All about a rooted rose
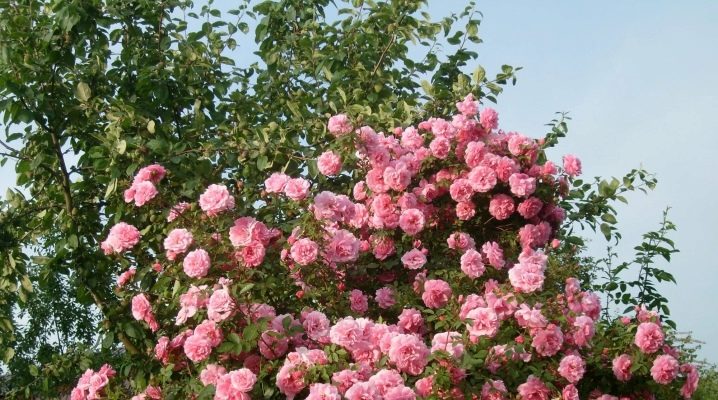

Rose is the queen of flowers, and this is a well-known fact. A beautiful plant with fragrant buds will adorn any garden, but the choice of a suitable shrub should be approached responsibly. Recently, own-rooted roses are gaining popularity. It is worthwhile to understand in more detail what they are and what features they have.


Description
Most of the modern varieties of roses are the result of many years of selection of rose hips, which gave wonderful fruits. Long ago, roses were used as a medicinal plant, but over time, rose oil has become a breakthrough in perfumery, and flowers have become a decoration of the garden.
Today, all bred varieties are divided into two groups:
-
own-rooted roses;
-
grafted roses.


The peculiarity of self-rooted roses is improved resistance to external factors. In case of severe frosts, such flowers may freeze, but all the characteristics of the selection variety will remain in the roots, and the plant will be able to germinate again. The vaccinated do not have such a feature, so they are not so popular.
Other advantages of self-rooted roses include:
-
immunity to diseases and pests;
-
abundant flowering;
-
inability to form root shoots.


Bushes of such flowers will not become wild, and in the event of an unsuccessfully experienced winter, the bush will literally rejuvenate, releasing new branches, and at the same time will not lose its decorative effect. The only disadvantage of such a plant is the increased demand for care. To grow powerful bushes with a strong and well-developed root system, it will take at least two years, during which the plant must be carefully looked after.

In addition, when choosing a place for planting a rose, you need to select only high-quality soils.
What is the difference from the vaccinated?
Own-rooted and grafted roses are the two main groups of the popular flower, into which all varieties are divided. What is the difference between them? Consider the characteristic differences between the former and the latter.
-
Demanding care... Gardeners do not dare to grow their own rooted roses only because they require careful maintenance in the early years. This is especially true for the hybrid tea group, which will take several years to look after.
-
High survival rate... Interestingly, this indicator for a self-rooted rose is higher compared to the grafted sample. They take root better in soils and begin to grow.
-
Slow growth... Here, grafted bushes win, which quickly start growing and delight with flowering in just 1-2 years. Own-rooted bushes will take at least 5 years to gain strength.
-
Long lifespan. Unlike the grafted, self-rooted ones are able to live up to 15 years, during which they will release a huge number of buds.
-
Lack of overgrowth. A characteristic feature of own-rooted plants.


As statistics show, gardeners in most cases, over time, tend to transfer grafted varieties to their own roots, and this is quite possible.
Types and varieties
There are a great many varieties and types of self-rooted roses. Here are the most popular ones.
-
Tea-hybrid... The rose was bred back in the 18th century by French gardeners by crossing remontant and tea cultures. The main characteristics include erect stems, a spreading crown, large buds of a refined shape.
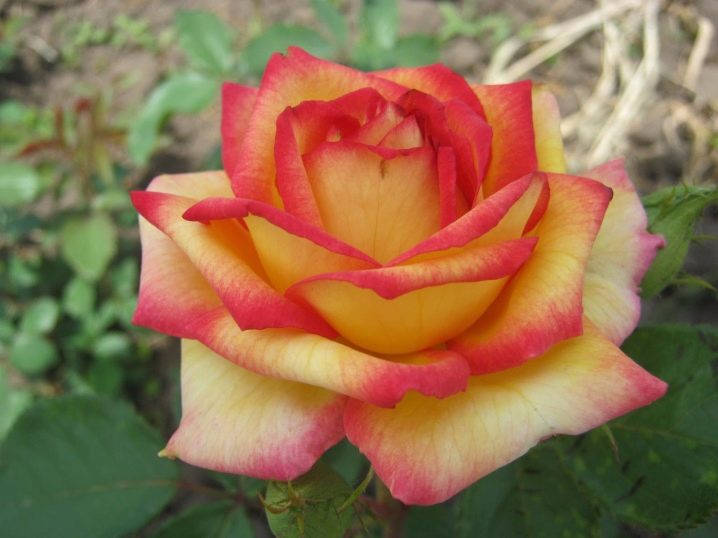

- Grandiflora... And also the rose is known as "Elizabeth".The variety is a hybrid obtained by crossing a hybrid tea rose and Charlotte Armstrong in 1954. The peculiarity of the bush is in long shoots, each of which grows from 2 to 5 flowers.
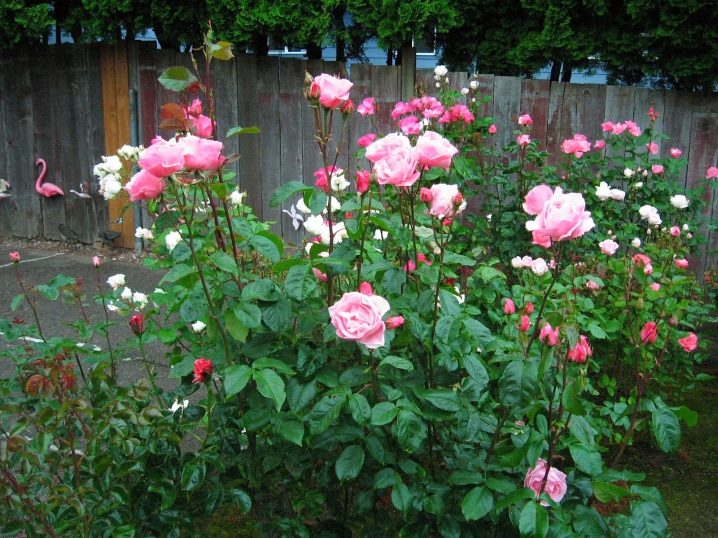

- Climbing... The variety was brought from China, it is distinguished by climbing shoots, the length of which reaches 5 meters with proper care. Other features of the rose: rich dark green foliage and different size of petals depending on the season. The climbing rose is suitable for growing both in the garden and at home.

- Floribunda... A fairly young variety, which is distinguished by its small height and fragrant buds. The flower petals are mostly double, with pointed tips. On average, the shoot releases up to 15 flowers.

- Park... A popular variety of roses, developed in the 16th century. It grows almost everywhere, for which it is appreciated by gardeners. Differs in high shoots, each of which contains a huge number of flowers. Duration of flowering - from mid-June to the first frost.

- Shrubs... The roses were bred in the twentieth century, the maximum length of the stems reaches 15 meters, and this is a unique feature of the variety. Curly shoots spread along the ground, forming multi-colored bright buds with a pleasant aroma.

- Miniature... Brought from China in 1810, they are small in size, the maximum height of the bush is only 45 cm. The plant forms small inflorescences, each includes 15 buds. During the season, it blooms up to three times, delighting with double and fragrant buds.

- Spray... Shrubs of small height, which are distinguished by small buds. During the flowering period, each stem forms up to 15 flowers, for which it is appreciated by gardeners. In addition, the variety is often crossed with other species, which allows you to get a variety of flower colors.

- Groundcover... Creeping species imported from Greece. It is still popular. Among the characteristics: the height of the stems is 45 cm, the leaves are dark green, the buds are small, colorful and fragrant. One inflorescence forms up to 15 buds.

- Centifol... A type of large bushes, the height of which reaches 2 meters. On average, 3-4 inflorescences are formed from large, spherical buds. One flower contains up to 45 petals, each of which exudes a light and unobtrusive scent.

- Japanese... Young roses bred not so long ago. The maximum height of the shoots is no more than 1.5 m, the diameter of the flower reaches 10 cm.

- Canadian... The peculiarity of roses is their increased resistance to frost. The bushes are able to withstand frosts down to -40 degrees Celsius without additional shelter. This species has both large and dwarf subspecies.
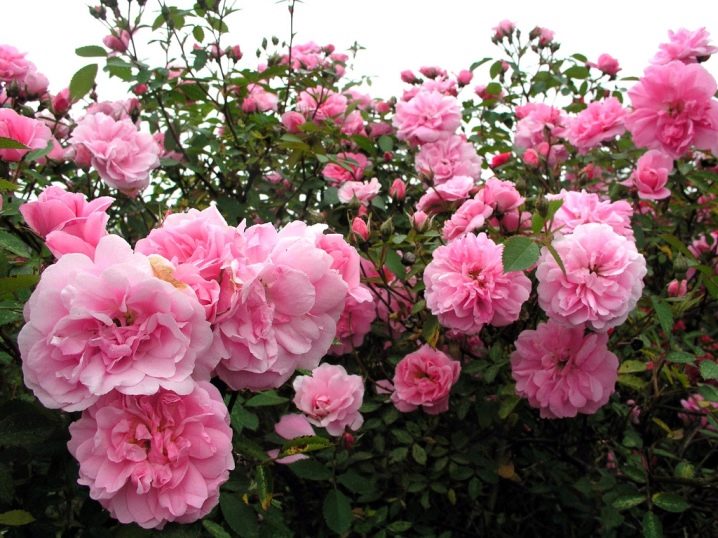

- English... It is not hard to guess where the variety was bred. It is distinguished by spreading shoots and large flowers with a diameter of 15 cm. The petals have a tongue-like shape, the average number is 50 pieces in each flower.

And this is not a complete list of existing varieties and types of self-rooted roses bred by breeders.
Bushes are in demand among both gardeners and landscape designers who use unique plants to create colorful compositions. Some varieties of self-rooted roses are suitable for growing at home.
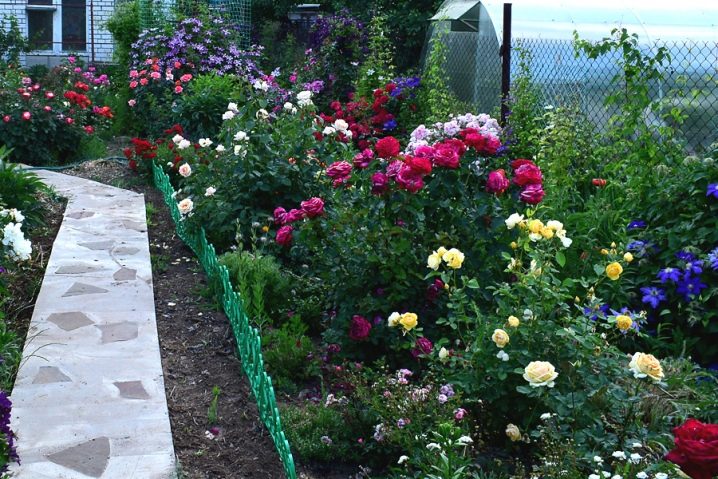

Growing
Before you start growing your own rooted rose, you need to carefully prepare the place for proper planting. This is especially true if the bush is planned to be planted in Siberia. Main steps.
-
First, you will need to independently dig a landing hole, the depth and diameter of which will be 50 cm.
-
A layer of expanded clay should be poured at the bottom of the pit to organize effective drainage and prevent moisture stagnation after irrigation.
-
Next, after expanded clay, it is necessary to lay out a layer of organic fertilizers. Humus mixed with ash or dolomite flour is perfect.


A young rose is planted in the prepared hole, grown from a cuttings or purchased in a gardening store, which is then carefully sprinkled with fertile soil and watered abundantly. After that, it remains to take care of the plant so that it quickly takes root and starts active growth.
Leaving includes a number of points.
-
Watering... If the rose is grown in a humid climate, then regular loosening of the soil in order to saturate it with oxygen is an excellent substitute. Under normal conditions, the shrub will need regular and abundant irrigation to prevent the risk of unnecessary disease and chopping of flowers. It is recommended to reduce watering only with the onset of autumn cold weather, and in winter it is worth completely abandoning watering the rose.
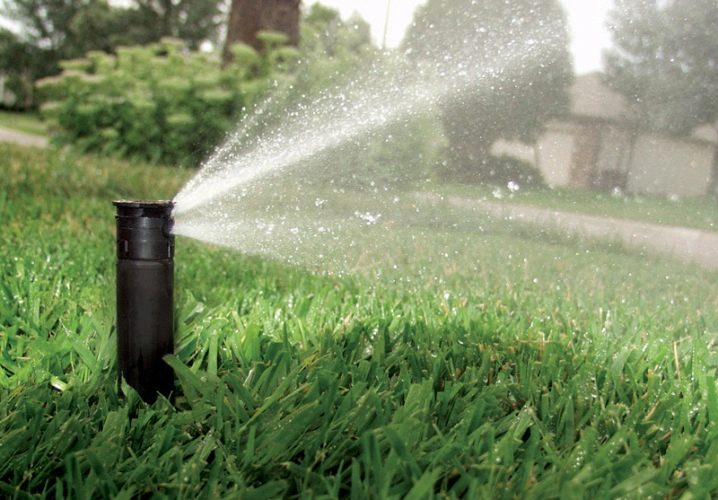

- Top dressing... Fertilize own-rooted bushes several times per season. The first fertilizers begin to be applied in the summer, then the soil is fertilized every 2 weeks using organic or mineral compounds. In the middle of summer, preference should be given to nitrogen-containing complexes, as well as compositions with potassium and phosphorus, in order to slow down the growth of stems.

- Pruning... It is carried out mainly in the fall to help the bushes survive the winter. It is recommended that a couple of weeks before the first frost, carefully remove all the tops of the bush and young branches, and then spud the plant.
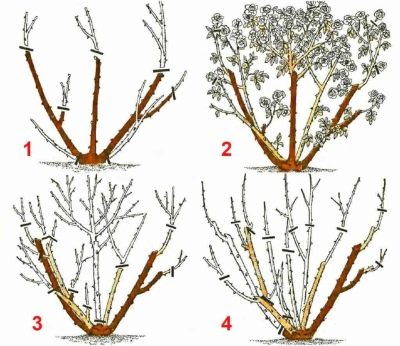
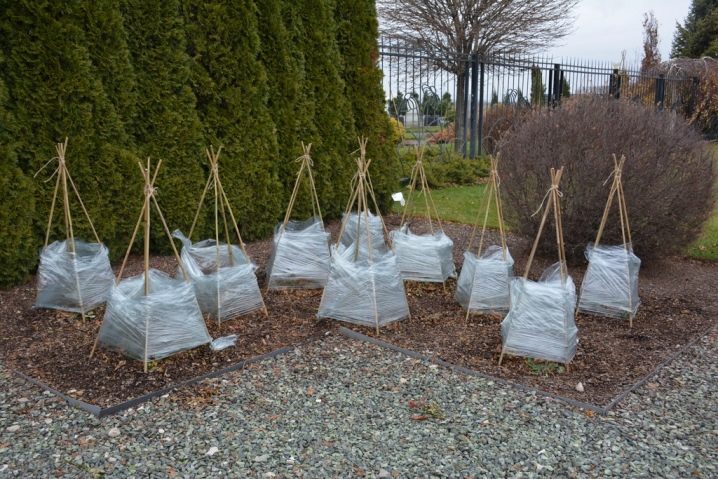
Particular attention should be paid to preparing roses for winter. When the thermometer drops to -10 ... 15 degrees Celsius, it is recommended to cover the bushes with spruce branches or a layer of dry foliage. And also sawdust or needles are suitable as a shelter material. The maximum layer thickness is 20-25 cm, this will be enough to protect the plant from frost.
To avoid the appearance of rodents who may like such a shelter, plastic or metal rods should be installed around the bush.


































































































The comment was sent successfully.