All about vinyl records

More than 150 years ago, mankind learned to preserve and reproduce sound. During this time, many recording methods have been mastered. This process began with mechanical rollers, and now we are already accustomed to using compact discs. However, vinyl records, which were popular in the last century, began to gain momentum in popularity again. The demand for vinyl records has grown, and with it people have begun to pay attention to vinyl players. Surprisingly, many representatives of the younger generations do not even have a clue of what a disc is and why it is needed.


What are vinyl records?
A gramophone record, or as it is also called a vinyl record, looks like a flat circle of black plastic, on which audio recording is made on both sides, and sometimes only on one side, and it is played using a special device - a player. Most often, one could find musical recordings on the discs, but, in addition to music, a literary work, a humorous plot, sounds of wildlife, and so on were often recorded on them. Records require careful storage and handling, therefore they are packed in special covers, which are decorated with colorful images and carry information about the content of the sound recording.
A vinyl record cannot be a carrier of graphic information, since it is only capable of storing and reproducing the sounds of an audio sequence. Today, many items released in the last century in our country or abroad are collectible items.
There are quite rare records, released in limited edition, the price of which among collectors is noticeably high and amounts to hundreds of dollars.



History of origin
The first gramophone records appeared in 1860. Edouard-Leon Scott de Martinville, a French-born and famous inventor of the time, created a phonoautograph apparatus that could draw a sound track with a needle, but not on vinyl, but on paper smoked from the soot of an oil lamp. The recording was short, only 10 seconds, but it went down in the history of the development of sound recording.


As history shows, subsequent attempts to make sound recording in the 18th century were wax rollers. The pickup device was hooked with its needle on the projections of the roller and reproduced the sound. But such rollers quickly deteriorated after several cycles of use. Later, the first models of plates appeared, which began to be made from polymer shellac or ebonite. These materials were much stronger and the sound quality was better reproduced with them.
Later, special devices were born with a large pipe, expanded at the end - these were gramophones. The demand for records and a gramophone was so great that enterprising people opened factories for the production of these products.


By about the 20s of the last century, gramophones were replaced by more compact devices - they could be taken with you to nature or to the country. The apparatus was operated by a mechanical device that was activated by a rotating handle.You probably already guessed that we are talking about a gramophone.
But progress did not stand still, and already in 1927, technologies for recording sound on magnetic tape appeared... However, large reels of recordings were difficult to store and often wrinkled or torn. Simultaneously with magnetic tapes, electrophones came into the world, which were already familiar to us record players.


Production technology
The way records are made today is a little different from the way they were made in the last century. For production, a magnetic tape is used, on which information is applied with the original, for example, music. It was the original base, and the sound was copied from the tape to special equipment equipped with a needle. It is with the needle that the base workpiece is cut out of the wax on the disk. Further, in the process of complex galvanic manipulations, a cast of metal was made from the wax original. Such a matrix was called inverse, it was possible to print a large number of copies from it. The most upscale manufacturers made another cast from the matrix, it was made of iron and did not show signs of inversion.
Such a copy could be replicated many times without loss of quality and sent to factories that produce phonograph records, which produced a large number of identical copies.




Device and principle of operation
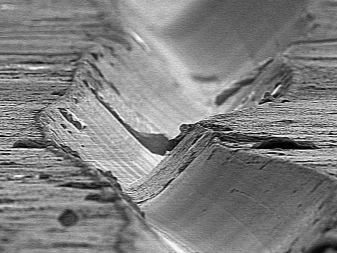
If you magnify an image of a vinyl record 1000 times under a microscope, you can see what the soundtracks look like. The dense material looks like scratched, uneven grooves, thanks to which music plays with the help of a pickup stylus during record playback.
Vinyl records are monophonic and stereo, and their difference depends on how the walls of these sound grooves look. In monoplates, the right wall does not differ from the left in almost anything, and the groove itself looks like the Latin letter V.
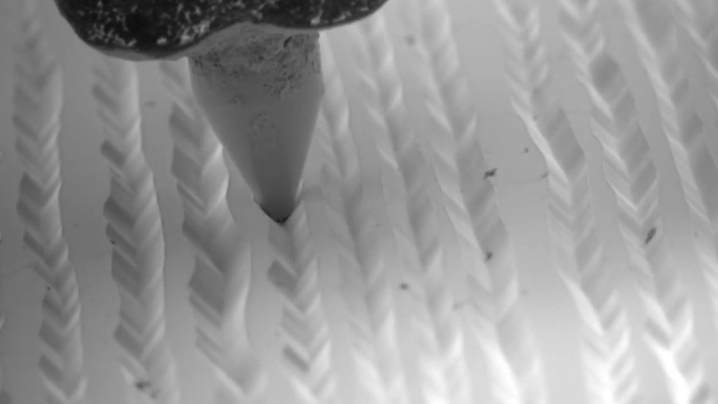
Stereophonic records are arranged differently. Their groove has a structure that is perceived differently by the right and left ears. The bottom line is that the right wall of the groove has a slightly different pattern than the left wall. To reproduce a stereo plate, you need a special stereo head for sound reproduction, it has 2 piezo crystals, which are located at an angle of 45 ° relative to the plane of the plate, and these piezo crystals are located at right angles to each other. In the process of moving along the groove, the needle detects pushing movements from the left and right, which is reflected on the sound reproduction channel, creating a surround sound.
Stereo records were first produced in London in 1958, although the development of a stereo head for a turntable was carried out much earlier, as early as 1931.
Moving along the sound track, the pickup needle vibrates on its irregularities, this vibration is transmitted to the vibration transducer, which resembles a certain membrane, and from it the sound goes to the device that amplifies it.

Advantages and disadvantages
Nowadays, it is much easier to use sound recordings in the already familiar mp3 format. Such a record can be sent in a matter of seconds to anywhere in the world or placed on your smartphone. However, there are connoisseurs of high-purity recordings who find that vinyl records have a number of undeniable advantages over the digital format. Let's consider the advantages of such records.
- The main advantage is considered to be the high quality of sound, which has the properties of fullness, volume, but at the same time it is pleasant to the ear and has no interference. The disc has a unique naturalistic reproduction of the timbre of the voice and the sound of a musical instrument, without distorting it at all and conveying it to the listener in its original sound.
- Vinyl records do not change their qualities during long-term storage, for this reason, many performers who highly value their work release music albums only on vinyl media.
- Records made on a vinyl record are very difficult to forge, as this process is long and does not justify itself. For this reason, when purchasing vinyl, you can be sure that a fake is excluded and the recording is genuine.


There are also disadvantages to vinyl discs.
- In modern conditions, many music albums are released in very limited editions.
- Recordings are sometimes made from low quality matrices. The original sound source loses its original properties over time, and after digitization, the source code is made from it for further execution of the matrix, according to which the release of records with unsatisfactory sound was established.
- Records may be scratched or deformed if stored improperly.


In the modern world, despite the digital formats of audio recordings, vinyl versions are still of great interest to music connoisseurs and collectors.

Record formats
The vinyl record is made of polymer plastic, it is quite durable, but also flexible. Such a material allows such plates to be used many times, their resource, with proper handling, is designed for many years. The service life of the plate depends largely on the conditions in which it is used. - scratches and deformation will make the audio recording unplayable.


Vinyl discs are usually 1.5 mm thick, but some manufacturers produce records that are up to 3 mm thick. The standard weight of thin plates is 120 g, and thicker counterparts weigh up to 220 g. There is a hole in the center of the record, which serves to put the disc on the rotating part of the turntable. The diameter of such a hole is 7 mm, but there are options where the hole width can be 24 mm.
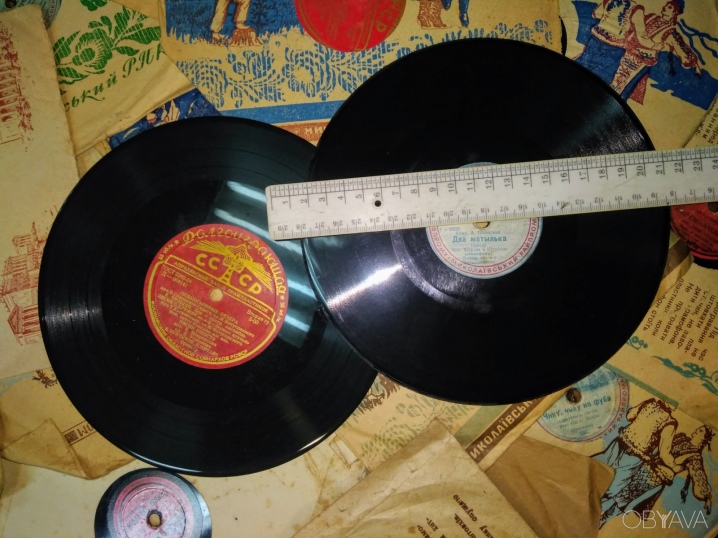

Traditionally, vinyl records are produced in three sizes, which are usually calculated not in centimeters, but in millimeters. The smallest vinyl discs have an apple diameter and are only 175 mm, their playing time will be 7-8 minutes. Further, there is a size equal to 250 mm, its playing time does not exceed 15 minutes, and the most common diameter is 300 mm, which sounds up to 24 minutes.

Views
In the 20th century, records have undergone changes, and they began to be made from a more durable material - vinylite. The bulk of such products have a certain rigidity, but flexible types can also be found.
In addition to durable plates, so-called test plates were also produced. They served as an advertisement for a full-fledged record, but were made on thin transparent plastic. The format of these test strips was small to medium.
Vinyl records were not always round. Hexagonal or square vinyl can be found from collectors. Recording studios often released records of non-standard shapes - in the form of figurines of animals, birds, fruits.
Traditionally, phonograph records are black, but special editions intended for DJs or for kids can also be colored.




Care and storage rules
Despite their strength and durability, vinyl records require careful handling and proper storage.
How to clean?
To keep the record clean, it is recommended to wipe its surface with a clean, soft, lint-free cloth before use, collecting dust particles with light movements. At the same time, you should try to hold the vinyl disc by its side edges, without touching the sound tracks with your fingers. If the record is dirty, it can be washed with warm soapy water, then gently wiped dry.


Where to store it?
It is necessary to store records on special open shelves in an upright position, so that they are located freely and can be easily reached. The storage space should not be placed near central heating radiators. For storage, packaging is used, which is envelopes. The outer envelopes are thick, made of cardboard.The inner bags are usually antistatic, they are used as protection against static and dirt. Two envelopes do an excellent job of protecting the record from damage.
At least once a year, the phonograph record should be removed and inspected using accessories made of soft fabrics, wiped off and put away again for storage.

Restoration
If scratches or chips appear on the surface of the record, it will no longer be possible to remove them, since the recording is already damaged. If the disc is slightly deformed by heat, you can try straightening it at home. To do this, the plate, without removing it from the package, must be placed on a firm and even horizontal surface, and on top place a load, which in its area will be slightly larger than the size of the plate. In this state, the plate is left for a long time.

Difference between records and discs
Vinyl records are very different from modern CDs. The differences between them are as follows:
- vinyl has a higher sound quality;
- popularity due to exclusivity in the global market for vinyl records is higher than for CDs;
- the price of vinyl is at least 2 times higher than that of a CD;
- vinyl records, if handled correctly, can be used forever, while the number of CD cycles is limited.
It is worth noting that many music connoisseurs value digital recordings, but if you have a collection of vinyl records, this speaks of a completely different approach to art and the high standard of your life.

Selection Tips
When choosing vinyl records for their collection, connoisseurs recommend paying attention to the following points:
- inspect the integrity of the appearance of the plate - if there is any damage on its edges, if there is no deformation, scratches, or other defects;
- the quality of the vinyl can be checked by turning with the record in your hands to the light source - a light flare should appear on the surface, the size of which should not exceed 5 cm;
- the sound level of a high-quality plate is 54 dB, deviations in the direction of decrease are allowed no more than 2 dB;
- for used records, use a magnifying glass to inspect the depth of the sound grooves - the thinner it is, the higher the record's preservation, and hence the longer its usability for listening.
Sometimes, purchasing a rare disc, connoisseurs of exclusiveness may admit that it has some minor defects, but this is unacceptable for new discs.

Manufacturers
Abroad, there have always existed and still exist many industries producing vinyl, but in Soviet times, the Melodiya enterprise was engaged in such products. This brand was known not only in the USSR, but also abroad. But during the years of perestroika, the monopoly enterprise went bankrupt, as the demand for their goods fell catastrophically. In the last decade, interest in vinyl records has grown again in Russia, and the records are now being produced at the Ultra Production plant. The launch of production began in 2014 and is gradually increasing its turnover. As for European countries, the largest vinyl producer located in the Czech Republic is GZ Media, which releases up to 14 million records annually.

How to make vinyl records in Russia, see the video.













The comment was sent successfully.