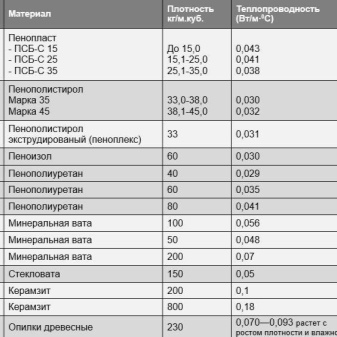
Thermal conductivity of foam

When building any building, it is very important to find the right insulation material. In the article, we will consider polystyrene as a material intended for thermal insulation, as well as the value of its thermal conductivity.


Influencing factors
Experts check thermal conductivity by heating the sheet from one side. Then they calculate how much heat passed through the meter-long wall of the insulated block within one hour. Heat transfer measurements are made on the opposite face after a certain time interval. Consumers should take into account the peculiarities of climatic conditions, therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the level of resistance of all layers of insulation.
Heat retention is influenced by the density of the foam sheet, temperature conditions and moisture accumulation in the environment. The density of the material is reflected in the coefficient of thermal conductivity.
The level of thermal insulation depends to a large extent on the structure of the product. Cracks, crevices and other deformed zones are a source of cold air penetration deep into the slab.

The temperature at which water vapor condenses must be concentrated in the insulation. Minus and plus temperature indicators of the external environment change the level of heat on the outer layer of the cladding, but inside the room the air temperature should remain at around +20 degrees Celsius. A strong change in the temperature regime on the street negatively affects the effectiveness of the use of the insulator. The thermal conductivity of the foam is affected by the presence of water vapor in the product. The surface layers can absorb up to 3% moisture.
For this reason, the absorption depth within 2 mm should be subtracted from the productive insulation layer. High-quality heat saving is provided by a thick layer of insulation. Foam plastic with a thickness of 10 mm, compared to a slab of 50 mm, is able to retain heat 7 times more, since in this case the thermal resistance increases much faster. In addition, the thermal conductivity of the foam significantly increases the inclusion in its composition of certain types of non-ferrous metals that emit carbon dioxide. Salts of these chemical elements endow the material with the property of self-extinguishing during combustion, giving it fire resistance.


Thermal conductivity of different sheets
A distinctive feature of this material is its reduced heat transfer.... Thanks to this property, the room is perfectly kept warm. The standard length of the foam board ranges from 100 to 200 cm, the width is 100 cm, and the thickness is from 2 to 5 cm. Thermal energy savings depend on the density of the foam, which is calculated in cubic meters. For example, a 25 kg foam will have a density of 25 per cubic meter. The greater the weight of the foam sheet, the higher its density.
Excellent thermal insulation is provided by the unique foam structure. This refers to foam granules and cells that form the porosity of the material. The granular sheet contains a huge number of balls with many microscopic air cells. Thus, a piece of foam is 98% air. The content of air mass in the cells contributes to a good retention of thermal conductivity. Thereby the insulating properties of the foam are enhanced.

The thermal conductivity of foam granules varies from 0.037 to 0.043 W / m. This factor influences the choice of product thickness. Foam sheets with a thickness of 80-100 mm are usually used for building houses in the most severe climatic conditions. They can have a heat transfer value from 0.040 to 0.043 W / m K, and slabs with a thickness of 50 mm (35 and 30 mm) - from 0.037 to 0.040 W / m K.
It is very important to choose the correct thickness of the product. There are special programs that help to calculate the required parameters of the insulation. Construction firms use them successfully. They measure the real thermal resistance of the material and calculate the thickness of the foam board literally down to one millimeter. For example, instead of approximately 50 mm, a 35 or 30 mm layer is used. This allows the company to significantly save money.

Nuances of choice
When buying foam sheets, always pay attention to the quality certificate. The manufacturer can manufacture the product according to GOST and according to our own specifications. Depending on this, the characteristics of the material may vary. Sometimes manufacturers mislead buyers, so it is necessary to additionally familiarize yourself with the documents confirming the technical characteristics of the product.
Carefully study all the parameters of the purchased product. Break off a piece of Styrofoam before purchasing. Low grade material will have a jagged edge with small balls visible at each fault line. The extruded sheet should show regular polyhedrons.


It is very important to consider the following details:
- climatic conditions of the region;
- the total indicator of the technical characteristics of the material of all layers of wall plates;
- density of the foam sheet.
Keep in mind that high quality foam is produced by Russian firms Penoplex and Technonikol. The best foreign manufacturers are BASF, Styrochem, Nova Chemicals.



Comparison with other materials
In the construction of any buildings, various types of materials are used to provide thermal insulation. Some builders prefer to use mineral raw materials (glass wool, basalt, foam glass), others choose plant-based raw materials (cellulose wool, cork and wood materials), and still others choose polymers (polystyrene, extruded polystyrene foam, expanded polyethylene)
One of the most effective materials for conserving heat in rooms is foam. It does not support combustion, it dies out quickly. The fire resistance and moisture absorption of the foam is much higher than that of a product made from wood or glass wool. The foam board is able to withstand any temperature extremes. It's easy to install. Lightweight sheet is practical, environmentally friendly and low thermal conductivity. The lower the heat transfer coefficient of the material, the less insulation will be required when building a house.
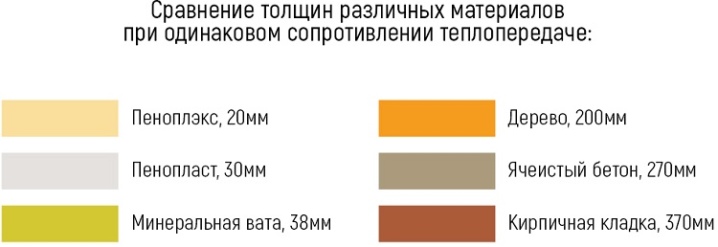
Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of popular heaters indicates low heat loss through walls with a foam layer... The thermal conductivity of the mineral wool is approximately at the same level as the heat transfer of the foam sheet. The only difference is in the parameters of the thickness of the materials. For example, under certain climatic conditions, basalt mineral wool should have a layer of 38 mm, and a foam board - 30 mm. In this case, the foam layer will be thinner, but the advantage of mineral wool is that it does not emit harmful substances during combustion, and does not pollute the environment during decomposition.
The volume of use of glass wool also exceeds the size of the foam board used for thermal insulation. The fiber structure of glass wool provides a rather low thermal conductivity from 0.039 W / m K to 0.05 W / m K. But the ratio of the sheet thickness will be as follows: 150 mm glass wool per 100 mm of foam.


It is not entirely correct to compare the heat transfer ability of building materials with foam plastic, because during the construction of walls, their thickness differs significantly from the foam layer.
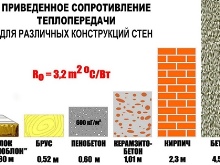
- The heat transfer coefficient of bricks is almost 19 times that of foam... It is 0.7 W / m K. For this reason, the brickwork should be at least 80 cm, and the thickness of the foam board should be only 5 cm.
- The thermal conductivity of wood is almost three times higher than that of polystyrene. It is equal to 0.12 W / m K, therefore, when erecting walls, a wooden frame should be at least 23-25 cm thick.
- Aerated concrete has an indicator of 0.14 W / m K. The same coefficient of heat saving is possessed by expanded clay concrete. Depending on the density of the material, this indicator can even reach 0.66 W / m K. During the construction of a building, an interlayer of such heaters will be required at least 35 cm.


It is most logical to compare foam with other related polymers. So, 40 mm of a foam layer with a heat transfer value of 0.028-0.034 W / m is enough to replace a foam plate 50 mm thick. When calculating the size of the insulation layer in a particular case, the ratio of the thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.04 W / m of foam with a thickness of 100 mm can be obtained. Comparative analysis shows that 80 mm thick expanded polystyrene has a heat transfer value of 0.035 W / m. Polyurethane foam with a heat conductivity of 0.025 W / m assumes an interlayer of 50 mm.
Thus, among polymers, foam has a higher coefficient of thermal conductivity, and therefore, in comparison with them, it will be necessary to purchase thicker foam sheets. But the difference is negligible.
















The comment was sent successfully.