Lightweight floor slabs: features, dimensions and use

Researchers of the palace structure in Tsarskoye Selo claim that our compatriots used reinforced concrete as early as 1802. However, the material was patented in 1847 by an ordinary gardener from Versailles. At the very beginning of the 20th century, the Russian engineer, architect, designer and inventor Livchak Fedor Osipovich appreciated the wide possibilities for using such a material as bentonite. In 1909, the first building of the "Livchak" panels was erected.

What it is?
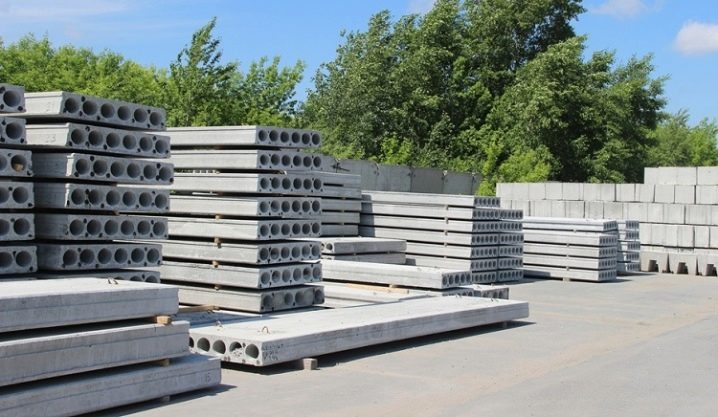
Overlapping is what in everyday life is called the floor and ceiling. Lightweight floor slabs are rectangular U-shaped or flat reinforced concrete slabs. Inside the latter, there are through voids along the entire area.
During the construction of structures, there are only 2 types of floors: monolithic (they are reinforced and poured with cement mortar directly on site) and prefabricated (assembled from finished slabs, and the gaps between them are filled, if necessary, with reinforcement and concrete).


In contrast to monolithic floors, prefabricated structures have their own advantages.
- They are cheaper due to the low consumption of materials during manufacture due to voids, both for the manufacturer and the buyer.
- Easier and faster assembly. They have high strength due to existing stiffeners and an even rectangular shape.
- For installation, it is enough to hire a crane and slingers, because the blocks are light in weight and not very wide.
- The voids in the slabs reduce the noise level and provide additional thermal insulation due to the resulting "air cushion".
- In the factory, the panels are made of better quality and more reliable, since the indicators are controlled at every stage of production.
- The cavities can be used for various communications.
- Installation can be done in all weather conditions.


However, nothing is perfect. Parameters by which precast slabs are inferior to monolithic coatings:
- installation is impossible without the use of lifting equipment;
- the level of hardness is lower;
- there are always gaps between the plates that need additional processing;
- their service life is insignificant, but less, concrete floors are only gaining strength for about 50 years;
- dependence on factory dimensions (a popular section of 1500 mm is available in all nomenclatures), so sometimes you have to use additional additional elements;
- finished blocks have a large height due to voids or shape (U-shaped slabs);
- additional calculations and drawing up are required.


Views
Only specialized factories are engaged in the manufacture of lightweight boards, which in Russia today cannot yet cope with the increasing demand. These floors are actively gaining popularity, and re-equipping production is not an easy task, and it also requires large investments.
Therefore, it takes time to manufacture and deliver an order.

At first glance, lightweight floor slabs are not significantly different from each other. In fact, there is a difference between them, and a big one. There are 4 main types in total.
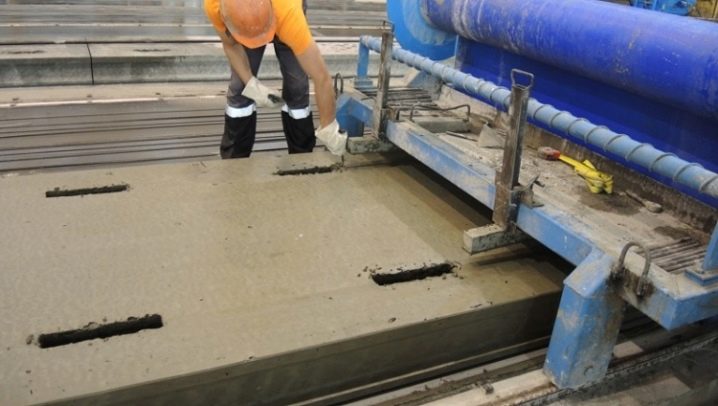
- Hollow core slabs of the PC series. For their manufacture, sand, crushed stone, cement and ordinary or stressed reinforcement are used (before pouring concrete, it is pulled with jacks or electrothermally) in special metal forms.


Manufacturing takes place in several stages:
- install reinforcement and void-forming elements;
- molds are poured with concrete;
- compacting concrete on vibrating tables;
- the first heat treatment takes place;
- make minor repairs, install plugs;
- the product is steamed in special chambers;
- a second heat treatment takes place;
- cut off excess pieces of reinforcement.


The reinforcement can be positioned along and across the slab. The voids are round, 127, 140 or 159 mm in diameter. To increase the strength, cavities are sometimes filled with concrete (it is possible to order at the factory). To simplify installation, 4 sling loops are mounted in them along the perimeter. The standard height is 220 mm. Length - from 1180 to 9700 mm (variable in steps of 300 mm), width - from 990 to 3500 mm. Standard load - 600 kg / cm², 800 kg / cm² (on order can be increased to 1250 kg / cm²).
There are practically no restrictions regarding the application - from a garage to a multi-storey building.

- Hollow core slabs of the PB series. The tensioned reinforcement is located longitudinally. During the production, the technique of non-formwork continuous forming on long stands is used.
For this, special equipment and special technologies are used:
- extrusion (from the English extrusion - pushing out, squeezing out) and extrusion combined with vibration (extruder is a machine in which the concrete mixture is squeezed out and simultaneously formed);
- Split forming (from the English split - separation, bifurcation) is fiber forming combined with thrombosis (side formwork of a splitformer, which compresses 2 layers of concrete mix alternately, and the vibration is created by the slab voids).


According to the specified parameters, the cutting of the resulting tape is performed by another device. The voids have a semicircular shape. There are no mounting rings. The height of the slabs is from 160 to 330 mm, the length is up to 12000 mm (depending on the order, it can vary in increments of 100 mm), the width is from 1000 to 1500 mm. Standard load - from 300 to 1600 kg / cm². Application - low-rise construction. Unlike the previous series, the slab can be cut at an angle of 45 degrees (there are more possibilities in application regarding design solutions). Thanks to the processing with a smoothing machine, the surface is smooth (allows you to reduce the consumption of materials for the subsequent leveling of the floor during repairs).
Qualitatively, the plate has higher performance due to the use of new production technology.


- Plates of the PNO series. Formwork and stand technologies are used for manufacturing (the entire production process is similar to formwork, only it takes place on stationary stands). The voids are round and have a larger diameter in comparison with PC slabs. Mounting rings are not always available. The diameter of the voids is 144 mm. Height - 160 mm. Length - from 1580 to 6280 mm, width - from 990 to 1490 mm. Standard load - from 300 to 1000 kg / cm². They are used in low-rise construction. Distinctive features of the PNO slab from the PK and PB series - due to the increased diameter of the voids, weight decreases, production becomes cheaper and stiffeners are strengthened, more durable concrete and thickened reinforcement are used in the manufacture.
- Ribbed U-shaped plates. In manufacturing, a reinforcing mesh is used (intersections are connected by welding). Concrete in prepared forms is laid in 2 layers. Each is vibrated strictly for 1 and 2 minutes, respectively. This is followed by heat treatment and subsequent trimming. The mounting rings are installed. Height - from 220 to 600 mm, length - from 4780 to 18000 mm, width - from 1190 to 3000 mm. Standard load - from 350 kg / cm². Ribbed panels are used in the construction of non-residential buildings, heating plants and water supply systems.


From the above, you can see that all lightweight floor slabs differ among themselves in the following parameters:
- section type - hollow and ribbed;
- number of layers - single-layer and double-layer;
- reinforcement method;
- dimensions;
- normative load;
- preparation method;
- application area.


In addition, there are other differences:
- different grades of concrete are used for production;
- available holes can be of different diameters and shapes;
- different weight.

Installation technology
Before proceeding to the installation of the floor, drawings are drawn up, in strict accordance with which they begin to act. This helps to find the optimal positioning of the plates, as well as their dimensions. When drawing up drawings, the main thing that is paid attention to is the load-bearing walls. According to the finished plan, it will be possible to calculate the required length and width of the panels in order to minimize the gaps between them.
The installation process itself is as follows:
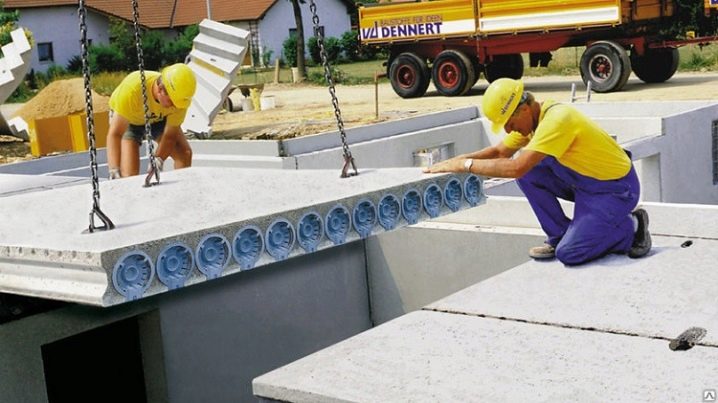
- blocks are lifted and stacked using a truck crane;
- for a strong connection and in order to avoid the formation of gaps, the blocks are fixed on a cement mortar;
- in accordance with the standard laying scheme, the slab should go 120-150 mm onto the supporting wall;
- the panels are fastened to each other using steel rods, mounting rings and welding;
- the seams are poured with concrete (if necessary, reinforcement is carried out).


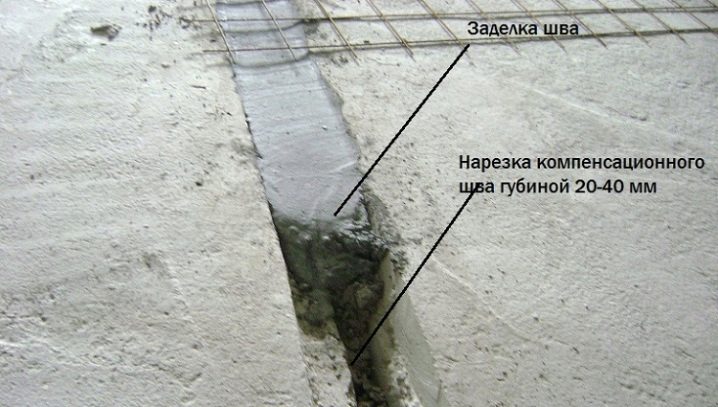
This scheme also provides for the sealing of the ends, which will prevent freezing of the house, which is done as follows:
- you need to fill the voids with mineral wool 200-300 mm;
- fill voids with lightweight concrete 120-200 mm;
- close with concrete plugs;
- take an ordinary red brick in mortar and seal the surface with it.

Selection rules
With any action, you always want to save money and not lose quality. In such an issue as construction, the scale of the savings is significant, as is the responsibility for the result. Based on the above conclusions, it will not be difficult to draw - for low-rise construction, the PNO series cover plate is ideally suited.
Its height and smooth surface allow not only to save on finishing materials, but also to increase the ceiling height by at least 60 mm. Larger voids improve thermal and acoustic insulation and stiffening ribs, reduce weight and reduce production costshence the cost of the stove. In addition, cavities allow you to hide not only the wiring, but almost any communications. The blocks are resistant to changes in temperature and humidity.
The disadvantages include the need for a lifting device.
Delivery times for finished products can be long and, of course, you will have to deal with calculations and drawing up drawings, taking into account the peculiarities of the design of buildings.


You can find out how to evenly lay floor slabs by watching the video below.












The comment was sent successfully.