How to plant grafted roses correctly?

It's no secret that a well-groomed rose garden will adorn any site. However, it should be borne in mind that the cultivation of these rather whimsical flowers requires certain theoretical knowledge and relevant skills. That is why it is necessary to know how to properly plant grafted roses. It is important to remember that even seemingly minor mistakes can have serious consequences.

The right time for planting
Modern flower growers plant roses in open ground in spring, summer and autumn. Moreover, each of the periods has certain characteristics in the context of the creation and development of the rosary. And one of the key factors is the climatic conditions typical for a particular area.
Naturally, there is a list of the most favorable and recommended terms.
- The best time for planting is spring.... This is primarily due to the fact that young plants will have enough time to develop and get stronger before their first wintering. During the summer months, the bushes actively grow their root system. However, planting too early in the ground can have negative consequences. The factor of recurrent frost should be taken into account.
- Most experts consider summer not the best period for performing the described work within the framework of growing roses.... But some still plant the grafted young in these months. It is important to implement all agrotechnical measures in June, that is, before the peaks of solar activity.
- As part of the autumn planting, the most favorable period will be from mid-September to mid-October. But it is important to consider that this option is most relevant for the southern regions with warm autumn and late frosts. The obvious advantages of the autumn landing can be confidently attributed to the increased air humidity. In such conditions, moisture from the foliage evaporates more slowly, and the seedlings themselves take root much more actively and faster.

How to determine the site of vaccination?
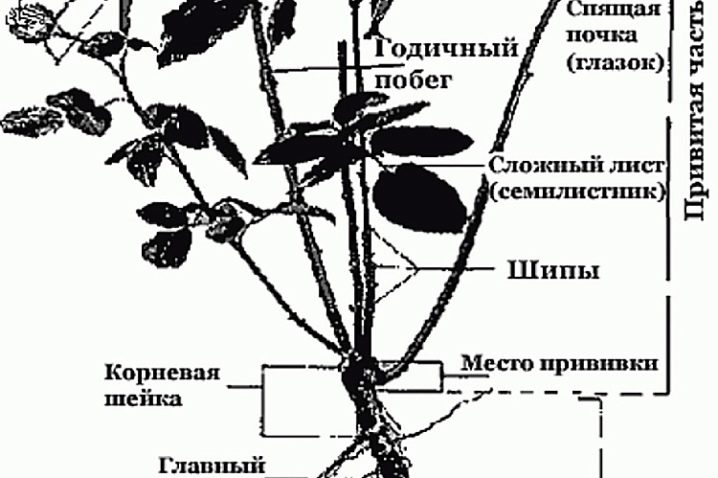
In principle, finding exactly where the vaccine is located is quite simple. At the same time, beginners often face certain problems when finding the appropriate place. However, finding it is not difficult. The fact is that we are talking about the root collar or the stem of the rose hip, which is the starting material.
The scion point is a characteristic thickening, and most importantly, this is the very beginning of the branching of the shoots of the rose bush.
When planting roses, should the vaccine be buried or not?
The answer to this question remains a topic for quite heated disputes of flower growers for many years. However, there are more supporters of the fact that the grafting site of roses when planting should be buried in the ground than opponents of this method. But it is important to take into account that the depth at which the described point of the seedlings is placed is directly determined by the composition of the soil.
Two confirmations of this statement can be distinguished.
- David Austin's recommendations, who managed to personally breed 169 varieties of roses. This respected florist advises immersing the graft in the soil to a depth of 8 to 12 cm. In his opinion, this approach guarantees the formation of strong young shoots. However, it is worth highlighting one important point, which is that the soil must be loose.
- Long-term observations of experienced florists over the development of rose bushes, planted in two different ways: with and without grafting. In the second case, as a rule, a distinctive feature of the bushes is the absence of new shoots against the background of a single and thin stem. In such a situation, roses release their own roots, spending almost all their strength on this. Predictably waiting for abundant flowering does not make sense.

It would be useful to give some more weighty arguments. It is important to note that an open basal neck inevitably becomes covered with bark, which in itself prevents the development of new buds. In addition, under the influence of ultraviolet rays, this part of the plant, remaining above the ground, stratifies and dries.
By the way, some growers find other reasons for such phenomena. Naturally, everyone chooses personally how to plant the grafted roses.

If the option with the deepening of the graft is chosen, then it is strongly recommended to take into account the following important points regarding the immersion depth.
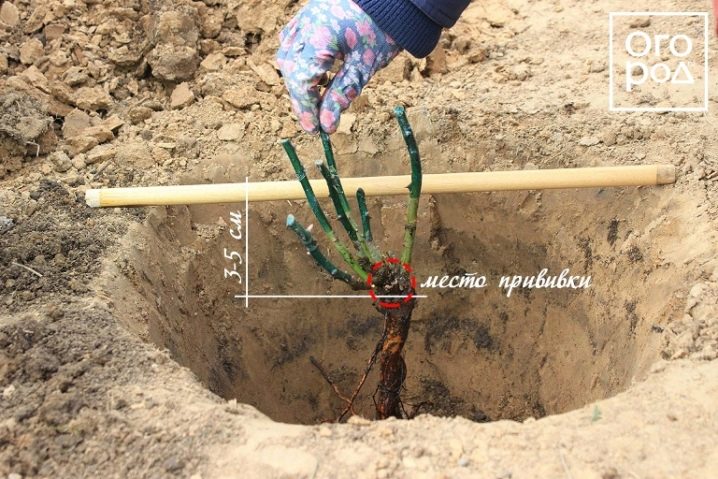
- Fertile and loose soil - 8-12 cm.
- If there is sand in the soil, a clay layer about 20 cm thick is arranged in the planting pit, then humus or compost is poured. The seedlings are placed so that the grafting point is deepened by at least 10 cm. All these actions are due to the fact that moisture quickly leaves the sand.
- There is clay on the site - sand is added to the holes in front of the fertile layer. In such cases, grafting is deepened by only 3-5 cm. In this way, moisture stagnation, which is detrimental to the root system of roses, can be prevented.

In addition to the depth of the root collar and the scion point, as well as the planting pit itself, the width of the latter will be an important parameter. And here two factors will be decisive.
- The size of the root system and the degree of its growth. All roots in a straightened state should be freely located in the hole.
- The type of the rose itself. This means dwarf, climbing, standard, tea-hybrid and other varieties.
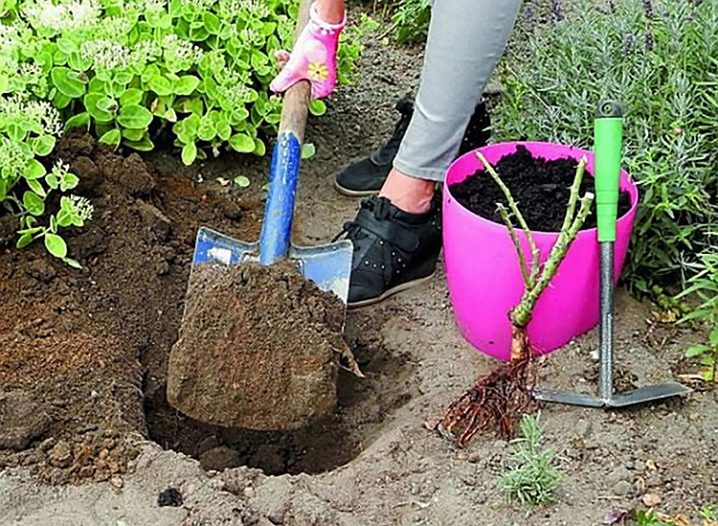

So, for climbing varieties up to 2 meters or more, planting pits with dimensions of 0.5x0.5 and 1x1 m, respectively, will be required. If we are talking about small ground cover roses, then it will be enough to make holes of 30x30 cm.For a hybrid tea beauty, holes of 0.4x0.4 m are needed.

Step-by-step instructions and basic mistakes
After the seedling and the place for it have been properly prepared, you can proceed directly to planting the rose bush in the ground. By the way, when choosing a site, it is important to take into account that the grafted individuals have a rather weak aboveground part, which will have to be covered for the winter. The very process of planting in open ground includes several successive stages.
So, if the described operations are performed in the fall, then at the preliminary stage it will be necessary to shorten the shoots, leaving from 5 to 8 buds, and remove all the leaves. This will allow the buds to develop, which will later give strong skeletal shoots.
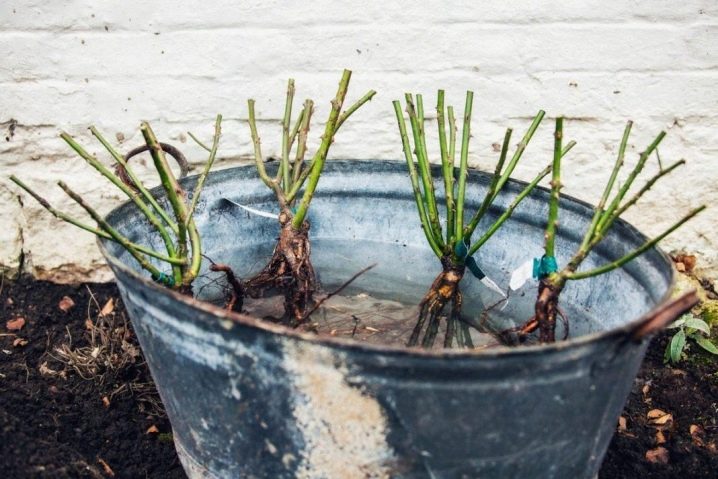

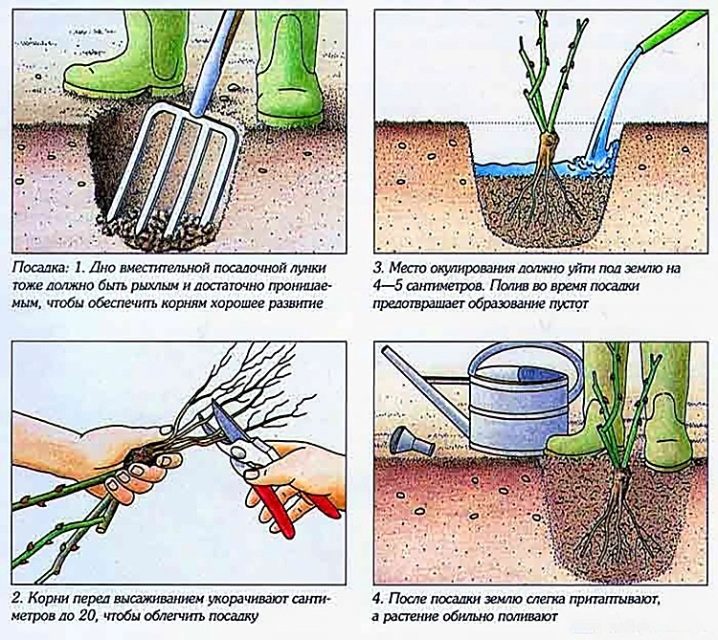
Planting grafted roses on the site step by step.
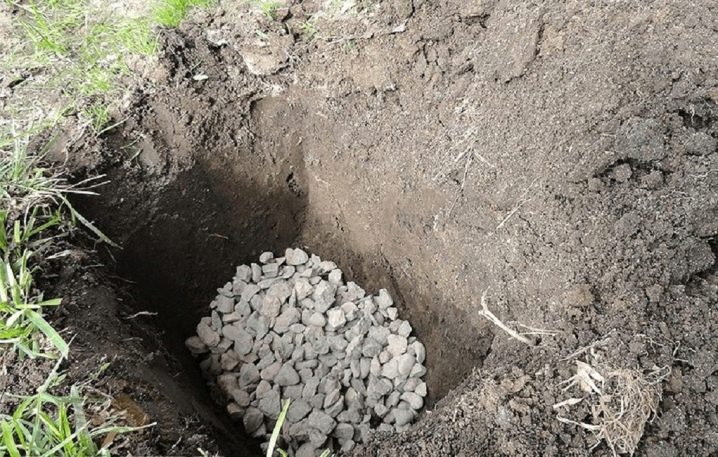
- Place a shallow drain at the bottom of the hole.
- Add a fertile layer.
- Make a clay chatterbox. The clay is diluted with water to the consistency of sour cream and the roots of the seedling are placed in the resulting solution. Planting should be carried out before the mixture dries.
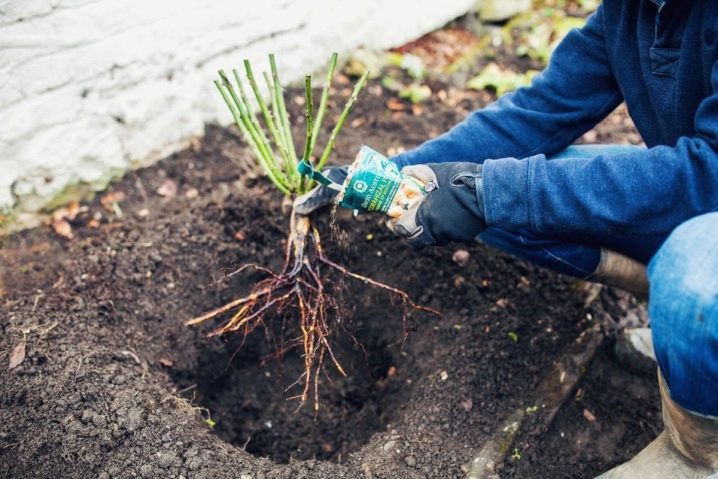
- Place the rose in the planting hole and spread the root system.
- Cover the hole with soil mixture and tamp lightly.
- Sprinkle the planted bush with plenty of heated water. This should also be done in situations where the soil is already wet.
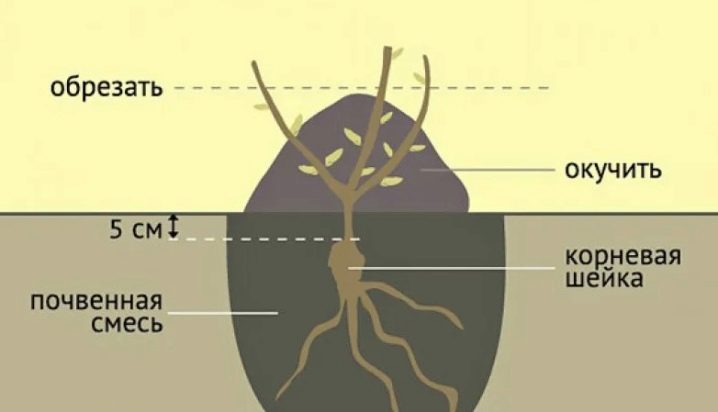
At the final stage, it will be necessary to spud the bush with soil to a height of about 10-15 cm.This technique will avoid drying out the trunk and simultaneously retain moisture. If the rose was moved to a permanent place in the fall, then before winter it will need to be huddled again to a height of 30 cm.
This layer is removed only in spring, after the appearance of the first shoots 2-3 cm long.
Most often, when planting grafted roses, flower growers (both beginners and some more experienced) make the following mistakes.
- Planting plants in areas with shallow groundwater... Roses react extremely negatively to excessively moist soil. If it does not dry out for a long time, root decay is likely to begin. It is also worth considering that in winter, wet soil will cool more actively.
- Selecting a shaded location, which will turn out to be extremely unfavorable for light and heat-loving plants.
- Excessive deepening of the vaccination site. The risk of kidney decay increases, and therefore the death of the bush.
- Poor soil preparation. It is important to remember that before planting, it must be dug to a depth of at least 15 cm with careful removal of weeds and the introduction of nutrients. Many growers also treat the soil with a potassium permanganate solution.
- Planting rose bushes in a draft, which poses a serious danger to thermophilic flowers.
- Placing bushes under wide tree crowns. The latter will shade roses, as well as take away a significant part of moisture and nutrition.
- Substrate use with high acidity.

Summing up, it should be recalled that without competent subsequent care, it is hardly worth counting on the full development of the bush and the abundant flowering of the rose. Without appropriate agrotechnical measures, it will be very difficult for a young plant to take root in a new place after planting in the ground.


































































































The comment was sent successfully.