The nuances of caring for blueberries in autumn
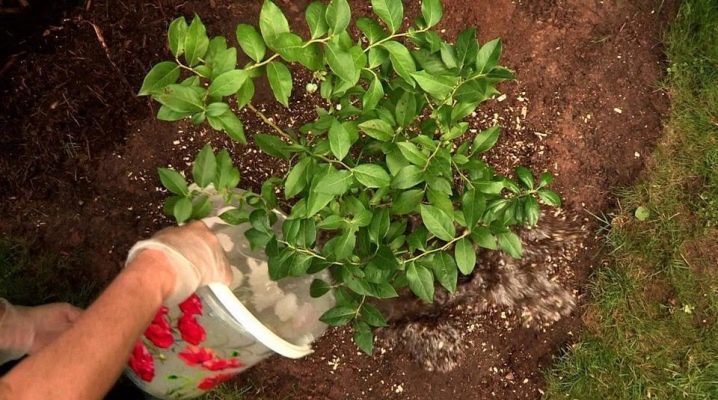

Blueberries are one of the few fruit crops that do not require special attention from the gardener. However, minimal care for this plant is still required, especially in autumn. This will allow the culture to better prepare for winter and achieve a rich harvest of tasty and fragrant berries for the next season.
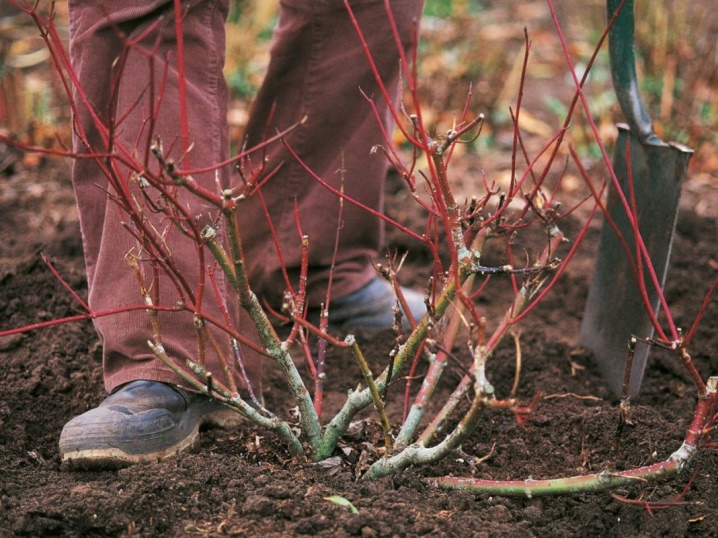

The nuances of trimming
Caring for blueberries in autumn is very important for the full growth, development and active fruiting of the shrub for the next year. Pruning becomes one of the most important activities. If you do not pay enough attention to it, then this can lead to a rapid degeneration of culture into an ordinary wild.
With the onset of spring, a large number of young shoots appear - it takes away nutrients from the plant and weakens the culture. Thickening leads to the fact that the fruiting branches become thin, and this most unfavorably affects the taste characteristics of the fruit.
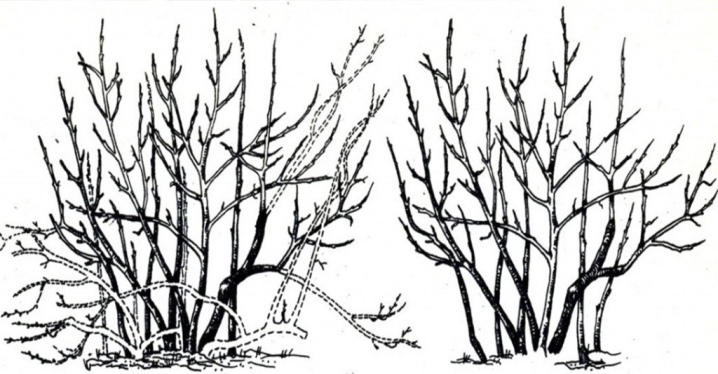
In addition, the dense crown attracts a large number of fungi, pests and other parasites, so blueberries become a breeding ground for dangerous infections.
Of course, it is necessary to cut out sick, weak and injured branches throughout the growing season. Frozen shoots are cut in spring, excess growth is removed in summer. And in the fall, special attention is paid to sanitary, as well as formative scraps.
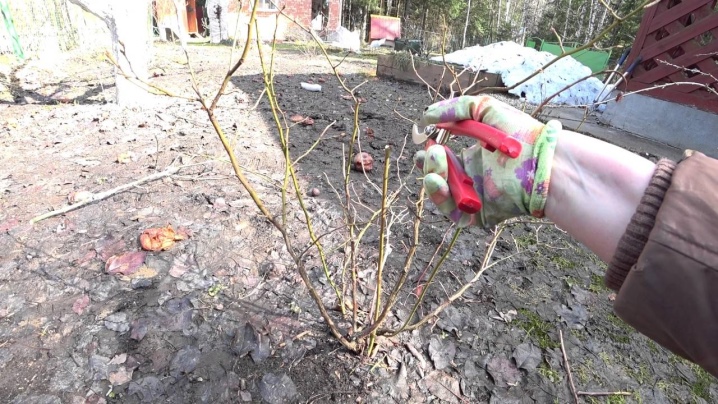

Formative
Pruning of blueberry branches is done for the correct shaping of the bush. These works must be carried out after the completion of fruiting and the cessation of sap flow. In central Russia, this time falls on the second half of October.
At this stage, all branches that thicken the crown should be removed. At the same time, the saw cut zones are covered with garden pitch - such a measure will protect the plants from the ingress of pathogenic microflora.
It is very important to complete pruning before the first cold weather, otherwise the shrub may suffer during frosts.

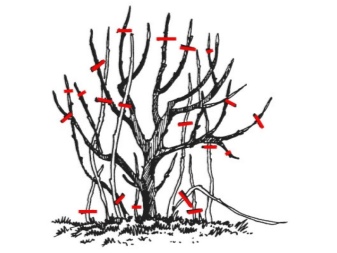
It is necessary to remove young shoots from the first year of blueberry development, since the root shoots growing during this time take a lot of strength from the plant. For blueberries planted in spring, the entire summer root growth and young branches must be cut down in the autumn months. After pruning, a seedling should remain, consisting of several straight columns 35-40 cm high, all lateral branches are also cut off.
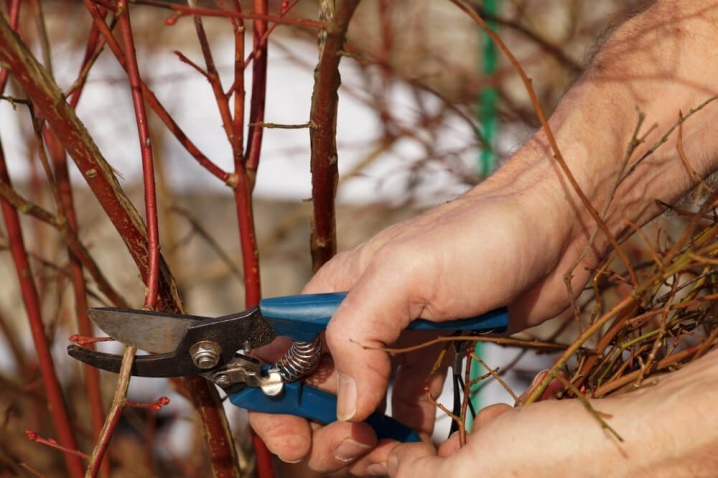

Pruning an adult plant is done according to the following scheme:
-
horizontal shoots are cut down to the most powerful branch growing vertically;
-
remove shoots growing down and deep into the crown;
-
cut off the tops of the branches, spoiled by pests or cold;
-
all branches less than 30 cm long are also subject to removal.
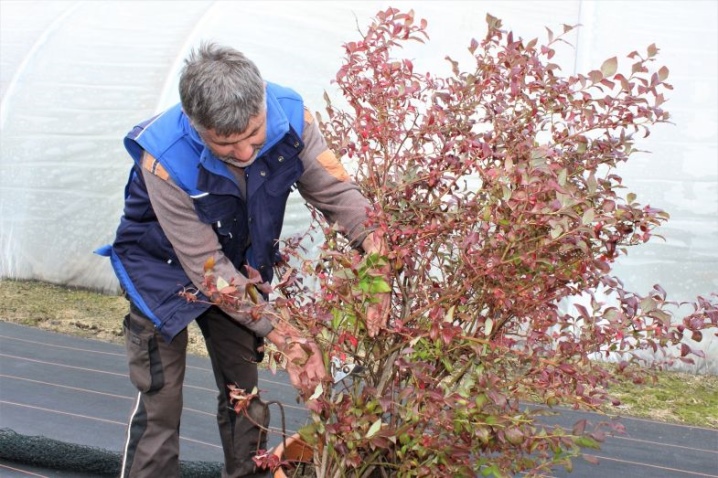

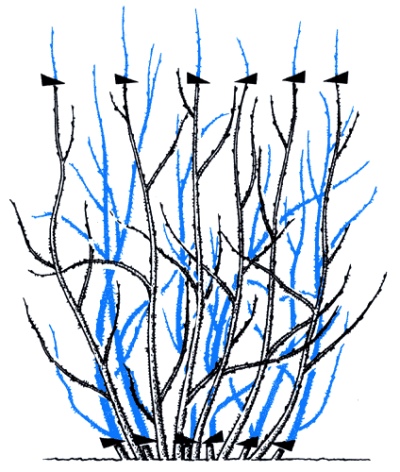
Rejuvenating
The shoots of mature plants are usually cut to rejuvenate them. At this stage, all non-fertile old branches are cut, which do not yield a crop, but at the same time take away from the bush a large proportion of useful macro- and microelements for their growth. After rejuvenating pruning, new branches with the onset of spring actively start growing and give a large harvest.
Fertilization
In autumn, any berry crops require additional feeding. The goal of applying nutrient fertilization during this period is to help the blueberries cope well with the winter and establish young buds for the subsequent growing season.
Fertilize blueberries from 2 years of age. In the autumn months, compositions with potassium and phosphorus give a good effect, such a top dressing significantly improves the taste of the berries. At the same time, 50 g of superphosphate and potassium sulfate are usually used for each bush, potassium monophosphate and potassium sulfate give a good result.
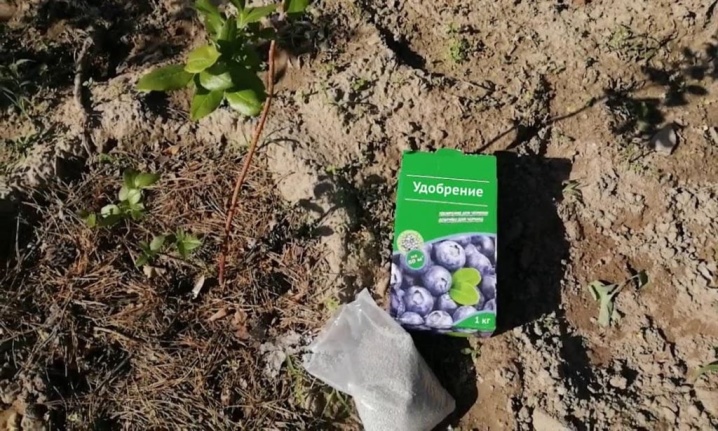

As an option, you can feed the bush culture with ready-made mineral compositions; you can buy them at any store for gardeners and gardeners. Preference should be given to preparations for heather plants - they are suitable not only for blueberries, but also for cranberries, viburnum, lingonberries, they are used to fertilize rhododendrons, hydrangeas and azaleas. They contain a balanced complex of minerals, as well as a soil acidifier.
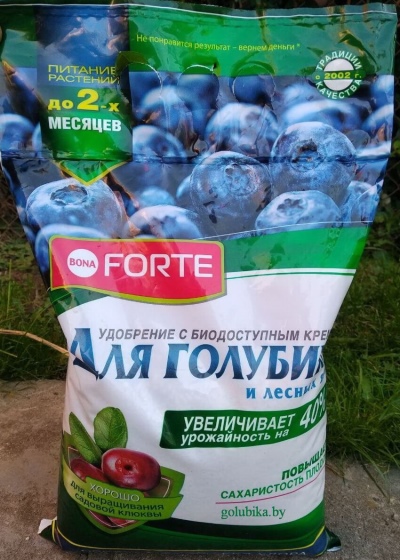

For this culture, the following compositions are most in demand.
-
Florovit - the preparation is specially designed for better fruiting of blueberries, in addition to basic minerals it contains copper, magnesium, zinc, and iron.
-
Bona forte - composition for blueberries and many other forest berries. This is a long-acting drug, it is enough to add it once a year.
-
"Good power" - suitable for blueberries and other berry bushes.
In addition to top dressing, it is very important to acidify the soil in the fall. Neutral and alkaline substrates are not suitable for blueberries. It develops best at a pH of 4-5.


If the acidity parameters are exceeded, the blueberries will start to hurt. Soil microorganisms, salts and minerals will be inaccessible to it, since in an alkaline environment, plants cease to absorb useful minerals.
As a result, all growth processes are suspended and the risk of developing chlorosis, late blight, black rot, stem cancer and other dangerous diseases increases.

To acidify the soil, you need to add special solutions to the soil.
Based on acetic acid - 100 ml of vinegar 9% table vinegar is diluted in a bucket of water and consumed at the rate of 10 liters per 3 m2 of berry.
Based on citric acid - 1 tsp. lemons dissolve 4 liters of warm water and spill the pre-moistened soil of the near-trunk zone at the rate of 3 liters of diluted composition per 1 m2 of landing area.

Some gardeners use electrolyte for acid batteries or concentrated sulfuric acid. However, in both cases, a pH test must first be carried out to determine the exact dosage of drugs.
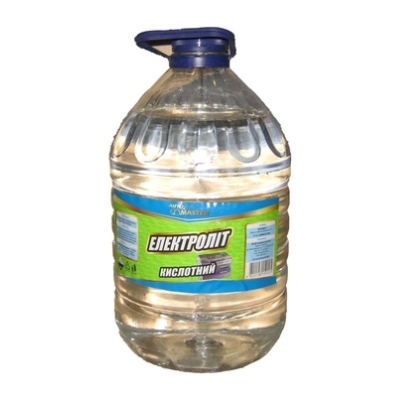

In everyday life, this is not the most convenient way, since it requires special knowledge and skills. If the dosage is slightly exceeded, the plant will quickly die.
Mulching
It is very important to mulch any plant. This measure helps to reduce the growth of weeds, retain moisture in the soil and smooth out temperature fluctuations. In autumn, crushed pine bark or coniferous needles are used as mulch, less often straw and sawdust are used. The protective layer is laid with a thickness of 7-10 cm, every year it is increased by another 5 cm.

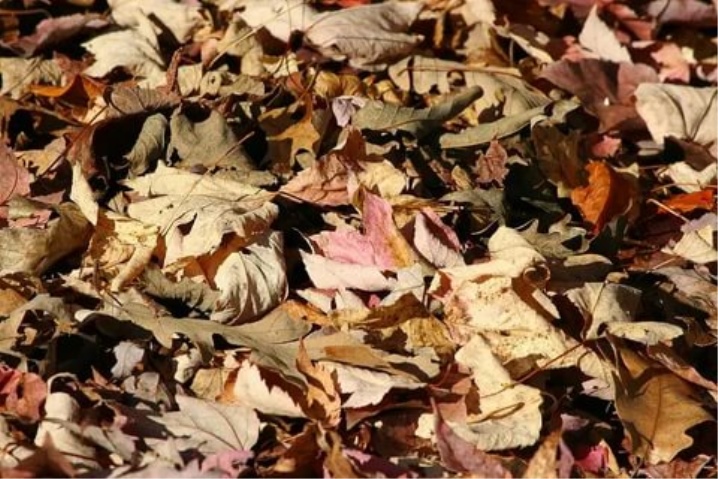
Alternatively, you can use fallen leaves. During the winter they will mate and in the spring they will begin to work as valuable fertilizers. If you use green manure crops or cut grass as mulch, then the entire plant mass must first be chopped up. But synthetic covering material for blueberries is undesirable, if the winter is warm - the roots of the plant will begin to rot.

Watering
With the onset of autumn, the amount and volume of irrigation is reduced. If it rains outside, they cancel it altogether. For watering blueberries, acidic water with a pH of 4-5 units is suitable. The most effective solution is obtained at the rate of 1 tsp. citric acid in a bucket of water.
2-3 weeks before the first frost, it is important to carry out water-charging irrigation, it will protect the roots from freezing. It is better to water the berry with a splitter - this will prevent the erosion of the substrate and exposing the roots. The amount of water should be such as to completely saturate the soil layer by 40-45 cm with moisture.On average, a 3-4 year old plant will need 2 buckets of water.

Depending on the regional weather conditions, the timing of such irrigation varies. In the central and middle zone, it most often occurs in the second half of September, in the south of Russia - in the first decade of October. In the northern regions, it is better to carry out water-charging irrigation at the very beginning of the first autumn month.
Treatment against diseases and pests
Like any other fruit and berry crop, blueberries are often infested with fungi and parasites. They can cause serious diseases of the berry.
Stem cancer - the most common enemy of blueberries, which infects plants, regardless of the climatic zones and varietal characteristics of the plant. The causative agent rings the shoot and completely destroys the bark.
Shrinking stem - manifests itself in the appearance of convex spots on the stems.
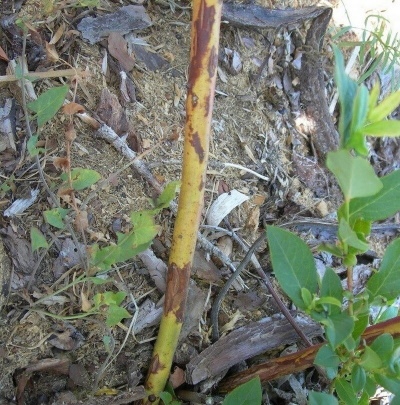

Double leaf spot - in this case, dark gray spots with burgundy edging appear on the leaf blades.
Anthracnose - causes many brown spots, they cover leaves, stems and even berries. This fungus makes it impossible to preserve the crop.
The activity of pathogens also often leads to decay of the roots of the stem and late blight. Most of these diseases make themselves felt in early spring, at temperatures from 0 to 10 degrees, as soon as the snow melts. At this time, the plant is still inactive, it does not enter the growing season and therefore practically does not resist.

In order not to give the pests a single chance, even in the fall, after the leaves have fallen, it is necessary to process the berry to prevent lesions. This requires systemic drugs that penetrate into the cells - the "Skor" agent is most effective.
If during the growing season the plant encountered spots of different types, then contact fungicides should be used before hibernation. - they eliminate myceliums and spores on the surface. For the prevention of fungal, bacterial and viral infections of leaves, root system and trunk in autumn, Bordeaux liquid, iron or copper sulfate are used.

Shelter
Blueberries can be classified as cold-resistant crops; they easily tolerate frosts down to -20 degrees. However, if the region is characterized by harsh winters, then it is best to insulate the bushes. Besides, the survival rate of blueberries is significantly reduced if the winter is snowless. Therefore, in the central and northern regions, experienced gardeners are advised to always make a winter shelter.

Warming is carried out in stages.
Before the onset of frost, the shoots are carefully straightened and bent to the ground. So that they do not rise, they are fastened with twine, or fixed with special hairpins.
As soon as the first cold weather comes, the blueberries should be immediately covered with burlap or spunbond. You cannot take a film for this, since in such conditions the plant will rot and become susceptible to fungal infections.
When the first snow falls, it must be thrown over the top of the bush to the maximum. This will create additional insulation, and in addition, provide the plant with the necessary moisture in the spring.

Preparing for winter in different regions
In Russia, the Moscow region is considered the best place for growing strawberries, although the winter there is often quite harsh. Therefore, you should not neglect a warm shelter. The bushes must be bent to the soil, covered with a canvas, or covered with pine spruce branches.
In the Urals and Siberia, specialized varieties of blueberries are used, adapted for cold areas. It is best to plant hybrid varieties there - "Canadian nectarnaya", as well as "Wonderful" or "Taiga beauty". The bushes of this blueberry can grow up to 80-90 cm, they are distinguished by high frost resistance.

All preparatory work in September-October is carried out in a typical manner. There, shelter for wintering is not necessary, it will be enough to cover the bush with snow, especially since in these places precipitation falls quite abundantly.
The climate of the Volga regions is not suitable for the cultivation of blueberries. Therefore, here they are content with imported berries, and the shrubs themselves are not planted.

Common mistakes
Despite the fact that blueberries are a very unassuming plant to care for, many summer residents take care of it incorrectly. This lowers the overall yield and degrades the nutritional characteristics of the fruit.

We list the most common mistakes when caring for this crop in the country.
-
Excessive watering - leads to waterlogging of the soil. The result of such irrigation is a lack of oxygen, the roots experience it and therefore often freeze in winter.
-
Exceeding the limiting concentration of acetic or citric acid. This causes the death of the mycorrhiza fungus, which is important for the complete assimilation of all macro- and microelements.
-
Excessive thickening of the crown or planting a bush in the shade - causes a deterioration in the taste of the fruit and lowers the plant's resistance to infections.
-
Avoiding nutritious fertilizers - leads to a deterioration in the decorative characteristics of the shrub, crushing of berries and a decrease in the volume of fruiting.
-
Use of organic substances as nutritional supplements - this significantly reduces the yield.
-
Improper loosening - loosening the substrate to too great a depth causes damage to the root system of the crop, which is located close to the soil. Therefore, autumn loosening is allowed no more than 2-3 cm.














The comment was sent successfully.