OSB thickness for floor

OSB for flooring is a special board made of wood chips, which is impregnated with resins and other compounds for adhesion, and also subjected to pressing. The advantages of the material are high strength and resistance to various influences. One of the important indicators of OSB boards is thickness. It is worth figuring out why you need to pay attention to it.



Why is thickness important?
The thickness of the OSB for the floor is a parameter that will determine the strength of the future foundation. But first, it is worth considering how such a material is made. The technology for creating OSB resembles the method for manufacturing chipboard boards. The only difference is the type of consumable. For OSB, chips are used, the thickness of which is 4 mm, and the length is 25 cm. Thermosetting resins also act as binders.

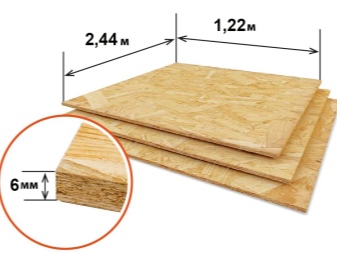
Typical OSB sizes:
-
up to 2440 mm - height;
-
from 6 to 38 mm - thickness;
-
up to 1220 mm - width.

The main indicator of the material is thickness. It is she who affects the durability and strength of the finished material, determining its purpose. Manufacturers make different variations of slabs, focusing on the thickness of the products. There are several types.
-
OSB sheets of small thickness for assembling packaging and furniture blanks. And also temporary structures are collected from the material. They are lightweight and easy to use.
-
OSB boards with a standard thickness of 10 mm. Such products are used for assembly in dry rooms. Basically, they make rough floors, ceilings, they also level various surfaces and form boxes with their help.
-
OSB boards with improved moisture resistance. This property was achieved due to the addition of paraffin additives to the material. Plates are used both indoors and outdoors. Thicker than the previous version.
-
OSB boards with the highest strength, capable of withstanding impressive loads. The material is in demand for the assembly of load-bearing structures. Products of this type have a high density, so working with them requires the use of additional equipment.

There is no better or worse option, as each type of stove has its own purpose. Therefore, it is worthwhile to carefully approach the choice of material, taking into account its thickness, depending on the type of task being performed.
Regardless of the type and thickness, the key advantage of wood material is the ability to withstand impressive loads.
It is also worth noting that OSB structures are resistant to temperature and humidity extremes, are easily processed and do not require much effort during installation.

Finally, the demand for OSB is explained by its high heat-insulating properties. Quite often, flooring manufacturers recommend laying the underlayment before laying the flooring on the subfloors. OSB is used as such a substrate.


Which one to choose for different screeds?
The thickness of the floor slab is selected depending on what you plan to put the sheets on. Manufacturers today produce different types of OSB, so it will not be difficult to decide on plates of suitable sizes.


For concrete
In these cases, OSB-1 should be preferred. A product with a thickness of up to 1 cm will level the surface. The slab installation procedure involves a series of steps.
-
First, the concrete screed is pre-cleaned, ridding the surface of dirt and dust. This is necessary to ensure adhesion of concrete and wood surfaces, since the fastening is carried out with glue.
-
Next, the screed is primed.For this, a primer is used, which increases the adhesion properties of the surface, making it more dense.
-
At the third stage, OSB sheets are cut. At the same time, during cutting, indents of up to 5 mm are left along the perimeter, so that the sheets are laid more securely. And also in the process of distributing the sheets, make sure that they do not converge into four corners.


The last stage is the arrangement of sheets on a concrete surface. For this, the bottom layer of the slabs is covered with rubber glue, and then the material is fixed on the floor. You won't be able to put the material just like that. For a tighter adhesion, dowels are driven into the sheets.


For dry
When performing such work, plates with a thickness of 6 to 8 mm are used, if the laying involves the use of 2 layers of plates. In the case of a single layer, thicker versions are preferred. It is wood products that play the role of a screed, since they are laid on a small expanded clay or sand cushion.
Consider the OSB stacking scheme.
-
The dry backfill is leveled according to the pre-exposed beacons. Only then do they start laying out the plates.
-
If there are two layers, then they are placed in such a way that the seams diverge without coinciding with each other. The minimum distance between the seams is 20 cm. Self-tapping screws are used to fix the plates, their length is 25 mm. Fasteners are arranged with a step of 15-20 cm along the perimeter of the upper layer.
-
Drywall is laid on a dry screed. Subsequently, a clean floor covering will be laid on it: laminate or parquet. The most rational version of the coating is linoleum, if it is planned to use boards of wood shavings for arranging the screed.


Before screwing in the self-tapping screws, small holes with a diameter of 3 mm are first made in the sheets, which are subsequently expanded at the top using a drill.
The expansion diameter is 10 mm. This is necessary so that the fasteners enter flush, and their cap does not stick out.

For wooden floors
If you plan to lay OSB on boards, then you should give preference to plates 15-20 mm thick. This is explained by the fact that over time, the wooden floor deforms: it crumbles, puffs up, becomes covered with cracks. To avoid this, the laying of wood products is performed in a certain way.
-
First, pay attention to the nails, as it is important that they do not stick out. They are hidden with the help of steel bolts, the diameter of which coincides with the size of the cap. Using a hammer, the fasteners are driven into the material.
-
Further, defects and irregularities of the wooden base are removed. The work is performed with a plane. Both hand and power tools will work.
-
The third stage is the distribution of OSB boards. This is done according to the previously made markings, paying attention to the seams. Here, too, it is important that they are not coaxial.
-
Then the sheets are fixed with self-tapping screws, the diameter of which is 40 mm. The screw-in step of the self-tapping screws is 30 cm. At the same time, the hats are also sunk into the thickness of the material so that they do not stick out.
At the end, the joints between the sheets are sanded with a typewriter.


For lag
The OSB thickness for such a floor determines the step of the lag from which the base is made. The standard pitch is 40 cm. Sheets up to 18 mm thick are suitable here. If the step is higher, the thickness of the OSB should be increased. This is the only way to achieve an even distribution of the load on the floor.
The chip board assembly scheme includes a number of steps.
-
The first step is to calculate the step between the boards for their even laying. When calculating the step, it is worth looking to ensure that the joints of the slabs do not fall on the supports of the lag.
-
After placing the lags, their position is adjusted so that at least three of them have the same height. For corrections, special linings are used. The check itself is carried out using a long rule.
-
Next, the lags are fixed using screws or dowels. At the same time, the logs, which are made of dried wood, are not fastened, since they will not shrink or deform in the process.
-
After that, the sheets are laid. The sequence is the same as in the case of arranging the base on a wooden floor.
The last stage is fixing the sheets of wood chips with self-tapping screws. The step of the fasteners is 30 cm. To make the installation faster, it is recommended to mark in advance how the logs will be located on the plates.


General recommendations for the selection of the thickness of the slabs
Before proceeding with the installation of the base for the flooring, you should carefully consider the choice of OSB. It is especially important to choose the right thickness of the wood sheets in order to organize the reliable operation of the structure. To determine the thickness, it is worth looking at the type of base on which the slabs are planned to be laid.
In addition to thickness, you also need to consider the following parameters:
-
product size;
-
properties and characteristics;
-
manufacturer.



The most common type of wood-based floorboards is OSB-3. For older floors, thicker slabs are recommended. Other types of sheets are used for the construction of various structures or assembly of frames.
For information on how to make a floor from OSB sheets, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.