All about cellular polycarbonate
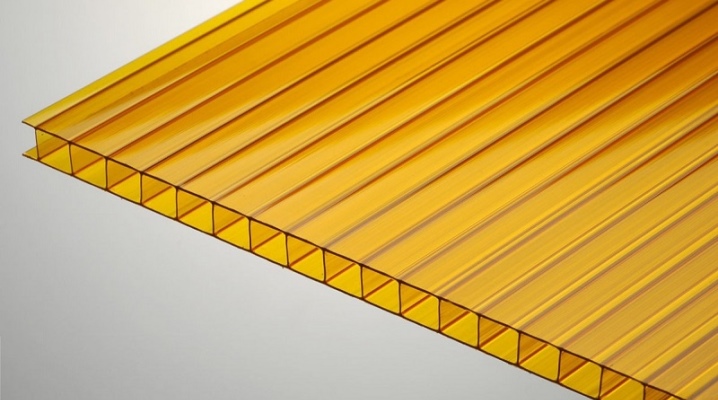

The appearance on the market of building materials made of plastic polycarbonate has significantly changed the approach to the construction of sheds, greenhouses and other translucent structures, which were previously made of dense silicate glass. In our review, we will consider the main characteristics of this material and give recommendations on its choice.


What it is?
Cellular polycarbonate is a high-tech building material. It is widely used for the manufacture of awnings, gazebos, the construction of winter gardens, vertical glazing, as well as for the installation of roofs. From a chemical point of view, it belongs to complex polyesters of phenol and carbonic acid. The compound obtained as a result of their interaction is referred to as thermoplastics, it has transparency and high hardness.
Cellular polycarbonate is also called cellular. It consists of several panels, which are fastened to each other with internal stiffening ribs. The cells formed in this case can have one of the following configurations:
- triangular;
- rectangular;
- honeycomb.


The cellular polycarbonate presented in the construction segment includes from 1 to 5 plates, the parameter of the sheet thickness, as well as the operational parameters, directly depend on their number. For example, thick polycarbonate is characterized by increased noise and heat insulation ability, but at the same time, it transmits much less light. Thin ones transmit light in full, but differ in lower density and mechanical strength.
Many users confuse cellular and solid polycarbonate. Indeed, these materials have approximately the same composition, but the monolithic plastic is slightly more transparent and stronger, and the cellular one has less weight and retains heat better.

Main characteristics
At the production stage, polycarbonate molecules enter a special device - an extruder. From there, under increased pressure, they are extruded into a special shape to create sheet panels. Then the material is cut into layers and covered with a protective film. The manufacturing technology of cellular polycarbonate directly affects the performance properties of the material. In the course of processing, it becomes more durable, resistant to mechanical stress, and has exceptional bearing capacity. Cellular polycarbonate in accordance with GOST R 56712-2015 has the following technical and operational characteristics.

Strength
Resistance to impacts and other mechanical damage of cellular polycarbonate is many times higher than that of glass. These properties make it possible to use the material for the installation of anti-vandal structures, it is almost impossible to damage them.


Resistant to moisture and chemicals
The plates used in finishing are often exposed to external unfavorable factors that worsen their structure. Cellular polycarbonate is resistant to the vast majority of chemical compounds. He is not afraid:
- high concentration mineral acids;
- salts with a neutral or acidic reaction;
- most of the oxidizing and reducing agents;
- alcoholic compounds, with the exception of methanol.
At the same time, there are materials with which it is better not to combine cellular polycarbonate:
- concrete and cement;
- harsh cleaning agents;
- sealants based on alkaline compounds, ammonia or acetic acid;
- insecticides;
- methyl alcohol;
- aromatic as well as halogen type solvents.


Light transmission
Cellular polycarbonate transmits 80 to 88% of the visible color spectrum. This is less than that of silicate glass. Nevertheless this level is quite enough to use the material for the construction of greenhouses and greenhouses.

Thermal insulation
Cellular polycarbonate is characterized by exceptional thermal insulation properties. Optimum thermal conductivity is achieved due to the presence of air particles in the structure, as well as due to the high degree of thermal resistance of the plastic itself.
The heat transfer index of cellular polycarbonate, depending on the structure of the panel and its thickness, varies from 4.1 W / (m2 K) at 4 mm to 1.4 W / (m2 K) at 32 mm.
Life time
Manufacturers of cellular carbonate claim that this material retains its technical and operational properties for 10 years if all the requirements for installation and maintenance of the material have been met. The outer surface of the sheet is treated with a special coating, which guarantees high protection against UV radiation. Without such a coating, the transparency of the plastic can decrease by 10-15% during the first 6 years. Damage to the coating can shorten the life of the boards and lead to their premature failure. In places where there is a high risk of deformation, it is better to use panels with a thickness of more than 16 mm. Besides, cellular polycarbonate has other characteristics.
- Fire resistance. The safety of the material is ensured by its exceptional resistance to high temperatures. Polycarbonate plastic is classified in category B1, in accordance with the European classification, it is a self-extinguishing and hardly flammable material. Near an open flame in polycarbonate, the structure of the material is destroyed, melting begins, and through holes appear. The material loses its area and thus moves away from the source of fire. The presence of these holes causes the removal of toxic combustion products and excess heat from the room.
- Light weight. Cellular polycarbonate is 5-6 times lighter than silicate glass. The mass of one sheet is no 0.7-2.8 kg, thanks to which it is possible to build lightweight structures from it without the construction of a massive frame.
- Flexibility. The high plasticity of the material distinguishes it favorably from glass. This allows you to create complex arched structures from the panels.
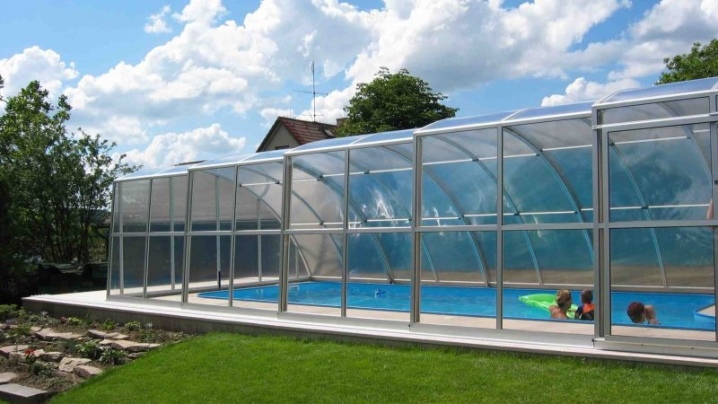
- Load bearing capacity. Certain varieties of this type of material are characterized by a high bearing capacity, sufficient to withstand the weight of a human body. That is why, in areas with increased snow load, cellular polycarbonate is often used for installing roofing.
- Soundproofing characteristics. The cellular structure results in reduced acoustic permeability.
Plates are distinguished by pronounced sound absorption. So, sheets with a thickness of 16 mm are capable of dampening sound waves of 10-21 dB.


Species overview
The technical and operational characteristics, as well as the variability of the sizes of polycarbonate panels, make it possible to use this material for solving a number of construction problems. Manufacturers offer products that come in a variety of sizes, thicknesses, and shapes. Depending on this, the following types of panels are distinguished.
The width of the panel is considered a typical value, it corresponds to 2100 mm. This size is determined by the characteristics of the production technology. The length of the sheet can be 2000, 6000 or 12000 mm. At the end of the technological cycle, a 2.1x12 m panel leaves the conveyor, and subsequently it is cut into smaller ones. The thickness of the sheets can be 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 25 or 32 mm. The higher this indicator, the more difficult the leaf bends.Less common are panels with a thickness of 3 mm, as a rule, they are produced on an individual order.


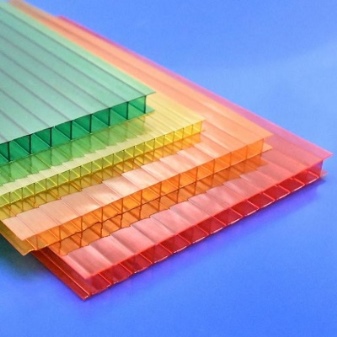
Color spectrum
Cellular polycarbonate sheets can be green, blue, red, yellow, orange, brown, as well as gray, milky and smoky. For greenhouses, a colorless transparent material is usually used; for the installation of awnings, matte is often preferred.
The transparency of polycarbonate varies from 80 to 88%, according to this criterion, cellular polycarbonate is very slightly inferior to silicate glass.

Manufacturers
The list of the most popular manufacturers of cellular polycarbonate includes the following manufacturing enterprises. Polygal Vostok is a representative of the Israeli firm Plazit Polygal Group in Russia. The company has been producing sample panels for almost half a century; its products are considered a recognized example of quality. The company offers cellular polycarbonate 4-20 mm thick, with sheet dimensions 2.1x6.0 and 2.1x12.0 m. The shade range includes more than 10 tones. In addition to the traditional white, blue and transparent models, there are also amber, as well as silver, granite and other unusual colors.
Pros:
- the possibility of applying an anti-fog or infrared absorbing coating;
- decorative embossing;
- the possibility of manufacturing panels with the addition of a combustion inhibitor, which stops the process of destruction of the material when exposed to open fire;
- a wide range of sheet options by specific weight: lightweight, reinforced and standard;
- high light transmittance - up to 82%.

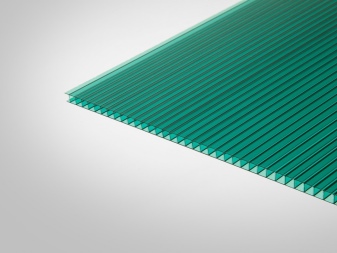
Covestro - a company from Italy that produces polycarbonate under the Makrolon brand. The most advanced technologies and innovative solutions are used in production, thanks to which the company offers high-quality building materials in demand by consumers on the market. The panels are produced with a thickness of 4 to 40 mm, the size of a typical sheet is 2.1 x 6.0 m. The tint palette includes transparent, creamy, green and smoky colors. The operating period of polycarbonate is 10-15 years, with proper use, it lasts up to 25 years.
Pros:
- high quality material - due to the use of only primary raw materials, and not processed;
- high fire resistance;
- the highest impact resistance in comparison with other brands of polycarbonate;
- resistance to aggressive reagents and adverse weather conditions;
- low coefficient of thermal expansion, due to which polycarbonate can be used at elevated temperatures;
- resistance to temperature extremes;
- reliable water-repellent coating on the inside of the sheet, drops flow down without lingering on the surface;
- high light transmittance.
Of the shortcomings, a relatively small color gamut is noted and only one size - 2.1 x 6.0 m.
"Carboglass" leads the rating of domestic manufacturers of plastic polycarbonate, manufactures premium products.
Pros:
- all panels are coated against UV rays;
- presented in one- and four-chamber versions, models with a reinforced structure are available;
- light transmission up to 87%;
- the ability to use at temperatures from -30 to +120 degrees;
- chemical inertness to most acid-base solutions, with the exception of gasoline, kerosene, as well as ammonia and some other compounds;
- a wide range of applications from small household needs to large construction.
Of the minuses, users note the discrepancy between the actual density declared by the manufacturer.

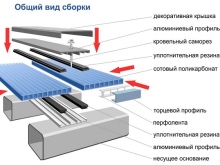
Components
Not only the general appearance of the structure, but also its practicality, reliability and resistance to water largely depends on how competently the fittings will be selected for the construction of a polycarbonate structure.Polycarbonate panels have a tendency to expand or contract with temperature changes, therefore, corresponding requirements are imposed on accessories. Components for polycarbonate plastic have an increased margin of safety and cause noticeable advantages when installing building structures:
- provide strong and durable fixing of sheets;
- prevent mechanical damage to panels;
- ensure tightness of joints and joints;
- eliminate cold bridges;
- give the structure a structurally correct and complete look.


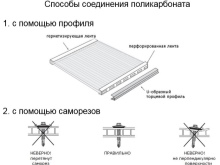
For polycarbonate panels, the following types of fittings are used:
- profiles (end, corner, ridge, connecting);
- clamping bar;
- sealant;
- thermal washers;
- self-tapping screws;
- sealing tapes;
- fasteners.



Applications
Cellular polycarbonate is widely in demand in the construction industry due to its exceptional technical and operational characteristics, long period of use and affordable cost. Nowadays, it successfully replaces glass and other similar materials with lower wear and impact resistance. Depending on the thickness of the sheet, polycarbonate can have different uses.
- 4 mm - used for the construction of shop windows, billboards and some decor items. Only permitted for indoor use.
- 6 mm - relevant when installing canopies and awnings, when installing small greenhouses.
- 8 mm - suitable for the arrangement of roof coverings in regions with a low snow load, as well as for the construction of large greenhouses.
- 10 mm - found their application for vertical glazing.
- 16-25 mm - suitable for creating greenhouses, swimming pools and parking lots.
- 32 mm - used in regions with increased snow load for roof construction.


How to choose a material?
Despite the fact that cellular polycarbonate is offered in a wide range of building supermarkets, nevertheless, choosing a high-quality model is not as easy as it seems at first glance. Material specifications, performance and market value must be taken into account. Special attention should be paid to the following parameters.
- Thickness. The more layers in the structure of the polycarbonate material, the better it will retain heat and withstand mechanical stress. At the same time, it will bend worse.
- Sheet dimensions. The cheapest way will be to buy polycarbonate of the standard size 2.1x12 m. However, the transportation of such oversized material will cost an impressive amount. It is advisable to stop at 2.1x6 m panels.
- Colour. Colored polycarbonate is used for the construction of awnings. Exceptionally transparent is suitable for greenhouses and greenhouses. Opaque ones are used for the construction of awnings.
- The presence of a layer that inhibits ultraviolet radiation. If the panels are purchased for the construction of greenhouses, then only polycarbonate with a protective coating can be used, otherwise it will become cloudy during operation.
- The weight. The greater the mass of the material, the more durable and sturdy frame will be needed for its installation.
- Load bearing capacity. This criterion is taken into account when polycarbonate plastic is needed for the construction of a translucent roof.


How to cut and drill?
To work with plastic polycarbonate, the following types of tools are usually used.
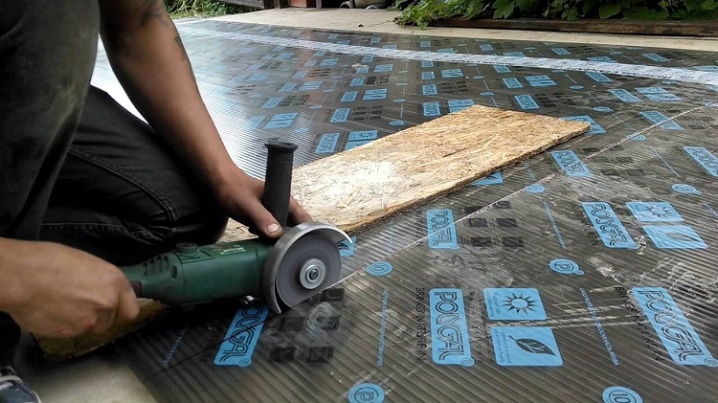
- Bulgarian. The most common tool that is available in every household, while it is not at all necessary to buy expensive models - even a budget saw can easily cut cellular polycarbonate. To make accurate cuts, you need to set the 125 circle used for the metal. Advice: it is better for inexperienced craftsmen to practice on unnecessary scraps of material, otherwise there is a high risk of damage to the workpieces.

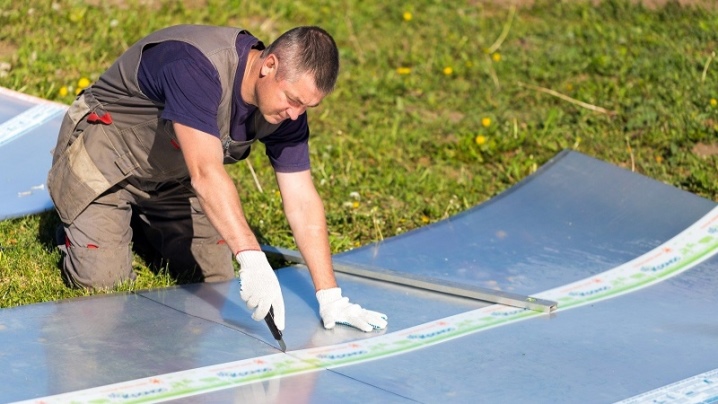
- Stationery knife. It copes well with cutting polycarbonate sheets.The tool can be used for polycarbonate plates with a thickness of less than 6 mm, the knife will not take thick plates. When working, it is extremely important to be careful - the blades of such knives, as a rule, are sharply sharpened, therefore, if carelessly cutting, you can not only ruin the plastic, but also seriously injure yourself.

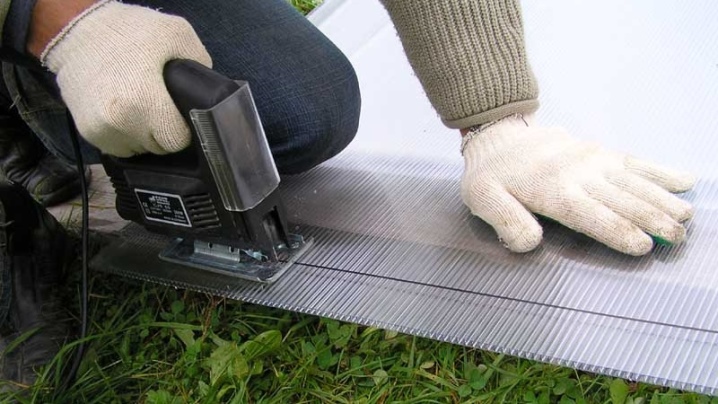
- Jigsaw. Widely used to work with cellular polycarbonate. In this case, you will need to install a file with small teeth, otherwise you will not be able to cut the material. The jigsaw is especially in demand if you need to round off.

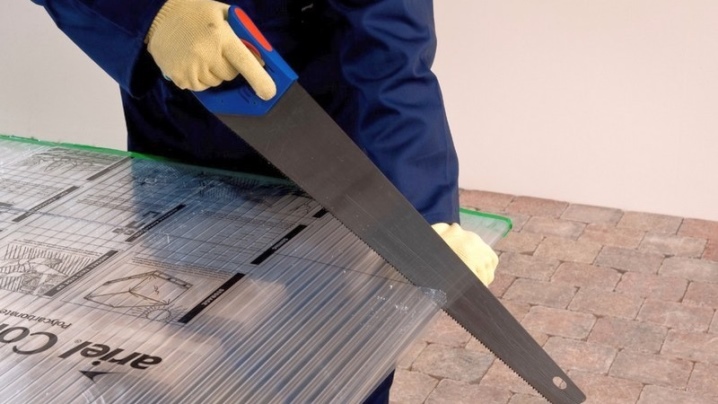
- Hacksaw. If you do not have experience in the relevant work, then it is better not to take this tool - otherwise, along the line of cuts, the polycarbonate canvas will crack. When cutting, you need to fix the sheets as firmly as possible - this will minimize vibration and remove stress during the cutting process.

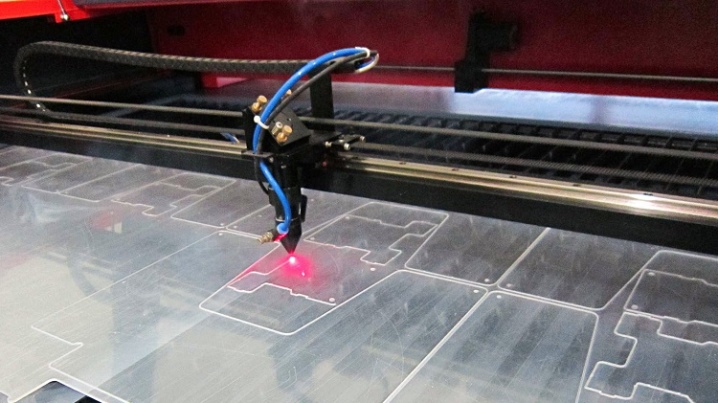
- Laser. Cutting of panels can also be carried out with a laser, it is usually used in professional work with plastic. The laser provides an exceptional quality of work - the absence of any defects, the required cutting speed and cutting accuracy within 0.05 mm. When cutting at home, you need to follow the rules. Before starting work, any foreign objects (remnants of boards, building materials, branches and stones) must be removed from the work site. The place should be perfectly flat, otherwise scratches, chips and other damage will appear on the canvases. To ensure maximum quality, it is better to cover the surface with fiberboard or chipboard panels. Further, using a felt-tip pen and a ruler, markings are made on the plates. If at the same time it becomes necessary to move along the plastic, then it is better to lay the boards and move strictly along them. On both sides of the markings made, boards are laid, in the same sections the boards are also placed on top. You need to cut strictly along the marking line. If you plan to work with mirror or laminated material, then the board must be placed with the cover facing up. At the end of the work on cutting plastic with compressed air, you need to thoroughly blow all the seams to remove dust and small chips.
Important: When cutting cellular polycarbonate with a grinder or jigsaw, you must wear protective glasses, this will protect the organs of vision from the ingress of small particles. Drilling of the material is carried out with a hand or electric drill. In this case, drilling is performed at least 40 mm from the edge.
Mounting
Installation of a structure made of cellular polycarbonate can be done by hand - for this you need to read the instructions and prepare the necessary tools. To erect a polycarbonate structure, it is necessary to build a steel or aluminum frame, less often the panels are attached to a wooden base.
The panels are fixed to the frame with self-tapping screws, onto which sealing washers are put on. The individual elements are connected to each other using connecting elements. For the construction of awnings and other lightweight structures, polycarbonate plates can be glued together. High quality of fastening is provided by one-component or ethylene vinyl acetate adhesive.
Keep in mind that this method is not used to fix plastic to wood.

For what you need to know when choosing cellular polycarbonate, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.