We make formwork from planks for the foundation with our own hands

The board is considered one of the best materials for formwork under the foundation. It is easy to use and can later serve for other purposes. But, despite the ease of installation, before making the formwork from planks for the foundation with your own hands, you need to study in detail all the rules and recommendations for assembling and installing the structure.

What material do you need?
For the construction of strip and slab foundations, you can use both edged and unedged lumber - the main thing is that its inner part, which will be adjacent to the concrete, has a smooth surface. That's why, if it is not possible to purchase ready-made smooth boards, it is recommended to plan and grind the material on one side by yourself. In the future, this will simplify the work with the finished solidified base, eliminate the need for additional finishing work.


The thickness of the board will depend on the size of the future foundation and the volume of concrete mixture that is planned to be poured. The larger the volume of the concrete mass, the thicker and more durable it will be necessary to select the material for the formwork. As a standard, material with a thickness of 25 mm to 40 mm is used for formwork from boards, in rare cases, 50 mm wood is used.
If the dimensions of the foundation are so large that 50 mm is not enough, then metal structures will already be required here.

In general, thickness is a very important criterion that should not be neglected. Too thin boards will begin to deform when pouring concrete, as a result, the surface of the foundation will turn out to be wavy, and it will have to be leveled after hardening. In the worst case, a thin board may, in general, not withstand the pressure of the concrete mass, the formwork will simply fall apart, and the expensive mortar will most likely deteriorate, since it will be almost impossible to collect and reuse it.
It is important that the thickness of all boards in the structure is the same. The shape of the future foundation will also depend on this - if one or more boards are thinner than the others, then the concrete mass will bend them, and in these places on the foundation, bumps and waves will form.

The width of the material is also determined by the specific dimensions of the foundation and the working conditions. It is optimal to use boards with a width of 15 to 20 centimeters, but there are no strict rules for choosing. Since the lumber will still knock into shields, you can also use a relatively narrow board (10 centimeters), but in this case the assembly of the shields will become much more complicated - you will need to use more supports and transverse bars to connect the boards to each other.
Too wide lumber can deform under the pressure of concrete, forming a so-called belly in the structure.
Let us analyze what to look for when choosing boards for formwork.
- It is important that the lumber is resistant to cracking, so it is not recommended to use softwood planks. Planks made of birch and other hardwood trees will not work. The use of such lumber is allowed only for a non-removable single-use system, which, after the solution has solidified, will remain in the foundation structure. In other situations, it is better to collect shields from spruce, pine or fir. For massive systems, aspen boards are perfect, they better withstand the weight of a heavy mortar.
- It is highly discouraged to knock down the shields under the formwork for the oak planks foundation.Because such oak products have high acidity, which negatively affects the composition of the concrete mixture - the solution will set worse and harden longer. In addition, because of this, the overall strength of the foundation may also decrease, especially if concrete is used without special additives.
- It makes no sense to purchase expensive lumber from valuable wood species, since even with careful use, after disassembly the boards will be unsuitable for finishing and other similar delicate work. It is most correct to choose a standard 3 or 4 grade pine board for the formwork, if necessary, modify its surface to the desired state with your own hands.
- Wood that is too dry should not be used; its moisture content should be at least 25%. The dry board will actively absorb moisture from the concrete mix. Subsequently, this will negatively affect the strength of the foundation, not to mention the fact that the cement milk after hardening inside the lumber will significantly reduce its quality and limit the range of works for reuse. It is not at all necessary to measure the moisture content of the wood when assembling the boards - it is enough just to wet the boards well. Excessive moisture will not affect the strength of the concrete structure; in extreme cases, in cloudy weather, the foundation will harden a little longer.
The length of the boards does not play a big role, it is selected based on the length of the foundation tape or walls, the main thing is to make a stock of 3-5 centimeters. When buying, it is important to carry out a visual inspection of the wood, there should be no chips and cracks on it - when pouring concrete, they will lead to the mixture flowing out, formwork deformation and deflection of the supporting shields.
It is advisable that the boards are with an even cut of the edges, otherwise they will then have to be trimmed on their own. If this is not done, the shields will have slots through which the concrete mixture will flow. It is worth paying attention to the porosity of the material: this indicator should be as low as possible.
Experienced builders recommend purchasing foundation boards directly at the sawmill - professional organizations offer better materials and provide services for sawing products according to specified sizes.


Calculation features
Before assembling the formwork for the foundation, you should calculate the required amount of material in advance, then you will be able to keep within the budget, and you will not have to buy additional boards during the construction process. To correctly calculate lumber, you need to take into account the following factors:
- measure the exact length of the perimeter of the foundation and the height of the pour;
- divide the total length of the perimeter by the length of one board to find out how many boards are required for one row;
- divide the height of the future foundation by the width of one unit of lumber, and find out the required number of products vertically;
- multiply the obtained indicators by length and height, and display the total number of boards.
When selling boards, as a rule, they are measured in cubic meters, in order to find out how many units are in one cube, the following calculations are carried out:
- determine the volume of one board by multiplying its length, width and thickness;
- then divide the cubic meter by the resulting number.

Having learned how many boards are in one cubic meter, they calculate the required volume for their particular case. For this, the total number of boards that will be needed for formwork under the foundation is divided by their number in one cubic meter. The calculation can also be made using the formula. For example, the total length of the perimeter of the future structure is 100 meters, and the height is 70 centimeters. The optimal lumber thickness for such formwork is 40 millimeters. Then you need to multiply 100 × 0.7 × 0.04, as a result, the required volume will be 2.8 cubic meters.
And also to create the formwork you will need the following materials:
- bars;
- plywood;
- polyethylene film;
- fasteners - self-tapping screws.
When choosing bars, you need to take into account that their dimensions should be at least 50 by 50 millimeters, and the total length will be approximately 40% of the total length of the boards.
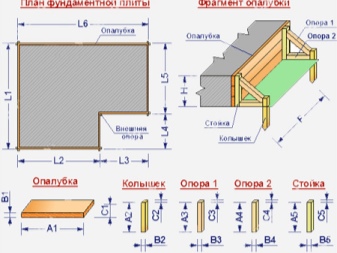
Step-by-step instruction
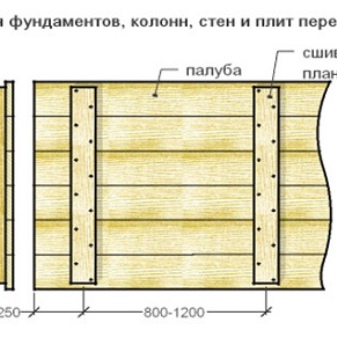
Do-it-yourself installation of formwork for the foundation should be carried out only on a flat, well-prepared surface - you should clean the area and remove all debris. It is necessary to expose the formwork strictly vertically, so that the shields are butted to the ground. The inner surface of the boards, which will come into contact with the concrete mix, must be flat and smooth. If it did not work out to grind the material, you can stuff sheets of plywood on it - the main thing is that the distance between the parallel shields exactly matches the design width of the future foundation wall.
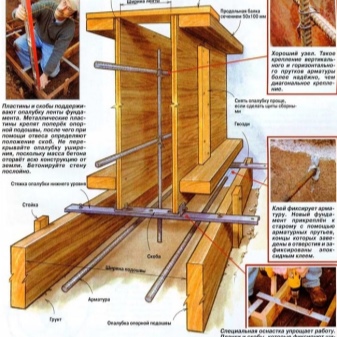

Knocking down the shields, the boards must be adjusted to each other so that there are no gaps between them, especially if, for better shrinkage of the concrete mixture, it is planned to vibrate it with special devices.
The gap between the boards should be no more than 3 millimeters.


Slots of 3 mm or less will go away by themselves after the material swells upon preliminary wetting. If the configuration and quality of sawing the boards do not allow knocking down the shields without significant gaps, then the slots of more than 3 millimeters must be caulked with tow, and the distances over 10 millimeters will need to be additionally hammered with slats.
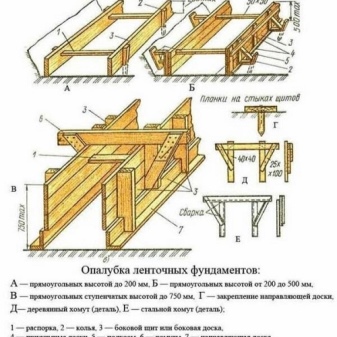
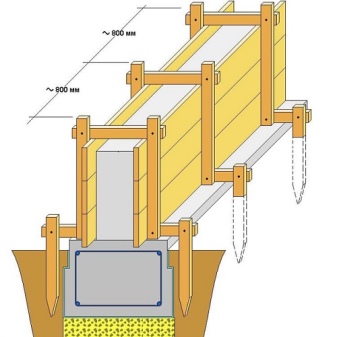
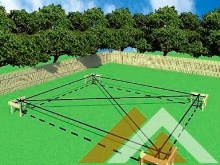
It is necessary to correctly assemble the formwork for the strip foundation with a height of up to 0.75 meters from the fastening of the guide boards. They are fixed in the ground with fixing pegs. To make an accurate installation, you must first pull the rope around the perimeter of the future foundation and fix it at both ends. Having installed the guide boards, you should make sure that they are installed correctly - using a level check that they are level, there are no deviations. Then you can start installing the shuttering boards, while the plane of the boards must exactly match the edge of the guide boards.
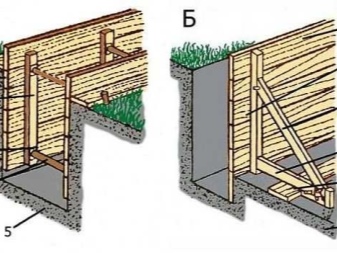

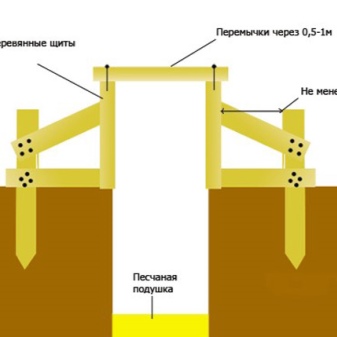
The formwork, as a rule, is driven into the ground with the help of pointed bars, which connect the boards to each other, forming shields. It should be borne in mind that the concrete mass will exert strong internal pressure on the structure, therefore, so that the shields do not disperse in the lower part, it is imperative to drive additional pegs into the ground. Their exact number will depend on the width and height of the foundation, but in general, experienced builders recommend using pegs at least every meter.
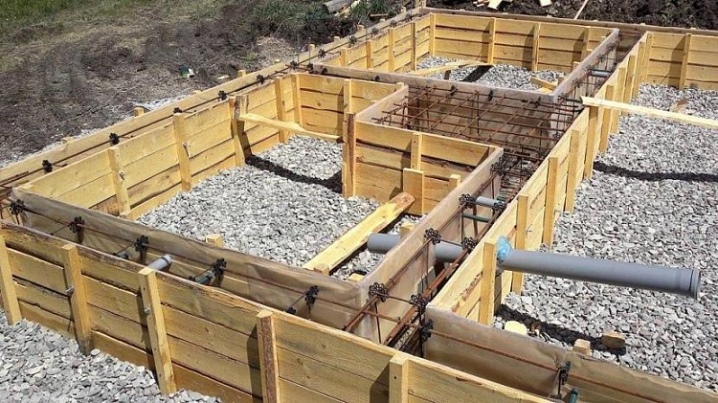

If the height of the future foundation does not exceed 20 centimeters, then some pegs from the connecting bars will be enough. When the foundation is higher, it is imperative to use additional external stops - bars of a certain length, which are set diagonally at an angle.
One end of such a bar rests against the upper part of the formwork wall or a peg and is fastened there with a self-tapping screw. The second end rests firmly on the ground and is slightly buried in (in these places you can drive in more pegs that will hold back the stubborn bars so that they do not jump off and burrow into the ground).



Step-by-step instructions for assembling and installing do-it-yourself foundation formwork:
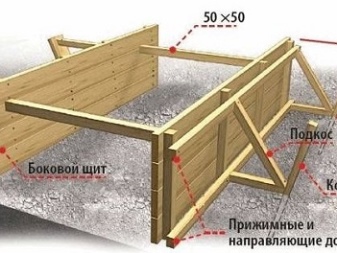
- on a prepared flat base, the boards are stacked close to each other;
- on top, transverse slats or bars are applied, which will connect the boards to each other, and are fixed with self-tapping screws (the distance between the slats is at least 1 meter);
- self-tapping screws need to be screwed in from the inside so that their hats sink into the board, and the ends stick out on the other side by at least 1-2 centimeters, these tips should be bent;
- ready-made shields are mounted on the edge of the trench - they are driven into the ground using sharpened connecting bars and are attached to the guide boards with wire twists;
- close to the shields, additional vertical stakes are driven in, which are connected to the shields with self-tapping screws;
- horizontal (laid on the ground) and diagonal struts are attached close to the stakes, which are fixed on the other side with another peg driven into the ground;
- experts recommend connecting the shields to each other, using additional jumpers in the upper part, they will not allow the structure to disperse to the sides when pouring the concrete mixture.


For information on how to make a wooden formwork for a strip foundation with your own hands, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.