Dice sizes
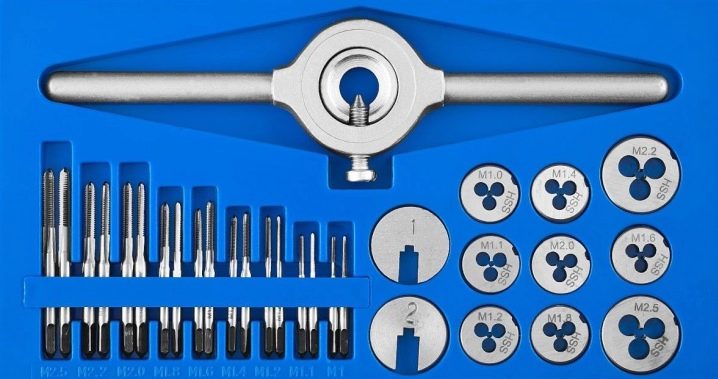
Dies for threading are produced for a specific pitch and diameter. In order not to collide with the American system for determining quantities, turning into inches, the fractional units of which are divided by two, up to 1/64 of an inch, they use a certain marking that has developed in countries that were under the influence of the USSR.


What are the sizes?
According to GOST 9740-1971, the diameter of the thread to be cut is from 1 to 68 mm, the pitch is from a quarter of a millimeter to 6 mm, the outer diameter of the cutter is 12-120 mm, the length (it is cylindrical) is 3-36 mm.... In addition to the parameters listed above, the marking informs about the range of permitted values and the manufacturing option.
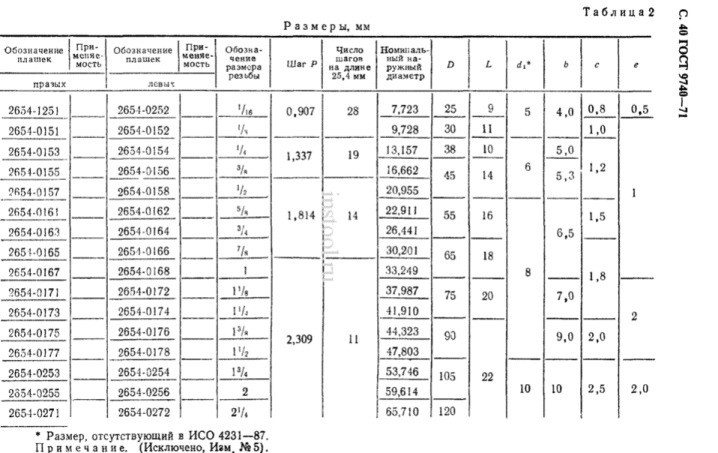
So, the stick 2650-1573 6G GOST is round, for typewriters, it cuts a threaded groove by 6 mm, step - 1 mm, right. To cut a pipe threaded groove, the levers report their dimensions in fractions of an inch, multiples of a divisor equal to 2, and fit into a specific outer diameter of the workpiece.
According to GOST 9150-1981, the main and fine threads have a clearer division: the fine thread has two modifications, and there is a third - especially fine.
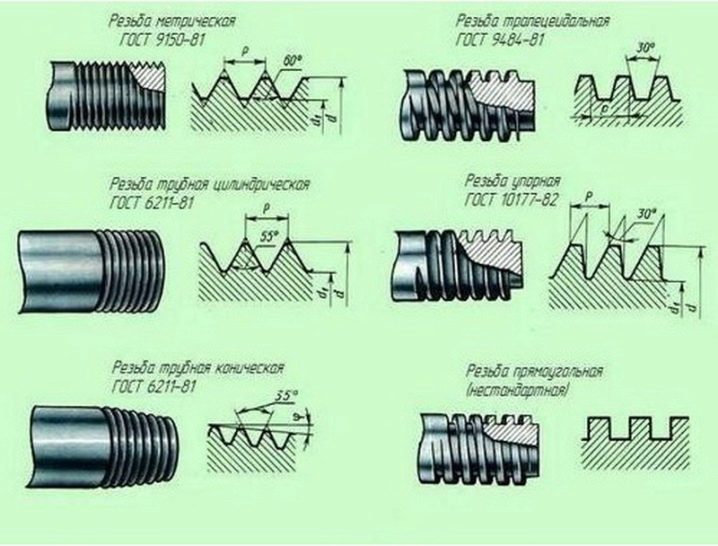
The fine pitch within the same die diameter is different - for example, these are M-10 threaded bolts and studs with a pitch of 1.25 mm, or M14 * 1.5. When buying a tool with a known diameter, the buyer is faced with only the basic cutting step. Fine threads have proven themselves in constant vibration to resist accelerated loosening of bolts and nuts.
Dies of different diameters are available with universal die holders. For example, small dies are combined - up to 10 mm, medium - 12-24, large - 27-42 (by cutting diameter). The tool is installed inside the ram holder and tightened with a steel tie, which is fixed with a screw and nut.

Left-hand thread dies are used in rotating accessories. For example, bicycle wheels, pedal carriages, transmission sprockets (modular assemblies with screw-on threads) are left-handed: the right-hand thread would immediately unwind, or the cyclist would ride backwards. Unscrewing the wheels of vehicles at full speed is fraught with accidents and death - not even a spring washer would have helped. The entire rotating tool also falls under a similar limitation: chucks for drills and screwdrivers, flanges of grinders, and more.

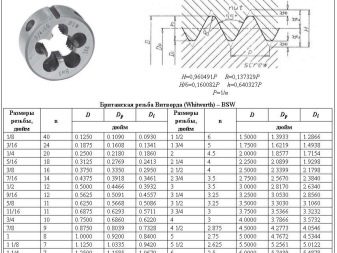
Diameter of inch levers - from 1/16 to 2.25, thread pitch - 0.907-2.309 mm, outer diameter - 25-120 mm, tool length - 9-22 mm. The thread angle is 60 degrees, the threads are pointed, with a slightly blunt edge.
Inch dies in their assortment proceed from the rule: 2.54 cm in an inch.A half-inch pipe - 1.5 cm, 3⁄4 - 20, an inch - about 25, an inch and a quarter - about 32.3⁄4 and 1⁄2 inches - the most common pipelines, an intermediate place is taken by 5⁄8, often used in air conditioning heat exchange ducts.

There are also specific dies that do not work with metals or commercial grades of technical steel. A dies with a flag, with a non-standard threaded diameter, for example, 29 mm, brass or aluminum, is designed for just such work. It is used with softwoods, soft composites, hot melt sticks, and so on.


Marking
Tapered pipe dies have a K marker. The use of such cuts is on machine tools. High-speed steel of Soviet and Russian design is a quality mark on the domestic market, such dies serve for many years - especially from old stocks released during the Soviet era.
To determine the dimensions of the die (die), select one of the standard types of threads used as the main ones:
-
pipe - it is still recalculated in inches, used in 90% of cases;
-
metric - cut into smooth reinforcement.
The second type is designated by the letter M, it is produced from tool steel P18, P6M5, P9 or from alloyed grades KhVSG, KhSS and 9KhS.
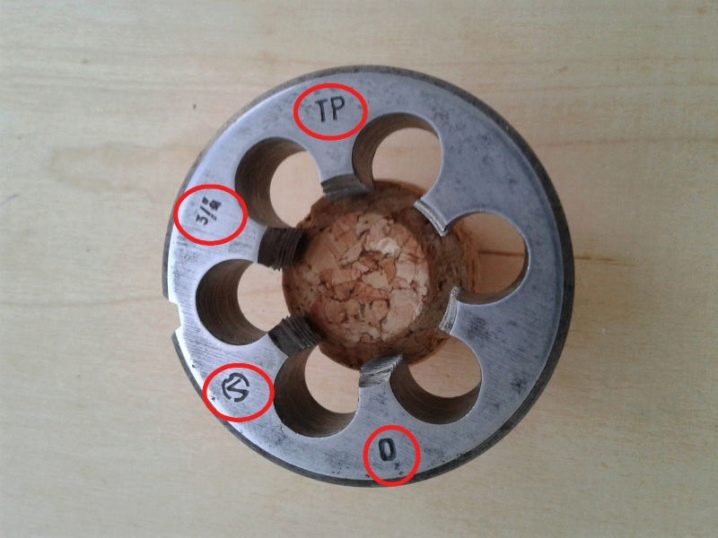
How to determine size?
The easiest way to find out the parameters of the stick is to screw this die onto commercially available bolt and stud samples. An experienced sales consultant will immediately determine the thread pitch, knowing the article number of the products. An ordinary customer does not need this, he can come to the store with samples of pipes / rods, on which he needs to cut threads in large batches of blanks. As the experience of numerous self-builders and garage craftsmen shows, it is enough just to clarify which parts need to be made anew by threading the blanks, what step was used on the damaged component. If the part is light, again, it will not be difficult to bring it to the store and show the seller to pick up a die for it.
For example, for a die on M12, the thread pitch is 1.75 mm. But on sale there are also standard sizes M12 * 1.5, M12 * 1, M12, * 0.5.


Dies M16 and M10 may have the same thread pitch - 1-1.5 mm, it all depends on the repeated specific requirements of the consumer mass.
Non-standard thread is a way to avoid loosening of the structure under very harsh operating conditions, including shaking and strong impacts... Such dies are used for non-standard designs, for example, bicycle hubs, where it is impossible to use a standard (construction) stud made of unhardened steel - that step corresponds to the value for ordinary studs. It is easy to find this feature - the turns are located closer than on ordinary hairpins.











The comment was sent successfully.