All about polycarbonate
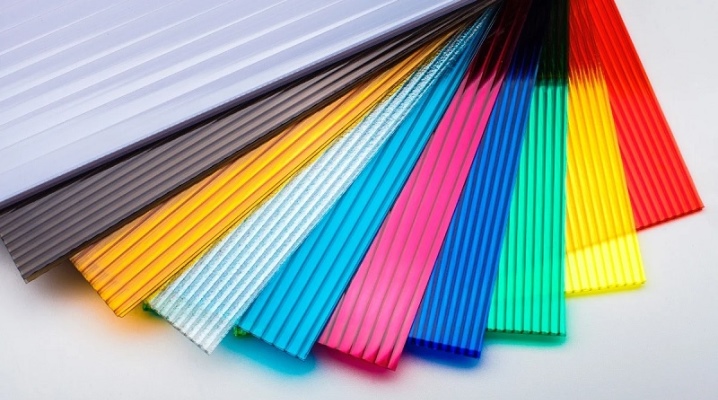

Polycarbonate is a popular sheet material widely used in the field of advertising, design, repair, in summer cottage construction and in the production of protective equipment. The consumer reviews received indicate that polymers of this type are well justified in their popularity. About what they are and why they are needed, how different types differ, what they are and what properties polycarbonate sheets have, it is worth learning in more detail.


What it is?
Construction polycarbonate is a polymer material with a transparent structure, a kind of plastic. Most often it is produced in the form of flat sheets, but it can also be presented in figured products. A wide range of products is made from it: headlights for cars, pipes, glasses for protective helmets. Polycarbonates are represented by a whole group of plastics, which are based on synthetic resins - they can have different compositions, but they always have common characteristics: transparency, hardness, strength. This material is widely used. It is used in the decoration of building facades, in the construction of awnings and other translucent structures.
Polycarbonate in sheets has a unique set of properties - it surpasses acrylic and silicate glass in strength, it is fireproof, since it melts when heated, and does not ignite. The invention of the thermoplastic polymer was a by-product of the pharmaceutical industry. It was synthesized in 1953 by Hermann Schnell, an engineer at Bayer in Germany. But his method was long and expensive.
Improved versions of the thermoplastic polymer soon appeared, and sheet versions began to be mass-produced already in the 70s of the XX century.



How do they do it?
All types of polycarbonate are produced today in three ways, each of which provides sufficient cost-effective manufacturing processes.
- Phosgene and A-bisphenol polycondensation (interfacial). It takes place in organic solvents or in an aqueous-alkaline medium.
- Transesterification in vacuum of diphenyl carbonate.
- Phosgenation in pyridine A-bisphenol solution.


Raw materials are supplied to factories in bags, in the form of granules. Light-stabilizing components are added to it, ensuring the absence of the clouding effect that previously occurred in this group of plastics upon contact with ultraviolet rays. Sometimes a special film acts in this capacity - a coating that is applied to the surface of the sheet.
The production process takes place in factories equipped with special autoclaves, in which raw materials are transferred to the desired aggregate state. The main method of manufacturing products is extrusion, it is this that determines the standard sizes of the honeycomb variety. They correspond to the width of the working blade of the machines. Monolithic polycarbonate is produced by stamping, with preheating in an oven where air is circulated.


Basic properties
According to the requirements of GOST established for polycarbonate, products from it must have certain characteristics. They are also possessed by a shower partition, a greenhouse or a translucent roof. For cellular and monolithic varieties, some parameters may differ. It is worth considering them in more detail.
- Chemical resistance. Polycarbonate is not afraid of contact with mineral oils and salts, it can withstand the effects of weakly acidic solutions. The material is destroyed under the influence of amines, ammonia, alkalis, ethyl alcohol and aldehydes. When selecting adhesives and sealants, their compatibility with polycarbonate should be taken into account.
- Non-toxic. Material and products made from it are allowed for use in the storage of certain types of food products.
- Light transmission. It is about 86% for completely transparent honeycomb sheets and 95% for monolithic ones. Tinted ones can have rates from 30%.
- Water absorption. It is minimal, from 0.1 to 0.2%.
- Impact resistance. It is 8 times higher than that of acrylic, and quartz glass is 200-250 times higher than polycarbonate in this indicator. When destroyed, no sharp or cutting fragments remain, the material is injury-free.
- Life time. Manufacturers guarantee it in the range of up to 10 years; in practice, the material can retain its properties 3-4 times longer. This weather-resistant type of plastic is easily adaptable to a wide variety of operating conditions.
- Thermal conductivity. For a honeycomb, the coefficient varies from 1.75 to 3.9, depending on the thickness of the material. In a monolithic, it is in the range 4.1-5.34. This material retains heat better than conventional quartz or plexiglass.
- Melting temperature. It is +153 degrees, the material is processed in the range from +280 to +310 degrees Celsius.
- Hardness and rigidity. The material has a high viscosity relative to shock loads of more than 20 kJ / m2, monolithic even withstands a direct bullet hit.
- Stability of shape, size. Polycarbonate retains them when temperatures change from -100 to +135 degrees Celsius.
- Fire safety. This type of plastic is one of the most harmless. The material does not flare up during combustion, but melts, turning into a fibrous mass, quickly decays, does not emit hazardous chemical compounds into the atmosphere. Its fire safety class is B1, one of the highest.
Polycarbonate, among its other advantages, has high load-carrying capacities and flexibility inaccessible to glass and some other plastics. Structures made of it can have a complex shape, withstand significant loads without visible damage.



Applications
Depending on the thickness of the polycarbonate sheet, many designs can be made. Corrugated or trapezoidal sheet metal is considered a good alternative or addition to roofing. It is also used for the construction of awnings, canopies, terraces and verandas. Honeycomb sheets are most often found in greenhouses and greenhouses - here their properties are most in demand.
And also the use of sheet polycarbonate is relevant for the following areas:
- construction of a shower for a summer residence;
- creating a shelter for the pool;
- fencing of sports grounds and public areas;
- glazing of greenhouses, winter gardens, balconies;
- manufacturing of swings, benches, gazebos, and other garden structures;
- the formation of internal partitions in offices, banks, other institutions;
- production of advertising and information structures;
- road construction - as noise-absorbing shields, stopping pavilions.



Products made of polycarbonate sheets can have a decorative appearance due to the simple and convenient cutting of the material. With its help, stylish transparent grilles for windows, curly fences and framing gazebos are made. Smooth sheets are widely used in the upgrade of cars, bicycles, motor vehicles, they can be given different shapes.
Glasses in protective helmets, goggles for carpentry work - it is difficult to find an application in which polycarbonate would not be useful.


What are the types and how do they differ?
There are several types of polycarbonate sheets at once. The rarest of them are decorative. This includes corrugated or embossed polycarbonate obtained from a monolithic material. It is produced in the form of sheet modules, it looks very attractive, it can be matte, with different types of relief. Such products have increased strength, they are often used in the construction of forged gates and fences.
Some varieties of polycarbonate are referred to as reinforced - they have additional stiffeners. For example, a corrugated monolithic or with a trapezoidal profile allows for the creation of an aesthetic transparent or colored roof covering. It is used in the form of inserts on roofs with different types of ramps. Despite the fact that polycarbonate in rolls is most often viewed as a summer residence, its monolithic counterparts are highly aesthetically pleasing. It is worth considering some of the features of the main types in more detail.
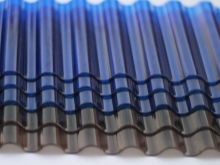


Monolithic
Outwardly, it is similar to silicate or acrylic glass, but more flexible, which allows the material to be used in radius structures, arches. High transparency and wide range of colors make monolithic polycarbonate attractive for use in glazing of greenhouses, balconies, and shop windows. The sheets can withstand significant shock loads, they can be called vandal-proof.
The surface in the usual design is smooth, without relief on both sides.


Cellular
The structure of this polycarbonate uses a honeycomb - a hollow cell connected by jumpers along the length and width. The main monolithic layers are rather thin, located outside. Inside, the space is divided into cells by stiffening ribs. Sheets of such material do not bend across, but they have a rather large radius in the longitudinal direction. Due to the air gap inside, cellular polycarbonate is very light.


Dimensions and weight
The dimensional parameters established for polycarbonate of different types are determined by the requirements of GOST R 56712-2015. According to this standard, the nominal width of all types of panels is 2100 mm, length - 6000 or 12000 mm. The thickest cellular polycarbonate reaches 25 mm, the thinnest - 4 mm. For the monolithic variety, the characteristic dimensions of the sheets are 2050 × 1250 mm or 2050 × 3050 mm, the maximum length is up to 13 m. In the first variety, the thickness is set at 1 mm, in the second it varies from 1.5 to 12 mm.
Product weight is calculated per 1 m2. It is determined individually based on the thickness of the sheet. For example, for a honeycomb variety of 4 mm, the mass of 1 m2 will be 0.8 kg. For sheet monolithic polycarbonate, this indicator is higher, since there are no voids. A 4 mm panel has a mass of 4.8 kg / m2, with a thickness of 12 mm this figure reaches 14.4 kg / m2.

Manufacturers
Polycarbonate production was once the exclusive domain of European brands. Today, dozens of brands are produced in Russia, from regional to international. A list of the most famous manufacturers and a rating on the quality of their products will allow you to navigate in all the variety of options.
- Carboglass. Russian-made polycarbonate is of high quality. The company uses Italian equipment.

- "Polyalt". A company from Moscow produces cellular polycarbonate that meets European standards. In terms of price and quality ratio, it is one of the best options.


- SafPlast. A domestic brand that is actively introducing its own innovations and developments. The cost of production is average.

Among foreign brands, the leaders are Italian, Israeli and American companies. Brand is popular in Russia Polygal Plasticsoffering both cellular and monolithic material. The Italian segment of manufacturers is represented by the company Bayerproducing products under the brand Makrolon... There is a wide selection of colors and shades.
It is also worth noting the British manufacturer Brett Martin, which is considered the leader in its region.


Selection and calculation
When deciding which polycarbonate is better to choose, you should pay attention to the main characteristics of a quality material. There are several indicators among the main criteria.
- Density. The higher it is, the stronger and more durable the material, but the same factor in honeycomb panels noticeably affects the light transmission. For them, a density of 0.52-0.82 g / cm3 is considered normal, for monolithic ones - 1.18-1.21 g / cm3.
- The weight. Lightweight slabs are considered temporary or seasonal coverage. They are not suitable for year-round use. If cellular polycarbonate is noticeably lighter than the norm, it can be assumed that the manufacturer has saved on the thickness of the lintels.
- UV protection type. Bulk implies the addition of special components to the polymer, but retains its properties for no more than 10 years. Film protection works better, almost doubles the service life. The safest option is bulk filled polycarbonate with a double UV barrier.
- Minimum bending radius. It is important when installing curved structures. On average, this figure can vary from 0.6 to 2.8 m. If the recommended bend radius is exceeded, the panel breaks.
- Light transmittance and color. This indicator differs for different versions of the material. The highest for transparent: from 90% for monolithic and from 74% for cellular. The lowest - in red and bronze, does not exceed 29%. The colors in the middle segment are green, turquoise and blue.
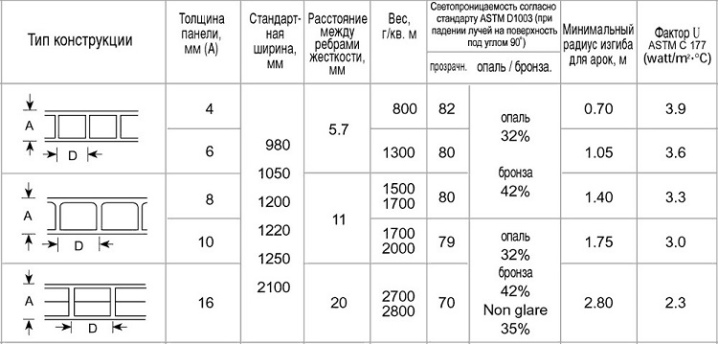
The calculation of polycarbonate is carried out by the footage of the covered area. In addition, parameters such as accurate calculation of strength and deflection loads are important. These parameters are best illustrated by the table.
Features of working with material
Polycarbonate can be sawed and cut with an ordinary knife, electric jigsaw. Monolithic sheets lend themselves well to laser cutting. It is also possible to bend the material without heating and effort. It is enough to give it the desired shape with the help of a vice and clamps. When cutting solid material, it is important to lay it on a flat, flat surface. After cutting, it is better to glue the edges with aluminum tape to close the ends.
Cellular varieties after cutting also need edge insulation. For them, special moisture-proof adhesive tapes are produced. This ensures the necessary tightness, protects against the ingress of dirt and dust into the cells. Transparent polycarbonate can be painted to further enhance its protective properties. That's just the sheets are contraindicated in contact with many chemicals.
The paint must be water-based. It is better to choose acrylic options, odorless, quick-drying and well-laid on the surface without preliminary preparation.


Storage and shipping tips
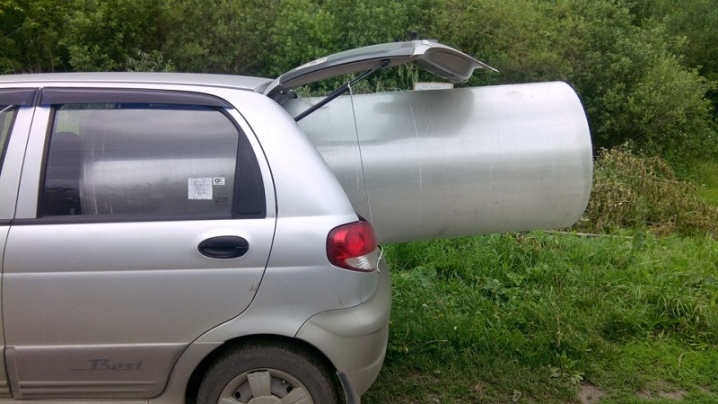
The need to transport polycarbonate on their own in a car arises for many summer residents. We are talking mainly about the honeycomb type of material used in the arrangement of greenhouses. Transportation in light vehicles for monolithic polycarbonate is provided only in cut form or with small dimensions of sheets, exclusively horizontally.
When transporting a cellular option, certain rules must be followed:
- transport the material in a rolled form;
- the floor in the car must be flat;
- protrusion beyond the dimensions of the body with a thickness of 10-16 mm cannot exceed 0.8-1 m;
- it is necessary to take into account the bending radius of the panels;
- use harnesses or other rigging.

If necessary, polycarbonate can be stored at home. But here, too, certain recommendations should be followed. The material should not be rolled up for too long. During storage, observe the manufacturer's recommended diameter to avoid deformation or cracking of the polycarbonate.
Do not step on or walk on the surface of the spread sheets. This is especially important for cellular polycarbonate, the structure of the cells of which can be violated.During storage, it is also extremely important to ensure that there is no contact with direct sunlight from the side that is not protected by the film. If heating occurs constantly, it is better to remove the protective packaging in advance, otherwise it may stick to the surface of the coating.

Alternatives
Polycarbonate is available on the market in a wide range, but it also has alternatives. Among the materials that can replace this plastic, several types can be distinguished.
- Acrylic. The transparent material is produced in sheets, it is much inferior to polycarbonate in strength, but in general it is quite in demand. It is also known as plexiglass, polymethyl methacrylate, plexiglass.
- PVC. Modern manufacturers of such plastic produce molded transparent panels with low weight and profiled structure.
- PET sheet. Polyethylene terephthalate is lighter than polycarbonate and glass, withstands shock loads, bends well and transmits up to 95% of the light flux.
- Silicate / quartz glass. A fragile material, but with the highest translucency. It conducts heat worse, has low impact resistance.
Despite the availability of alternatives, polycarbonate is far superior in performance to other plastics. That is why it is chosen for use in a wide variety of areas of activity.

Review overview
According to the majority of people using polycarbonate structures, this material lives up to expectations. Monolithic varieties are not as common as honeycomb varieties. They are more commonly used by advertising agencies and interior designers. Here, colored varieties are especially popular, installed as partitions, suspended screens. It is noted that the material lends itself well to cutting and milling, it is easy to turn it into an original decorative element in the interior. Cellular polycarbonate is well known as a greenhouse base.
It is noted that the materials produced in accordance with GOST really meet the expected level of reliability, retain their strength and aesthetics for a long time. They are easy to assemble by yourself. Many people buy cellular polycarbonate for the construction of poultry pens, carports. In some cases, there are serious complaints about the quality of the products. Cellular polycarbonate, due to its availability and popularity, is often faked, produced not by standards. As a result, it turns out to be too fragile, poorly suited for operation at low temperatures. A low-quality product often becomes cloudy in the first year after purchase.

For information on how to properly attach polycarbonate to profile pipes, see the next video.












The comment was sent successfully.