Plotter paper: characteristics and features of choice

A plotter is an expensive equipment designed for large-format printing of drawings, technical projects, as well as advertising posters, banners, calendars and other printing products. The quality of the print, the consumption of the ink resource and the coordination of the operation of the equipment itself depend on the characteristics of the roll paper. In the article we will tell you about what it is, in what cases it is used and how to make the right choice.

Characteristic
Most often, fairly simple requirements are imposed on paper for a plotter, the density, width and length of the winding are taken into account. But in large copy shops or design bureaus, where paper is used on a large scale, know how important its other technical characteristics are.

For roll paper serving plotters, the following properties are important:
- color image transmission;
- tonality of ink for specific equipment;
- percentage of paint absorption;
- drying time of ink;
- canvas parameters;
- paper density.


These characteristics are common for different types of securities. But when making a choice, one should consider whether the paper product has a special coating or nott. For graphics and drawings, the high precision of parts is important, which can be provided by an uncoated material. It is also the most economical in terms of paint consumption. Coated paper is used for posters, posters and other bright products where high-quality color reproduction is required.


So, let's consider a number of characteristics that are inherent in plotter paper.
Density
Since the density of paper is directly related to its weight, the definition of this property is expressed in grams per square meter, that is, the denser the paper, the heavier it is.
Different types of paper are selected for laser and inkjet plotters, but universal varieties that can fit any type of equipment are considered optimal. For example, a product containing the S80 symbols in the article from the manufacturer Albeo (density 80 g per square meter) is acceptable for both types of equipment. This density is suitable for pigment inks and water-based dyes.


Thickness
To determine the thickness of the paper, GOST 27015_86 and the standard of the international category ISO 534_80 have been developed. Products are measured in microns (μm) or mils (mils, corresponding to 1/1000 of an inch).

The thickness of the paper affects its permeability in the printing equipment system, as well as the strength of the finished product.
The degree of compaction (plumpness)
The chubbier the paper, the more opacity it contains at the same weight as the heavily compressed material. Such a characteristic has no effect on consumer properties.

Humidity
Balance is important for this indicator. High humidity leads to material deformation and poor ink drying. Too dry paper is prone to brittleness and reduced electrical conductivity. A product with a moisture content of 4.5% or 5% is considered optimal, such indicators guarantee high-quality printing.

There are many more indicators that are taken into account in various types of printing work. These include:
- optical properties - whiteness, brightness;
- mechanical strength;
- tear resistance;
- resistance to fracture;
- roughness;
- smoothness;
- the degree of absorption of dyes.


Any of these characteristics can affect the final quality of the printed matter.
Views
There are many types of plotter paper, it can be produced on large sheets of any size or in rolls, but they all make up two large groups - coated and uncoated material. Besides, each variety has its own characteristics and is designed to solve specific problems. The capabilities of the equipment on which the paper is selected are also taken into account, therefore, before purchasing it for the plotter, you should make sure that it is supported by this equipment.

In the instructions for the plotter, the recommended standard size should be noted, the type of technical device is also important - inkjet or laser.
Without cover
Uncoated paper is one of the most inexpensive grades. It is used in design bureaus for printing various types of monochrome documentation, diagrams, drawings. It is used when high contrast and clarity of details is required, even the finest drawing lines are visible on it.
It is impossible to print a colorful poster or a bright calendar on such material, since the color rendering will be at the lowest possible level., but making color inserts in drawings, highlighting diagrams, graphs and other fragments is quite acceptable. To do this, select uncoated paper marked “for color printing”.
The density of such products usually does not exceed 90 or 100 g per square meter. For its manufacture, cellulose products are used. Good strength is achieved through the use of a large amount of forming material and not through additional coating.


Such paper is highly economical, since ink does not drain off the sliding surface.
Coated
Coated paper has its advantages. Due to the additional surface, the density of the material is increased and its ability to transmit bright, spectacular images. It is used for advertising purposes, for the release of colorful products, standard and design works. Modern coatings hold the paint well, not allowing it to spread and even more so to be absorbed into the structure of the paper, which guarantees a high-quality realistic drawing. The high density of the product does not allow the pattern to shine through and eliminates the mixing of colors.


Coated paper is available in two flavors: matte and glossy photo-based. These varieties have a different purpose and cost.
Matt products (matt) are used for posters, posters and other images intended to be placed in a high-light area. This material has a large spread in density, from 80 to 190 g per square meter, it absorbs ink well, but stops the possibility of spreading it along the fiber structure, which allows you to apply the smallest details in a color image to the surface, print maps, drawings, technical documentation. But matte coated paper is much more expensive than uncoated monochrome media, so it's not profitable to use it for engineering projects all the time.


The most expensive paper for plotters is glossy. It guarantees maximum image fidelity. The high run-up of its density (from 160 to 280 g per square meter) makes it possible to specify the choice. The photo-coated top layer keeps ink from penetrating the fabric of the canvas. The next two layers containing synthetic fibers prevent product wrinkling as the paper moves through the printing equipment.


Photo paper is classified into high-gloss, highest quality and microporous, which absorbs ink well and dries quickly.
Self-adhesive photo paper is used for labels and promotional items. It projects vibrant colors that do not fade over time. Images made on this material can be easily glued to glass, plastic and other smooth surfaces.


Formats and sizes
There are two types of plotter paper: sheet-fed and roll-fed.The last of the types is the most popular because it has no size restrictions and is cheaper than sheet.
Manufacturers roll out large-format paper rolls up to 3.6m in size, and then cut them into more accessible formats.
On sale you can find paper with the following dimensions: 60-inch has a width of 1600 mm, 42-inch - 1067 mm, product A0 - 914 mm (36 inches), A1 - 610 mm (24 inches), A2 - 420 mm (16, 5 inches).
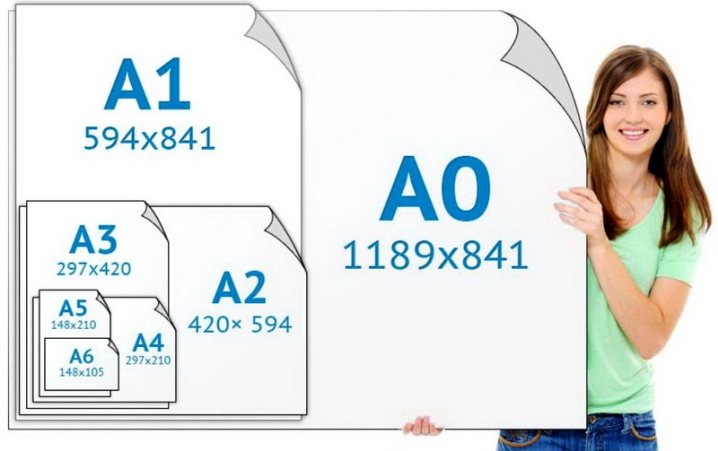
There is a relationship between the length of the roll and its density, the denser the material, the shorter the winding. For example, with a density of 90 g per meter, the square roll length is 45 m, and denser products are formed into rolls up to 30 m long.
The thickness of the paper is indicated by mils. One mils equals one thousandth of an inch. Plotters can use 9 to 12 mils paper, but some equipment can print on substrates up to 31 mils thick.

Choice
Choosing paper for plotters requires more care than for standard printers. Not only the final print quality depends on a reasonable choice, but also the durability of the equipment itself, since an incorrectly selected material will affect the operational properties of the plotter. The accompanying instructions for the machine provide information on the recommended paper (size, weight). Thinner material is more likely to wrinkle, and too dense material can get stuck.

When choosing paper, it is important to know the tasks that the plotter will have to face. For colorful advertising posters, glossy photo-based paper is required. For plotters, where greater accuracy of drawings and complex diagrams is required, material without special coating is required. For a cutting plotter, a surface with thermal film, self-adhesive or thermal transfer photo paper, designer cardboard, magnetic vinyl is suitable.

When choosing paper, they study the capabilities of the plotter and the requirements for the finished product, and also take into account the technical characteristics of the material. The right paper will give you amazing print results.
See the following video on how to choose paper for printing.













The comment was sent successfully.