Polyanthus roses: varieties, tips for choosing and care
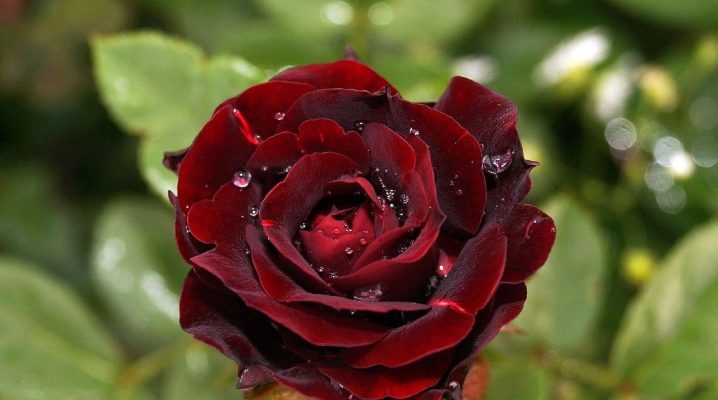

A lot has been said about the beauty of a blooming rose. There is probably no person who does not like these magnificent flowers that adorn city parks, squares of residential quarters, flower beds with their flowering. Rose plantings are widely used not only in urban landscape design, but also in private gardens, dachas and apartments.

Peculiarities
Polyanthus roses have their own characteristics, what distinguishes them from other types:
- almost complete absence of thorns;
- small flowers, collected in inflorescences, which sometimes reach 40 pieces;
- lack of aroma in almost all varieties of polyanthus roses;
- unpretentious and frost-resistant;
- easily propagated by seeds and seedlings, retaining varietal characteristics and color.

The best varieties and their characteristics
Here is a description of the most common varieties of polyanthus roses.
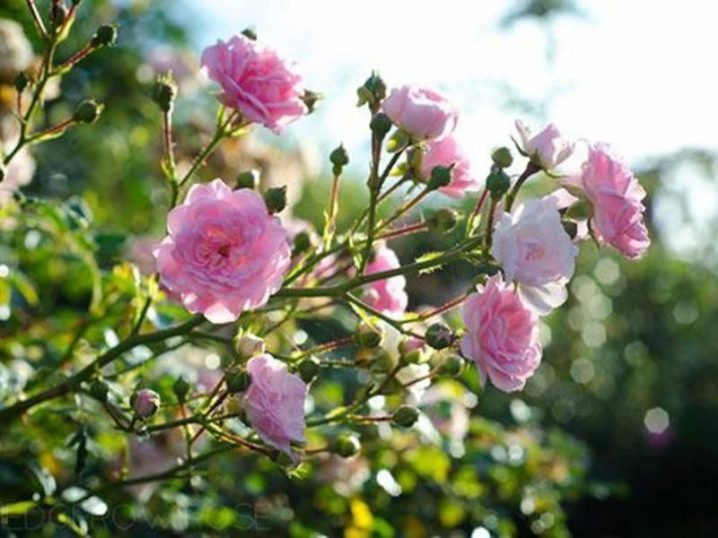

Animo
An almost fiery shade of rose, with yellow petals prominent at the core. An unopened elongated bud turns into a beautiful double rose, rather large - about 6-7 cm. A medium-sized bush looks picturesque throughout the summer season.
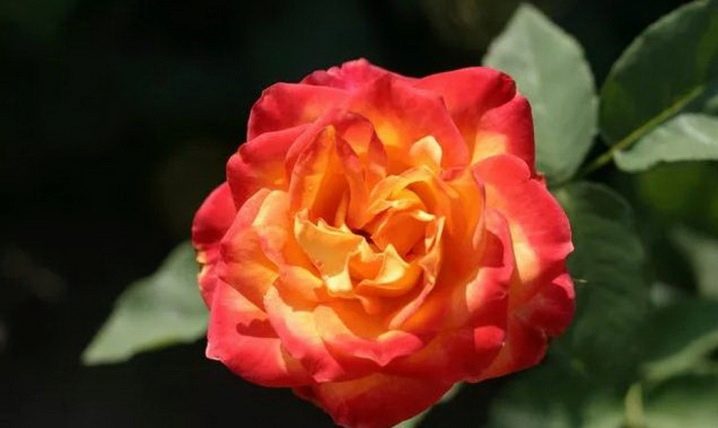

Wing Ding
Small roses blooming with an unusually rich red color. Bushes of medium height, no more than half a meter, sag under the weight of a huge number of incredibly bright buds and glossy leaves. They have a light pink scent. They bloom twice over the summer, until the onset of real cold weather.
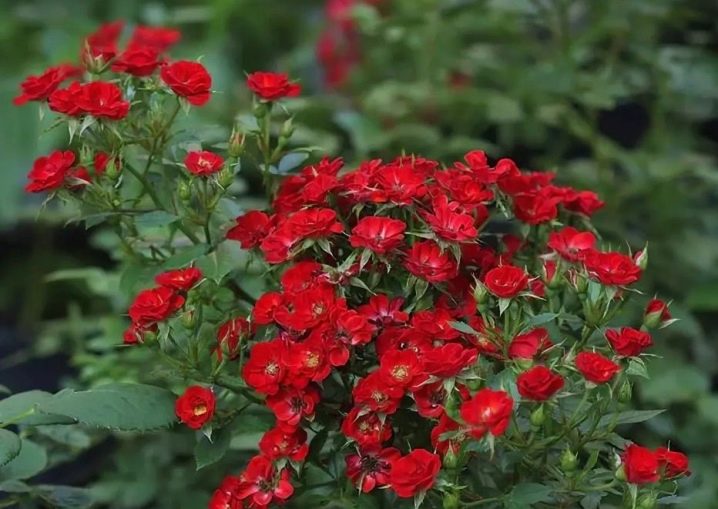

Garden scent
This variety is of Russian selection. A miniature, almost dwarf bush does not exceed 30 cm, is grown not only as a perennial for alpine slides and a rose garden, but also as a potted plant for the home. Easily wins primacy among its fellows in the abundance and variety of flowering. Double and semi-double flowers practically shower the bushes so that the foliage is not visible. To preserve all the characteristics, it is preferable to grow from seeds by seedlings.
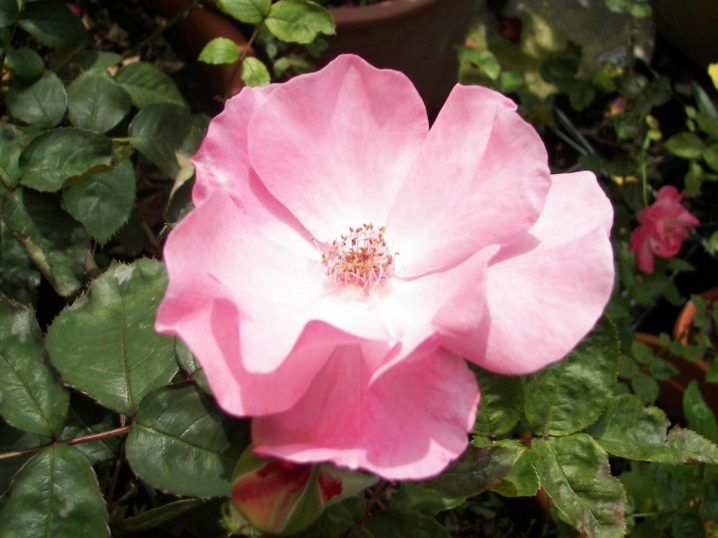

The Fairy
Quite tall bushes with rich green foliage adorn the garden from early spring, first with a riot of greenery, then with luxurious flowering. Small buds in inflorescences have 20-30 pieces. Unpretentiousness, easy care, continuous flowering, light aroma.
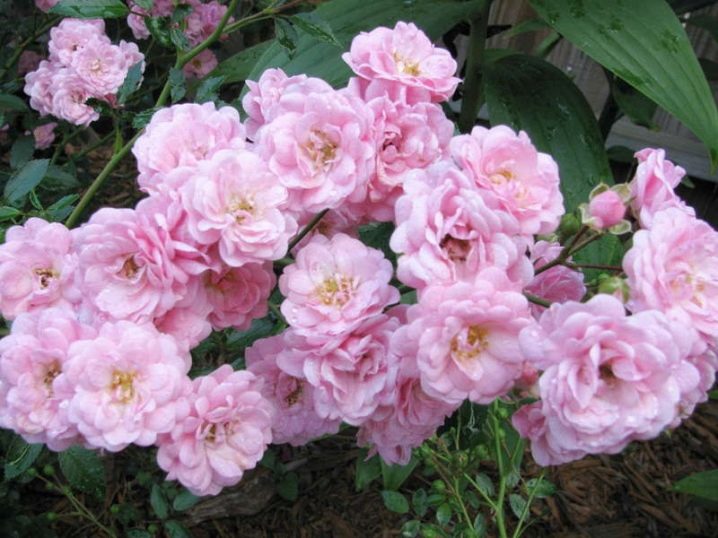

Polyantha Rose Royal Minueto
Gorgeous roses with a distinctive color transition. Bushes of medium height up to half a meter with glossy leaves and inflorescences of several buds.
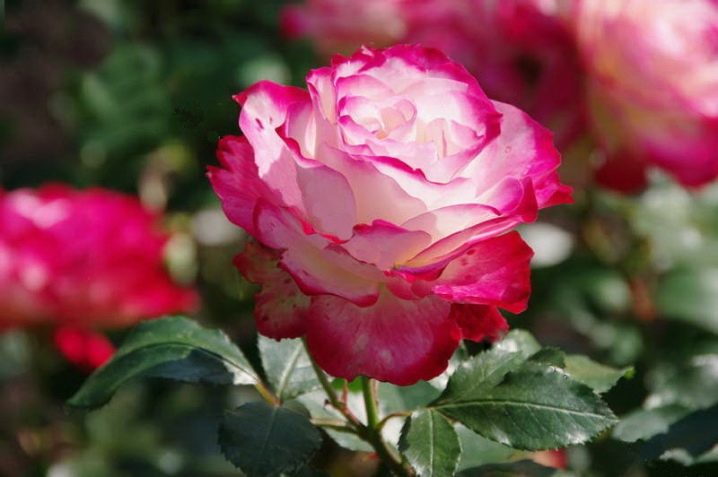

Border King
A low, abundantly flowering plant, often used in landscape design, in city parks and squares. It withstands temperature changes well, is not afraid of frost.
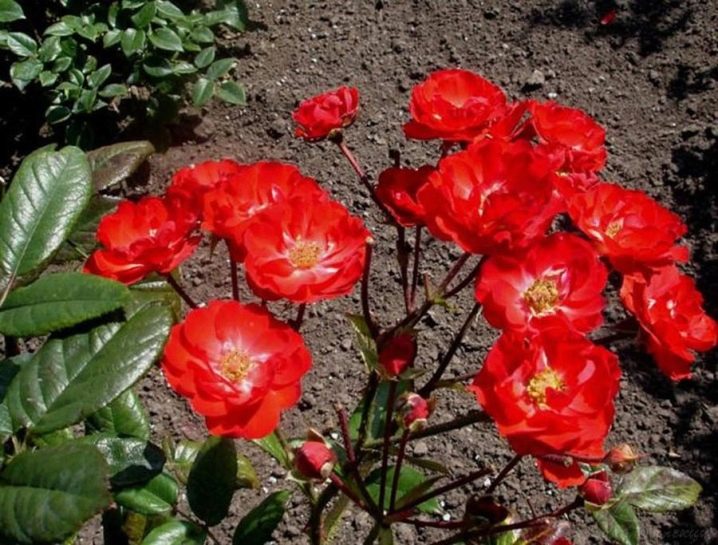

Manou meilland
An unpretentious rose for beginners, does not require special care, as it is distinguished by its endurance and frost resistance. Dark pink flowers have a scent, which is quite rare for polyanthus roses. Bloom until frost.

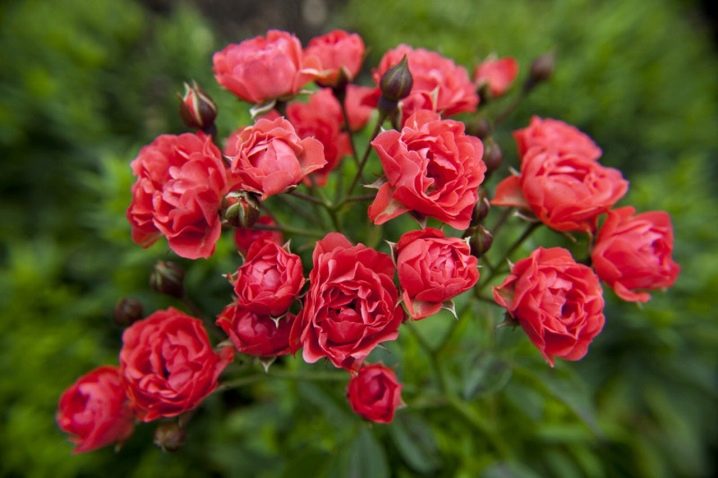
Orange triumph
Bright flowers that attract admiring glances. A strong plant, requires timely pruning.

Angel wings
Representative of indoor polyanthus roses. A miniature rose, only 25-30 cm in diameter, with a bud diameter of no more than 10 cm, has a weak aroma. Semi-double flowers of very delicate shades from white to almost lilac. Propagated by seed, even without the stratification required for other varieties. Has a good germination capacity. Interestingly, the "angelic" rose blooms within a few months after planting. Loves bright lighting, but cannot stand high temperatures. To create a comfortable environment, frequent spraying and gentle maintenance is required. Gentle watering, in winter it stops altogether so that the plant can rest.
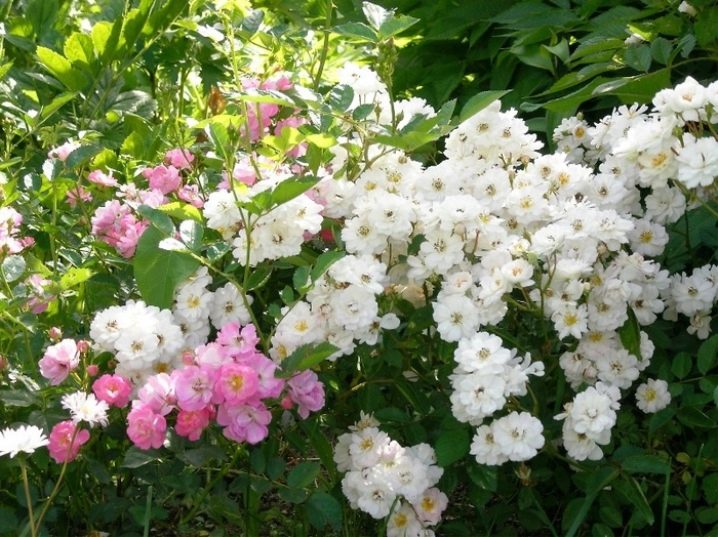

How to choose?
With all the diversity and beauty of varieties of Russian and foreign selection, the main criterion for choosing a variety is frost resistance. The harsh continental climate of Siberia with temperature changes and the milder climate of the Moscow region with possible return frosts and little snowy winters create rather difficult conditions for growing roses.


Landing rules


Planting pits are prepared for roses. They need to be made quite deep and wide. If a polyanthus rose with a closed root system, then the bushes are rolled over without injuring the plant. If a rose is transplanted, grown from seeds or acquired with an open root system, then when planting, all the roots are distributed and evenly laid. The pit is filled with a nutrient mixture of earth and humus, avoiding voids. The root collar of the rose should be slightly recessed. The hole is not completely filled with earth, leaving a little space in the hole for watering and mulching.



In landscape design, there are several methods of planting polyanthus roses: rose gardens, hedges, single and group plantings. The planted flowers in a group look amazing.
Selection and storage of seedlings
When purchasing seedlings, it is better to give preference to Russian and Canadian selection. Siberian nurseries represent unique planting material with high winter-hardy qualities, of course, subject to the purchase of a unique material. Grafted seedlings, which practically do not freeze out in winter, adapt better.
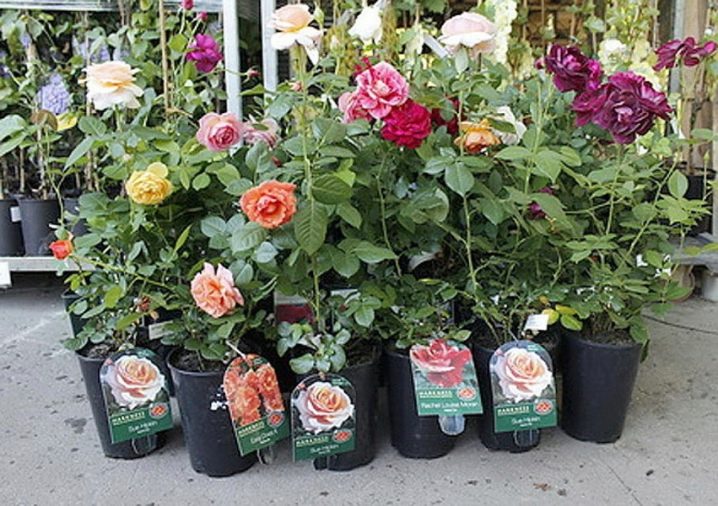

Disembarkation time and place
A soil suitable for roses is a light, loose loam that will allow air to pass through well and not retain water. Planting a rose involves the mandatory addition of humus. Clay soils are too hard to grow, bushes will grow poorly and grow slowly. For successful cultivation, it is enough to dig a hole, water it until it is completely saturated with water and fill it layer by layer with drainage, consisting of fine expanded clay, sand, broken bricks, and a nutritious earthen composition.

Sandy soils, although light and breathable, are also not suitable. They are low in nutrients for proper growth and flowering. In addition, they poorly maintain the temperature regime, as they get very hot in the heat and freeze in cold weather. To get a beautiful rose bush, it is very important to find a comfortable place for it that will meet the necessary criteria:
- suitable soil;
- abundance of the sun, full light during the day;
- calm place, not blown by strong winds;
- prevent stagnation of water - place on a dry area, make a drainage layer or embankment.


How to reproduce?
Roses grown from seeds at home usually inherit all the traits of the parent plant, but sometimes misfires occur and a completely different flower is obtained. For planting, the seeds must be treated with disinfectants and disease prevention agents. Then soak in a solution of biostimulants, for example, "Epine". The prepared seeds are planted in clean soil in a pot, which is covered with a film to create a humid microclimate, and placed in the refrigerator on the lower shelf. It is necessary to keep the seeds in the cold for at least three months.
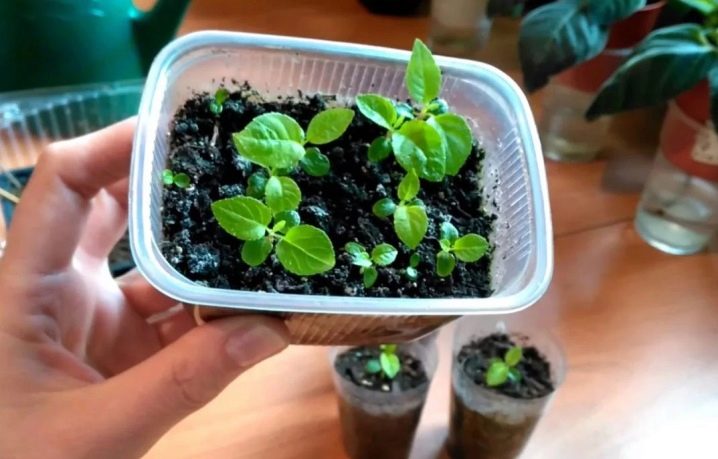

The second option for stratification of seeds is to plant them in the garden before winter, then at sub-zero temperatures, activation of internal forces will occur. In growth, they will move only in the spring, when the earth is warmed up by the spring sun.
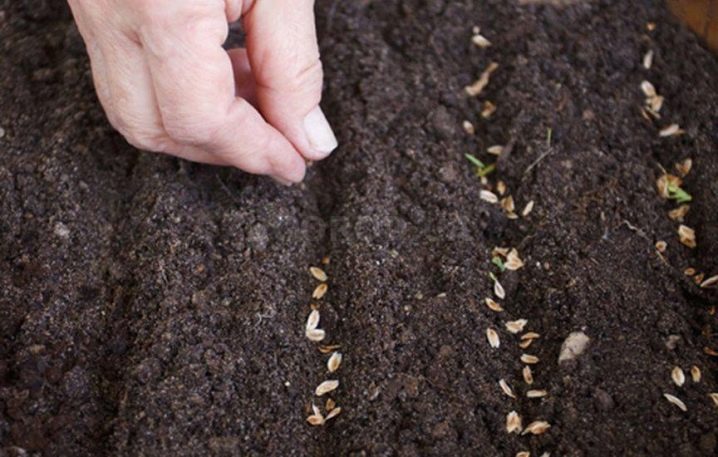

Polyanthus roses are propagated not only by seeds, but also by seedlings and cuttings. When choosing planting material, it is worth giving preference to seedlings from Siberian nurseries, where they have already been adapted and hardened. Seedlings purchased in winter can be stored in the refrigerator until spring.
Care and cultivation
In order for a rose to bloom profusely, it is necessary not only to choose a suitable planting material, but also to adhere to the rules of planting and caring for the plant. Proper care: timely pruning, watering, spraying, fighting diseases and pests is the key to a beautiful flowering.
Watering
Roses generally do not like too moist soil, so it is preferable to water once or twice a week. In hot weather, plants like a generous sprinkling or overhead watering. During rains, when the earth does not have time to absorb all the moisture, you need to stop watering and spraying in order to avoid stagnant water and possible decay.
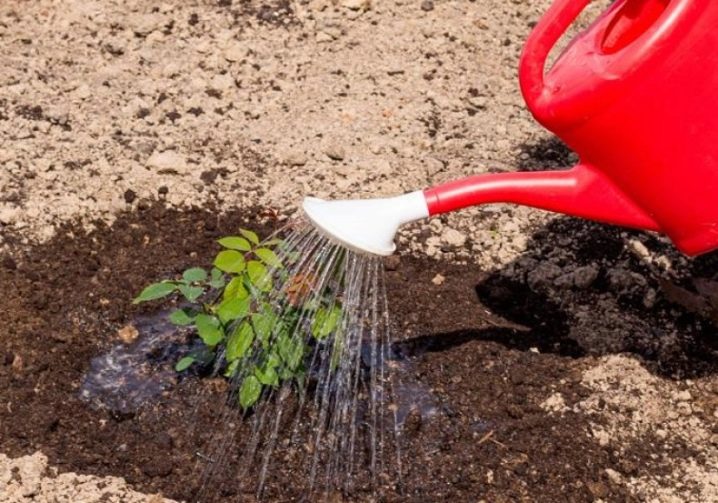

Top dressing
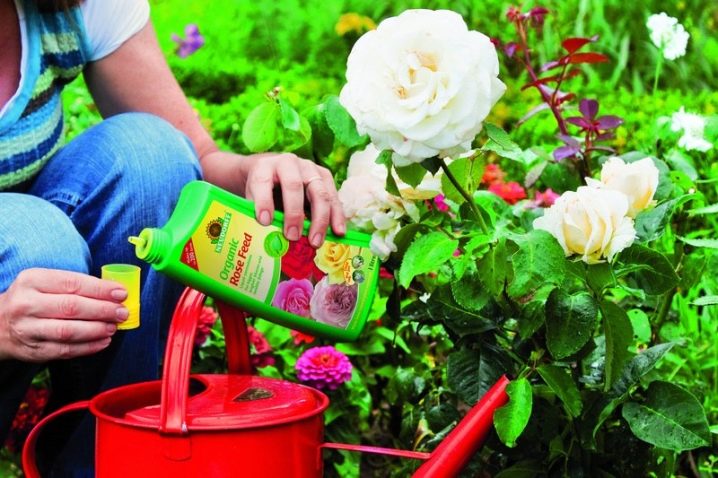
The introduction of mineral and organic substances must be carried out at a strictly defined time. In the spring, it is necessary to fertilize the plant with chicken droppings or mineral fertilizers with nitrogen. Avoid applying concentrated fertilizer, as this can burn the roots of the plant. This fertilizer must be diluted with water in sufficient proportions. A solution based on one part of fertilizer per 20 parts of water is infused for a week. Then the resulting amount is again diluted in a ratio of 1: 3.
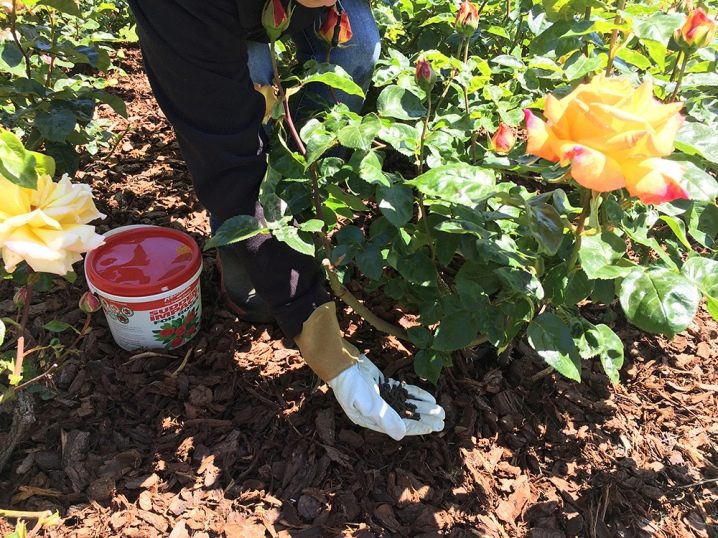

It is worth taking a dressing - apply fertilizer only after abundant watering. Then the root system of the rose will not suffer from chemical or organic substances and will gradually take all the beneficial properties from the ground. Incorrect feeding may not lead to the death of the plant, but it will create conditions for its incorrect development. So, an overestimated amount of nitrogen fertilizer applied to the soil will lead to active growth, an increase in green mass, but to poor flowering. In the absence of the necessary substances in the soil, the plant weakens, grows poorly and blooms, it does not have the strength to fight diseases and pests. Fertilization with a large amount of phosphorus has a good effect on flowering.

Disease and pest control
Fungi, pests, unfortunately, also occur in polyanthus roses. Diseases can be provoked by weather conditions, high humidity or, conversely, a dry hot summer. And it is also undesirable to plant a plant in a shady place, dense planting and lack of ventilation, or, conversely, strong drafts. Mechanical damage, planted aggressor plants and much more can become a source of infection. Correct planting and care, competent watering and feeding will help to avoid many troubles, but you will have to use special means from infectious diseases.

Infectious diseases cause spores of fungi that parasitize the plant, which persist for a long time, even in a cut or plucked form, therefore it is recommended to inspect plants, identify and destroy harmful insects, remove dead shoots and wilted flowers. Consider what diseases polyanthus roses are susceptible to.
Powdery mildew is probably the most common rose ailment caused by the fungus Sphaerotheca pannosa. Signs of the disease appear in a humid environment - the leaves are covered with a white bloom. Leaves gradually curl, flowers perish. The plant sheds its leaves and dies. In order to defeat the disease, all damaged parts must be collected and burned. Treat the remaining plant with a soapy solution containing vitriol in a 1: 2 ratio, diluted in water. It can be treated with solutions of 3% Bordeaux liquid or 30% ferrous sulfate.It strengthens the strength of the bush and helps fight diseases ashes, nettle infusion or cow dung.
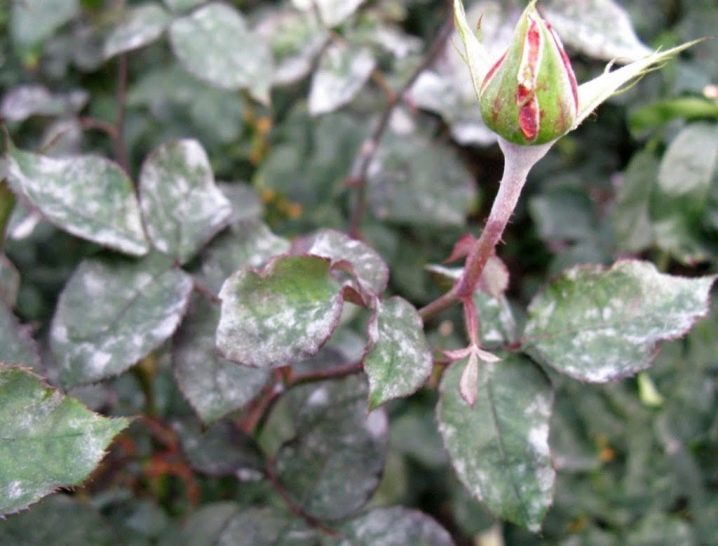

Black spot is caused by spores of the fungus Diplocarpon rosae. Usually, signs of the disease appear on warm summer days after heavy rains. Strong evaporation and lack of potassium causes damage to the front side of the leaves, which are covered with dark brown spots, the edges of the leaves turn yellow and soon fall off. Control measures are about the same: damaged parts of the plant are removed and burned, the remaining parts are treated with soapy water, you can use nettle infusion.
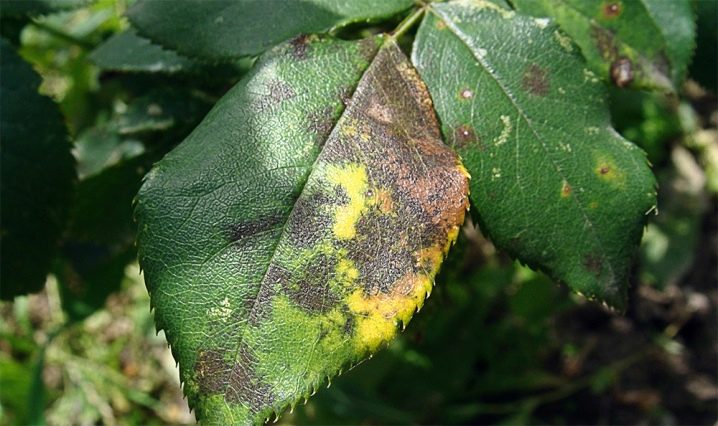

Rust is a Phragmidium fungus that appears on young green leaves and buds. Yellow and orange dots appear on the front side of the leaves, and dusty dents appear on the inside of the leaf, which become carriers of spores. Wet weather contributes to the onset and development of the disease. The rose turns yellow, leaves and flowers bend and dry out. Necessary measures: Infected shoots are cut and destroyed. Treatment of a diseased plant is carried out with 2% Bordeaux liquid, a decoction of wormwood or nettle.

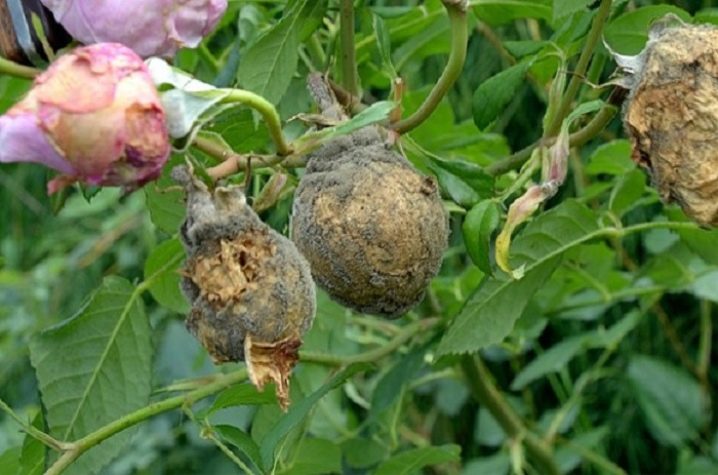
The gray rot is caused by the fungus Botrytis cinerea Ps, which covers the leaves of roses with a gray fluff. Buds on diseased bushes do not develop and fall off. Damp cool conditions, neglected planting, frequent watering can cause the onset of the fungus. To avoid the development of the disease, it is necessary to feed the plant with solutions with a high content of manganese, remove damaged leaves and flowers.

Pests parasitizing roses: spider mites, caterpillars, aphids, scale insects. Regardless of the species, plants feed on sap, reproduce and live in colonies, hibernate in the ground, under the bark and in yellowing fallen parts.
We list the main measures for pest control.
- Removing insects by hand using gloves, damp rags.
- Obligatory destruction of the collected fallen leaves, damaged parts of the plant.
- Thorough treatment of the whole plant with an interval of 10 days with insecticidal preparations such as Aktara, Aktellik, Fufanon.
- Using folk remedies can help in the onset of the disease, while the pest colony has not grown and caused significant damage to the plant. You can use soap solutions containing kerosene or garlic infusion, tobacco decoction. Pests are not tolerated by ash and pepper pollination.
- In order to prevent pests from overwintering, it is recommended, in addition to burning plant residues, deep plowing in spring and autumn, loosening the soil in summer, which will destroy larvae and eggs.
- To prevent diseases and attack of pests, it is good to strengthen the roses with the infusion of chicken droppings.




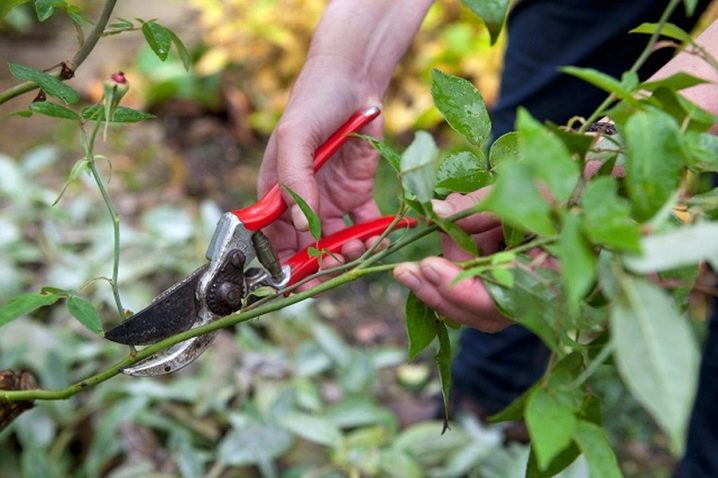
Pruning
Polyanthus roses are compact, so very little pruning is required. Usually, rose bushes are cut only in the fall, in order to remove all faded buds, to avoid the wintering of harmful insects, and to provide shelter for the winter. Pruning should not be carried out immediately after transplanting; time must be given for adaptation and rooting. Withered flowers must be removed in a timely manner, to prevent the formation of a seed capsule. This will allow the rose to bloom longer.
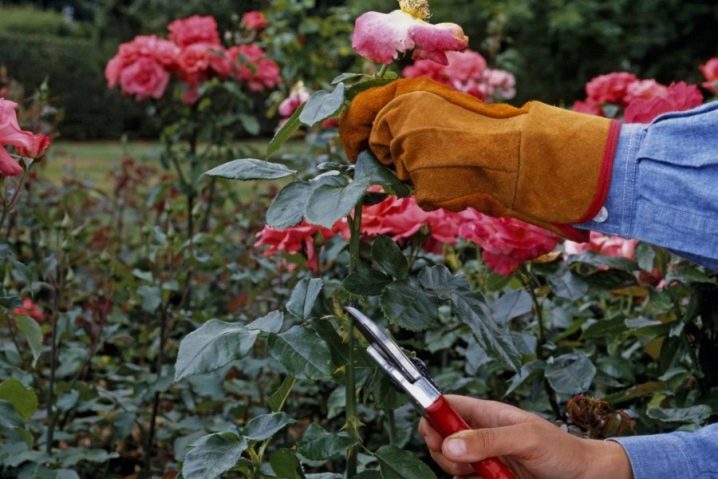

How to prepare for winter?
Polyanthus roses are quite hardy and do not suffer from frost. But while they are young and not strong enough, preparation for the winter is required. There is no need to hope that the winter will be snowy or there will be no severe frosts. It is worth protecting the bushes from the cold scalding wind. This means that it is enough for the inhabitants of the middle lane to pour a small mound at the base of the rose with a light earthen mixture, so the root collar is protected from freezing.

In colder areas or in winters with little snow, it is better to create a shelter. To do this, pour a layer of leaves or straw, and cover with a non-woven fabric on top. Do not use plastic wrap or dense, windproof materials that can provoke condensation when the day and night temperatures fluctuate in early spring.After the snow melts, the shelter must be removed.
See below for more details.

































































































The comment was sent successfully.