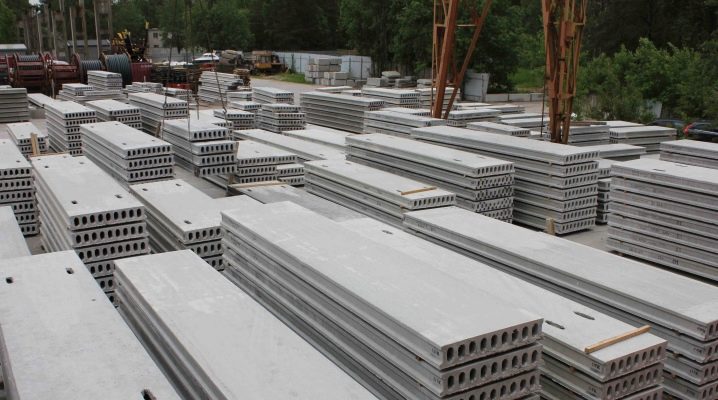
Dimensions and weight of floor slabs

Marking
Floor slabs are horizontal structural elements of a rectangular building that divide the space into floors. In addition to the load-bearing function, such slabs are part of the "skeleton" of the structure, responsible for the rigidity of the entire building. They are based on concrete, therefore, they have a number of advantages: strength, durability, fire resistance, weather resistance. The disadvantages include: relatively high mass, presence of own stresses, high thermal and acoustic conductivity.
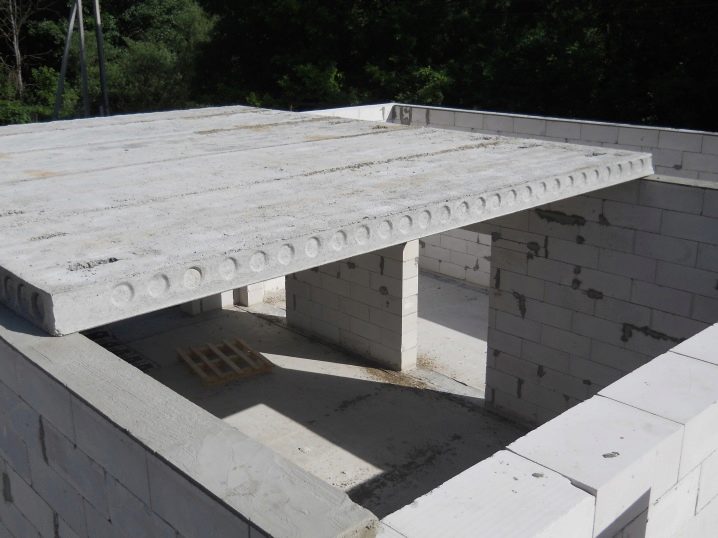

In order to simplify design and construction, the dimensions of the floors have led to a certain standard. Now the developer does not need to know all the intricacies of the production technology, it is enough to be able to decipher the marking. Marking means encrypted information about dimensions, main strength and design indicators.
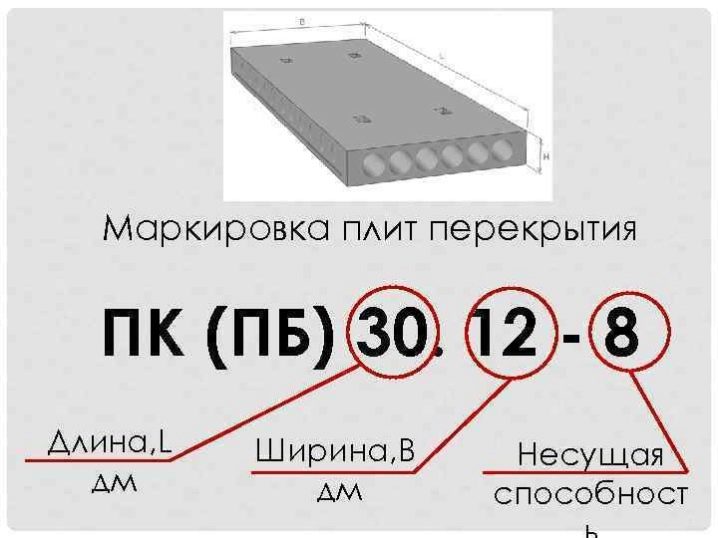
It is performed in accordance with GOST 23009 and is divided into 3 groups, which are separated by a hyphen. The first group includes data on the type of panel, in the second geometric characteristics (length / width). In the third group, strength indicators, the class of steel reinforcement and the type of concrete are indicated. Let us analyze the decoding of PC-48.12-8At-V-t, where:
- PC - hollow panel;
- 48 - length 48 dm (4.8 m);
- 12 - width 12 dm (1.2 m);
- 8 - for a uniformly distributed load of 800 kg per m2;
- At-V - prestressing reinforcement (class At-V);
- t - the type of concrete is heavy.
Element height 220 mm is not indicated, as it is standard for this type of product. Depending on the method of production, the slabs are subdivided into:
- prefabricated (factory);
- monolithic.
The latter are made directly at the construction site.


The process consists of assembling the formwork, installing reinforcing bars and meshes, placing concrete and dismantling the formwork. Based on the design solution, reinforced concrete slabs can be like this.
- Solid (full-bodied). The panel is flat, with high strength, low sound and heat insulation. Simple enough to manufacture, but more material-intensive. They have an impressive weight (600-1500 kg) with a small size. Most often they are used as interfloor floors of high-rise buildings.

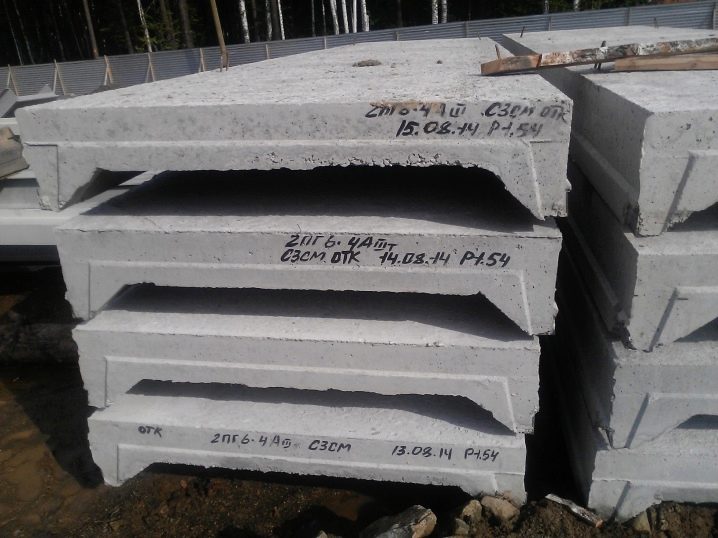
- Ribbed (U-shaped panels). Their distinctive feature lies in the alternation of thickened and thinner elements, due to which the necessary bending stability is achieved. They are more often used in the construction of industrial structures, since in residential construction this configuration is difficult to finish. (P2)

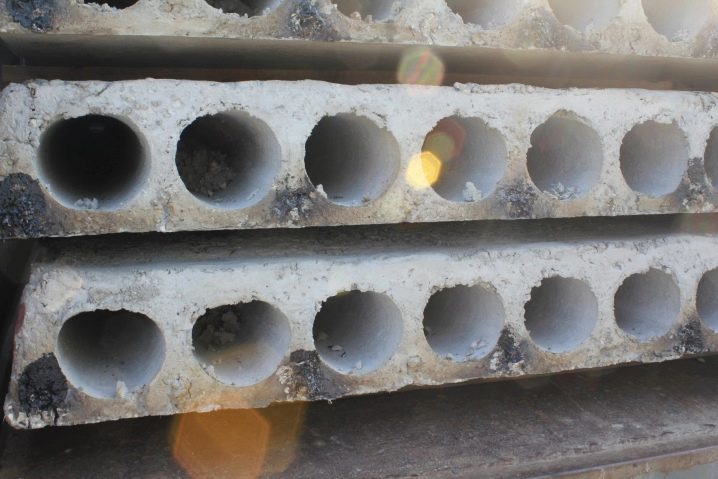
- Hollow. They are the most common type of concrete products. They represent a parallelepiped with cylindrical voids, thanks to which the slab works well for bending moment, withstands heavy loads, allows to bridge large spans (up to 12 meters), and facilitates the laying of communications.

- PC - the most demanded type of reinforced concrete floor, inside there are holes with a diameter of 140 mm and 159 mm, the thickness of the product is 220 mm.
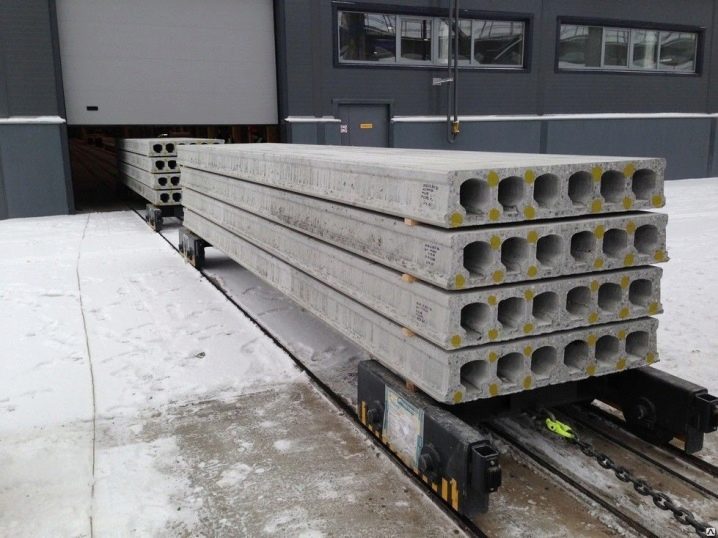

- PNO - an upgraded model with a smaller thickness of 160 mm. It can withstand heavy loads due to thicker reinforcement bars. Lighter than conventional hollow-core models, so this option is more economical.

- PPS (expanded polystyrene, BP) - bench panels, of a new generation, are manufactured by the formless molding method, which allows the developer to use their own sizes. The downside here is the high cost.

Standard sizes
Standard dimensions of slabs are specified in GOST 9561-91. We will present them in the form of a table.
Type of slabs | Length (m) | Width (m) |
PC (1PC, 2PC, 3PC) void diameter 159 mm, supported on both sides | from 2.4 to 7.2 times 0.3 up to 9.0 | from 1.0 to 3.6 times 0.3 |
1pc | ||
PKT (1PKT, 2PKT, 3PKT) with a hole diameter of 140 mm | 1,8 / 2,4 / 3,0 / 6,0 | from 1.2 to 3.6 times 0.3 |
PNO | from 1.6 to 6.4, there are up to 9.0 | 0,64 / 0,84 / 1,0 / 1,2 / 1,5 |
PG | 6,0 / 9,0 / 12,0 | 1,0 / 1,2 / 1,5 |
Ribbed | 6,0 | 1,5 |
Solid, height 120 mm | 3,0 /3,6 /6,0/6,6 | 4.8, 5.4 and 6.0 |
Solid height 160mm | 2.4, 3.0 and 3.6 | 2,4 / 3,0 / 3,6 / 4,8 / 5,4 / 6,0 |
The weight
Weight is one of the most important characteristics. In addition to calculating the distribution load, it will determine how the slab will be delivered to the construction site and installed. For this, the lifting capacity of the crane is calculated. Installation, as a rule, is carried out by a truck crane with a minimum lifting capacity of 5 tons.
The range of product weights in Russia varies from 960 kg to 4.82 tons.

Table "Standard weight of products"
Plate type | Thickness, mm | Width, mm | Length, mm | Estimated distribution load without taking into account its own weight, kg / m2 | Weight kg / 1m p. |
PC | 160 | 1500 | up to 7200 | 400 – 2100 | 404 |
PC | 220 | 1500 | up to 9600 | 400 – 2400 | 520 |
Standard PC specification | |||||
PK 48.12-8At-V-t | 220 | 1190 | 4780 | 1700 | |
PK 48.15-8At-V-t | 220 | 1490 | 4780 | 2250 | |
PK 51.15-8At-V-t | 220 | 1490 | 5080 | 2400 | |
PK 54.12-8At-V-t | 220 | 1190 | 5380 | 1900 | |
PK 54.15-8At-V-t | 220 | 1490 | 5380 | 2525 |
How to calculate correctly?
Initially, it is necessary to correctly arrange the slabs on the plan. Basic rule: floor slabs are supported only on two sides. Since the slab has a lower working reinforcement, local loads (posts, columns) must not be allowed. An important point will be on which walls the floors will rest (walls made of cinder concrete, brick, concrete), which affects the calculation of loads.
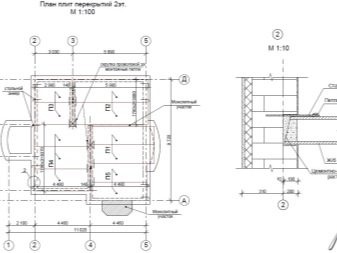
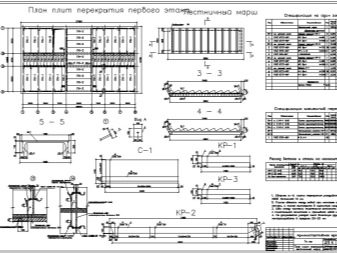
Determine the estimated length of the slab. It is smaller than the real one and is the distance between the most distant adjacent walls. It is set by geometric parameters. The next step is collecting loads. In order to determine the load on each product, it is necessary to indicate on the plan all the weights acting on the floors.
This includes: sand-cement screeds, thermal insulation, floor coverings, partitions.
Having summed up these components, you need to divide the resulting value by the number of plates. Thus, the maximum permissible load for each product can be obtained.
Naturally, it is impossible to load the building frame as much as possible in order to avoid reaching a critical level, for this the optimal value is calculated. For example, a slab weighs 2400 kg, it is intended for a site of 10 m2. It is necessary to divide 2400 by 10. It turns out that the maximum allowable value is 240 kg per 1 m2. The weight of the product itself, for which the load was calculated, should also be taken into account (assume that its value is 800 kg per 1 m2). Then it is necessary to subtract 240 from 800, which gives an indicator of 560 kg per 1 m2.
The next step is roughly assume the weight of all loading items. Let's say that it is equal to 200 kg per m2, then we subtract 200 kg per m2 from our previous indicator of 560 kg per m2 and we get 360 kg per m2. The last step is to determine the weight of people, finishing materials, furniture. On average, this is 150 kg per m2. Then you need to subtract 150 from 360. We got an optimal load of 210 kg per m2. The maximum bending moment can be calculated using the formula: Mmax = q * l ^ 2/8, where l is the span length.
In the next step the class of concrete and the cross-section of the reinforcement are selected according to the assortment... The last step is to check the limit states.
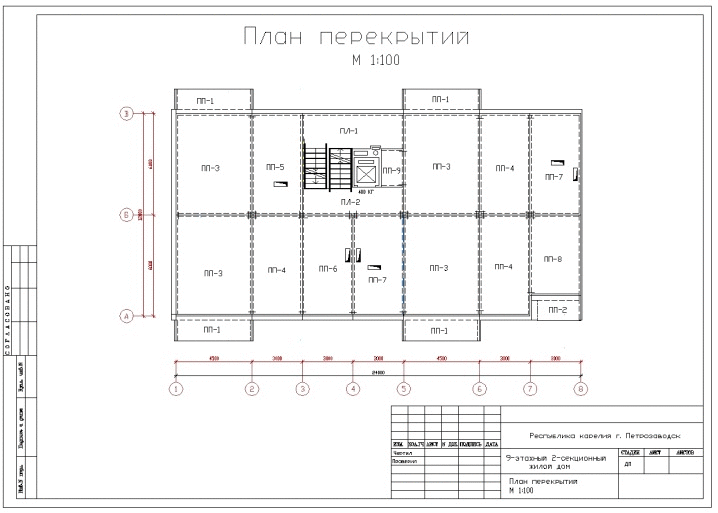
Drawing 1. Layout of slabs in a panel house.
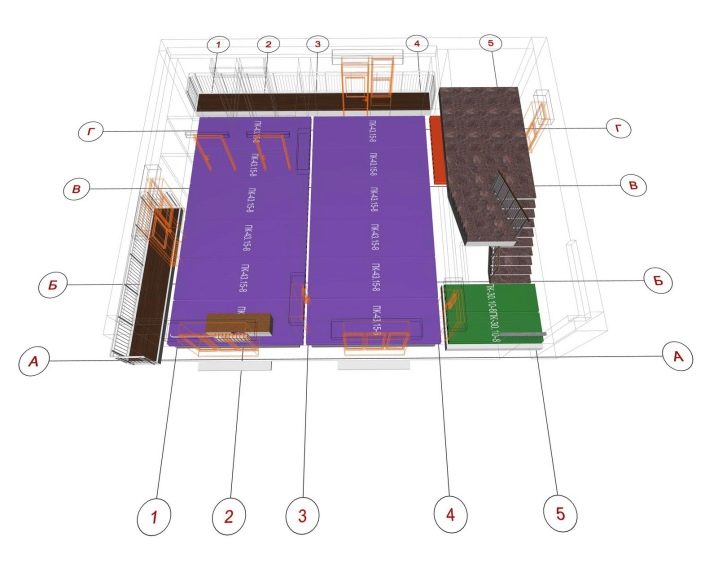
Drawing 2. Private house.
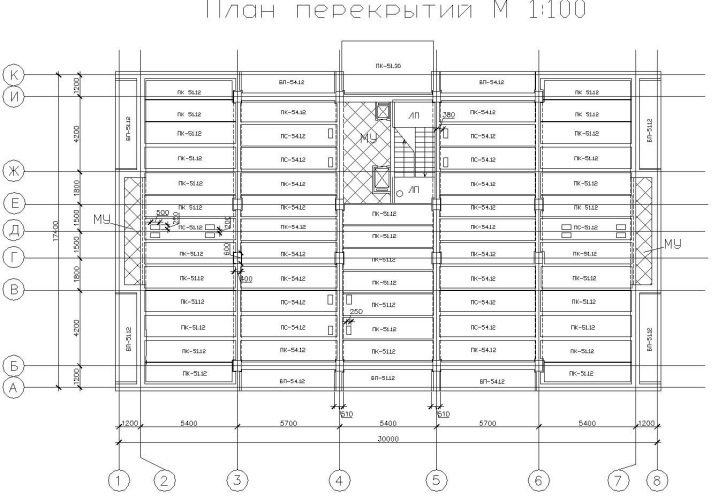
Drawing 3. Multi-storey building.
For a video on the dimensions and weight of floor slabs, see below.












The comment was sent successfully.