The nuances of the formation of cucumbers in the greenhouse

Delicious and crunchy cucumbers are always welcome on the dinner table. These vegetables are often eaten fresh, but they are also used in salads, snacks and other dishes. Many people prefer pickled or pickled cucumbers, which taste differently. Given the unstable and cold climate in many regions of the country, many gardeners grow this crop in greenhouses.
Caring for a plant indoors or outdoors is different, so you need to be familiar with certain features of this process.


The need for a procedure
When growing any fruit crop, you need to create suitable conditions for it that will promote active development and regular fruiting. Some summer residents believe that the formation of cucumbers in a greenhouse from polycarbonate or other materials is an optional procedure. Experienced gardeners note that this procedure greatly affects the yield, especially if the seedlings were planted in greenhouses. In such conditions, it is difficult for insects to pollinate.
Plants will intertwine with each other if they are not picked up from the ground in time and pinched. As a result, the seedlings turn into a ball, and it is difficult for the bees to get to the blossoming flowers. And also contact with the soil can provoke the development of fungal infections, and dangerous insects will easily reach the harvest and spoil it.
Competent formation of bushes will allow you to cope with the following problems:
- the risk of contracting diseases is significantly reduced;
- the process of collecting vegetables becomes easier;
- it is more difficult for pests to get to the fruit;
- pollinating insects are easier to cope with their task;
- plants do not intertwine and do not block each other's access to the sun's rays;
- the space in the greenhouse is limited, and the formation will allow you to use it as efficiently as possible;
- competent molding contributes to the correct growth and development of plants.


General rules
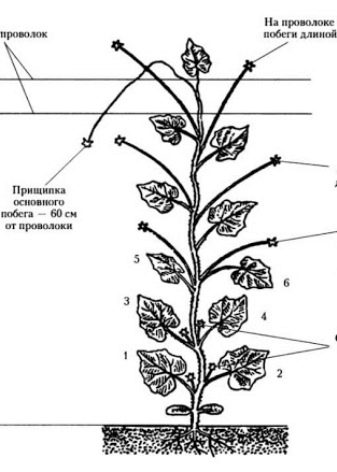
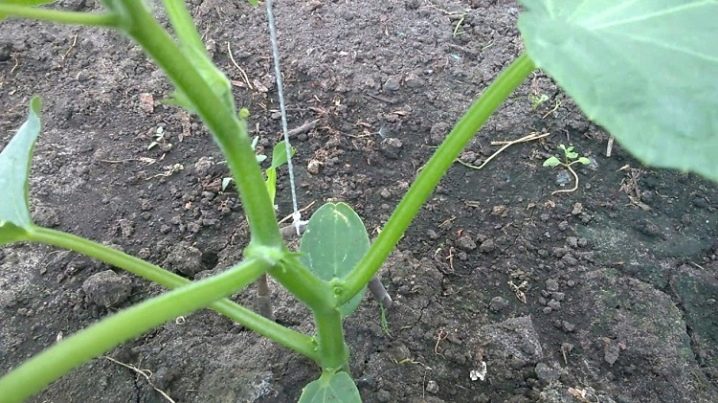
Before starting work, you need to know how to properly form a cucumber bush. First of all, the plants are tied up so that they rise above the ground and begin to grow upward. A rope or twine is suitable for fixing. The garter is performed as soon as the height of the seedling reaches 30 centimeters, and 4-5 full-fledged leaves appear on it. If at this stage the work has not been carried out, and the plant has already spread on the ground, you need to carefully raise the vine, untangle it, and make a garter. The main thing is that the stem remains intact. To neatly secure the vine, you need to tie a loop around the stem in the region of the third leaf. The other end is attached to the greenhouse bar. Leave the rope to sag a little around the plant and should not be overtightened to avoid damaging the plant. In the process of growth, the main stem will become larger, and a tight twine will only interfere with it. The plant is guided around the twine.
The next mandatory step is pinning. In addition to the main stem, the plant can form additional processes in the leaf axils. They are called stepchildren, and their pruning is called pinching. They take nutrients and strength from the plant, so you need to get rid of unnecessary growth right away.If the stepsons are left, the fruits will not receive the required amount of useful trace elements, as a result, the yield suffers. Vegetables need to receive as much nutrition as the main trunk takes. The process of removing the lateral processes is carried out by pinching. It is best to do the work early in the morning, so by the evening the plant will have time to recover... The gardening tool used must be clean and sharp, otherwise infection can enter the plant.
Cucumber bushes are formed 2 weeks after the transfer of seedlings to a permanent growing site. During this period, they also get rid of unnecessary mustaches and stepchildren, which are formed in the region of 4-6 knots.


Basic schemes
Experts have developed different ways of plant formation:
- in one stem;
- in two stems;
- bush with lateral fruiting shoots.
And also the working process is influenced by the way in which a particular variety is pollinated.
There are the following types:
- non-pollinated;
- self-pollinated (such species are able to independently pollinate due to the presence of flowers of both sexes and produce a rich harvest every season);
- species pollinated with insects.
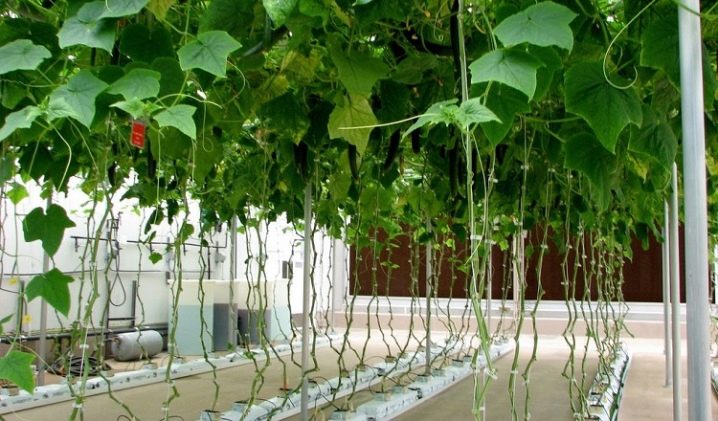

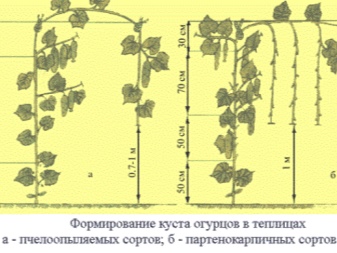
As a rule, on plants from the second group, ovaries appear on the main stem, so it is best to grow the bush in one stem. So it will take up a minimum of space, and all the fruits will be clearly visible. Plants can be easily inspected for symptoms of diseases and pests. Varieties from the third group differ significantly from self-pollinated varieties, since they do not form ovaries in the central part. For this reason, it is advisable to mold into several stems.
You can determine which of the species this or that variety belongs to by the buds. If they have ovaries, you have a self-pollinated culture. This means that you can safely choose the option in one stem. Otherwise, you need to wait until other shoots appear, and choose a method in which the plant is shaped into a bush.
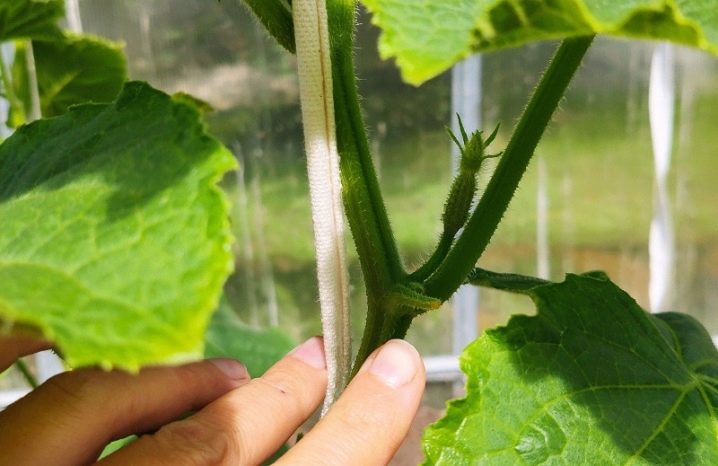

One stem
The step-by-step instructions look very simple. Pedicels, whiskers and ovaries are completely removed from the first five leaves. In the subsequent ones, only the ovaries are preserved, additionally getting rid of the remaining overgrowth.

Two stems and side shoots
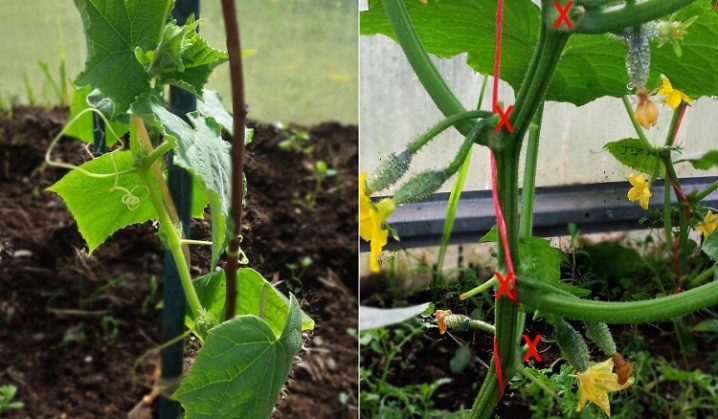
The plant is pinched only after the appearance of two full-fledged leaves. After a while, the plant will already develop into two stems. Each of them is tied up separately from each other and bred to the sides. The process of forming cucumber bushes while preserving lateral shoots is similar to the one-stem option. In this case, all available stepchildren are also cut off, which have grown in the first 4 leaf axils. Be sure to tie the main stem to the trellis.
In the area of the fifth leaf, the stepson is saved, and after the first leaf appears on it, they pinch him. This scheme is used to treat the entire plant. Every fifth stepson is left, and the rest are removed. Note: experienced gardeners advise not to cut off, but cut off the shoots so as not to harm the plant. Too strong a jerk can break the stem. Studying the features of caring for cucumbers, you can come across the term - blinding. This is the process of getting rid of ovaries or outgrowths in the leaf sinuses.
Plants are most often dazzled when the lower part of the bush is formed.

Features of the formation of different varieties
You should also take into account the peculiarities of growing numerous varieties of cucumbers. Compliance with the established formation rules allows you to achieve maximum yield.
Parthenocarpic hybrids
Species belonging to this category differ from varietal cucumbers in strong branching and fast growth. These features must be taken into account when planting and growing parthenocarpic hybrids.

The workflow looks like this.
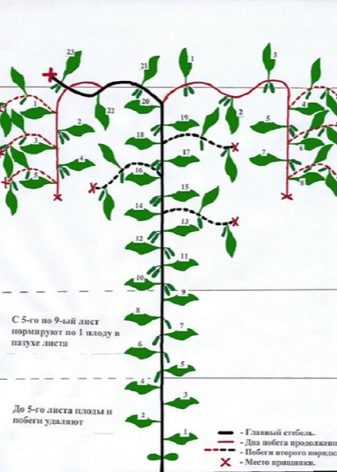
- The first step is to process the lower part of the plant (the interval from the first to the fourth nodes)... All ovaries, stepsons and whiskers found in the leaf axils are carefully removed.Experienced gardeners call this part of the bush the place of blinding.
- The process does not end at this stage.... As soon as the plants start to age, yellowed foliage appears on the vine. It is also disposed of to prevent thickening. Otherwise, the process of oxygen exchange will be disrupted. In dense foliage, diseases and infections develop faster.
- When moving to the next tier, which covers the area from 5 to 7 leaves, only the ovaries are left, removing everything else. They will be the first harvest. The stepchildren break out as soon as they become noticeable, so that the plant does not have time to spend energy on them.
- Now you should go up the stem (from 8 to 10 leaves). In this part, only the antennae are disposed of. The stepsons are left intact, and as soon as they grow up, pinching is carried out. On each of them, only one ovary and a full-fledged leaf are left.
- When moving to another tier (from 11 to 13 sheets), the same molding is performed, as in the paragraph described above, with one difference - after the stepson has been pinched, 2 ovaries and leaves are left.
- Moving up the stem (from 14 to 16 leaves), continue to carry out the work according to the above scheme, but keeping already 3 leaves and ovaries on each of the stepsons.
- The last tier should be counted from sheet 17... Here, the maximum number of leaves and ovaries (4 pieces each) are left on the stepson, which will later become fruits.
At this stage, the work does not end, and you need to start the process of forming cucumber bushes on the trellis. If a dense and long growth has formed, which has already outgrown the fixation element, it must be carefully thrown over the wire mount. So the plant will continue to grow downward. As soon as the distance from the wire to the growing point is about 60 centimeters, the vine should be pinched. This simple procedure activates the process of forming new stepsons, one of which will be a continuation of the main lash.
This part of the bush should also be pinched, but only when its length is at least 0.5 meters.

Bouquet, bunch and bush cucumbers
A separate work flow chart has been developed specifically for these varieties. From 3 to 12 ovaries grow in the leaf axils. This amount will be quite enough to harvest a full harvest. Experienced gardeners recommend single-stem formation.
The processing of the plant is as follows.
- When caring for young seedlings, you need to get rid of all buds, lateral processes and whiskers growing up to 4 knots. This will help the bushes develop quickly at the initial stage, and the excess plant mass will only overload the bush.
- After that, it is worth inspecting the whole plant as a whole, moving from the lower tier to the very top... In the process of work, all stepsons and mustaches are cut off.
- As soon as the lash grows to the trellis, it is thrown over it, changing the direction of growth. As soon as it approaches the ground surface at a distance of 25 centimeters, pinching is carried out.
Note: given the huge variety of varieties, even experienced gardeners find it difficult to make the right choice, let alone beginners. Parthenocarpic species with bouquet-type ovaries are in great demand. The main advantages of such varieties are high yields and ease of care, given the formation of the bush.


Bee-pollinated varieties
These varieties have certain features that must be paid attention to during the formation process. In the central part of the plant, male-type flowers grow, the so-called barren flowers. Experts advise to carry out the formation in several stems, which will contribute to a good yield.
The step-by-step workflow looks like this:
- the pinching of the main stem is carried out over the 5th leaf;
- after it is fastened with twine;
- as it grows, lateral processes will appear on the bush, they are fixed to the neighboring trellises, laying at an angle of 60 degrees in relation to the main stem;
- mustache and unnecessary stepchildren are periodically trimmed;
- as soon as the shoots grow to a horizontal trellis, they are wrapped around it several times, as soon as the stems grow a little more, they should be pinched.

Indeterminate species
This group includes old varieties well known to most agronomists. As a rule, these are long bushes, which are more convenient to grow in greenhouses. The bulk of the fruit is formed on the lateral processes. For this reason, the formation is carried out in several stems.
Scheme of the work step by step:
- the top of the main stem can be pinched only after 5 leaves appear on it;
- after the plant forms two shoots, which should be parted on the sides and fixed separately;
- in the future they are stepson;
- after the stems grow to the trellis, they are carefully thrown over, as is the case with other tall plants;
- cut the vine at a height of about a meter from the surface of the earth;
- these actions will lead to the fact that the plant begins to branch strongly.
Some gardeners do it differently. After pinching the main stem, all lateral processes are left, but each of them should be slightly shortened (after 2-4 leaves). Crown thinning is performed as necessary. Note: additional features of the work performance can be indicated in the description of a particular variety, therefore, before growing, you should familiarize yourself with its characteristics. European, Chinese, American and other varieties are cultivated within the borders of Russia.
And also the necessary information can be requested from the seed producers. On the manufacturer's website, you should look for a specific variety (for example, "Masha" cucumber), and find out which way of formation is best.

Follow-up care
Forming a bush is not a one-time process. The work is carried out in several stages during the development of the fruit crop and can take a long time.... Plants should be regularly inspected to assess their condition and the density of the green mass. The garter should be gentle and without the use of rigid clamps that can harm the vine.

Possible mistakes
The main mistake of agronomists lies in the wrong choice of the method of forming a bush, and when it comes time to harvest, instead of fruits, the gardener gets a dense plant mass. And also some gardeners make mistakes in the process of work, for example, using an unsuitable gardening tool, or fixing the vine with a stiff wire that can easily harm the plant.














The comment was sent successfully.