How to plant a rose that sprouted in a vase?

Sprouting roses from a bouquet is not such a rare practice. This is more than real, especially if you observe all the technological subtleties. A sprout in a vase can be turned into a rose on the site, provided that it is properly cared for. And, of course, there are certain features of such a reproduction of flowers.

Growing features
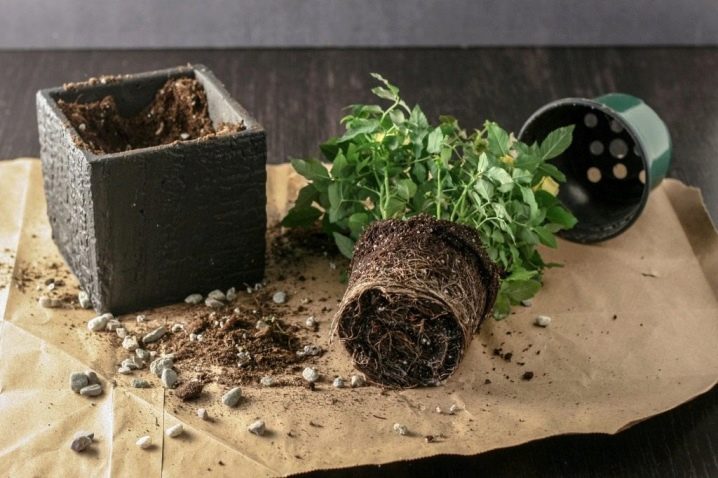
To get a flower from a rose standing in a vase, you must first root it, and then transplant it into the ground. This procedure will require a sterile, sharp knife (or garden pruner), a flower pot with drainage holes, a plastic bottle or bag (whatever, you need to create a mini greenhouse), and a potting soil suitable for rooting. Good drainage is also unlikely to be done. A complex fertilizer to stimulate root formation will also be useful. A spray bottle will also come in handy to help maintain moisture.
To root a rose accurately at home, you need:
- choose large and strong stems that are not damaged;
- give preference to domestic plants, because imported ones are treated with chemicals that make them unsuitable for reproduction.
You also need to be able to cut cuttings. Yes, the main thing is to notice the escaped shoot. On the handle, in addition to it, there should be two more buds. And the length of the cutting can be only 5 cm, and maybe 15.

About cutting cuttings:
- determine the place of the cuts on the stem (see above), then make the first horizontal cut, 2 cm away from the upper bud;
- under the lower bud, cut the stem at an angle of 45 degrees, creating sufficient area to absorb moisture and nutrients;
- cut the leaves at the bottom completely so that only a small stump remains;
- cut the top leaves in half, without stopping sap flow, but at the same time reducing nutritional requirements;
- cuttings can be sent to water, where any suitable growth stimulant has already been dissolved ("Kornevin", for example, or "Sprout", honey or lemon will do from natural remedies).
Water for cuttings is used only rain or settled, but boiled water is definitely not needed.
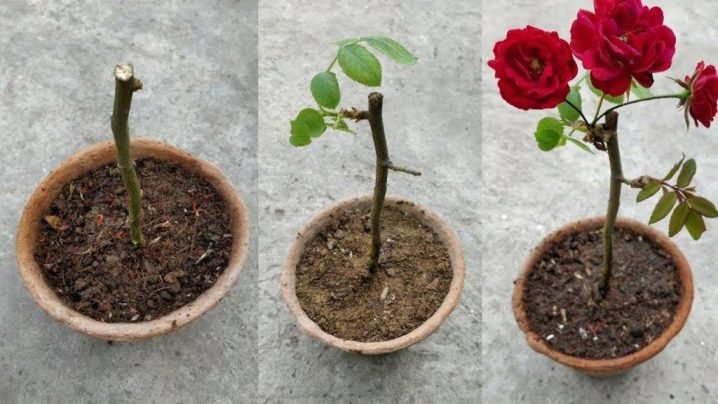
You can plant cuttings in a day or two. This option is only suitable if the rose in the vase has already sprouted.

Before transplanting a plant into a pot, you need to make sure that it is chosen correctly, and there will be no problems with the soil. The height of the pot, which is chosen for the cutting, should not be less than 20 cm. A drainage layer at the bottom is required, because water can be considered the main enemy of small roots. Expanded clay is quite suitable for this purpose. It is good if the pot itself is made of clay or ceramics, which better organizes the access of oxygen to the roots.
As for the soil, it is probably easier to buy a suitable mixture for roses in the store. It will be light, loose, not retaining excess moisture - exactly what is needed to grow a healthy flower from a purchased rose. If you want to make the soil yourself, you need to combine 2 shares of humus, 2 shares of land from the garden and 1 share of pure river sand. If the soil is heavy, it is mixed with sand in equal proportions. Necessarily the substrate must be disinfected, either using a weak solution of potassium permanganate, or by sending it to the oven for calcination.

Pot planting technology
Best of all, roses from a bouquet take root in the ground in spring or early summer.
How to properly plant a stalk.
- Make a suitable hole in the pot. Only one or two upper buds should be left on the surface, the rest of the cutting should be hidden under the ground.
- Dip the lower cut of the stem into powder (fertilizer), the same "Kornevin".
- Send the stalk into the hole, cover it with earth, slightly compact the surface.
- Sprinkle water over the ground, preferably at room temperature.
- Place a bag (or a cut-off plastic bottle) over the pot. If you decide to take a package, you need to put spacers in advance - any wooden skewers or something similar to them.
- From below, the package must be secured with a rubber band so that the greenhouse effect is not disturbed.
The pot must be sent to a cool place, the temperature +18 will be optimal. It is necessary to organize the plant with diffused lighting, not very intense. It is impossible for ultraviolet light to directly affect the flower. The stem should be sprayed every day, and at first it can be 7 times a day, after a week you can reduce the intensity to 2-3 times a day. Every day you need to remove the bag for a few minutes so as not to cause waterlogging. And as soon as the first leaves have sprouted, the rose should be ventilated more often. After it gets stronger, you can remove the mini-greenhouse completely.
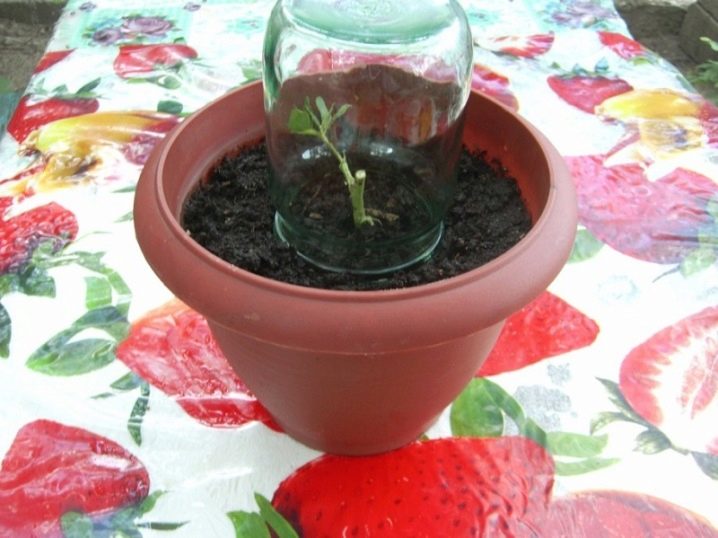

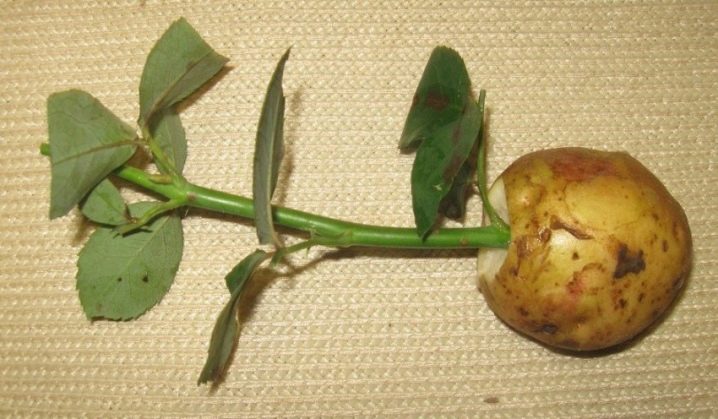
And there is another option for sprouting a store rose - in potatoes. It is the tuber in this case that becomes the source of moisture and nutrients. First, eyes are cut out of it so that sprouts do not go. Then they prepare such a pot so that the tuber can calmly enter it, and so that there is space under the ground.
What to do next:
- cut a hole in the middle of the tuber, so that the stem holds well in it;
- the stalk is dipped in dry Kornevin powder;
- the stem is inserted into the potato;
- together with the potato stalk, it is sent to the hole, covered with soil, one or two buds should remain above the surface;
- the earth is spilled with water;
- from above, all this is covered with a bag or a jar to create a suitable microclimate.
Further care is exactly the same as for a cuttings rooted simply in the ground. Potatoes help avoid infections and rot, which are dangerous for a young plant, especially for its fragile roots.

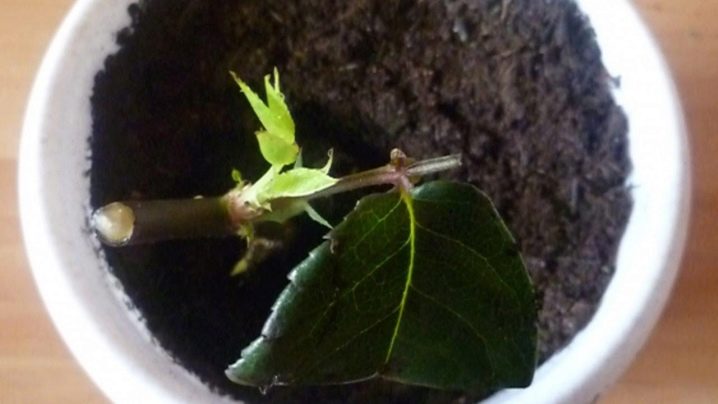
Follow-up care
The rose care complex needs to be painted separately. A healthy plant will like the southern window (and the southeastern one too), it will appreciate competent watering and regular balanced feeding.
Conditions
It is good if in the room where the rose rooted in the pot will grow, the humidity is maintained at about 50-60%. Conditions that are at least somewhat close to subtropical ones are not needed: domestic roses (and store-bought ones almost always root only at home) will not take them out, they will start to hurt and rot. You can create the necessary humidity by spraying with water in the evenings, the water should be at room temperature. If the room is cool, the water should be sprayed less frequently. If the flowerpot is on a windowsill, under which there is a battery, spraying should be more frequent.
And to additionally humidify the air, an open container of water is placed next to the pot.
In warm weather, the temperature should be up to +22 degrees, in winter it should be lower, up to +15 (therefore, it is better to take the pot out to a glassed-in balcony or loggia, in the conditions of a house - to the veranda). It is necessary to moisten the earth as it dries, to monitor the formation of a crust on it. By autumn, watering can be reduced to 2 times every 10 days. You can water with settled water, you can also use mineral water without gas. But only after 30 minutes it is necessary to drain the remaining water from the pan, otherwise the roots will begin to rot.

Top dressing
Everything here is as simple as possible - the rose needs mineral fertilizers with potassium and phosphorus in its composition. Subsequently, any antifungal drug, for example, "Fitosporin", can be added to the solution from these components.
In shops you can buy a special agricultural complex for roses.
Possible problems
To make a stalk from a donated rose and root it so that a new plant grows is a real and even interesting process. But not at all hassle-free... You can make a list of the most common problems that arise in the process of growing a rose from a bouquet.
12 nuances that make rose growing difficult (and all can be avoided)
- Heat... In extreme heat, the flower does not feel well, therefore, as soon as the thermometer rose to +22, an urgent need to transfer the rose somewhere. But the plant does not like frosts either, the leaves and buds will immediately leave the rose if it freezes.

- Insufficient watering. The rose does not need a lot of moisture, but watering should be regular. If it is hot, then twice a day it is necessary to water the flower, but in moderate doses. You can add ash to the water, and watering will also turn into top dressing.

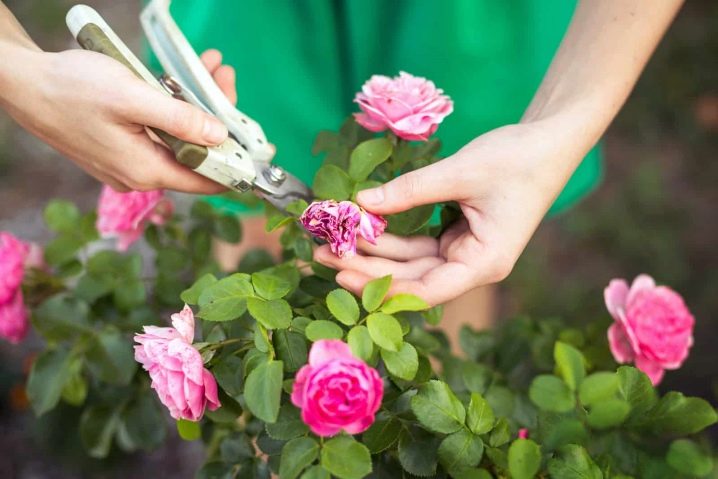
- Refusal to trim... It must be preventive and formative. Preventive maintenance is carried out no more than once a month - this helps to rid the flower of excess dried petals, on which it spends strength. Formative pruning gives the plant a beautiful look: you need to remove excess branches, cut off too large leaves and buds. Better to do this in the spring.

- Transplant at the wrong time... It is better to transplant in April: at this time, the adaptive properties of the rose are high, it will take root well. You can do this in the fall, but the chances of success are already lower. Planting a rose in the ground in other months is undesirable.

- There are no conditions for the formation of a sprout. Not every rose in a vase will sprout. For this to happen, you need to cut off the stem by 5 cm, wash off all the chemistry from the flower, put the plant in clean water in a vase. And be sure to expose to light: it is good if phytolamps are used. Then you need to inspect the flower for pests - it is possible that a spider mite appeared on it, for example. You need to look at the leaves - if there is a dusty layer on the back of the fallen leaf, and cobwebs are also found between the branches, you must immediately use an insecticide.
When the leaves begin to fall off, you need to carefully examine the stems - if there are shoots there, well, they can be used.

- Rooting in January and February. This is the most unfortunate period for rose germination. Technically, the process can be organized: temperature, backlight. But the rose has little strength during this period.

- The process is not taken there. Firstly, it is often a problem to try to take a shoot from an already fading flower. It's useless. Secondly, the wrong part of the stem is taken: the middle part is needed. A thick, juicy, green stem is what you need. The buds on it should be fully ripe and not dark.

- An attempt to grow a flower with a defect. If the rose has been cut for a long time and has been in the vase for a long time, most likely it is already unusable: after a long standing in the vase, pathogens start on the rose. If the stem of the flower is very thin, or it is already lignified, has a thick core, this option is also unsuitable. A stem darkened in water is a marriage, cracks on it are also not suitable. And if there is no skin in some parts of the stem, such a rose cannot be used either.
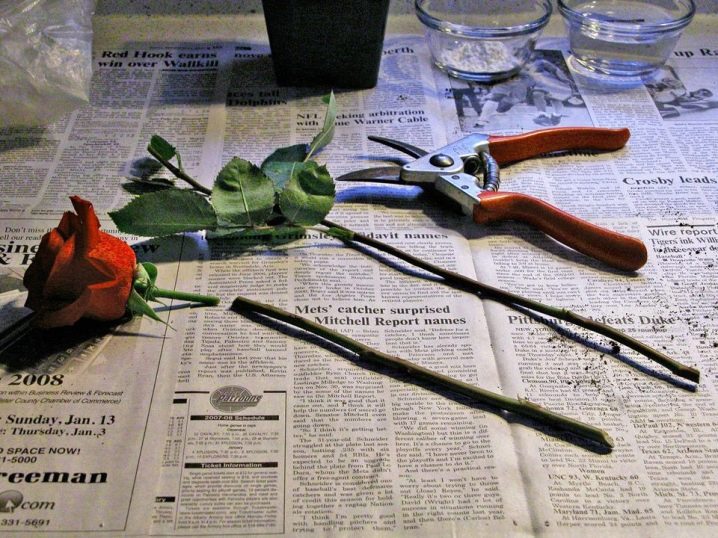
- Landing at the wrong time. Late spring is considered the best period, sooner or later - there is less chance of success.

- Unsuitable place for planting in the ground. A rose grown at home may not take root in the ground due to the fact that the place chosen for it is open to winds and drafts, as well as shady.
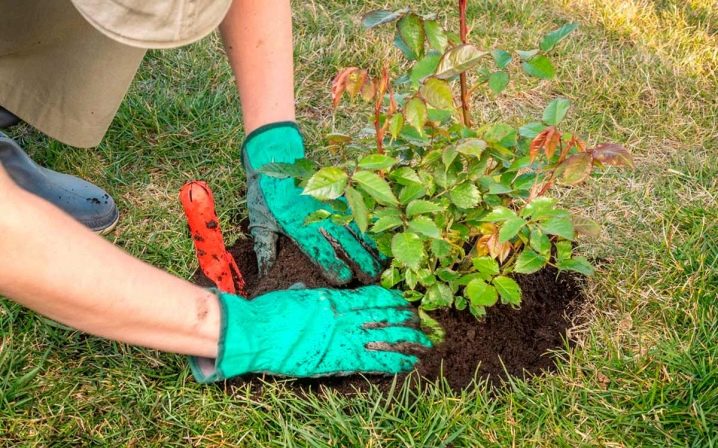

- There is no proper preparation even at the vase stage. For example, you need to change the water in it every day. And at night, the flowers can be lowered into a basin of water with their heads down.
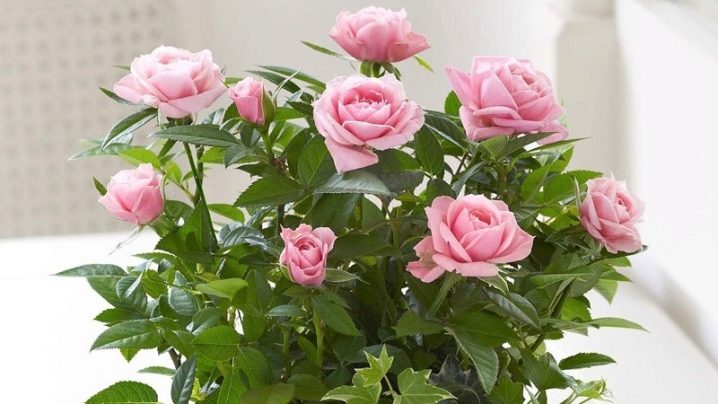

- Rapid budding. If they appeared on newly rooted seedlings, they will have to be plucked, otherwise the plant will give all its strength to them, and it is too early for it to spend them on flowering.
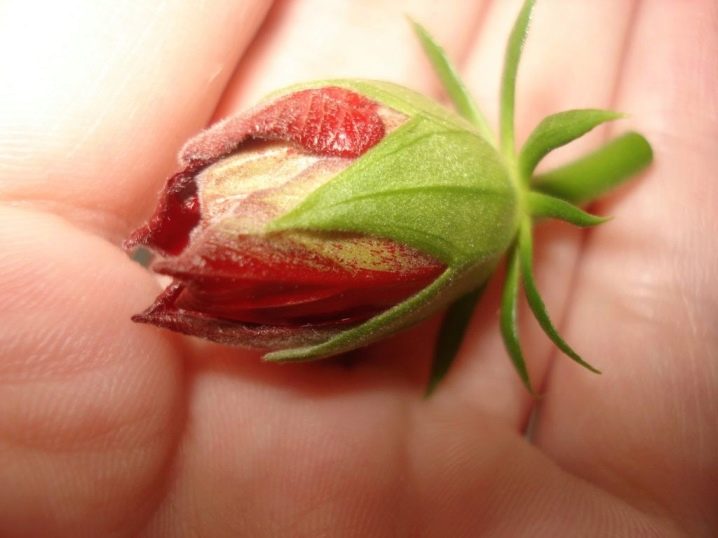

The growers themselves note that pink and red roses are best grown through the shoots of a flower in a vase.... But for a yellow rose to sprout, and it turns out to be viable, this is a rarity. For the rest, much depends on the timeliness of the procedures and the fulfillment of all conditions.


































































































The comment was sent successfully.