All About Foam Density

Expanded polystyrene foam for house insulation is chosen based on the density brand. In the article, we will consider the nuances of the density designation according to the old and new GOST, consider the features of using popular brands and provide recommendations for choosing.

How is it indicated and what does it affect?
Density (a value characterizing the ratio of mass to volume, measured in kg / m3) is the most important characteristic, on which the operational and strength properties of expanded polystyrene, weight, depend. The more cavities in the sheet - the lower its density, the thicker the polymer shells of the cells - the denser and stronger the material will be. The most common types of construction foam in everyday life have a density of 6 to 50 kg / m3, but some specialized types have a density of 100 kg / m3 and even higher. It is the density that underlies the accepted classification of polystyrene into grades.

But along with density, the strength of the foam also depends on its internal structure, cell size, and the use of various additives. Therefore, foam sheets of different types (non-pressed, pressed, extruded), even with the same density, may have different mechanical properties.
The best performance properties are possessed by extruded foam, which has a dense closed-cell structure. But it costs more.
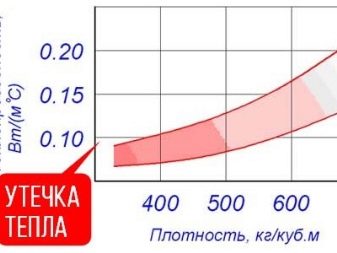

Therefore, in everyday life, for private construction, ordinary non-pressed foam is most often used. Its characteristics are related to density as follows.
- The weight - the higher the density, the heavier the sheet, this must be taken into account when choosing fasteners and calculating the effect on building structures.
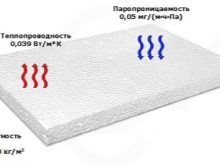
- Thermal conductivity - the smaller this value, the better the material is a heat insulator. For non-pressed foam, this indicator is 0.029-0.036 W / m. to, which is 4-5 times better than brick or wood. That is, a 3-5 cm layer of polystyrene is comparable in efficiency to a 20 cm layer of wood or brick. Considering the lightness and cheapness of the foam, this allows you to create more successful design solutions. Moreover, in the case of pressless foam, the lower its density, the greater the efficiency as a heater.
- Compressive strength, fracture, resistance to mechanical stress - the higher the density, the better these indicators.
- Sound absorbing properties - they are better for a material with a lower density.
- Price - the higher the density, the more expensive the material is.
Thus, although low density foams are ideal thermal insulators, they may be too brittle for applications where high mechanical strength is required. Therefore, when choosing a material, you need to find a certain optimal balance of all properties.
In the marking of conventional non-pressed foam, the density value is indicated by the number that comes after the first few letters (they indicate the type of material). The designation is made in accordance with GOST. But there is one caveat: although the new one is considered valid GOST 15588-14 of 2014, but not all manufacturers are in a hurry to update their technological lines, and even now you can often find on sale sheets issued and marked according to the previous GOST15588-86 of 1986.

You need to know the following about the difference in standards.
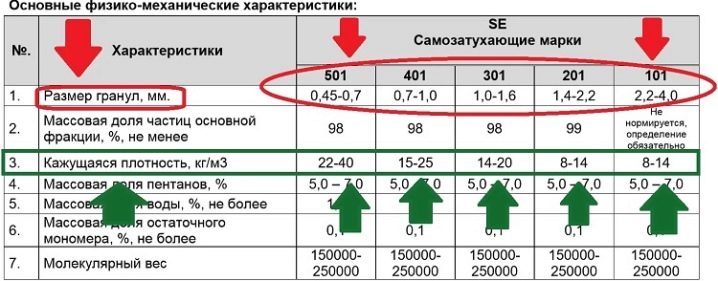
- According to the old GOST, the letter code of the foam is PSB, that is, suspended non-pressed polystyrene foam (if an additional letter is used, it means additional quality: for example, PSB-S means "self-extinguishing"). This is followed by a number indicating the density. That is, the short designation of the brand looks like this: PSB-15, PSB-40, etc. But it is important that the figure does not indicate the exact value in kg / m3, but the permissible range. For example, PSB-15 can have a density ranging from 6 to 15 kg / m3, PSB-25 - from 15.1 to 25 kg / m3, and PSB-35 - from 25.1 to 35 kg / m3.
- According to the new standard GOST 15588-14, the lettering of the foam is PPS (FoamPolyStyrol). Further, the figure of density is also indicated. But the new standard has become more stringent (modern production technologies make it possible to more accurately control the parameters of products during manufacture). In accordance with it, the figure in the brand name corresponds to the minimum allowed density parameter. So, for the PPS12 brand, the density should be at least 12 kg / m3, for PPS25 - at least 25 kg / m3, etc.
That is, the figure is the name of the brand, they are guided by it when choosing a material for a specific task, but it should not be confused with a specific density value in kg / m3. For accurate calculations, the density value must be specified in the technical documentation.
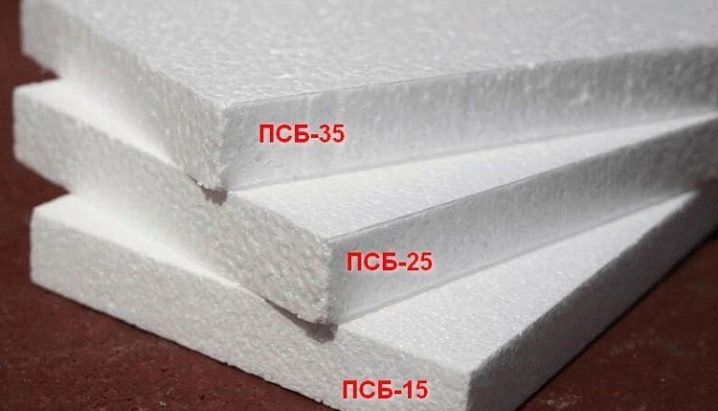

Views
Let us consider how the brands of non-pressed foam differ in properties and purpose, depending on the density, using the example of the most popular products according to the old GOST - PSB-S brands (with fire retardants).
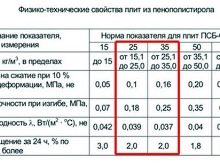
- PSB-S-15 - a material of relatively low density - up to 15 kg / m3, has good sound and thermal insulation properties (up to 0.042 W / mK), but low strength - it is easy to scratch it even with a fingernail, break it with your hands (compressive strength - 0.05 MPa, bending -0.07 MPa). Such foam is easy to process and is ideal for creating decorative items, volumetric inscriptions, containers and packaging, carriage cladding. For finishing, it is used for unloaded structures and planes, where the layer of material will be protected from external influences and damage - ceilings, interior decoration of roofs, the space between the rafters. They can also sheathe vertical surfaces, including walls, but only if no mechanical stress is expected, subsequent plastering.


- PSB-S-25 - polystyrene with a density from 15.1 to 25 kg / m3 and thermal conductivity up to 0.039 W / mK. In terms of strength characteristics, it is 2 times higher than PSB-S-15 (compressive strength - from 0.1 MPa, bending strength - from 0.18 MPa). Ideal for cladding and wall cladding, it can be used "under plaster". Good heat and sound insulation is provided by a layer already from 50 mm.
Can also be used for flooring and intermediate floors under moderate loads.


- PSB-S-35 - has a density from 25.1 to 35 kg / m3. It is 1.5 times stronger than the PSB-S-25 grade (for compression - from 0.16 MPa, for bending - up to 0.25 MPa), and can be operated under unfavorable climatic factors and under conditions of significant compression loads. It can be used for the installation of not only the floor, but also the foundation, basement, loaded floor slabs.


- PSB-S-50 - the most durable of the standard grades (withstands compression - from 0.20 MPa, bending - from 0.35 MPa), with resistance to mechanical stress. The material can even be used for road paving. In construction, it is used for very critical areas - loaded foundations, floors, floor insulation with a very high load.
Grades made according to the new GOST 2014 are divided by purpose in the same way and, with similar characteristics, can be considered as interchangeable with the "old" ones.


What is important: all "new" brands are necessarily equipped with fire retardants, in addition, the standard line was supplemented by special facade varieties (they have the letter "F" in the designation). Standard classes: PPS10, PPS12, PPS13, PPS14, PPS15, PPS15F, PPS16F, PPS17, PPS20, PPS 20F, PPS23, PPS25, PPS30, PPS35, PPS40, PPS45.
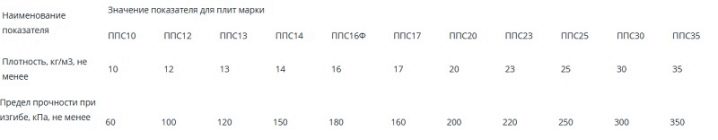
How to determine?
Since the density is directly related to the weight of the material, it will be easy to check the seller even at home: the allowable density limits (and therefore the weight) are determined by the documentation and are known in advance. You just need to compare with them a real sample of material. For example, if the insulation grade PPS-25 is chosen, then its cubic meter should weigh exactly 25 kg, if the grades PSB-25 or PSB-S-25 - the cubic meter of the material should have a weight in the range from 15.1 to 25 kg. If you purchase a sheet with special parameters according to TU, you need to find out the value in the documentation.
The verification algorithm is as follows.
- You need to calculate what should be the weight (cubic capacity) of a foam sheet of this brand.
- Weigh the product (or part of it) on a scale.
- We compare the obtained weighing value of the material with that which should be according to the standard or TU. If there are deviations from the standard weight more than the permissible error, the product does not correspond to the declared brand. If it matches - everything is in order, you can make a purchase.


What density should you choose?
When choosing a density, a number of factors should be taken into account (for example, whether the material will experience strong temperature changes, where is the dew point, etc.). Based on this, calculations and modeling are best done individually. However, there are general guidelines for choosing the minimum density of press-free foam for a number of jobs:
- for internal insulation of walls of buildings, ceilings, as well as insulation of balconies, terraces, attics - not less than 10 kg / m3;
- for external walls for cladding (siding, blockhouse), as well as floors on logs, interfloor and attic floors on wooden beams, pitched roof - at least 15 kg / m3;
- for external thermal insulation of building walls by the "wet facade" or "thermal fur coat" method, under plaster - less than 16 kg / m3 (and it is better to choose special varieties of the "F" brand - facade);
- for external cladding of walls of houses, erected using frame technology - an average density is suitable, but not less than 20-30 kg / m3;
- floor insulation under the screed - not less than 25 kg / m3;
- for underfloor heating installation - at least 25 kg / m3, and it is better to use not typical, but special foam plates "for warm floors" - with grooves for mounting pipes, a foil layer for better heat reflection (and it is better to choose extruded rather than pressless foam);
- for thermal insulation of floors on the ground, foundations (including for USHP, "insulated Swedish plate"), basements, flat and pitched roofs - increased strength is required, at least 25-35 kg / m3.



















The comment was sent successfully.