What are the warm cucumber beds and how to grow a vegetable on them?
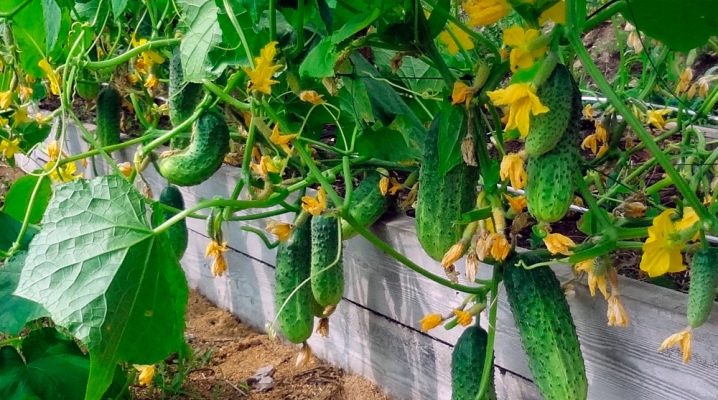

In order for the harvest of cucumbers to be early, special conditions must be created for them to grow. That's why they came up with warm beds. The earth is still cold and objectively not ready to accept seedlings, but 2 weeks can be won even from nature. And while everyone is buying cucumbers in the market and in the store, the owners of the warm beds will already have the harvest on the table.

Peculiarities
We will find out why warm beds stand out so much that they have advantages over ordinary ones. First, an early harvest that will definitely outstrip the standard ripening dates for cucumbers. Secondly, the number of dressings in the case of this type of vegetable cultivation is reduced, because organic matter has already been introduced during planting, and it will be gradually used throughout the growing season.
If, for example, manure was introduced into the garden - and a lot, organic matter may not be required at all: only magnesium, potassium and trace elements will be added.
Thirdly, the roots of cucumbers will always be warm, which means that bad weather and other force majeure will definitely be easier for plants to transfer.
After the harvest is harvested, organic matter also does not need to be introduced, and next season it will be possible to grow crops here that are sensitive to soil fertility. Warm beds, surprisingly, require less labor, time, effort, and material costs.
But alas, it was not without its drawbacks: in the greenhouses, for example, nitrates can accumulate. And this is almost impossible to prevent, because there is a lot of nitrogen in the soil. Increasing magnesium and potassium is not an option: they save little from the accumulation of nitrates. Finally, if the spring is particularly warm, the plants may even burn out. For the southern regions, such an outcome is not uncommon.

And now about the device of the warmest bed:
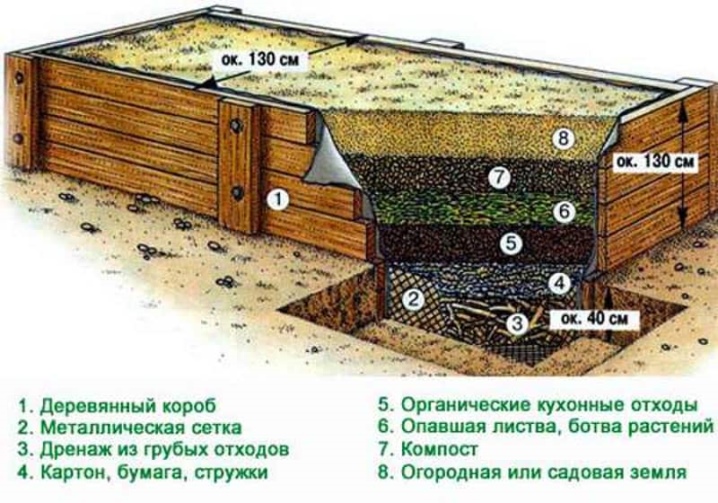
- by design, it can be compared with a puff cake, the main ingredient of which is organic matter, and there is also sawdust, food and plant residues, peat and fertile soil;
- due to a chemical reaction between the components, heat is actively released, which means that the soil is always warm, and therefore the culture can be planted 2 or even 3 weeks earlier;
- the sequence of layers is always the following: wood residues (branches or chips, sawdust), plant residues (for example, banana peels), compost or manure, fertile soil;
- not all components may be present in this "puff cake", but there must definitely be compost or manure in it, since they are the most productive in terms of heat release;
- sawdust and branches always go to the very bottom, because they will decompose for several years, and the final transformation will come in 3 years, but tops or kitchen cleaning - in 2 years (which means they will follow);
- different layers of the "pie" emit heat at different times, and therefore a warm bed can be used for several seasons and even without applying manure.
But this is just a diagram explaining how the agrotechnical "miracle" happens. The warm beds themselves are also different, even outwardly.
Views
There are three main types of warm beds, and it is not so difficult to make them.
Recessed
If it is decided to make a bed in an arid region, this is the option that will do. It will always be located below ground level and will last at least 3 years. It is difficult to equip such a greenhouse, but in the open field everything will work out. This is not the most labor-intensive option - no additional materials are required for such a bed. Finally, you don't even have to dig it up every year.


But she also has disadvantages:
- it can be washed away by water during the rainy season or due to over-watering;
- on such beds, water often stagnates, which means that the threat of root decay remains;
- pests (namely, crawling ones) will be "happy" with such an easy prey - it is easier for them to get into a buried space;
- if the bed is in the shade, insufficient heating by the sun will be a problem: the soil will not warm up well, again, to the detriment of the cucumbers;
- late spring frosts, as well as those that occur in early summer, are also dangerous for such a bed.
In the middle lane, I must say, they are rarely used. Because in such a climate, the effectiveness of buried beds is quite controversial: cucumbers will simply freeze in the very first serious frosts.
And this method of growing cucumbers is not always suitable for beginners: you can skip dangerous "symptoms", and the slightest failure (like over-watering) will call the future harvest into question.

Raised
As an antipode of a buried variety for the middle lane and even the northern regions, this method of growing early cucumbers is perfect. This is a bed raised relative to the soil level, which will last an average of 4-5 years. True, if you live in a northern area, you need to do it in a greenhouse.
She has a lot of advantages: it warms up perfectly by the sun, the risk of frost is no longer so great (more precisely, the fact that cucumbers will suffer at the same time), water stagnation is also unlikely, weeding and watering such a bed is comfortable, soil pests will hardly get on it.
Among the shortcomings, one can single out a decent amount of labor costs, material investments, and the need for frequent watering. In addition, most likely, in the summer, the soil will warm up strongly, and then burnt cucumbers in the heat are a possible prospect, albeit not very great.
Once again, it should be noted that this type of warm bed is optimal for the central and northern regions.


At soil level
And this is the simplest type of warm beds, which is easiest to make yourself both on the street and in a greenhouse. It will be raised by 3-4 centimeters above the ground. True, it will last only one or two seasons. A garden bed is made quickly and easily, does not require investments, the yield is predicted to be good (and in a cold summer too).
Of the shortcomings, the following can be noted: with rains and watering, the edges of the beds can be washed out, and the loss of nutrients in this case is a very real threat. In addition, it will be necessary to strengthen the edges of this ridge. Soil pests will also easily climb into it. And it also loses its shape rather quickly - it often has to be trimmed. Moreover, it is these beds that are considered the most popular among gardeners.
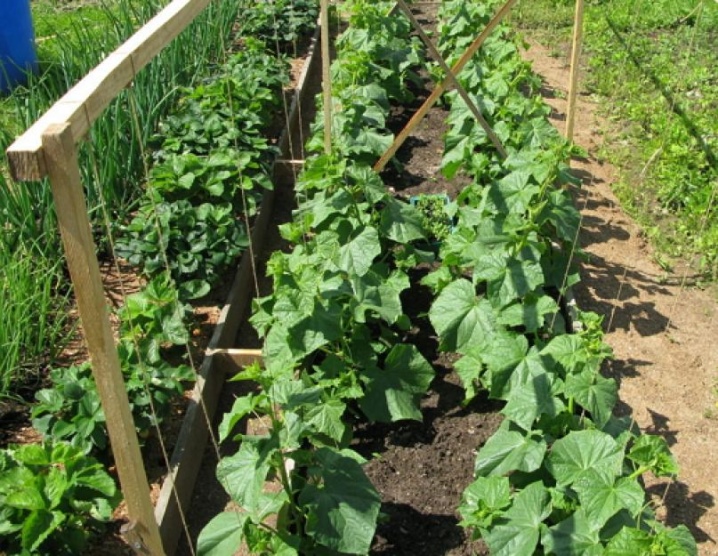

How to do it yourself?
All the types described can be done both outdoors and in the open field.
Let's start with a deep, warm bed in the greenhouse.
- All greenhouse beds usually have sides on the sides, therefore, to locate the insulation, the earth is removed from it on two bayonets of a shovel.
- Good drainage is more common in the greenhouse, so sawdust and branches are not used. You can immediately pour the tops or leaves, plant waste onto the bottom.
- The next layer will be organic matter (compost, humus). Fresh manure for cucumbers can also be applied, but not chicken droppings. But this is only if it was decided to prepare the garden in the fall, because it emits a lot of heat. The bed will turn out to be literally hot.
- When applying fresh manure, it must be covered with a 10-centimeter earth layer. When using compost, it mixes with the soil and is not covered.
- Ready-made beds are poured with hot water, covered with a dark film. Boiling water is needed to start the fermentation process, and this will generate a lot of the necessary heat.
After a couple of days, you can "settle" cucumbers in such a greenhouse.



We will describe how to make a warm garden bed outside.
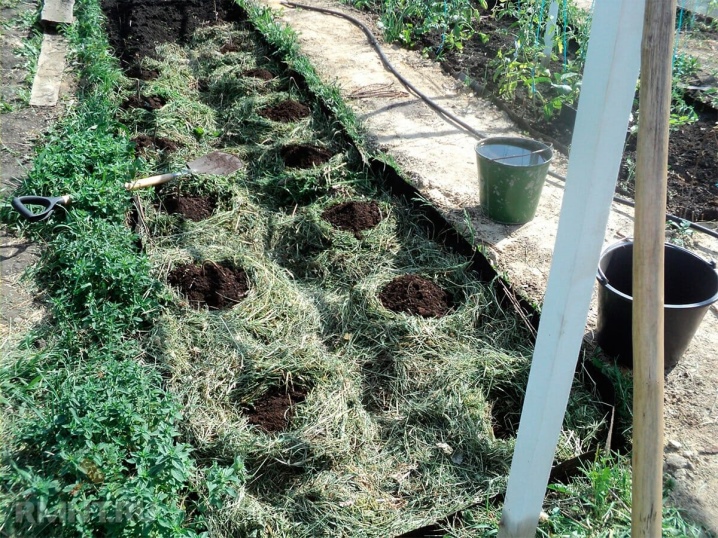
- Dig a trench 60 cm deep and one and a half meters wide or slightly more.
- The bottom of the trench is lined with branches or sawdust, or boards.This will be good drainage, water will not stagnate in the garden. The approximate height of such a layer is 20 cm, but with sandy soil, 10 cm is enough.
- The next will be a layer of plant residues: hay or straw, tops, leaves. And the approximate guideline for the layer height is 10 cm.
- The same height will be the layer of compost or manure.
- All this is covered with soil from above. This bed will be buried in the ground by 8-10 cm.
- Puff pastry should be spilled with boiling water, covered with a dark film.
After a week, you can plant cucumbers here.



It is not difficult to build a raised bed with your own hands.
- Knock down a box of what is suitable for this: slate, pipes, ordinary boards. The width of the box should not be more than one and a half meters, and up to 100 cm high, but usually it is 60-70 cm (it is easier to care for a borage of this height).
- The next layer of plant residues is placed on the bottom of the box. Woody materials can be used only if the soil on the site is clayey, and the beds are not higher than 35 cm.
- Compost / manure is applied.
- From above, all this is covered with earth.
- The ridges are watered with hot water, covered with a dark film.
4 days, and cucumbers can already be planted in such a cunning system.



The easiest option is to build a bed at ground level.
- First, you need to mark the boundaries of the future borage, a width of more than a meter will be inconvenient.
- The earth must be dug up onto the bayonet of the shovel.
- A bucket of manure and two buckets of compost (per square) are introduced into the dug soil.
- Organic matter must be leveled with a rake. And no more earth is dug up in such a bed, because biofuel is not covered with soil. If you re-dig, mix the layers, the heat release will greatly decrease, and the meaning of creating a bed will be crossed out.
- The finished borage is poured with water (hot), covered with black film.
In a week and a half, the garden bed will be ready to receive cucumbers. It is these designs that are often made in the spring.


The nuances of growing cucumbers
Caring for the plants that are cultivated in such borage will be slightly different. For example, in raised beds, the soil dries out rather quickly, which means that cucumbers require more frequent watering. There is nothing good in dryness: even the death of plants is not excluded, and the debate of organic matter will slow down.
By the way, about organic matter: a warm garden bed also consists of it. Therefore, there is no need for organic feeding of borage. It is possible to "powder" the soil a little with wood ash, so that it would be more difficult for pests and for plants to have enough nitrogen.
It is difficult to install trellises on a raised type of warm beds. Bush cucumbers will be a better choice in this case, because their stems will hang from the guardrails. In a buried bed with trellis, there are no problems - it is better to plant weaving varieties on it.
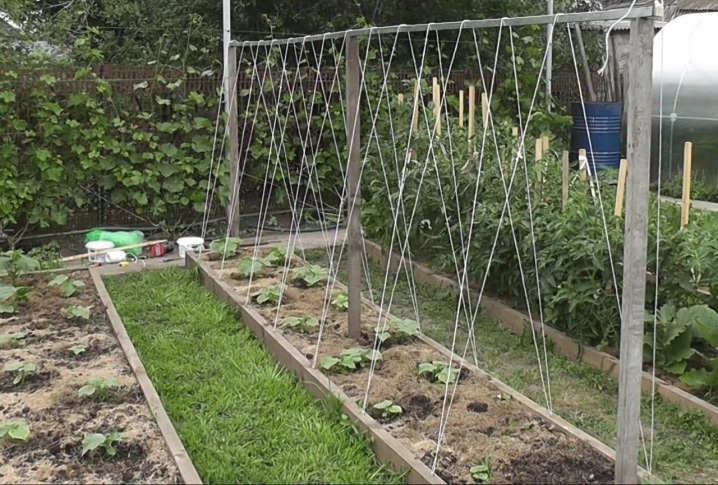

What else do the experts advise:
- plant cucumbers in the holes early in the morning;
- water the borage twice a week without eroding the top soil layer;
- in cool, damp weather, reduce the watering regime to once a week;
- do not water so that the water ends up on the leaves;
- a rise in temperature above normal under a film cover is an alarming moment, then the film will have to be replaced with lutrasil;
- the timing of planting cucumbers in a warm bed depends on the region, but it will always be 2 weeks earlier than the generally accepted dates;
- it is imperative to build bumpers around the plants, which will simplify watering.

There is nothing particularly difficult in the construction of warm beds, although you will have to tinker with them. If the importance of getting an early harvest is so strong, it makes sense to start this not quite familiar gardening "operation".













The comment was sent successfully.