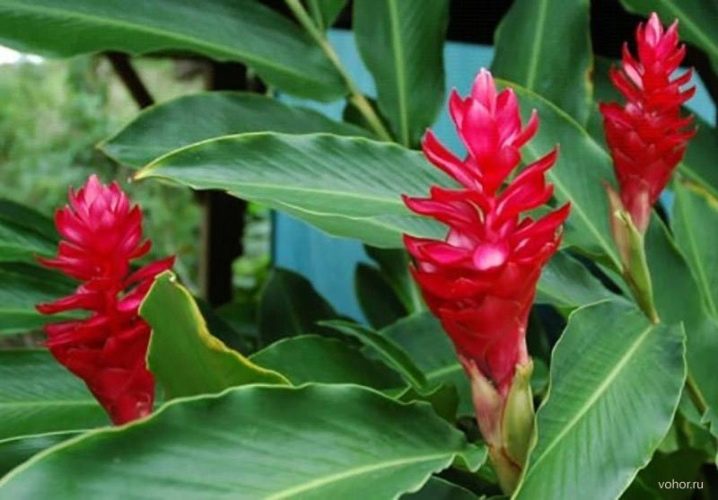
- Galanga. This herbaceous perennial plant is found in the wild in Indonesia. The main value is precisely the yellowish rhizome of alpinia, which is widely used for culinary purposes - for mashed soups, as a side dish or seasoning for meat. The plant also has medicinal properties.

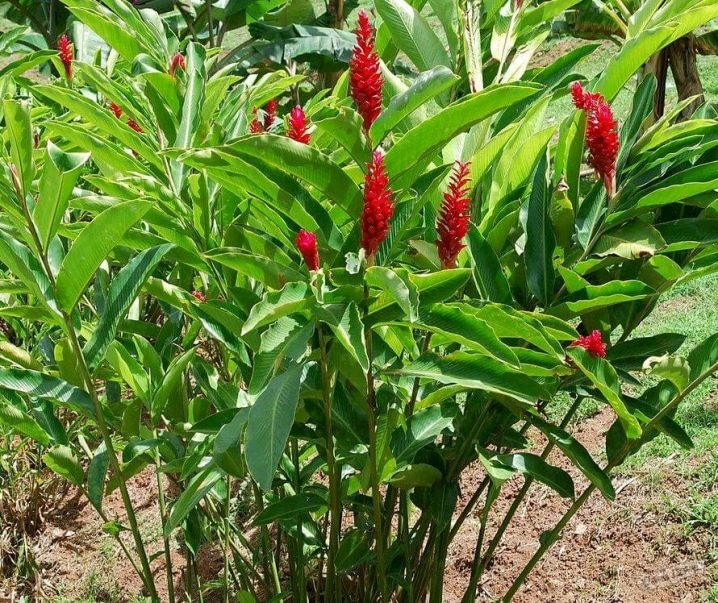
- Medicinal. The most valuable species of alpinia, also known as medicinal galangal. Even his seeds have beneficial properties. The plant gains stem height up to 1.5 m, its rhizome is strong, located horizontally. Stems in each rosette are from 20 to 40, they bear leaves and inflorescences, the spikelet in the upper part has petals of a white background color with noticeable dark pink veins. Alpinia officinalis is a perennial found in China and Japan, in India, it has spread by transfer to the Mediterranean, Africa, North and South America.

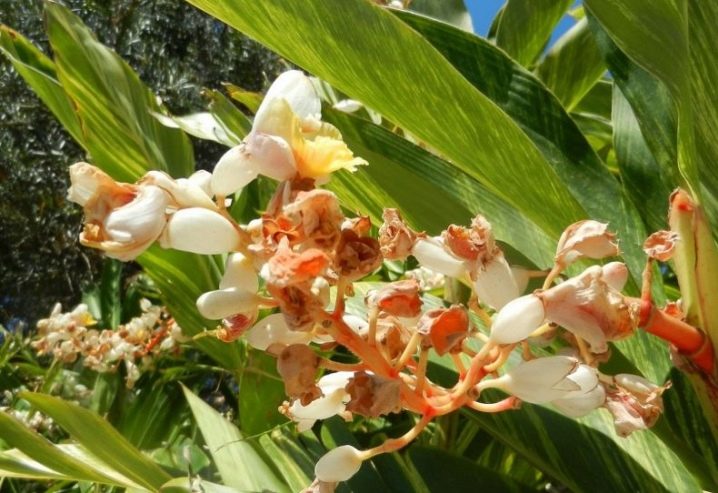
- Cerumbet. In nature, this type of alpinia is formed in the form of a large bush with a shoot height of up to 3 m.The leaves of the plant are elongated, the inflorescences-spikelets are white, collected in compact brushes. Alpinia zerumbet is found exclusively in parts of Japan and China. Here, for culinary purposes, the leaves of the plant are used, in which the rice is wrapped, in a crushed form, they are added to dishes together with berries.

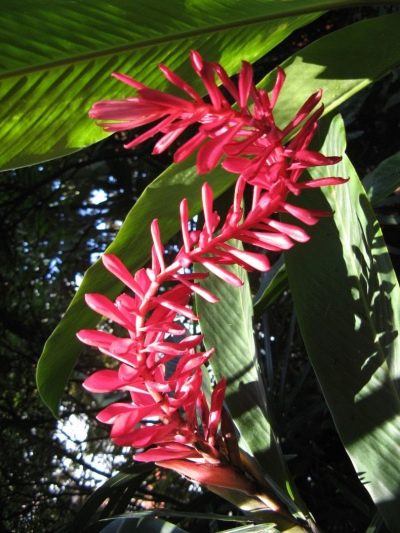
- Purple. A variety of alpinia with a creeping root system and a high stem, in natural growing conditions reaching 1 m. The leaves on the bush are lanceolate, up to 30 cm long, flowers are collected in brushes, the petals are unusually colored, white with red stripes. The essential oils in the plant are present in smaller quantities than in other species, but the pleasant spicy aroma in the roots and stems is retained. In Asia, purple alpinum is sometimes called red ginger.

- Yellow-fruited. In English-speaking countries, this type of alpinia is often called bamboo ginger. The stems of the plant are arranged in groups, reaching a height of 1.2-1.5 m. This species is closest to the galanga alpinia, highly valued in cooking for its spicy and sweet unusual taste. During the flowering period, the plants form scarlet sepals with white petals.

Some types of alpine remain rare guests for Russia. This includes Alpinia Vittata, tapered - a short plant with striped green leaves, long, lanceolate. It blooms in panicles with pale crimson corollas.
The plant is very decorative, but rather suitable for open ground in subtropical climatic zones.

Landing nuances
Alpinia feels quite comfortable when grown as an indoor flower. It is enough to provide her with good conditions, as well as to plant correctly.
-
After flowering, seed is collected in bolls.
-
The substrate is being prepared. It should consist of turf, sand and humus in equal proportions.
-
Seeds are sown. The optimal time for this comes in January, in 2-3 decades. The seeds are not deeply buried, they spray the soil surface from a spray bottle.
-
Germination is in progress. During this period, the ambient temperature in the place where the pot stands should reach +22 degrees and above. Before the emergence of sprouts, a film cover is used.
-
Getting seedlings. Until viable roots and shoots appear, the sprouts are sprayed, periodically ventilated, but kept in a greenhouse.
The grown seedlings are distributed in permanent pots. Alpinia will bloom only for 3-5 years.

Care features
It is difficult to achieve stable flowering from an exotic plant in indoor conditions, but it is quite possible if you properly organize its care. Alpines do not tolerate strong dry air and poor soil, they require maintaining stable temperatures in the room. All the subtleties of care should be considered in more detail.
Conditions
In home interiors, it is better to immediately place a spectacular alpine in a large hanging planter, or install it on a curbstone. A culture that initially gives a fairly compact rosette of leaves and stems will soon show its true size. When choosing a location, it is important to give preference to free spaces filled with light. Direct sunlight is contraindicated for this herbaceous culture, but it feels good in partial shade.
Plants can be placed not only on the windowsill, but also near it. It is better to choose the southern, in extreme cases, the western or eastern side, but the north of the alpine is contraindicated. Illumination directly affects the intensity of flowering. In summer, the pot can be moved to a balcony or loggia. It is recommended to keep the air humidity level above average. An indicator of 60-75% is enough.

For the alpine, it is detrimental to lower atmospheric temperatures to below +10 degrees. In summer, they try to maintain this level in the range from +18 to +28 Celsius. In winter, a decrease of 3-4 degrees is permissible.
Alpines need to simulate the climatic change of seasons.For this, a dormant period is arranged from autumn to spring. The ambient temperature drops, watering becomes less frequent. The plant is removed from the heating devices further away, but they continue to be kept in the light for 10-12 hours a day.
Watering and fertilizing
Alpines do not like overdrying or excessive moisture. The frequency of watering is adjusted so that the soil surface remains moist at all times, even in winter. In the summer, in the heat, the procedure becomes daily. The reduction in the rate is carried out at the end of the flowering period of this herbaceous perennial.
With the exit from the dormant period, with the subsequent beginning of budding, it is recommended to feed the alpinia with potassium fertilizers at an interval of 1 month, reducing the standard concentration. Ready-made solutions for indoor perennials are suitable. Fertilizers are not applied from autumn to spring.

Transfer
Too often it is not necessary to transfer the plant to a new place, once a year is enough. If the alpinia is sick, the soil is infected with parasites, the roots are rotten, the transplant is done completely, after having cleaned the old substrate, removing the damaged roots. After that, the seedling is transferred into a wide, low flowerpot, the bottom is covered with drainage of natural origin. The new soil should be light, a mixture of sand with humus, peat and leafy soil is used - it is used to underlay a layer at the bottom of the pot, put an alpine, then add the soil to the very edge.
A transplant of an overgrown perennial is performed in the 2-3 decade of February or at the beginning of March. The transshipment method is used, while preserving the old earthen lump. The diameter of the flowerpot increases by 1 cm every year. In the first 12-24 months after transferring to a new home, alpinia can significantly reduce the growth rate, but then it necessarily makes up for lost time.
Large adult plants are no longer transplanted. In their flowerpot, the top layer of soil is removed, and then a new substrate is backfilled.

Reproduction
The main breeding method for alpinia is by dividing the root. When transplanting in early spring, fragments with buds are separated from the underground part of a dug plant, the sections are powdered with crushed charcoal. The resulting root cuttings are then transferred to separate pots.
Another breeding method is seed. But there are some subtleties here. Seeds quickly lose their germination, they must be sown immediately after collection.

Diseases and pests
Alpines are not too susceptible to disease. They are attacked by fungi or infections only if the conditions of detention are violated. When the color or structure of the leaves changes, the formation of spots on the plates and the stem, the plant is isolated, treated with fungicides. Among the potentially dangerous insects, the spider mite can be distinguished - it is easy to detect it by the thin whitish filaments left on the shoots, as well as aphids. This sucking parasite deprives the plant of juices, but it is easily destroyed even with a solution of laundry soap.
Alpinia can get burned if it comes into contact with direct sunlight or a cold source. Its signs are considered to be drying out, discoloration of the plates, the discharge of all leaves. It is important to try to protect the plant from such negative effects.















The comment was sent successfully.