All about copper wire

The most ordinary things, widely used in technology and everyday life, rarely attract close attention. And this is completely undeserved. Knowing everything about copper wire is useful even for the most ordinary person, not an engineer or a technician.


Peculiarities
Modern copper wire looks like the same products from other metals, similar to a thin string. Technologists speak in such cases about a very small cross-section. Most often, industrial production of copper wire is carried out by hot or cold deformation.... There are almost no impurities in its composition, there should be copper of exceptionally pure grades. The current GOST for copper wire was put into effect on January 1, 1992.
According to the standard, production should be carried out according to the principles of the current technological regulations. The diameters, the level of deviations, the proximity of the wire and rods to the shape of an oval are normalized. The surface of the product must always be clean and smooth. Invalid by the standard:
- cracks;
- defects such as sunsets;
- breaks;
- rolled sheets (if the depth exceeds the standard deviations from the diameter).


But what may well be present without violating the established norms:
- reddened areas left after etching;
- coloring of tarnished tones;
- small inclusions of technological lubricants.
It is imperative to remove the remaining tensile type stresses. This is achieved by annealing at low temperatures or mechanical treatment. Removing such defects is the most important component in technology design. Entanglement of wire rows and appearance of kinks is not recommended. The binding is done so that the density of the rows is not disturbed.
Only one piece of wire should be used for 100% of skeins, drum or other packaging.



Properties
The main advantage of copper wire is its low resistivity. That is why it is actively used in the power industry and the construction of various electrical appliances. The production of wires is greatly facilitated by the high ductility of the metal. High quality copper is easy to process in high precision mode. The alloy formula is selected in different cases individually, starting from what target properties should be achieved. The melting point of pure copper is 1083 degrees Celsius or 1356 degrees Kelvin. And the density of this metal is 2.07 g per 1 cm3. Therefore, it is not difficult to calculate the mass over the section:
- with a thickness of 1.5 sq. mm. - 0.0133 kg per 1 m3;
- with a cross section of 4 sq. mm. - 0.035 kg per 1 m3;
- with a cross section of 6 sq. mm. - 0.053 kg per 1 m3.


Species overview
Tinned copper wire is quite common... The bottom line is that it is tinned with electroplating. The coating layer can vary from 1 to 20 microns, depending on the situation. However, on a specific product, it is always the same. Tin layering increases wear resistance, allowing thinner wire than usual. The service life of tinned products is much longer than that of uncoated wire. In addition, the basic technological characteristics are also improved with such processing. But it would be very reckless to evaluate the diameter only from the point of view of the durability of the material.
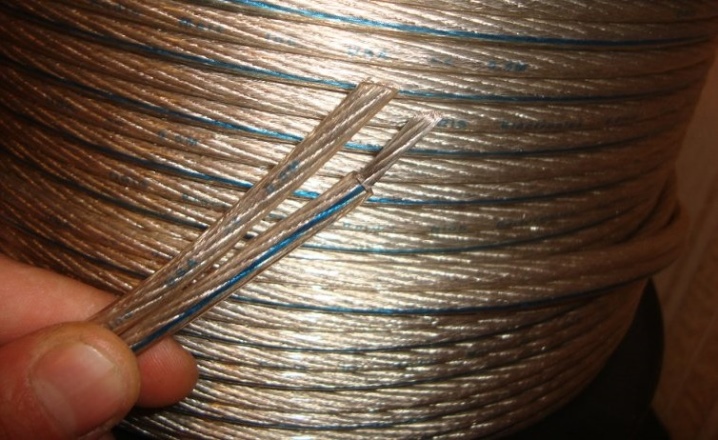

The thickness of the product directly affects its price. So, in many cases it is much more profitable to buy a thin wire with a cross section of 1 mm or 2 mm. But this is not always possible.For the manufacture of wires, it is also necessary to take into account the level of electrical resistance and resistance to heat. In many household appliances, you even have to use copper conductors with a cross section of 3 mm, 4 mm, and sometimes more. It all depends on how strong the current is to be passed through a particular circuit.
For hidden wiring and installation inside electrical appliances, thicker copper is needed than with external laying.

A serious problem for many DIY craftsmen and even industrial workshops is that insulated copper wire is extremely expensive.... The price of enamel protection is especially high. Therefore, quite often they acquire "bare" metal and cover it with a layer of varnish insulation. But only trained specialists or real enthusiasts of electrical engineering can cope with such work. Soft wire is obtained by annealing, and it is appreciated mainly where it is required to knot, bend metal.
But both hard and soft varieties of products can have:
- square;
- semicircular;
- flat section (it is superfluous to talk about a typical round).



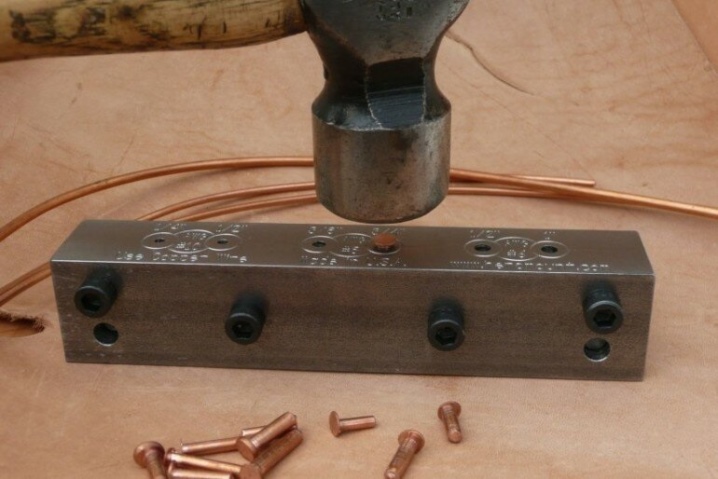
For rivets
Industrial consumers often buy coils and drums of copper wire to make rivets. The diameter and length of these rivets are very different. In addition to pure copper, they also use various alloys, including those containing phosphorus. The peculiarity is that during molding they produce a base in the form of a cylinder and a cap in the form of a semicircle.... The size of the rivets varies greatly and must be selected individually. Riveted products are hollow, supplemented with a washer, designed for engagement or for hammering.

Electrotechnical
With the help of this type of wire, network wires and cables for electrical appliances are made. It is also used in the production of enamel-coated wires, network cables for the LAN protocol. The nominal diameter of the electrical wire can be 1.15-4.5 mm. At shipment, boxed coils are sometimes secured with plastic tape. When sending wire in steel baskets, stretch film is wound on them.
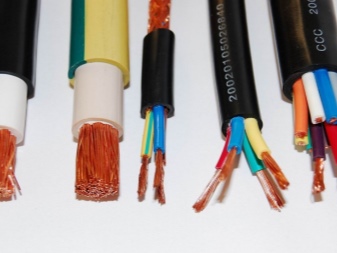

For the electrovacuum industry
The wire intended for it is evaluated primarily by such an indicator as vacuum density... It is determined by the ability of specific parts and parts to prevent the suction of gases and the ingress of other substances from the outside. Therefore, special attention is paid to the elimination of miniature cracks and hairs. Problems can also be caused by pores and shells that communicate with the external atmosphere. The use of metal containing impurities hazardous to the quality of the vacuum environment is categorically unacceptable.
That is why wire for the electrovacuum industry is produced with strict concentration control:
- zinc;
- cadmium;
- manganese;
- tin;
- phosphorus;
- bismuth;
- antimony and a number of other elements.

If we assume the presence of such impurities, then during the production of various products, they will evaporate and create deposits on the parts in the vacuum cavity. The limiting concentration of all harmful substances that can evaporate during the production of vacuum equipment is 0.0001%. Not only pure elements are taken into account, but also their oxides, oxides. The concentration of alloying additives is also strictly standardized, and in different heats within the same series, it can vary very slightly.
Alloys of copper with substances with a high melting point are usually obtained by mixing the powders and then sintering them. In any case, there are only three key electrovacuum copper grades - MV, MB, MVK. The presence of oxygen is also normalized - no more than 0.01% by weight. Smelting of copper-tantalum alloy is carried out in induction vacuum furnaces with minimal residual pressure.
Of course, only experienced engineers can choose a specific alloy and type of wire.

Welding
No matter how big the demand for copper wire is from the radio engineering industry, it is still much more used in welding. Since copper and alloys obtained on its basis in a liquid state react violently with oxygen and hydrogen, they are used only in an atmosphere of inert gases. The best results are obtained by welding in an environment of helium and argon... But, for reasons of economy, often use nitrogen - with skillful use, it turns out to be no worse. Copper wire is used in manual and semi-automatic welding, and in fully automated production.
Conventional gas welding with such a wire is also sometimes used.... But this is more typical for jobs that do not require special responsibility. Copper is useful for surfacing operations when special additional properties (wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.) are imparted to the treated surfaces.
Foreign-made welding products are labeled in accordance with the AWS (USA) standard or in accordance with the EU requirements.


Important: it is worth distinguishing between copper filler and copper-plated wire. When a seam is created without special requirements for strength, industrial copper is used (for example, M1 products). Cooking constantan, cupronickel is advised with copper-nickel additives. Here are some more matches:
- additives based on copper and nickel are suitable for bronze obtained from aluminum;
- copper-silicon wire is used to work with silicon-copper, zinc-copper structures, as well as for electric arc welding of galvanized steel surrounded by argon;
- copper-tin wire is needed for the electrical connection of tin-based bronzes in an inert environment;
- brass (L60-1, L63 and others) is needed to perform gas welding of brass and overlay coatings on steel with an increased carbon concentration.

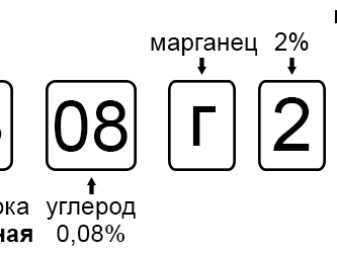
Marking
The special designations clearly show what the copper wire is for:
- М1 or М1р - automated electric welding in a chemically stable environment, obtaining electrodes;
- М2р - gas welding of universal copper products;
- MSr1 - responsible gas welding (as well as the production of electrical devices);
- MNZh5-1 - production of welding electrodes;
- BrAMts9-2 - manual welding of some alloys in a protective environment, manual and mechanized surfacing on steel;
- BrKh0.7 - auto electric welding of bronze based on chromium under a layer of flux;
- MML - for electrical purposes and conductive conductors;
- MS - creation of overhead communication lines.

Where is it applied?
It depends on the grade of metal; M1 wire can be used for grounding. It is distinguished not only by excellent electrical conductivity, but also by excellent heat conduction. This product will bend without any problem. On the basis of M1 wire, various wires are made for air and sea transport, for cryogenic equipment. But electrical round wire is needed to receive:
- winding of electric motors;
- cords;
- cables and wires.



The welding wire disassembled in detail above is used as a connection of semiconductor elements, during annealing and processing of silicon crystals. In addition to these applications, copper wire is needed for:
- crushing posts;
- receiving rivets, nails and other accessories;
- creation of building structures and printing machines;
- production of light industry apparatuses;
- production of bijouterie and decorative goods;
- creating chains, rings, bracelets, beads;
- some medical interventions (only externally!).


How to clean?
Even the best copper wire is inevitably coated with oxides in everyday use. Other contaminants can also accumulate on it. A very good cleaning method is to put the wire in a 70% vinegar solution. In such a solution, a dirty object must be boiled; the liquid should be slightly above the level of the metal."Cooking" takes 30 minutes, after which the wire is washed with water and the oxide is removed from it purely mechanically.
Slight contamination is removed with tomato ketchup. But you cannot count on cleaning in this way in case of serious oxidation. The most effective option has long been recognized to use an ammonia solution (at a concentration of 10%). It is necessary to keep the part in such a solution for no more than 10 minutes. After processing, it is thoroughly washed and mechanically cleaned.


For information on how to make nails or rivets from copper wire, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.