All about ivy

Ivy is a plant that can have a different “appearance” depending on the species diversity. However, common to all species and varieties is the presence of vines and aerial roots, thanks to which the plant easily climbs to any surface.



Characteristic
Ivy is a clinging plant that is known to many for its ability to "climb" the walls of buildings, fences, arches. He belongs to the Araliev family. Represents liana-like evergreen shrub plant with a strong stem and numerous aerial sucker roots.
From the German name the plant is translated as "sit" (an indication of the ability of ivy to cling, sit on the surface), from Celtic - as "cord". The plant has another official botanical name - hedera.


As already mentioned, in addition to the main root located in the ground, ivy has additional aerial roots. Their task is not to get nutrients from the ground, but to cling to surfaces, ensuring the ability of the plant to climb almost any vertical surface.
If ivy "chose" another tree, then at first, while the shoots are young and weak, ivy serves to some extent as a support to its "partner". However, having entangled most of the crown, ivy begins to dominate and choke the plant.


The aerial antennae of the plant are highly sensitive. They are able to make circular movements until they find a possible support. After that, they go to the support, cling to it and pull the vine towards them. In the future, the tendrils become lignified and folded into a spring.
Ivy can be grown as a ground cover plant, resulting in a lush green "grass" that covers the ground and hibernates under the snow.
Despite the unpretentiousness and attractive "appearance" when growing an evergreen "cord", it is important to remember about precautions. This is due to the fact that the plant contains toxic substances. Their concentration is especially high in fruits. After you have watered or cut off the leaves, in a word, have come into contact with the plant, you need to wash your hands with soap, and care for the plant should be done with gloves.


Flower
Ivy blooms at the end of August and lasts until November. Inflorescences are nondescript yellowish-green umbrellas. Flowers are male, bisexual and female. The first 2 species can be recognized by the presence of 5 stamens. Female flowers have 5 to 10 ovary nests.
Flowers are noticeable mainly on old shoots, only adult plants at least 7-10 years old bloom. The further north the heder is grown, the later it will bloom. Apartment varieties almost never bloom.


Sheet
The plant has three or five-lobed dark green leaves with a heart-shaped base. In adult plants, they are more oval. The leaves are matte, attractive in appearance. They are located on a flexible stem very close to each other. this allows the heder to form a thick carpet.
Botanists distinguish 2 types of leaves. Dark green in color, large leathery leaves are formed on vegetative stems. Flowering branches have smaller leaf blades. Their shape is more oblong, elongated. The shade of the leaves also differs - they are colored in a softer "grassy" green.
The appearance of the leaves may vary slightly between plant varieties. Leaves with pronounced veins and covered with white or cream spots are especially appreciated by gardeners and professional landscape designers. However, such varieties are more capricious in nature - they are more demanding in care, need a longer daylight hours.



Fruit
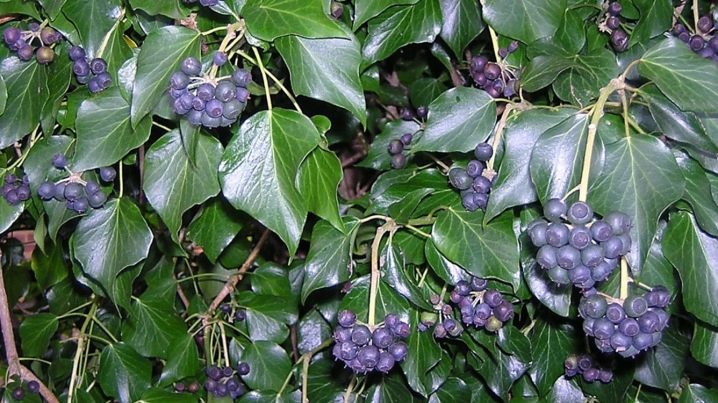
The flowering period is followed by fruiting. Ivy bears fruit in small "peas" up to 1 cm in diameter, which finally ripen in December.
By this time, they acquire a bluish-black color and are able to persist on the bushes throughout the winter.

Distribution in nature
The habitat of heders is territories with a warm and humid climate. In the wild, ivy is widespread throughout Eurasia. In Western Europe, the plant grows in floodplain and light forests. Twigs climb the trees, sometimes wrapping around the trunk to the crown. In the glades, you can find a carpet of creeping ivy. Thickets of plants can be found in the Caucasus and Transcaucasia. Favorite places are beech forests, various thickets, rocky slopes.
In Russia, ivy is not found in the wild, it is cultivated as an evergreen "loach" to decorate parks, summer cottages and suburban areas, public buildings. In addition, varieties have been bred that are suitable for indoor cultivation.


Views
Ivy has 15 species, which, in turn, include many varieties. However, despite such a rich varietal variety, they are all united by common features - the presence of creeping clinging lashes with aerial roots.
For decorating a personal plot - creating green hedges, decorating unsightly walls of buildings, it is recommended to use decorative varieties of heders.
For outdoor planting or growing as a pot plant, common ivy is usually chosen. The most popular types are Tauride, Finger, Miniature, Winter, Bordered.
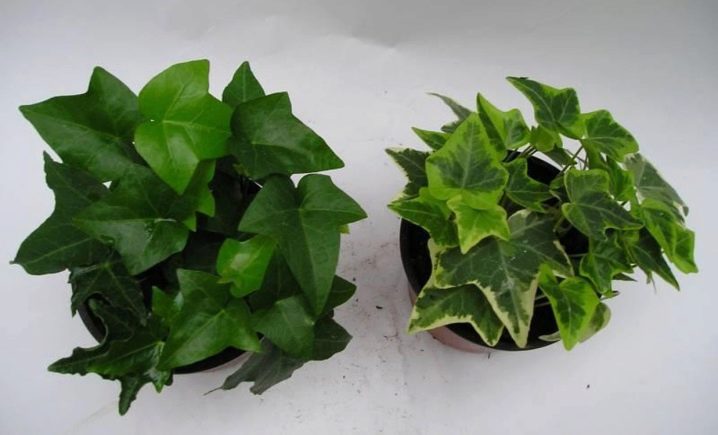

The Canary variety, which is native to the Canary Islands, has an unusual "appearance". It is a variegated plant with dense, heart-shaped leaves. Their peculiarity is their color - it is green-white.
The "Gluard de Marengo" variety also belongs to the decorative variety, which, by the way, grows very quickly. Variety "Gray", whose homeland is Afghanistan, is characterized by a gray bloom on green leaves. Colchis ivy with variegated leaves has pronounced decorative properties. However, in the domestic climate, it grows very slowly, areas with a milder climate are still optimal for it.


Irish ivy has an interesting "appearance". It has a dark green leaf plate with light veins. The veins can be light gray or light green, and the cuttings are purple. Finally, the leaves themselves are slightly bent upward.
Irish ivy spreads very quickly and easily "climbs" to a height of 6-20 m.
For outdoor cultivation, consider the garden variety. the appearance of this ivy changes with the age of the plant. At the same time, the garden view has many varieties that differ in the shape, size and color of the leaves.
In the western part of Russia, in the Caucasus and in the Crimea, common ivy is widespread. It is interesting that it is also called English, apparently due to its widespread use in gardens in the English style.


It grows in deciduous forests, the tree crowns of which give a dense partial shade. At the same time, common wild ivy looks like a climbing plant with woody stems, which entwines the trunks and crown of trees.
If ivy grows in mountainous regions, then with its antennae-roots it clings to the mountain slopes, so the mountain range is completely entwined with lianves. In central Russia, ivy, if preserved for the winter, is only under a thick layer of snow.Caucasian, Crimean and Carpathian ivy species are characterized by high cold resistance. Interestingly, such varieties can be transplanted to more northern regions, but in this case, their growth rates noticeably slow down.


Common ivy also has its own varietal varieties. Among the most popular are several.
- "Brilliant golden", a distinctive feature of which are small-sized green-golden leaves.
- "Small" characterized by small leaf blades with small, three-leafed shoots. It is characterized by strong branching.
- "Palmate" - a plant of this variety can be recognized by the five-lobed "foliage" of a dark green color with lighter veins.
- "Twisted" - ivy, characterized by a slow growth rate. It has small leaves, serrated and wavy along the edge. This gives the impression that they are wavy.
- "Triangular" - the leaf plate is heart-shaped, three-lane, which is why it resembles an inverted triangle with mild corners in shape. The leaves themselves are small.
- "Arrowhead" - five-cavity form of plates of dark green color.
- "Tricolor" - the leaves are a mix of white and green foliage. In autumn, they acquire a reddish tint, in addition, red shoots appear on the plant.



For growing indoors, the Helix header is suitable. Has dense leathery plates of a dark green hue. The leaves are speckled with lighter veins. There are variegated varieties of Helix heders.
Depending on the variety, the leaves have from 3 to 7 blades.


Breeding features
Ivy can be propagated in 3 ways.
By cuttings
With this method, you need to cut off small shoots with aerial roots and root them in the soil by 2-3 cuttings. You need to choose cuttings with leaves and adventitious roots (at least with a formed node) for cutting. The size of the roots is 10-14 cm, they need to be cut off at an acute angle. The lower leaves (if any) near the cut are removed, and it is advisable to treat the cut itself with a special solution of a growth stimulator.
Then the cuttings are rooted in the ground. The soil is a mixture of hardwood and sand. First, the cuttings are rooted under a film, which is opened once or twice a day. As the cuttings take root, the film is removed, and after 1.5-2 months they are ready for planting in open ground.
It is better to use lignified cuttings, since young green shoots take root less well. In addition, under the slightest unfavorable conditions (for example, night temperature drop), cuttings in most cases die.
It is optimal to cook cuttings in early spring, although you can do this during the summer. But in the fall, it is not recommended to cut cuttings, since ivy is preparing for wintering.




Shoots
With this method, a cut and strong ivy shoot with 8-10 leaves is taken. It is pressed into the sand so that only leaves remain on the surface. After 1.5-2 weeks, a full-fledged root system will form in the sand from the aerial roots. After that, the shoot must be carefully removed from the ground and cut into cuttings. Each stalk must have at least 1 leaf and roots. Cuttings can not be rooted in water, but immediately planted in the ground or a pot.


Layers
To propagate by this method, you should take a long and strong ivy branch, make small cuts on one side of it and bend these places to the ground. In order for the branch to take root, it must be fixed to the ground with special brackets. As soon as the branch takes root, the staples are removed, and the branch is carefully "cut" into layers. The latter are transplanted to the right place.
An interesting fact - although ivy forms a hemicarp, it does not propagate by seeds.
This is due to the fact that the plant from the seed does not retain its maternal properties.


The nuances of care
Despite the fact that hedera is a light-loving plant, it does not tolerate excessive heat and dry air. First of all, it depends on this whether ivy will form a green carpet or wither away, barely reaching a meter in height.
Ivy does not like the hot sun, it is optimal to let the sun warm green leaves in the morning and evening, and during the midday heat, it is better to shade the plant. When growing ivy in an apartment, you need to maintain a suitable air humidity. Heder with green leaves is easier to care for than variegated ones.
The optimum temperature for growing a green "carpet" is 18-20 degrees, in winter - 8-12 degrees. The plant is able to withstand temperature fluctuations, is not afraid of drafts.


Choosing the right plant location will help to avoid excessive exposure to the sun's rays on the leaves. Ivy is a shade-tolerant plant, so it can be planted on the northern, north-western sides. This, by the way, is convenient, because sometimes it is not easy to choose plants that will take root in such a place. However, if you choose variegated heder varieties, remember that they are more demanding on light.
Ivy belongs to moisture-loving plants, and in addition, it has aerial roots, which can easily dry out in the heat. This is why watering should be abundant and frequent. When determining the frequency of irrigation and the volume of water, one should be guided by the state of the earthen coma. It is optimal if it is always moisturized. However, it is important to avoid stagnant moisture, as this will lead to root rot.
In winter, if the plant is in a heated room, the frequency of watering remains almost unchanged. If ivy hibernates in a cool room (winter garden, basement, veranda), then watering should be reduced.


If ivy is grown at home, then on hot summer days, as well as with the onset of the heating season, you should regularly spray the leaves and the space around the plant with water from a spray bottle. Use humidifiers whenever possible. If the air temperature is less than +20 degrees, then you do not need to worry about air humidity, it will be suitable by itself.
Ivy responds very gratefully to the fertilizers applied. The main thing is to enter them correctly. In the spring-summer period, this should be done every 14-16 days. Top dressing for indoor deciduous plants is suitable.
In winter, the growth of the plant, although it slows down, does not stop - it also needs feeding. At this time, it is enough to apply fertilizers once a month. Although it is more correct to focus on the conditions of "wintering" ivy.
With an excess of fertilizer, the header will signal this with yellowing and falling leaves.


Young plants should be replanted every year. Better to do this in early spring. A 4-5 year old hedera is considered an adult plant and needs to be transplanted every 2-3 years. Ampel species (including ivy) have a superficial root system, and therefore do not need deep pots.
It is much more important to make a drainage layer using fine and medium-sized gravel or expanded clay. This will save the plants from stagnant water in the pot. As for the soil, ivy is undemanding in this matter. You can use a ready-made substrate for decorative deciduous plants.
To prepare the soil with your own hands, you can mix leaf and turf soil, peat and sand. All "components" are taken one piece at a time. Another "recipe" - taken in the same amount sod land, humus, sand. In short, ivy feels good in a slightly acidic loose substrate.


To obtain a lush carpet, bushiness, ivy should be constantly trimmed. Shoots without leaves, dry leaves should be cut off. This should be done during the period of active growth (summer-early autumn). For better branching, you can also pinch the cuttings of young shoots. In the spring, too long, protruding lashes are trimmed, shortening them by a third.The cut pieces can be used for rooting in water and then in soil.
The soil of the cheder for the winter should be mulched to avoid freezing. For this, peat or humus is suitable. On low curbs, the plant can be covered with hazel, apple or oak foliage. It is important that the shelter is not too dense and too warm. Shoots must still "breathe", otherwise they will rot and rot. In spring, shoots are raked without using a rake, otherwise the plant may be damaged.


Possible diseases and pests
Despite its unpretentiousness, the heder can get sick. In most cases, this is due to improper care. TAs, excessive watering, a dormant period and an abundance of fertilizers lead to the fact that the whips begin to bare - the leaves turn yellow and fall off.
If you were planning to grow variegated ivy, and the leaves suddenly turned green, the plant probably does not have enough light. The increased distance between leaves also speaks of the lack of lighting.
The appearance of a brown "dry" rim on the leaves indicates excessively hot and dry air, moisture deficit.


Rarely enough, ivy can be affected by pests. First of all - a spider mite. In this case, a cobweb is visible on the shoots and the inside of the leaf with the naked eye. The leaves may be covered with silvery dots - these are insect bite marks. The ivy itself begins to wither and wither.
Thyroid infection is possible. In this case, black dots appear on the plant.
As a treatment, as well as preventive measures, you can use insecticides for garden plants - "Karbofos", "Aktara", "Aktellik". The dosage and frequency of spraying with each drug should be seen on the package.



Interesting Facts
Ivy belongs to the most ancient decorative cultures, as indicated by its cultivation in Ancient Rome. One kind or another of it is found on almost every continent.
As an evergreen, ivy symbolizes immortality. however, this interpretation is not the only one. Ivy is also associated with fertility - it is not for nothing that it adorns the rod and wreath of the god Dionysius. Since ancient times, the image of a climbing plant has been adorned with cups and vessels for wine.
This vine is also a sign of faithful and devoted love. This is indicated by the legend of the lovers Tristan and Isolde, on whose grave vine and ivy grew and intertwined.

Ivy was also considered a plant that helps women maintain youth and beauty. He was included in wreaths, woven into his hair. It was believed that a twig placed on the chest of a sleeping girl would prolong her youth.
Such attention to the plant has led to the fact that it often "appears" in dream books. Seeing evergreen twigs is a sign of success and health. For girls, such a dream promises pleasant meetings and unexpected surprises.
Accordingly, dried ivy is a sign of illness and failure.
It has been proven that the plant purifies the air and reduces the content of pathogenic microbes in it by 30-40%. That is why it is recommended to breed it in office and industrial premises, as well as in facilities near factories, factories, highways.


Hedera brings positive energy to the room. It is believed that it gives energy and strength, and self-confidence to indecisive people. However, when growing a plant at home, it is important not to forget that it is poisonous.
During the time of Avicenna, ivy gained even more popularity due to its medicinal properties. However, if you turn to ancient literature, you can find that with the help of evergreen leaves, Odysseus got rid of his wounds. In the Middle Ages, Leonardo da Vinci spoke about the healing properties of ivy.
For a long time, modern medicine did not recognize the healing properties of heder, but recently its components have been used for traditional therapy (for example, Prospan, prescribed for bronchitis, cough) and in homeopathy.The plant has antitussive, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and tonic properties, heals wounds.

Lianas are also used in cosmetology - as a component of creams and other formulations to combat cellulite.
Consider the most interesting and common options for landscaping household plots with ivy.
It goes well with stone, brick, wood. One of the advantages of the plant is the ability to save land, since ivy is used for vertical gardening.
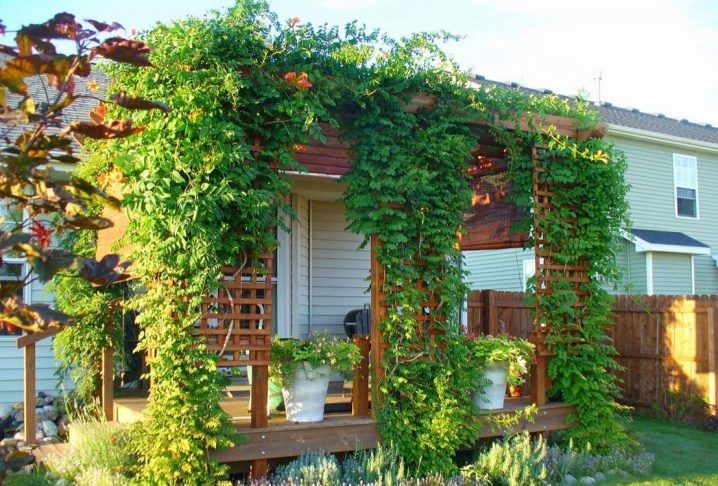

The plant climbs easily on any surface, with the exception of perfectly smooth glass and metal surfaces. In this case, it is better to consider a system of ivy supports. In hot regions, ivy can be damaged by too white and light walls, which strongly reflect light. The shoots will wither.
Hedera is widely used for greening roofs. By the way, such a "coating" has not only aesthetic, but also a practical function. The ivy wall protects against overheating in summer heat and prevents strong heat loss in winter.
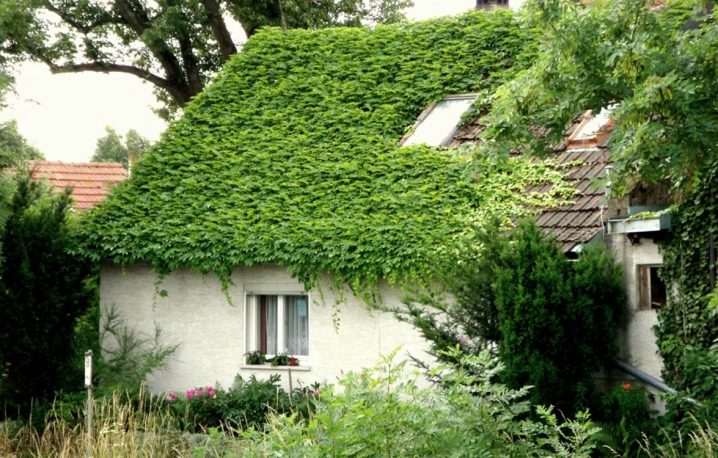

If ivy is grown as a ground cover plant, it can be combined with maple, birch.
Due to the highly developed root system of the latter, it is usually not easy for them to find "neighbors".


Plush goes well with low shrubs (especially variegated or purple shades), standard roses. In the spring (and autumn) period, the hedera takes on a reddish tint, which makes it possible to combine it with primroses. The reddish palette in a special way emphasizes the tenderness of the latter.
For landscaping fences and fences, as well as in shaded areas, it is better to use Irish ivy as it is more winter-hardy.
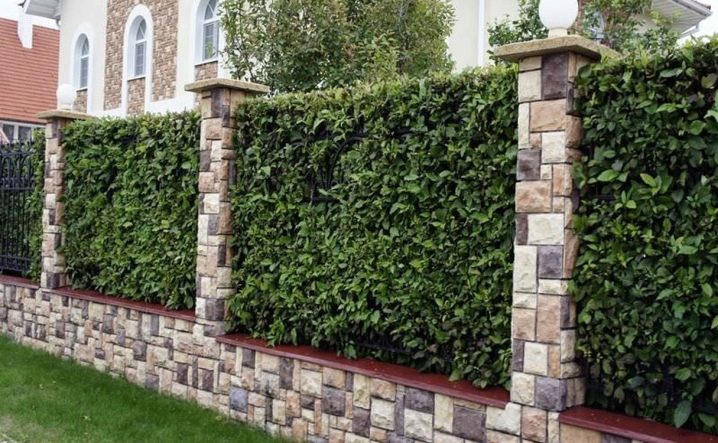

Carpathian ivy is also characterized by resistance to low temperatures. However, it does not form a solid bedspread, so it is better to use it to decorate individual elements.
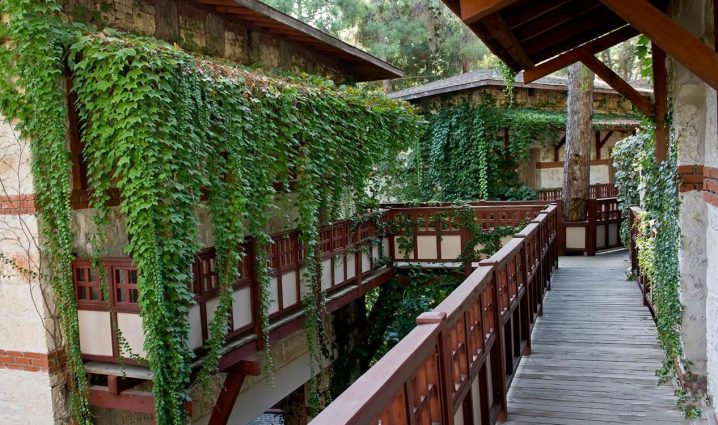
If the task is to hide the unsightly surface of buildings in a short time, to create a hedge, then garden ivy is used. It grows rapidly to form a lush green canopy. Against the background of such a hedge, bright bushes look great.
In boxes outside the window or small containers on an open veranda, dwarf varieties look attractive.

For the secrets of ivy care, see the next video.
































































































The comment was sent successfully.