The nuances of the formation of pepper in the greenhouse
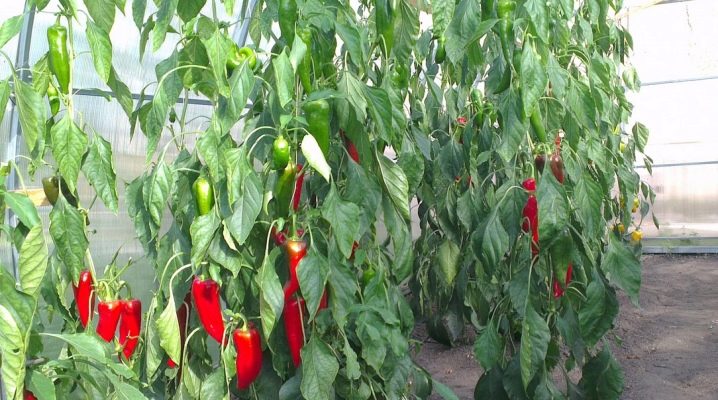

The formation of greenhouse bell peppers is an obligatory stage of care to achieve a high yield. From the material in this article, you will learn about all the nuances of work, including the rules and methods of agricultural technology, as well as subsequent care procedures.

The need for a procedure
The conditions in the greenhouse are far from the street ones, where each bush of the cultivated crop receives the required amount of moisture, air, food, light. With a dense planting of peppers in a polycarbonate greenhouse, competition occurs between the bushes. As a result, one will have good fruits, while the other bush will not be able to grow strong. The yield will be approximately the same in the total mass.

However, with the uncontrolled release of shoots, you should not count on large and sweet fruits.
In greenhouse conditions, the growth of green mass is accelerated. Poor ventilation and dampness often provoke illness and weakness. Competent prioritization contributes to the correct growth and development of the vegetable.
During the formation of vegetable bushes, it is possible to achieve an improvement in the taste of the fruit. At the same time, they grow sweet, large and fleshy, have thick walls. Formation gives the peppers a presentation. Thanks to it, the likelihood of the occurrence and development of diseases is reduced. It helps to ventilate the bushes, simplifies their care, accelerates the ripening of fruits.
Formation controls the number of shoots on which ovaries form over time. It prevents the formation of ovaries until frost and saves nutrients. Allows fruits to ripen juicy and healthy. Pinching "informs" the bush about the cessation of growth and the direction of forces to ripen the fruit. It is used in a shortened growing cycle. This is especially important when there is a lack of light and heating.

Variety selection
You can not pinch all types of peppers. This procedure is indicated for indeterminate and tall determinate varieties of vegetables. Without proper care, they waste energy on growth. The fruits practically do not get anything, so they do not have time to gain weight and ripen. Formation is necessary for large-fruited thick-walled cube-shaped varieties.
Most of them do not mature after harvest. Stimulation allows you to achieve biological ripeness before breaking off the bush.
The procedure is suitable for pepper varieties with a fast ripening period, thin walls and a conical shape. Formation is prohibited for bouquet crops, undersized varieties are also not subjected to this. Their number of peppers is genetically limited.

It is not necessary to form such hybrid varieties as Dobrynya Nikitich, Lastochka, Buratino, Othello. They already have weak branching. No pruning is needed for Gemini and Mercury varieties.




Fundamental rules
The agrotechnical procedure takes place in several stages. It is important to cut off injured and yellowish leaves in a timely manner, do not forget about the garter, entwining the stems around the supports. Based on the chosen scheme, you need to remove the crown (first) bud, which is formed at the place where the branches are dividing. If necessary, this is done before transplanting the crop into the greenhouse. The crown bud appears at different stages of pepper cultivation. After cutting, level 1 stems grow in the place of its former location. This is the beginning of the perfect formation pattern.



We must not forget about removing excess stems. The number of trunks must correspond to the selected scheme. Only the strongest and most powerful stems are left, formed from the fork where the first bud grew. Anything else must be deleted. Initially, this is trimming the top, the main point of growth. The optimal time is the presence of 10 true leaves. Formation should start with skeletal stems.

During growth, skeletal stems divide and branch. At each branch point, proceed in the same way. Get rid of frail shoots, leaving only powerful ones.
According to the established rules, you need to cut the shoot in such a way that a small part of the trunk with 1 leaf remains on the bush. It is needed to feed the ovary on a powerful shoot. All empty, sterile stems and shoots are removed in order to provoke the growth of strong shoots. The rate of foliage removal depends on the bushiness of the variety and the nuances of cultivation.
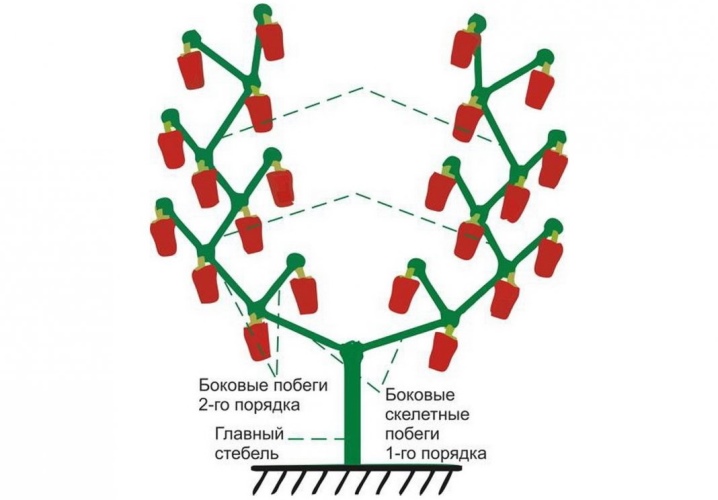
The plant should not be naked. The bush should have a main stem (stem), skeletal branches, as well as shoots of the 1st and 2nd order. When normalizing the number of shoots, special attention is paid to the removal of the lower leaves, as well as sterile branches. Flowers are often formed on them, which do not bear fruit in the future. All useless is cut off. In the course of formation, the buds formed in the internodes are removed. In total, no more than 15-25 ovaries are left on the bush.
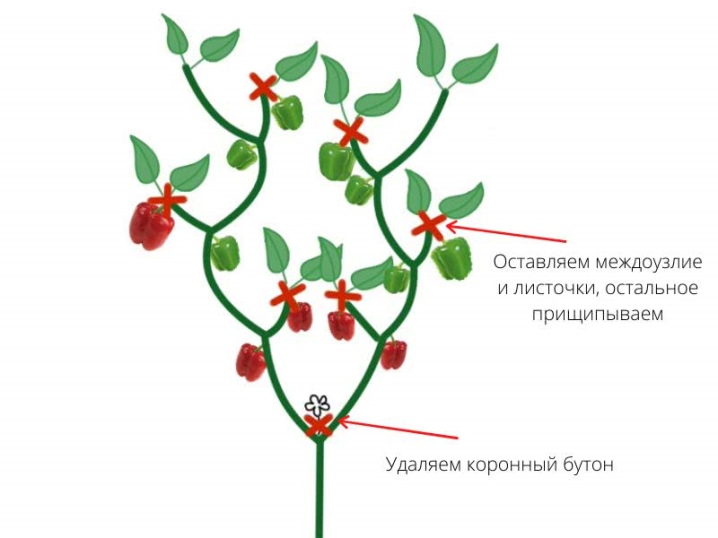
Along with this, you need to get rid of diseased foliage and stems in time. If there is not enough light for the bushes, the leaves are thinned out. On the main trunk, this is done when the fruits of the first cluster reach biological maturity. It is imperative to pinch the skeletal branches, which is resorted to after the formation of a sufficient number of ovaries. As a rule, this procedure is performed 1.5 months before the end of growing a vegetable.
Seedlings grown independently are subject to formation. Depending on the variety, control is started when the height of the seedlings is 15-25 cm. However, the division into trunks in some varieties may occur earlier. Therefore, one must not miss the moment when the division of the bush begins. The crown bud that appears soon is left only at the bush of a rare variety in order to obtain seeds. In the next season, strong vegetables will grow from them with the preservation of varietal characteristics.

Technique overview
Key techniques for shaping peppers are pinching, pinching, pruning. The implementation of each of them has its own characteristics, and therefore it is important for beginners.
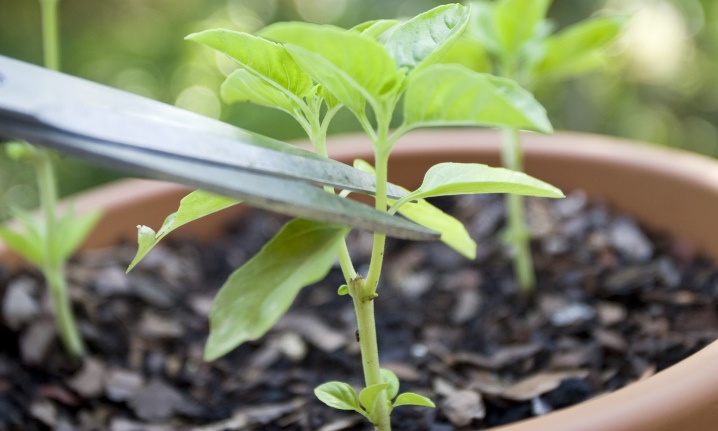
Stepping
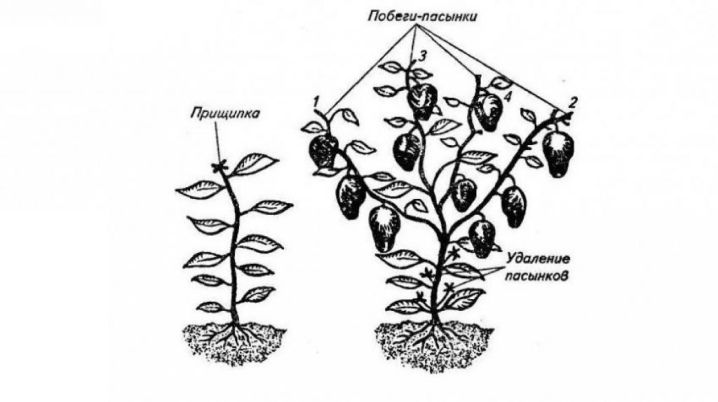
Grasshopping is nothing more than cutting off the lateral branches that grow from the axils of the leaves. Ignoring this technique is fraught with increased costs of the plant for growth and development. At the same time, he has practically no strength left to pour the fruit. It is necessary to correct the bush in a greenhouse or greenhouse correctly.
This is usually done while it has not yet reached a height of 30 cm.
Each slice is sprinkled with crushed chalk or activated carbon. You need to remove all small shoots growing to the fork of the stem. The length of the stumps should not exceed 3 cm, otherwise they will grow. It is better to do this in the morning in order to minimize the stress of the plant, which often suffers from greenhouse conditions. Agricultural technology involves further loosening between rows and watering the bushes.
In the course of work, disinfected instruments are used. The scissors used must be sharp to cut each stepchild in one stroke.

Pruning
Leaves are pruned according to their own rules. Dense foliage often provokes air starvation of bushes in a greenhouse. Odoes not allow them to be ventilated. However, it is not only diseased, dry and yellowish leaves that need to be trimmed. Be sure to cut the leaf plates of the first stem. This is best done when the level 1 peppers are technically mature.
The foliage growing under the level 2 shoots is cut according to a similar principle. Only one pair should be removed for 1 procedure. It is impossible to completely cut off the leaf plates, since they nourish the fruits. If removed, the peppers will be small and tasteless.To avoid this, it is enough to leave 1-2 leaves near the ovary. About 1.5 months before harvest, the pruning is finished.
Without pruning, many of the ovaries on the bushes will be underdeveloped. Do not be greedy, trying to get an unprecedented amount of peppers from each bush. It's impossible. Like other procedures, pruning should be done in stages as the fruit ripens.

Uniform pruning is also important. You can not leave the shoots without flowers.
Topping
This procedure controls the indicators of crop yield and the timeliness of ripening. Excessive ovary volume harms the bushes. They simply do not have time to ripen the fruits. To prevent this from happening, they carry out pinching, pruning. Initially, the preservation of the skeleton is monitored. Control assumes the preservation of no more than 2-3 powerful shoots.
Pinching is resorted to whenever another fork grows on the skeletal stem. It is important to leave exclusively developed shoots. Such branches will be able to support the weight of large peppers. A powerful branch is left on the escape of 1, 2 levels. Everything else is cut above the flower ovary. The pinching is finished when the number of vegetables that the bush can withstand is reached. At the same time, it is important to avoid overloading the bush with green mass. You can’t cut too much, so that it does not harm the culture.

The ways
It is possible to form a vegetable crop grown in greenhouse conditions in different ways. They do this in compliance with generally accepted rules. The choice of technique is associated with the variety of the vegetable, the nuances of its growth and development, the number of planted bushes. Formation is carried out in several successive steps so that the plant does not experience stress.
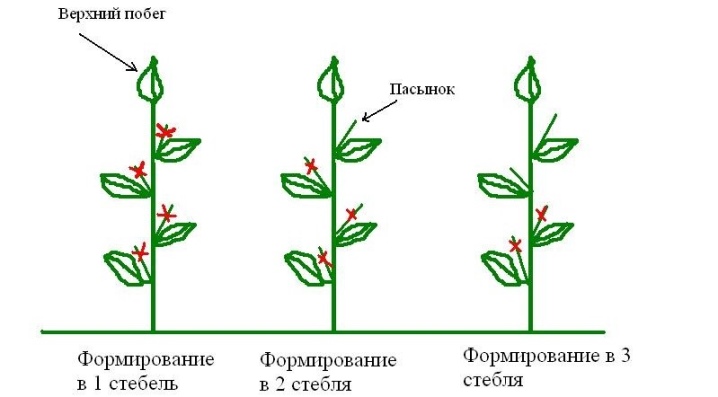
One stem
This agricultural technique is based on pruning all lateral branches that appear on the main stem. The technique is used in small greenhouses, where tall plants are forced to compete with each other for light and nutrition. If they are not planted at the proper spacing, thinning is the best way of grooming. In a limited space, thickening provokes diseases, due to which fruits deteriorate and yield decreases.
The step-by-step instruction consists in the step-by-step formation of the bushes. At each fork that appears, the side shoots are removed, leaving a short length and a leaf under the cut branch. This is done until there are 10-20 flower buds. After that, pinch the top of the stem. From this, growth immediately stops, all forces go to the ripening of vegetables.
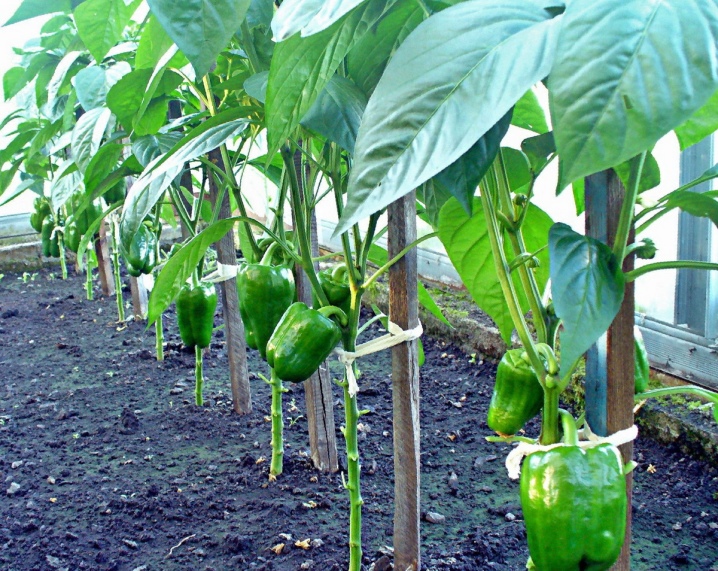

The formation of seedlings after planting according to this scheme increases the vertical growth of the bushes, enlarges the size of the fruits.
Two stems
The scheme for the formation of a bush in 2 stems (V-shape) is considered the most common. It is used in spacious greenhouses. Allows to grow up to 20 large and fleshy fruits on each bush. To obtain this form, stepchildren are left growing from the central stem. First, 1 is left the strongest at the bottom, as it grows, the procedure is repeated.
The same number of peppers are left on each part of the V-shaped bush. Subject to the control rules, each fetus will receive an equal amount of food, air, and light. Formation also applies to shoots of the 2nd, 3rd order. The upper part of the bush is cut off after a sufficient number of ovaries have formed on it. This will help the fruit juice.
Three stems
Removal of shoots with molding into 3 stems is performed after several stepsons have been removed on the main trunk. Such bushes need more space, light, air, which is justified by higher yields. Formation after branching is performed with the removal of side shoots from each of the three main trunks.
It happens that the fork is formed from 2 branches. In this case, you cannot get rid of the lower shoots on the skeleton of the bush. They are allowed to grow a little, then the most powerful one is selected. Others clean up. The skeleton of the 1st level is formed by the 2 most powerful trunks. All weak stems are removed.They are engaged in shaping until the required number of ovaries is set. After that, immediately pinch the top, stopping growth.
Follow-up care
In order for the bushes to grow strong, withstand the weight of the fruit, they are provided with proper care. In addition to timely watering, they equip a system of supports and garters, which can be horizontal and vertical. It simplifies pinching, streamlines the weight load on the bush. Most vegetable growers build a trellis system, thanks to which it is possible to tie up each growing order.



A garter is a must, as the stems often break without it.
Bush holders are made of wood, metal, plastic, fiberglass. In addition to the traditional crossbeams, it is possible to construct classic rope garters with equal pitch. At the same time, their appearance differs. These can be ropes tied up from stakes to top bars. In one case, 1 garter is used for 1 peg, in the other 2 ropes go from one support, which is good for forming V-shaped bushes.
You need to fix the stems while maintaining their natural shape. This will be kink prevention. In this case, the tying scheme should correspond to the variety and number of ovaries. If the fruits are heavy and large, some vegetable growers resort to non-standard solutions. Someone plunges long stakes into the soil near the roots, gradually braiding the skeletal stems of plants with a rope.



Other gardeners hang a hook, attach as many ropes to it as there are ovary bush. You can fix the bushes with wire, twine, fibrous thread. Someone prefers to use unnecessary nylon tights and woven ribbons for tying.
For peppers grown in 1 stalk, a regular rope garter with moderate entanglement of the skeleton is needed. It is also used when it is necessary to support the stem with a high division. With a large number of ovaries, the number of ropes per bush is increased.
During tying using threads and ropes, make sure that the knots are movable. Thanks to this, at any time it will be possible to loosen the fastening without harming the stems. In polycarbonate greenhouses, fastening is often performed using the existing crossbars.
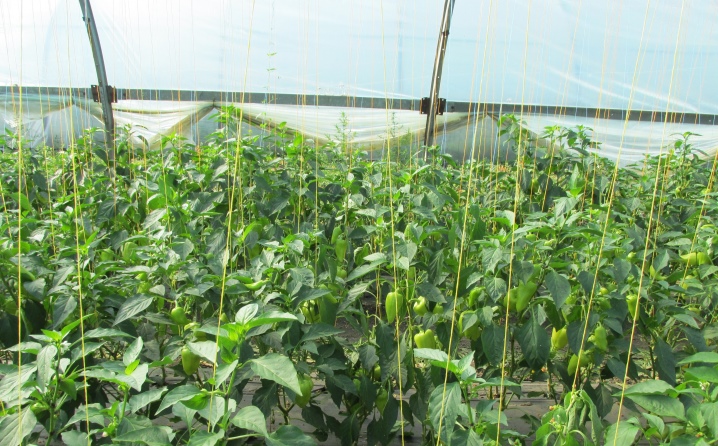

In this case, the ropes (wire) are usually placed with the same pitch. This will prevent competition between bushes.
We must not forget about the timely loosening of the soil and the introduction of fertilizers. Loosening is also necessary in case of excess moisture. After it, the earth is saturated with oxygen, excess moisture leaves. Mulching, carried out with peat, straw, rotted leaves, also contributes to the improvement of aeration. So that the fruits do not rot and the foliage does not curl, you need to maintain an optimal microclimate. Peppers are quite capricious in their care, without regular airing they often get sick.



Useful Tips
In order for vegetables to please with a high yield, it is necessary to avoid common mistakes that novice gardeners make.
- Formation must be balanced. Otherwise, it will be difficult to synthesize the required energy. Everything must be timely.
- Cutting long stems is strictly prohibited. They must be removed when their length does not exceed 5-6 cm.
- It is not necessary to carry out procedures for highly sparse bushes. In this case, the greens are the protection of the bush from the destructive heat and dryness. It signals a problem with twisting and yellowness.
- You can not carry out pinching and pruning in heat and drought. This will cause sunburn to the bush. It is better to water the plant with settled water heated in the sun.
- It is undesirable to form bushes with an abundance of moisture inside the greenhouse. Because of this, a painful microclimate will be created, and the drying of the sections will slow down.
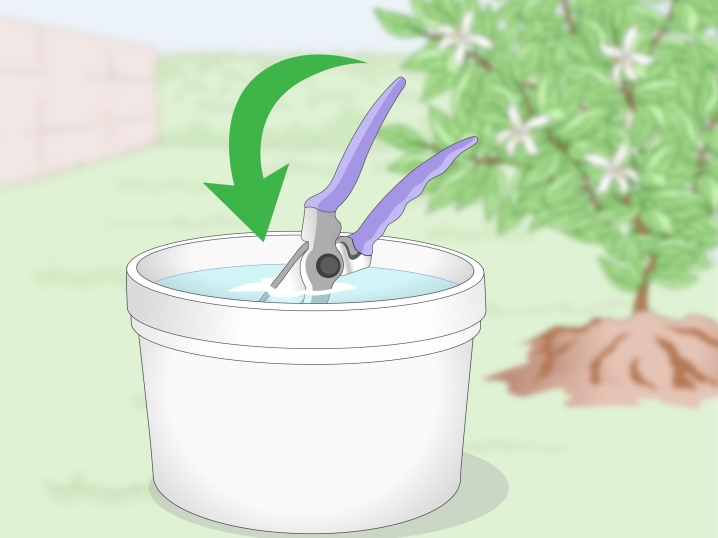
- You can not engage in the formation of diseased bushes. In most cases, this leads to their death. You can not work with an untreated tool that was used on diseased plants.The use of non-sterile instruments will provoke an infection that will require treatment. After the procedure, the bushes are carefully examined, monitoring their condition.
- The planting pattern corresponds to 40x50 cm between the bushes. The gap between the rows is 70-80 cm. On average, 8 bushes should be located per 1 m2.
- When shaping, you need to be extremely careful and careful. You can not break branches, tear the stems mercilessly, stressing the roots of plants.
- We must not forget about pinching the growth points located on the skeletal stems. Tall (more than 1 m) varieties form in 1 stem, medium-sized ones - in 2 and 3. When varieties of medium growth in 1 stem are formed, yield suffers.
- As for the registration of the region, in the southern latitudes of the country, pepper is formed into 3 stems. Where summer is short, it is better to limit yourself to options of 1 or 2 stems.
- It is necessary to plant peppers in a greenhouse taking into account the future increase in the bush by a couple of branches. In this case, the bushiness of the selected variety is also taken into account. Ideally, the load on the stem should not exceed 6 large fruits.
- The average number of fruitful shoots should not exceed 4-6. If the summer is hot, then the climate in the greenhouse is especially stifling. In this case, the lower leaves are not removed. They will contain excessive heating of the earth.
- In conditions of constant humidity and dampness, on the contrary, you need to bare the bottom of the bush. This will prevent moisture stagnation, due to which the plant is affected by fungi and bacteria.
- With the simultaneous appearance of 2 primary buds, both must be removed immediately in order to increase the growth of the bush and fruiting. Formation must comply with the control schedule.
- Disinfecting tools (scissors, secateurs) is necessary not with water, but with alcohol and chlorine-containing preparations.
- The best time for processing is dry or cloudy weather. After some time after that, you need to spray the bushes with lukewarm water. You cannot use a cold one in a hot greenhouse, as it provokes stress.
















The comment was sent successfully.