How to prepare a climbing rose for winter?

The climbing rose is an incredibly beautiful flower that can easily ennoble even the most unsightly fence. Of course, such beauty is very demanding both to its cultivation and to its care. Not only does this culture need to be grown, but it also needs to be properly prepared for the winter cold so that next year it will delight the owners with its beautiful buds and amazing aroma.

When should you cover?
Probably, only the southern regions of Russia can not take care of the winter shelter of roses. In all other areas, the shelter of a climbing rose is a prerequisite and a guarantee that next year the rose will delight the gardener and his guests with beautiful dense buds.
Despite the need for shelter, there is still no need to rush with it. Frosts at minus 5 degrees temper rose bushes well, and they can easily withstand cold temperatures up to minus 10 degrees. Among other things, if you cover the rose ahead of time, then the plant, under the influence of the warm air formed under the film, will begin to rot, and therefore, young shoots may die, and, therefore, you can not expect a beautiful color on them.
Shelter time depends on the geographic location of the gardener's site, and if this is the Moscow region, then roses need to be insulated at the end of October, but when growing a climbing rose in Primorye, it should be sent for wintering no earlier than early December.


Preparation
A rose, like any garden plant, must be properly prepared for the cold weather, since one shelter will not be enough for it. Before the cold weather, you need to carry out a number of procedures that will help the plant to more easily tolerate low temperatures.
Top dressing
In autumn, the rose needs minerals such as potassium and phosphorus, which strengthen the plant's root system and enable it to withstand unfavorable wintering conditions.
The mistake is made by those gardeners who continue to feed flowers with standard fertilizers. They also contain nitrogen, which is necessary for the color and growth of new shoots.
The introduction of nitrogenous fertilizer will provoke the appearance of new leaves and shoots, which, as a result, will not be fully formed and will not give a lush color next year, if, of course, they themselves will survive to the spring flowering. Therefore, the introduction of fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate, urea and ammonium sulfate should be postponed until spring.

Top dressing for rose bushes can be done in the following ways:
- dry dressing for plant roots;
- liquid top dressing for the root system;
- top dressing in liquid form for spraying the aerial part of the plant.
The first autumn feeding in liquid form is carried out on sunny September days.



For 4 sq. m. of the area of the site, the following composition must be prepared:
- water - 10 l;
- superphosphate - 27 g;
- potassium sulfate - 12 g;
- boric acid - 3 g.
The bushes are watered with this solution in early September.




The second autumn feeding of the climbing rose is scheduled 2 weeks after the first.
For her you will need:
- water - 10 l;
- potassium monophosphate - 15 g;
- superphosphate - 14 g.
After preparing the solution, you should not postpone feeding for a long time, since the composition may lose its qualities after 12 hours.

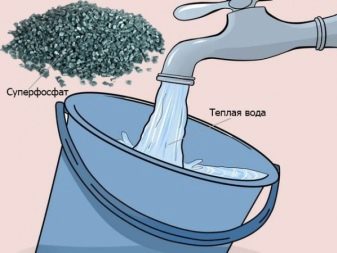
Before fertilizing, it is necessary to loosen the soil a few centimeters deep, and then water the bushes with the prepared solution.After that, each bush is sprinkled with ash at the rate of 200 g per 1 plant.
Also, potassium-magnesia preparation is used as a top dressing in September. It is not only a plant nutrient, but also a disinfectant. It is usually sold in granules and is scattered by the trunk over the entire adjacent surface in early November.
Experienced gardeners also have a folk remedy for additional rose nutrition. This is a banana peel. It is ground into small crumbs and dug up with the root soil. Sometimes banana peels are added to the trunk of the bush. The main thing is to have time to do this in early September or late August.



As a top dressing of the ground part, the same composition is used, only in different proportions:
- water - 30 l;
- potassium monophosphate - 10g;
- superphosphate - 10 g.
This composition is sprayed with a rose every three weeks until the third week of October.


Treatment
Rose bushes, before sending them to a shelter, are also treated against various pests, as well as huddled and pruned.
The rose is most often sprayed with either iron vitriol or Bordeaux liquid. Both drugs work well against pests such as slugs and spider mites.
Pruning is a very important procedure. The appearance of a climbing rose next year depends on the correctness of its implementation, therefore experienced gardeners advise not to neglect this procedure.


At the very beginning, before pruning, remove all wilted leaves from the bushes so that they do not start to rot or spread infections. As soon as the thermometer starts to display zero temperature outside the window, you can start pruning the plant.
The first thing a beginner gardener should do before pruning is to buy a good, sharpened pruner., since the rose does not accept clamps and cut cracking. Inaccurately cut branches become a hotbed of various infections and diseases.
High stems are cut by 1 cm, but the cut is made 1 cm above the last bud and carried out inside the bush. If the cut is made 5 centimeters higher, then the resulting "hemp" will begin to die off and spread infections. The branches should be cut at an angle of 45 degrees, after which all shoots are treated with greenery or charcoal.
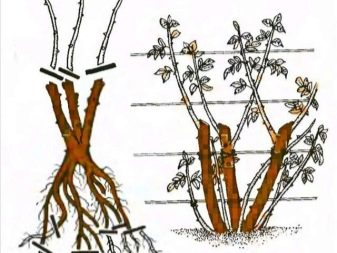

The location of the kidney is also important. If you plan to form a sprawling bush, then you need to cut off at the bud, which looks outward, if you form vertical bushes, then the bud should "look" into the bush. Low rose bushes are cut no more than 10 cm.
The appearance of new shoots or buds in the fall weakens the plant, and therefore it is necessary to pinch new branches in advance and prevent the rose from growing so that it does not weaken and endure the winter staunchly. Mature, but nevertheless healthy, bushes are usually not removed, as they can be rejuvenated by short pruning.
By the fall, the frequency of watering decreases in order to reduce humidity, which is a wonderful platform for the development of fungus. But you still cannot neglect it, since the lack of water increases the concentration of salts in the soil, which is reflected in the growth of bushes. Gardeners advise watering roses in the first month of autumn no more than two times, and if autumn began with torrential rains, then watering a climbing rose is not at all necessary.



In September, gardeners often paint the trunks of spray roses. The paint acts as a protection against pathogens that can infect roses at the most inopportune moment. To do this, use garden or water-based paint, which is pre-diluted with copper chloride. Coloring starts from the bottom, and ends at a height of about 30 cm. After the paint has dried, you can start hilling the bushes.
Gardening experts advise to huddle the rose as high as possible. Thus, it is possible to improve air circulation, establish the supply of oxygen to the roots of the plant and protect the trunk from freezing.


Hilling one adult bush is performed to a height of 30 cm.Usually they use soil between rows and for one young bush a bucket of earth is poured into the center, two buckets are needed for an adult plant. It turns out a high enough cone in order to keep the life of a demanding plant in frost.
They also try to sprinkle the soil with dry mulch, and a layer of humus is poured under it. The very same mulch from above is fixed in place with the help of spruce branches.
Spruce branches perform not only the function of fixing the mulch at the trunk of the plant. The smell of spruce and pine effectively fights rodents, scaring them away, and preventing mice from wintering in a cozy and warm mulch.


The preservation of the root system of the rose is very important, because even if the ground part of the rose is damaged by frost, the healthy roots of the plant will allow the bush to throw out new branches.
If the pruning of rose bushes is not performed, then they are twisted with twine and carefully bent to the ground, and then fixed with arcs near the ground, covered with spruce branches or foliage.
Also, gardeners who do not pick off the leaves spray them with sulfur preparations.


In addition, it is necessary to free the land from fallen leaves and weeds, so that dangerous pests do not start in them and fungal spores do not multiply.
The soil near the bushes, on which the bent rose bushes are laid, is covered with roofing material or wooden shields are laid to minimize the contact of the stems with the frozen ground.


How to properly cover?
Selective roses are very sensitive to any temperature fluctuation. This is due to the fact that in winter they cannot enter a state of vegetative dormancy.
Usually their growing season ends as soon as outside the temperature drops below 0, and the plant falls asleep. But if it suddenly gets warmer in the middle of winter, then the movement of sap inside the plant will resume, and then, when the temperature drops, it will turn into ice. This happens at minus 3 degrees.
The ice breaks the stems from the inside, forming long cracks in which parasites start in the spring, and the plant can become sick. To prevent this from happening, it is important to keep the rose bushes dry for early wound healing.


Therefore, a rose shelter should perform several functions:
- keep the temperature inside the shelter at least minus 10 degrees;
- create dry air around the bush;
- protect bushes from adverse conditions.


Roses are covered exclusively in dry form, therefore, if suddenly, before the gardener's procedure, it is raining, then all manipulations should be postponed until the roses are completely dry. The same applies to processing: after it, you cannot immediately send the bushes to the shelter. You need to wait until the rose bushes are completely dry.
The rainy autumn also complicates the preparation of roses. In this case, over the roses, after their bushes were tied and bent, it is necessary to arrange an impromptu roof that will protect the plants from rain and allow the bushes to dry thoroughly.


There are several ways to cover a climbing rose.
The first method, which is the most budgetary one, is dripping. To do this, the bushes are twisted together and bent down to lay them on the ground. At low temperatures, all manipulations with the bushes must be carried out very carefully, since in the cold the branches become very fragile and can be very easily broken. Some experts recommend performing this procedure in advance, so that by November all the bushes in a prepared state are waiting for shelter.
Further, the bushes need to be covered with dry foliage and spruce branches. This is done immediately before the snow falls and not earlier, since the foliage must be absolutely dry. While waiting for snow, you can bury the bushes, covering them with earth before the first snowfalls.


If you cover a rose with spruce and pine branches, then you must first inspect them for the presence of parasites, since you need to cover the rose only with clean and always dry branches. Raw specimens must be dried.
The branches can get wet, therefore, in order to isolate the natural shelter from moisture, after covering the rose with spruce branches, it is covered with polyethylene and, then, if there are large snowdrifts on the site, the shelter is covered with snow.


The most common way to hide a rose is to create various ground structures.
The very design of protecting a rose from frost depends on the location of its bushes, and the planting of a bush rose is as follows:
- in the line;
- in groups;
- separate bushes.
In the first method of planting, the rose is insulated with a shield method.



A bush rose, planted by a group, is covered with a frame structure, which is covered from the wind with agrofibre or other covering material.
In a single planting, the rose is protected depending on the average annual temperatures. If they are not too low, they spud the rose, cut it off and cover it with spruce branches for the entire winter season. At very low temperatures, experts still advise building at least some kind of shelter for the bush from a frame structure in order to close and insulate a demanding plant.


There is also a way to protect the rose from low temperatures by wrapping vertical stems with fabric material, however, this method is rarely used.
In this case, the pink branches are not removed from the support and the roses are wrapped directly on it. For this, several layers of fabric are usually used, most often burlap, and everything is covered with polyethylene on top. But wrapping roses in order to protect them is possible only in areas with a mild climate. In central Russia, the gardener will have to work hard to build a shelter.


It will not be difficult to assemble a structure to protect the plant from snow and frost. To do this, you need shields and plywood, which is installed on the supports and on the sides of the structure. Then the shelter is covered with agrofibre or any other material to protect it from moisture and wet snow.
Rose huts are the most common hiding place where two shields lean against each other and create a "house". Their height reaches about 80–90 cm. There is enough free space in such shelters so that in spring the water that forms after the ice on the boards melts quickly evaporates and does not create a greenhouse effect inside the "hut".
The advantage of this design is the ability to raise the covering material and occasionally air the roses during thaws.


In shelters made of boards, it is permissible to have gaps, since a rose, as already mentioned above, is a rather frost-resistant flower. An important point is the fact that rose bushes cannot be kept in such a shelter at positive temperatures, and as soon as in spring the temperature begins to rise above zero degrees, it is necessary to remove the covering material from the structure, and then disassemble the structure itself. Roses need to be opened gradually due to the fact that the plant is likely to risk getting sunburn.
The choice of covering material is also important, and you need to approach it very responsibly. The canvas for sheltering roses is completely different, and the decision to purchase is made depending on what the gardener is pursuing.


Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. And the first, most common version of the covering material is a plastic wrap. In Soviet times, this was practically the only covering material that was available to the average gardener. Its thickness varies from 0.04 to 0.4 mm.
Among its advantages are:
- available sunlight for plants inside the shelter;
- reliable protection from wind, rain and snow;
- budgetary material.
The film also has a number of negative qualities that can negatively affect the plant, and these are:
- low quality material, fragility (lasts no more than a year);
- without ventilation, the water in such a greenhouse condenses, which leads to damage to the plant;
- inaccessibility of fresh air for rose bushes.


Spunbond replaced the film and quickly gained the confidence of gardeners due to its positive qualities:
- sufficient illumination of the bushes;
- the possibility of air intake through the material;
- does not retain moisture inside the shelter;
- not damaged by washing or stitching.
Spunbond also has disadvantages, and they are as follows:
- we blow, poorly keeps the temperature inside the shelter;
- the possibility of moistening the soil under the plant;
- the canvas is easily damaged by the claws of birds or animals.


Burlap is another fairly common covering material. Plants are covered with it in winter, which must be protected from sunburn. But he still has more disadvantages:
- gets wet;
- is a source of pathogenic bacteria if not used once.


For shelters, they also use cardboard, which often remains after large purchases. This option is undoubtedly budgetary, and this material perfectly protects the rose from cold weather and wind gusts.
The disadvantages of the cardboard design include wetness, inaccessibility of sunlight and air. But cardboard in a composition with a film is a fairly good shelter and is often used in garden plots.
In the protection of climbing roses, building material such as roofing material is often used. In such a shelter, the rose is not afraid of cold, wind, or rodents. In combination with spunbond, they provide reliable protection for flowers and help them survive frost resistance.

General recommendations for care in the fall
Yes, caring for this beauty is not an easy task, and remembering all the subtleties of a caring attitude to a plant can be very problematic, and therefore novice gardeners at the initial stage need only general recommendations to properly cover a rose that will help him keep his beautiful rose intact ...
Before sheltering, it is necessary to carry out a number of simple manipulations with the plant, which are usually divided by months:
September:
- finish cutting flowers into bouquets;
- reduce the amount of watering;
- remove the nitrogen component from top dressing;
- feed the rose exclusively with potassium and phosphorus;
- loosen the soil near the bushes for the last time;
- weed the soil;
- remove the leaves at the base of the trunk;
- painting the trunk of a rose with water-based compositions.


October:
- finish watering the plant;
- stop feeding the bushes;
- build a roof over the bushes if the fall is rainy;
- spray the rose bush with Bordeaux liquid from possible diseases;
- clean the trunks of dead leaves;
- trim a climbing rose;
- remove the bushes from the supports, collect the stems and tie them not tightly, bending them to the ground.


Further, with the onset of a stable negative temperature, the shelter process begins. During this period, the rose is not watered, not fed, and all care is reduced to creating shelters and warming the trunks of the plant.
At the final stage of care, all actions are aimed at protecting the rose from bad weather, and the entire November is devoted to preparing the rose for frost:
- huddle bushes 30 cm in height;
- a shelter is prepared from shields, boards and covering material to protect the rose from strong cold and wind.
For the intricacies of sheltering climbing roses for the winter, see the video below.

































































































The comment was sent successfully.