Everything you need to know about facade styrofoam

Facade polystyrene is a popular material in construction, used for insulation. From the material of this article, you will learn what its advantages and disadvantages are, what it is, how to choose and apply it correctly.


Advantages and disadvantages
Facade polystyrene has a number of advantages. It is suitable for thermal insulation of walls and ceilings in apartment buildings and private houses. It has high thermal insulation characteristics.
It is made from expanded foam. The material is gas-filled and has a finely porous cellular structure. This ensures the required level of energy savings. Construction insulation is inexpensive, it has a long service life.
The material is easy to work with, cutting, fitting parts, and is light in weight. It is versatile in use, suitable for insulating basements, walls, roofs, floors, ceilings of industrial and residential buildings.


Resistant to temperature extremes, does not lose its qualities at values from -50 to +50 degrees Celsius. It has dimensions that are convenient for transportation, which means that it allows you to save on delivery. Does not shrink and does not change qualities during operation.
Does not undergo biological corrosion. Resistant to alkalis, copes with thermal insulation of any type of structure. The best facade foam is non-toxic. It belongs to safe insulation materials. Perfectly absorbs noise, resistant to moisture absorption, fungus, microorganisms, insects.


Economical in comparison with analogues from other raw materials. Does not load the base. By volume of liquid taken, it absorbs no more than 2%. In terms of frost resistance, it can withstand up to 100 cycles.
Along with the advantages, the facade foam has several disadvantages. It loses stability when exposed to direct sunlight. Therefore, it is covered with finishing materials (plaster, protective sheathing).
Varieties without flame retardants are fire hazardous. When burned, they melt and release toxins. The material is not breathable, it is not suitable for insulating wooden houses, it is characterized by high smoke generation. Vulnerable to spoilage by rodents.


Despite the variety of assortment, not every type of facade foam is suitable for outdoor insulation. This is due to the different values of compressive and flexural strength.
In addition, a lot of debris is generated when it is cut. The material is fragile, it cannot withstand enormous loads. Because of this, you have to resort to the use of reinforcing mesh and plaster. Facade polystyrene is vulnerable to the effects of paints and varnishes. Because of this, it cannot be used together with finishing raw materials, which include a solvent.


Due to natural aging, insulation may give off an unpleasant odor. It has low vapor permeability, so it should not be used in ventilated facade systems.
The material differs in grade. On sale there are products of poor quality, without observing the necessary standards. They are short-lived, unreliable, and release styrene during operation.


Classification
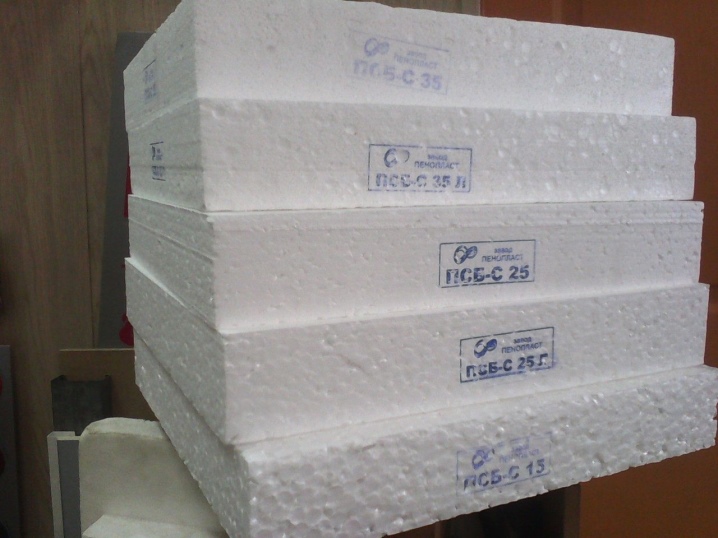
Facade foam can be classified according to different criteria. For example, products differ in size. On sale there are varieties with parameters 50x100, 100x100, 100x200 cm. Many manufacturers make plates according to the dimensions of the customer.


By production method
Insulating insulation is produced in the form of plates with different thicknesses and densities. During production, polystyrene granules are foamed with boiling hydrocarbons and blowing agents.
As they heat up, they increase in volume 10-30 times. Thanks to carbon dioxide, isopentane foaming of polystyrene occurs. As a result, the material contains very little polymer. The main part is gas.
PPP is produced in two ways. In the first case, they resort to sintering the granules with simultaneous shaping of the product. In the production of the second method, the granular mass is foamed, and then a blowing agent is added to it.
Both types of facade insulation are similar in composition. However, they differ in the density of cells, as well as in structure (they are open and closed).


By type of marking
Insulation marking indicates the production method and the differences between analog products. The material may differ in density, composition.
Two types of facade foam are supplied to the building materials market. Pressed insulation create through the use of pressing equipment. Varieties of the second type are sintered thanks to high-temperature technology.
The differences between the two types are noticeable visually and to the touch. Products created by pressing have a smooth surface. The unpressed counterparts are slightly rough.
Extruded facade foam plastic is moderately strong and tough. Externally, it is a plastic cloth with closed cells.

It is resistant to negative external factors. Depending on its characteristics, it can have high hardness and resistance to electric shock penetration.
-
PS - facade extruded foam panels. Particularly durable and expensive. They are used for insulation quite rarely.

-
PSB - pressless suspension analogue. It is considered the most demanded thermal insulation material.

-
PSB-S (EPS) - a brand of suspension self-extinguishing foam with flame retardant additives that reduce the flammability of the plates.

- EPS (XPS) - a kind of extruded type with improved characteristics and long service life.

Besides, other letters may be indicated on the label. For example, the letter "A" means that the material has the correct geometry with an aligned edge. "F" indicates the front view, such slabs are used in conjunction with decorative trim.
"H" on the product label is a sign of exterior decoration. "C" indicates the ability to self-extinguish. "P" means that the web is cut with a hot jet.


Thickness and density
The thickness of the facade foam plastic can vary from 20-50 mm in 10 mm increments, and there are also sheets with an indicator of 100 mm, etc. The choice of thickness and density values depends on the climatic nuances of a particular region. Usually, for facade insulation, varieties with a thickness of 5 cm or more are taken.
Density grades are as follows.
- PSB-S-15 - practical thermal insulation products with a density of 15 kg / m3, intended for structures without load.
- PSB-S-25 - facade counterparts with a density of 25 kg / m3 with average density values, suitable for vertical structures.
- PSB-S-35 - plates for thermal insulation of structures with high loads, resistant to deformation and bending.
- PSB-S-50 - premium products with a density of 50 kg / m3, intended for industrial and public facilities.

Nuances of choice
When choosing a high-quality type of facade foam, it is necessary to pay attention to a number of factors. For example, one of them is geometry. If it is flawless, it simplifies the installation and fitting of the joints.
As for the choice of the type of production, it is better to purchase extrusion-type foam panels. Such material serves without loss of performance for about 50 years. It has closed cells, which provides low thermal conductivity.
Extrusion foam for facade insulation is equipped with locks at the ends. Thanks to this system of connections, the appearance of cold bridges is excluded. It is malleable in work, as durable as possible.


To choose a good insulation, you need to pay attention to the price. Suspiciously cheap materials can be toxic and too fragile. They have poor sound insulation and insufficient density.
For insulation, options with a density of 25 and 35 kg / m3 are suitable. At lower values, the efficiency of thermal protection is reduced. At high costs, the cost of the material increases, and the volume of air in the material also decreases.
The thickness of commonly purchased insulation boards is 50-80-150 mm. Smaller values are chosen for insulating houses located in the southern regions of the country. Maximum protection (15 cm) is needed to insulate buildings in latitudes with frosty winters.


The purchased insulation must be reliable, capable of withstanding the load in the form of facade decoration. PPS-20 can be used as a base for plastering.
The best option for insulation is the front polystyrene PSB-S 25. In comparison with other analogs, it does not crumble too much when cutting. Does not let heat out.
However, it is not easy to choose it, since unscrupulous sellers often sell goods of inadequate quality under this brand. To buy a good insulation, you need to choose a trusted supplier and require a quality certificate when buying.
Product quality is determined by correlating the brand with the weight. Ideally, the density should correspond to the weight of a cubic meter. For example, PSB 25 should have a weight of about 25 kg. If the weight is 2 times less than the indicated density, the plates do not correspond to the marking.
When deciding on the level of sound and wind protection, it is worth considering: the thicker the slab, the better. You should not take a siding with a value of less than 3 cm.


On sale there is foam with a brick coating. It differs from its usual counterpart in that it is a reinforced insulation consisting of two layers. The first is expanded polystyrene, the second is made of polymer concrete.
The slabs have a square shape, they are decorated on the front side to resemble brickwork, do not require additional processing. The only thing you need is to put them on the glue.
This material is produced using a special technology. This allows for maximum adhesion of the two layers to each other.... The production uses sand, cement, water, polymer suspensions.
Decorative facade foam forms architectural forms on the building. This is a separate type of material that can imitate columns, stone, friezes.


What walls can be insulated?
Facade polystyrene is used to insulate external walls made of aerated concrete, gas silicate blocks. It is used as a heater for brick and timber structures. It is attached to the OSB. Structures of brick, stone and concrete are finished with liquid foam.
As for wooden houses, in practice, foam insulation is inferior to the cladding of buildings with mineral wool. Unlike polystyrene, it does not impede evaporation.


Facade insulation technology
It is not difficult to insulate the facade of a building with foam plastic with your own hands, without resorting to the help of professional builders. Warming the house outside with foam panels involves laying the panels in a monolithic layer without gaps with the most tight fit to each other.
It is necessary to fix the foam panels on the walls correctly. In the work, special glue is used, as well as dowels of a suitable size. Prepare the foundation first. A step-by-step instruction consists of a series of sequential steps.


They clean the surface of the facade, rid it of dust, and perform reinforcement. Any bumps and pits are leveled, the existing cracks are plastered. If necessary, get rid of the remnants of the old finish.
They take a deep penetration primer with an antiseptic additive and cover the entire surface with it for future finishing.The primer is allowed to dry. It provides better adhesion of the adhesive to the wall. The composition is spread over the walls with a brush or spray.
If the wall is too smooth, in order to strengthen the adhesion, the surface is primed with a solution containing quartz sand.


Marking is performed, after which they are engaged in fixing the basement profile. The corners are fixed at an angle of 45 degrees using screws and plates. The profile is fixed along the bottom and the entire perimeter, thereby creating support.
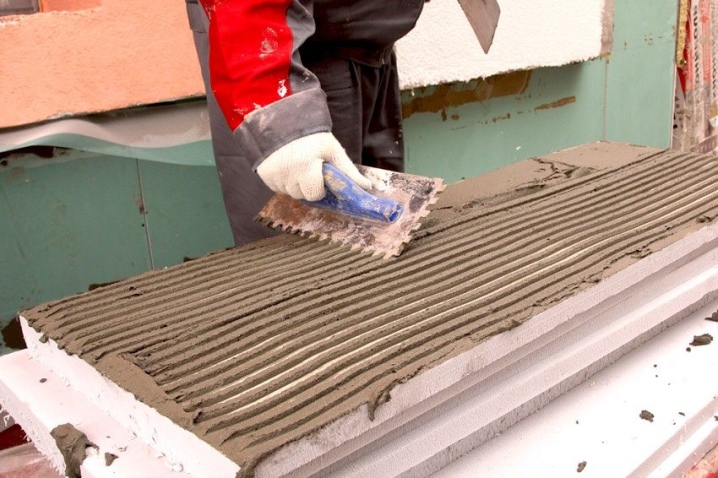
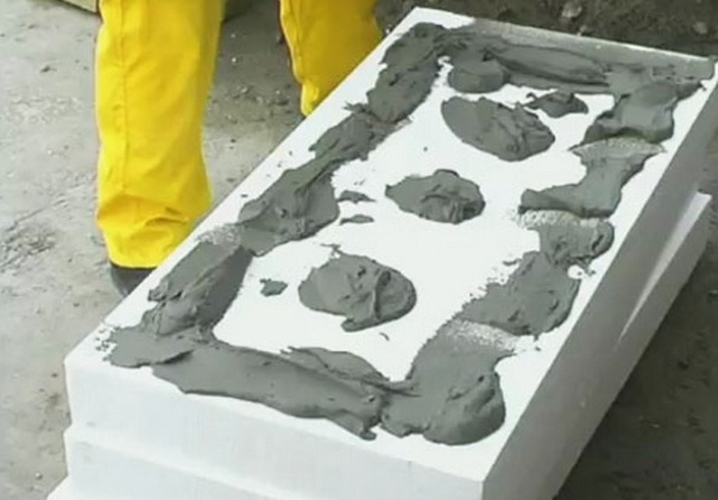
Calculate the consumption of glue and perform a batch from a dry mixture. Reinforcing adhesives are suitable for pasting. They are distributed over the reinforced surface of the PPS mesh. This technique is used when the facade plastering is performed with a cement-sand composition.

A layer of glue is applied to the inside of the PPS board and leveled using a wide spatula. Typically, the thickness varies between 0.5-1 cm. After spreading the glue, the board is applied to the base profile and pressed for a few seconds.
Excess glue that has come out is removed with a spatula. After that, the panel is fixed with self-tapping screws with mushroom caps. These plugs do not cut through the foam structure. The seams are finished with polyurethane foam.

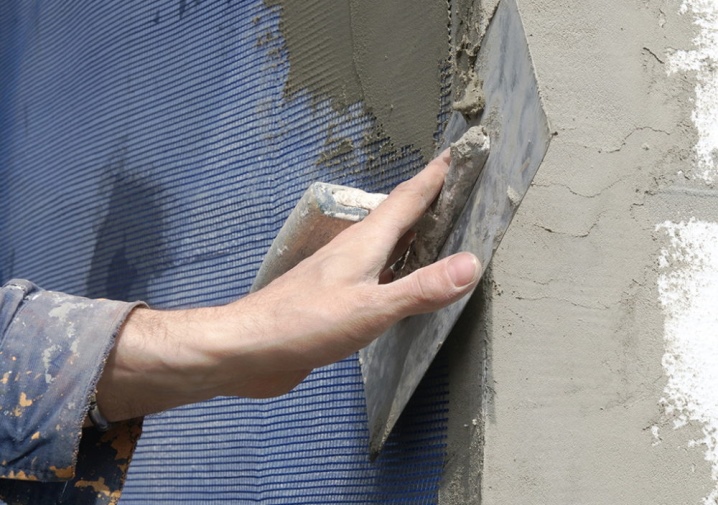
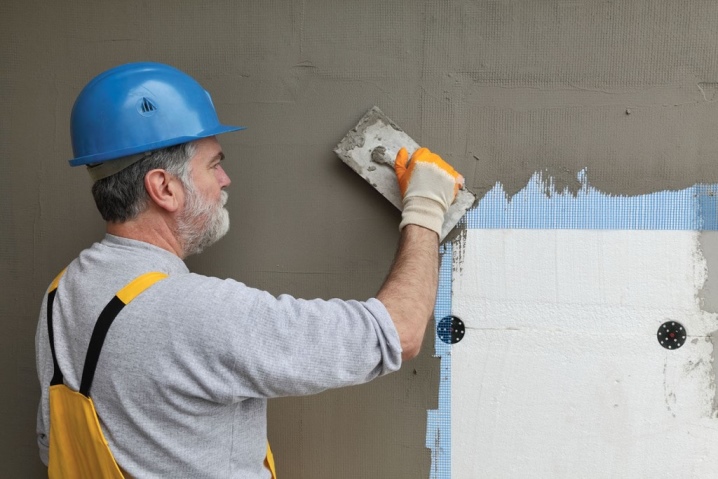
The reinforcing mesh is fixed with glue. Excess is disposed of with metal scissors. Then a layer of reinforcing mortar is applied and leveled, the facade is finished with plaster.
At the last stage of the work, a protective primer solution is used. It will prolong the operation of the insulation, increase its resistance to negative external factors.

The adhesive for work is selected with the mark "for polystyrene boards". It can be universal, intended for foam plastic and subsequent finishing of the facade (fixing the mesh, leveling).
You can also buy glue exclusively for polystyrene. However, it may not work for other layers. The universal product is good in that it involves fixing the slabs not only to the facade, but also to the slopes.
In addition, it can be used to smear joints, fastening caps, mesh on corners and slopes. Consumption of the compositions based on the work is approximately the same. On average, 1 sq. m account for 4-6 kg.
The maximum permissible distance between the plates should not exceed 1.5-2 mm. After the glue has set, such seams are completely clogged with polyurethane foam.


Installation errors
Often, during installation work, they make a number of common mistakes. Before you start insulating the facade, you need to designate the entry and exit points of utilities (if this has not been done), as well as air vents.
For this purpose, you can use cut pipes or large wood chips. This outline will simplify the laying of foam panels, eliminating the need to drive fasteners into voids and wall openings close to the edges.
Working with canvases with a density of 25 and 35 kg / m3, some craftsmen neglect the foaming of the seams. Regardless of how tightly the slabs fit, this step cannot be ignored.
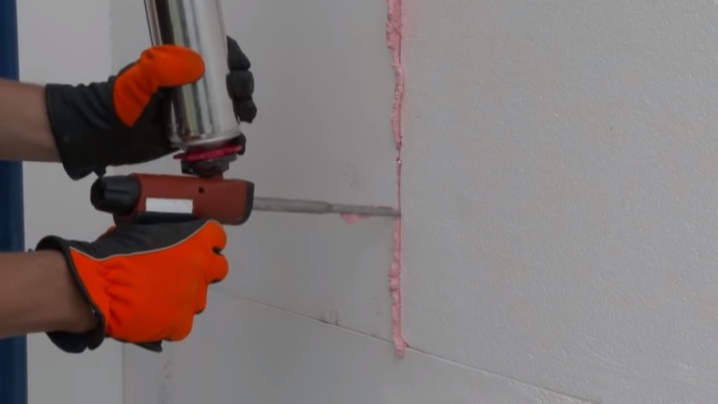

Despite the technical characteristics, over time the material can crumble at the edges. Without additional protection, this will cause the facade to blow through and moisture penetrate under the slabs.
You need to glue the foam panels from the lower left corner. When insulating a house, the first row should rest on the installed ebb. To improve the thermal insulation of an apartment building, a starting bar is needed, otherwise the panels will crawl down.
When using an adhesive, pay attention to the following point. The mixture should be applied in a continuous layer on boards located around the perimeter. Point distribution is possible in the central part.

It is impossible to do without the use of dowels. In this case, you need to choose the fasteners correctly. The length of the dowel should completely pierce the foam layer, sinking deep into the base of the house.
Dowels for insulating a brick facade should have a length of 9 cm more than the thickness of the foamed insulation.For concrete walls, fasteners with a margin of 5 cm are suitable, except for the thickness of the slab.
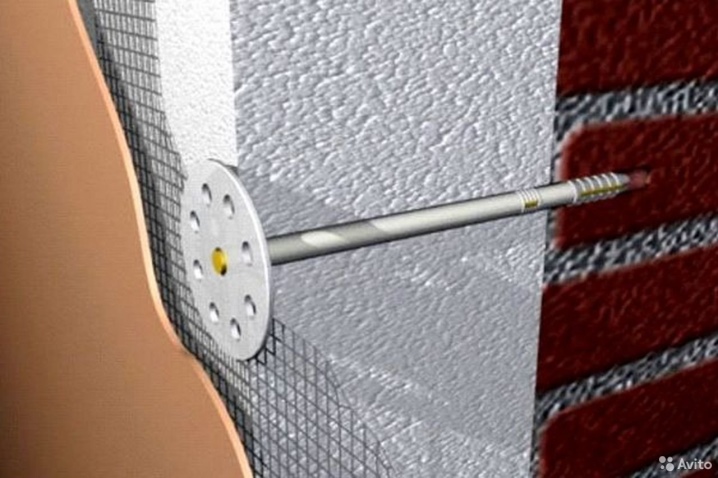
You need to hammer in the clips correctly. If you embed their caps too much in the foam, it will quickly tear, nothing will stick. The sheet should not crack during fixing, it should not be planted on dowels close to the edges.
Ideally, about 5-6 dowels should go per square, located at least 20 cm from the edge. In this case, both the glue and the fasteners must be evenly spaced.
Some builders do not cover the attached foam with a finishing material for a long time. Due to the instability to ultraviolet light, the process of destruction of the insulation begins.

Next, watch a video with expert advice on the choice of facade foam.













The comment was sent successfully.