- Authors: Kononov A.N., Krasnikov L.G.
- Year of approval: 2003
- Growth type: vigorous, indeterminate
- Branching: weak
- Fruit weight, g: 80-83
- Fruit length, cm: 12,2
- Fruit color: green with stripes up to 1 / 3-1 / 2 length
- Ripening terms: early
- Pollination: bee-pollinated
- Fruit shape: cylindrical
Petersburg Express is a variety of cucumbers, medium in length and weight, but with a good yield. Consider how to properly grow the Petersburg Express on the site.
Breeding history
The plant appeared in 2002 as a result of the work of Russian scientists A. N. Kononov and L. G. Krasnikov. In 2003, the Petersburg Express entered the State Register.
Description of the variety
The variety is vigorous and indeterminate. The bush, although it is bee-pollinated, is intended for cultivation using a film cover.
Characteristics of the appearance of plants and zelents
The bush of the Petersburg Express has a predominantly female type of flowering. The plant can grow in height (with proper formation and garter) up to 2 m or more. The ovaries are formed in bunches.
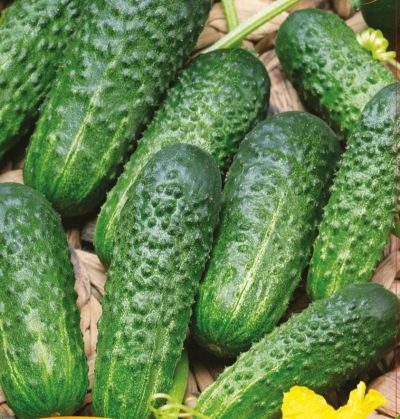
The bush has large dark green leaves and short striped fruits. The latter reach 12.2 cm in length and 3.2 cm in diameter. On average, the mass of one green plant is 80-83 g. Fruits have a large tuberous surface.
Purpose and taste of fruits
They are universal fruits. The taste is good and without bitterness. Cucumbers have dense crispy flesh.
Maturation
This is an early variety of cucumbers. Already after 40 days after the emergence of seedlings, the first waves of the harvest begin to form.
Yield
Petersburg Express is a high-yielding variety. An average of 12.4 kg of harvest falls on 1 m2.
Growing regions
Regions prescribed for the cultivation of this variety include:
- Northern;
- Northwestern;
- Central;
- Volgo-Vyatsky;
- TsCHO;
- North Caucasian;
- Middle Volga.
Growing and care
Before planting seeds or pre-prepared seedlings in open ground (which is used with this variety much more often), the site (preferably on the sunny side) is prepared. The first time the earth is dug up, and they do it in the fall, applying mineral and organic fertilizers.
The seeds of the St. Petersburg Express are often germinated. First, they are soaked in a solution of potassium permanganate for half an hour: this is how disinfection takes place. Then the seeds are left in a damp cloth to germinate, the material is removed to a dark warm room (+25 degrees Celsius). The first roots appear in 3-5 days. After they are transferred to a slightly cooler place (+ 18-20 degrees).
Seedlings are prepared about a month before the expected date of transfer to the ground. The seeds are placed in pre-prepared peat pots, plastic cups with soil. They additionally need to put wood ash, humus or 1-2 tablespoons of complex fertilizer. Planting seedlings is carried out when each plant has at least 3 fully formed leaves.
They moisten both small plants and adult bushes with lukewarm, settled water. This is an important condition as it affects the normal functioning of the root system. Water the bushes at the root. Adult plants are watered in the morning or evening every second day (or depending on weather conditions and rainfall).
Planting time in open ground or greenhouse is determined by weather conditions. The optimum temperature of the earth is +15 degrees. Under film shelters, the Petersburg Express is planted at the end of May, and in greenhouses - half a month earlier.
For tying a hybrid, nets or trellises are well suited. It is rarely pinched, since the bush has few lateral shoots. It is also important for a plant to loosen the soil in a timely manner: this is necessary not only for saturating the earth with oxygen, for the normal functioning of the roots, but also for the prevention of certain diseases.

In order to collect strong, tasty and beautiful cucumbers on your site, you need to make top dressing. Lack of nutrients can negatively affect the appearance of the plant and significantly reduce the yield. Fertilize cucumbers with organic fertilizers in combination with mineral fertilizers. With the right balance of these components and adherence to the fertilizing schedule, the cucumber yield will be maximum.
Disease and pest resistance
The hybrid has high cold resistance and good immunity. Among the diseases that it resists well, root rot and powdery mildew are especially distinguished. However, there are a number of ailments that need to be covered.
- Fusarium. It is characterized by the appearance of yellow spots. It is treated with drugs, preventive loosening and disinfection of the soil.
- Rhizoctonia. It appears as yellow spots that turn brown. The affected areas dry out and die off. It is treated with bacterial drugs.
- Ascochitis. It appears as gray spots on the leaves and other parts of the bush. It is treated by disinfecting the soil and spraying the plants with a Bordeaux mixture (5 g per 10 l of water).
- Root rot. You can notice it not only by the general condition of the cucumbers (wilting), but also by the brown spots at the base of the stem. It occurs more often with high humidity and improper watering. For treatment, infusions of wood ash, biological and chemical preparations are used.

Despite their popularity, cucumbers are often attacked by diseases and pests. From them, cucumber plantings often die before the start of fruiting. In order to prevent this from happening, it is necessary to try to prevent ailments or get rid of them at the very beginning, having studied in detail their causes of occurrence, signs and methods of treatment.