Standard roses: description, types and subtleties of planting

Lush pink trees have long been an adornment of the southern cities of Russia and European countries. They have become popular in the middle lane, often found in the landscape design of cottages.


Peculiarities
In fact, standard roses are not trees - they are obtained by grafting different varieties to the root shoot - the stem (trunk). By varying its height, you can get trees with different heights.


Views
- Dwarf. Such trees are from 0.3 to 0.5 m in height.
- Half-stamp options. Their height can reach 0.8 m.
- Ordinary boles. Such options have a height of up to 1.3 m.
- High-standard roses. They are "weeping" trees up to 3 meters. These are the largest standard roses.
It should be noted that grafted roses retain their properties. For example, the cascading varieties in the standard version are “weeping” trees.
Plants on a trunk look great in any landscape design, for example, in group plantings, on lawns or on multi-tiered cascading compositions.


Experienced gardeners say that these trees can be obtained from any crop.
According to the recommendations for the stock, it is better to choose a rosehip, as it is the most resistant. The specimen must have a strong root system and flexible shoots.
When buying a ready-made stem, it is imperative to study the description for it, which contains a detailed algorithm for care and describes which plants were grafted.
It should be remembered that decorativeness is highly dependent on the quality of the original seedling., therefore, it must be carefully inspected. It is better to purchase an escape in special stores, where you can consult with a good specialist - this way you can be sure that quality products are being purchased.


You need to ask about the age of the seedling. It is better if he is 2 years old, since during this period strong roots and trunk are formed. If dry shoots or cracks are seen in the root system, then it is better not to take such a stock - the stem should be even and smooth.
The trunk diameter is determined based on the type of tree. For example, for "weeping" types, the best option would be a diameter of up to 2 cm, the rest - up to 1 cm. The crown must have at least two vaccinations - in this case, it will become lush.
The substrate must be fresh and moist. If moss, weeds grow on it, or it is completely dry, it means that the shoot was poorly maintained - it is better not to purchase such products. It is important that the root system is closed.

It is worth deciding in advance on the grafted variety and familiarizing yourself with the requirements for its care, as well as with climatic characteristics.
The best varieties
Breeders distinguish three main types of rootstocks for the formation of a stem, some of which have subspecies.
- The caninae - the most common type. However, it has conflicting characteristics.
- Rosa canina - long-lived rootstock. But when choosing this option, one should take into account its slow growth, while there are problems with reproduction. The species is not characterized by a high degree of frost resistance, but hybrid tea varieties grafted on it tolerate cold weather very well.
- Heinsohn's Record. This option is mainly used by the Germans for planting yellow roses.
- Pfander's canina - the species is highly frost-resistant. It fits perfectly with any varieties of roses, with the exception of yellow hybrid tea species.


- The Synstylae. This option is rather unpretentious. Resistant to pests and diseases. Easily adapts to sandy loam soil. Breeders use this type of rootstocks to breed vigorous varieties.
- The indicae - more used in regions with a mild climate. Suitable for all types of roses.
Professionals advise some varieties for grafting on a bole.
These will be discussed below.


- "Super Excels". A climbing species with a trunk height of 1 to 2.5 m. The flowering period is summer and September. It has small flowers with a mild aroma. The variety is resistant to many pests and diseases, except for powdery mildew. The tree is frost and drought resistant. Perfect for breeding in the middle lane.

- Swany. This variety is considered the most productive among the ground cover types. Its progenitor is a wild rose from East Asia. The plant itself is creeping, so the stem will turn out to be "weeping". This variant has medium-sized white flowers (up to 6 cm in diameter) with a double structure and a delicate aroma. Umbrella-shaped inflorescences consist of 15-20 buds. The rose is characterized by versatile decorativeness, frost resistance, intense flowering. Recently, breeders have bred several subspecies of this variety with a pink and red tint.
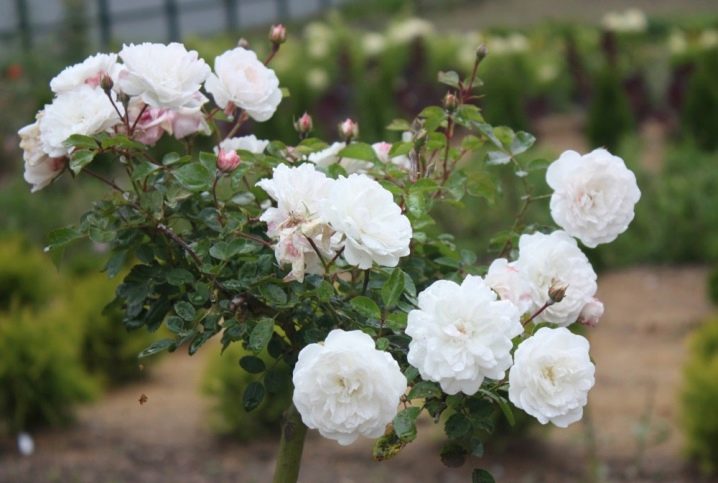

- Crocus Rose variety bred by renowned breeder David Austin. Roses were specially bred in such a way as not only to be lush and fragrant, but also resistant to frost and disease. Interestingly, depending on the flowering period, the buds change their color. The variety belongs to the Shrub class (half-leafed). By the way, the flowers of this rose are small - only 8 cm, but very terry and lush, so the crown will be almost all covered with them, creating an unsurpassed decorative effect.


- "Charlotte" (Charlotte). Rose is considered to be one of the most beautiful yellow varieties. The flowers are not brightly saturated, but rather creamy, soft yellowish shades. Inflorescences are small - 3-5 pieces. The variety is compact, branching, in the standard version forms a dense standing crown. Blooms all summer. Among the advantages should be noted unpretentiousness, an average degree of resistance to powdery mildew and excellent resistance to other types of pests.


- Every autumn, a flower show is held at the French castle of Versigny, which brings together many gardeners. It was in honor of this event that the amazing salmon-pink rose variety "Versaini"... The dense double flowers exude a pleasant orange-peach aroma with hints of anise and vanilla. You can admire them all season. Great as a scion for a standard rose - the crown turns out to be lush, bright, thick. The branches are upright.

- German floribund varieties include Berstein and Schackenborg. They are compact bushes with double flowers. At Berstein they are amber-yellow, while at Schackenborg they are pink to orange.
The inflorescences are small in size, include from 3 to 5 buds.
The varieties are quite branchy, so they are well suited for growing a standard tree. Resistance to various diseases is moderate. Both of them are pretty unpretentious.


- Have German roots and two more varieties: "Rosarium Utersen" and "Sonneshirm". Sonnenschirm is a representative of ground cover varieties. Roses are very unpretentious, densely growing and abundantly flowering, therefore they are often grafted onto stems. The resulting "weeping" trees perfectly decorate any landscapes. Rosarium Uetersen is also a climbing variety.
The flowers are large in size, and unlike the "Sonneshirms" they are bright and double. Roses are characterized by a high degree of resistance to rain, frost and powdery mildew.Since the variety itself is tall, then standard trees with its use are tall and lush.


- Among American varieties suitable for bole grafting, breeders distinguish "Burgundy Ice" from the floribunda group. The rose is unique in its color - it has a rich plum, sometimes purple hue. The texture of the petals is velvety and pleasant to the touch. Among the advantages, abundant flowering is also noted. Resistance to abrupt changes in weather conditions is moderate, as well as to diseases.


- If you need to buy bright scarlet roses, then you should pay attention to the Canadian grade "Adelaide Hoodless"... The flowers may not be fluffy, but the plant grows very quickly and blooms profusely. Canadian breeders have taken care of the absolute frost resistance of the rose. If the plant freezes out in forty-degree frosts, then it can be restored, since it is genetically laid down. Among the advantages, it is worth noting high resistance to diseases and pests. A standard rose based on this variety turns out to be spreading with a lush crown.


Landing
To get a beautiful and healthy tree, you must follow certain planting rules.
Seat selection
Before planting, you need to decide on a place where the rose will feel comfortable.
Rosewood is a very delicate plant. Arid and open to the sun areas are not suitable for him - in the sun they can burn and grow.
Shaded areas are also not suitable.
Selection roses do not like dampness, drafts and the north wind. The proximity of groundwater is a negative factor for the trunk. The best solution is a shady place on the south side of the house or fence.
In the event that you cannot choose a permanent place, or the climate does not allow you to leave plants for the winter on the street, then there is a way out - to grow a standard rose in a pot.



Landing dates
Professionals unconditionally recognize that the best period for stem rooting is from April to May.
The date will be different in each region. You need to wait until the ground warms up to at least 15 degrees. Weather conditions should achieve stability - there should be no sudden temperature changes.
Site preparation
The operation to prepare the site for planting should begin in the fall.
Basically, all actions consist in good plowing of the land and its fertilization.
There are no fundamental requirements for the soil, but it has been noticed that standard roses feel most comfortable on loamy soils, diluted with river sand for looseness and peat with compost for nutrition. Also, the soil is enriched with organic additives.


In some cases, they resort to agronomic adjustments.
- Fatty rich black soil is mixed with clay.
- With a lack of phosphorus, a special mixture of bone meal, superphosphate and infused mullein is added. It should be remembered that the manure must be pre-mixed within 2 years. Its alternative is humus obtained during the life of earthworms.
- In the case of high acidity of the soil, phosphoric flour is used to neutralize it.
- The sandy soil is well ventilated and heated, but does not retain nutrients well, so clay powder, sod and humus are added to it.
- Ordinary loams are corrected with a mixture of coarse sand, compost and turf.
- If the soil on the site is heavy with a lot of clay, then it dries for a long time and is poorly ventilated. It needs to be improved by introducing sod soil, humus, compost and rotted leaves.


If roses have already grown on the site and died, then when it is reused, it is necessary to remove the top layer with a thickness of at least 70 cm and replace it with fresh soil.
Before winter, the ground must be carefully dug twice in order to pull out the remaining roots - pathogenic bacteria or pests can nest on them.
Such treatment will reduce the risk of plant diseases in the future.

Disembarkation scheme
Standard roses must be planted correctly, following a previously drawn up scheme in order to improve the design of the site and take into account the care requirements.
Trees should not be crowded - the optimal distance between them should be about 1.5 m.
When creating a composition, it is worth considering the growth of all plants included in it: trees and bushes, as well as the scope of their crown.
Before creating a diagram, it must be borne in mind that not all plants get along with roses. For example, chamomile or rudbeckia is completely unsuitable for such a tandem - it is better to choose lavender, sage, petunia or lobelia.


Landing rules
- The trunk pit usually has a square shape with dimensions of 70x70 cm.If the rhizome is not large, then it needs to be increased. The calculation should be carried out depending on how freely the root system is located inside the depression - it should not be cramped.
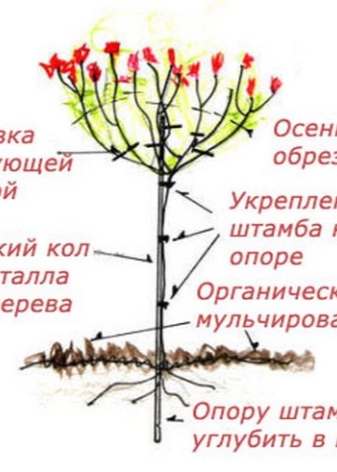
- In the center of the hole, a support stake is driven in to a depth of at least 0.5 m. The height of the cutting is selected below the rootstock.
- The bottom should be loosened and covered with expanded clay.
- On top of the expanded clay flooring, a mixture of turf, rotten foliage, peat, river sand and clay is poured into the center in equal proportions. The height of the slide should be 5 cm. The specified composition is optional - the components can be changed depending on the characteristics of the soil.
- The landing ball is carefully removed from the container and placed inside the prepared recess. The roots of the stem are covered with a fertile substrate. The pit is watered and compacted in such a way that the stalk is 5 cm deep.





No need to spud. When planting, it should be remembered that standard roses are covered for the winter, therefore, they will have to be bent. For this reason, the trunk should initially be positioned slightly downhill, depending on the natural curve of the tree.
- The branches of the crown and stock should be tied with soft fabric ribbons to the support stake.
- The rooted tree is covered with a film for the first time. Experts recommend putting on a plastic bag filled with damp moss or cotton wool, which will keep the crown from drying out. When the plant takes root, you can remove it for a while, gradually accustoming the rose to temperature changes.



Care
To grow a beautiful and lush tree, you need to properly care for it - this is especially important during the growing season.
It is important to monitor the soil moisture and the degree of its aeration. Do not forget to carry out preventive treatment measures against pests and feed them on time.
Before planting, you should study the cultivation step by step, care at each stage, possible critical situations and their correction.


Watering and weeding
Since roses are moisture-loving, they need to be watered regularly throughout the warm season.
Many professional gardeners organize drip irrigation using special installations.
In the absence of such equipment, an adult plant needs 20 liters of liquid, which is poured into the grooves near the roots.
The crowns of newly planted standard trees should not dry out - it is for this reason that they are covered with polyethylene with wet moss.
A procedure such as sprinkling is contraindicated for boles, as it can cause the death of young shoots.

Roses do not tolerate the presence of weeds - they suck the necessary moisture and nutrients from the soil. In addition, harmful insects can breed in them. For this reason, weeding is an important step in maintaining your rose garden.
For comfortable growth, standard roses need loose earth. Therefore, regular weeding, loosening and mulching will be required.
Since loose soil dries out rather quickly, it is recommended to mulch the soil to retain moisture in it.This should be done with humus, straw or sawdust.


Garter
After the tree gets stronger, the original support needs to be replaced. It is best if it is metallic. They also use durable plastic, fiberglass or bamboo. In the latter case, the support will have to be changed as it deteriorates.
The stick is stuck into the ground on the other side of the inclination of the trunk at a distance of 0.1 m.
The branches of the crown are tied up with soft fastening tapes that do not injure the plant. These include electrical tape, as well as foam rubber and fabric. Usually use a "figure eight" mount just below the vaccination site.


Top dressing
When planting, the stem is fertilized immediately. The nutrient mixture is added to the planting hole. During the growing season, feeding will be required twice: in spring and after flowering.
Ready-made products - mineral complexes specially designed for standard roses - include the compounds of potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen and magnesium necessary for such plants. The quantity is indicated in the instructions. Adult roses require about 6 kg of fertilizer per 1 sq. m.
Natural top dressing - rotted mullein and vermicompost. They are laid out in a thin layer around the trunk every year.
Mineral dressing is well absorbed if it is applied to moist soil.


Prophylaxis
Roses are susceptible to attacks by various pests, harmful bacteria and fungal diseases.
Immunity can be increased by choosing a stock and a grafted variety with resistant genetics.
One should not abandon preventive measures for treating trees at the initial stage of the growing season. For this, insecticides "Aktara" or "Bi-58 New" are produced.


To save roses from rot, spotting or chlorosis, professionals advise to conduct regular inspections of the crown and trunk, and remove damaged branches. You can spray it with a solution of ferrous sulfate (4 liters of product for 14 liters of water), repeated after a month.
Since it has been experimentally proven that it is almost impossible to remove infectious diseases, you need to monitor the cleanliness of inventory tools - you need to regularly disinfect them with potassium permanganate, start pest control in time so that they do not appear on the garden plot.

Pruning is the cleansing of a standard rose from old, diseased and damaged branches, the elimination of overgrowth around the trunk and crown. The work is recommended to be carried out in the spring.
Miniature and hybrid tea roses should not be cut short - there must be at least six buds, otherwise the crown will be of an irregular shape, and the lateral shoots will go into growth.
In a climbing tree, skeletal shoots that have faded last year are cut out. It is better to cut off young branches a little. If it turns out that there are no overgrowths, then last year's lashes are not removed, but only the tops are cut off.
Pruning is also carried out when preparing a plant for wintering.

Reproduction
Some gardeners claim that it is extremely difficult to grow a standard rose on your own, but it is possible. The main thing is to have a lot of patience and have some skills in plant grafting.
Experts advise using rose hips as a stock. His seedlings give a 40% result when selected. Rosehip is the most resistant to various adverse factors: frost, heat, insects, diseases.
A rose hip can be grown from a seed, or a cut from an already mature plant can be used. The main thing is that the trunk is flat, strong and high.

Growing from seeds
Harvesting fruits for sowing is carried out closer to mid-August. It is better to choose berries that are evenly brown in color. Seeds are taken from them and sown in moist soil. In drought, crops need to be watered.
Seedlings appear in spring or in the second spring. The shoots grow until autumn, after which the selected strong seedlings are transplanted to a separate ridge.
The row spacing should not be less than 1.5 m, since the rose hips need to be hilled.
The distance between plants should be 20 cm.

Cuttings
First of all, the necessary bushes are chosen from the wild rose hips, they are dug up and planted in a separate area, where they are grown. Seedlings during this period are carefully examined and selected.
Further actions are carried out in the same way for both cases.
For 4 years, the shoots are looked after: they are watered, fed, preventive procedures are carried out, and they are loosened.
In the spring of the fifth year, all branches are cut off from the seedling at the level of the root collar, leaving only the central shoot. At the end of July, they pinch him.
Closer to mid-August, different varieties in the amount of 4-5 buds are engrafted on the stock, the grafting height is about 1.2-1.5 m.

Grafting
Grafting of roses on a stem is carried out in the same period as in ordinary rose crops.
Budding
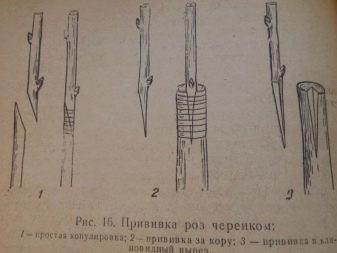
The most commonly used procedure is called budding - grafting is carried out with the help of a bud from a cuttings of a selected variety of roses.
To get a positive result, it is recommended to take 3 or 4 buds at once from the central part of the one-year shoot. Experts advise to cut the chip from the bottom up.
Then on the rootstock at the grafting site, the bark is cut in the form of the letter "T". A cut kidney is inserted into the incision, the entire area is carefully tied with tape, capturing 2 cm from above and below. Only the peephole should remain outside.
The result of the procedure will become apparent in a month - the bud will begin to grow, and the leaf petiole will disappear.


Cuttings
You can graft varieties of roses to the stock using cuttings. To carry out this procedure, a split is made on top of the rootstock. Young healthy cuttings are cut off from the grafted bush, sharpened from below and inserted into the prepared split. For high-quality pressing, the barrel is wrapped with tape.
To protect open sections from insect larvae, diseases and decay, they are coated with garden pitch.
In both cases, after grafting, the trunks are prepared for wintering: they cover, undermine and bend down.

After the onset of spring, the buds should begin active growth. All the next summer, one should deal with the formation of the crown of a rose tree, achieve its splendor and uniform shape.
To plant the variety effectively, it is best to use proven, climate-resistant roses.
In total, the cultivation of a standard rose takes about 7 years.


The subtleties of preparing for winter
Preparation for winter frosts should be started well in advance. Professionals recommend starting pruning of branches in the first days of October, depending on the variety of the trunk. For example, a hybrid tea group is cut off by about 40 cm, while the cascade version is almost not sheared, but only the tops are trimmed.
The undergrowth that has not formed is removed, since wintering is beyond its strength.


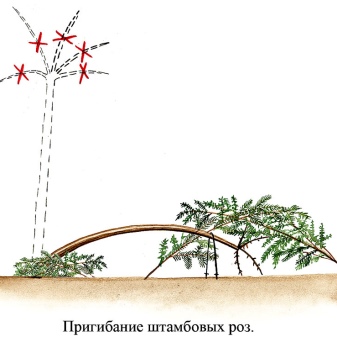
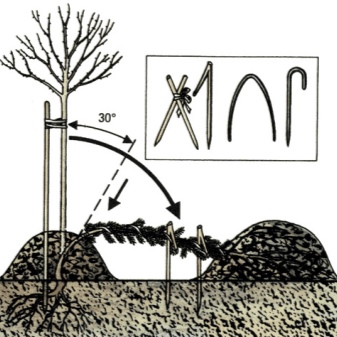
Preparation operations:
- remove leaves from the crown;
- dig a tree on one side in such a way that, without bending it, lower it to the ground;
- drive a metal hook into the ground and secure the stem with it;
- so that the branches do not touch the ground, spruce or fir spruce branches are laid under the crown;
- cover the crown from above with a plastic bag;
- organize a shelter for the root system from a dry substrate;
- after the snow falls, the standard rose must be spud.

The shelter can be disassembled when a constant temperature of at least 15 degrees is established, the earth warms up, and the danger of frost passes. For this reason, this period varies by region. For example, in the Moscow region, it begins in mid-April.
Examples in landscape design
Standard roses are planted singly or in a composition.


Miniature varieties up to 45-50 cm tall are often planted in pots and used to decorate paths, balconies, alleys or terraces.


Half-stemmed roses up to 80 cm tall can be used to decorate closed patios or shady open gazebos.



Conventional standard plants up to 130 cm are suitable for any open landscapes.


High-stemmed roses need large areas: parks, palace gardens and alleys.




For information on how to grow standard roses at home, see the next video.

































































































The comment was sent successfully.