Blueberry breeding methods

It is unlikely that blueberries can be called one of the most common inhabitants of personal plots, dachas and vegetable gardens. However, those who are well aware of the beneficial properties of this berry try to plant a shrub and take care of its timely renewal. There are several ways of breeding garden blueberries, each of which has its own characteristics, and, therefore, both supporters and opponents. For example, breeders prefer to use the generative variant to breed samples with new varietal qualities. Gardeners, on the other hand, opt for the vegetative method.

How does it reproduce in nature?
Analyzing the peculiarities of the reproduction of blueberries in their natural habitat, it is necessary to take into account that we are talking about the most hardy representative of the numerous heather family. This short summer-green plant often lives up to its 100th anniversary. By the way, in the northern regions the bushes are much shorter.

Another important point is that the described berry belongs to the category of plants that are difficult to propagate vegetatively. This is due primarily to the demanding nature of the shrub. The fact is that for the active distribution and development of blueberries, the most constant conditions are required. And we are primarily talking about humidity and temperature conditions. An equally important factor is the length of the rooting process.

In their natural environment, blueberries reproduce normally mainly in places characterized by high humidity, long winters, and short but hot summers. You can meet bushes with beautiful berries:
-
in the swamps;
-
along the banks of various reservoirs;
-
in the highlands;
-
in the lowlands of the tundra;
-
on the edges of pine and spruce, as well as deciduous forests;
-
in permafrost regions.
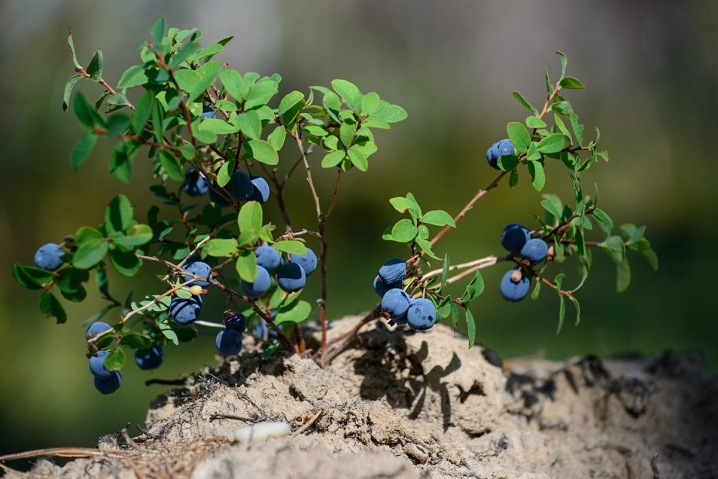

Like all other plants, this shrub is able to reproduce vegetatively and by seeds. Of course, for wild blueberries in nature, the second option is often relevant. At the same time, the bushes are able to grow by layers and multiply by root shoots.
Cuttings
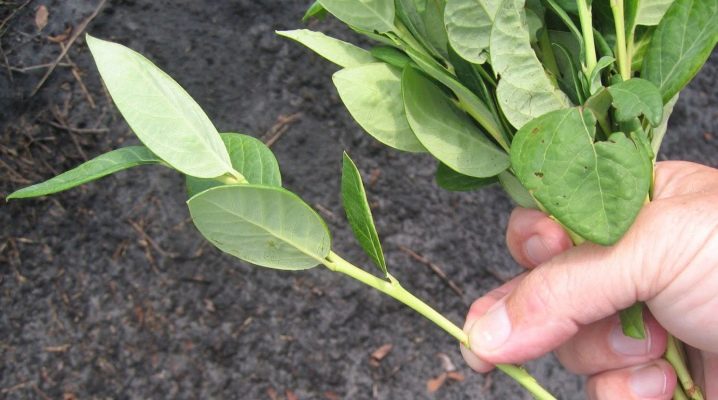
At the moment, the most popular method among gardeners is the cultivation of blueberries by cuttings. There are two ways to achieve the desired results. When it comes to lignified planting material, it is harvested in early spring. If the gardener decided to cut the shrub in warm regions, then the harvesting period falls at the end of the winter period. As a rule, blueberries are pruned at the start of the next warm season. This will be the right time for the formation of blanks for future seedlings. The main thing is that the mother plant is in complete rest.
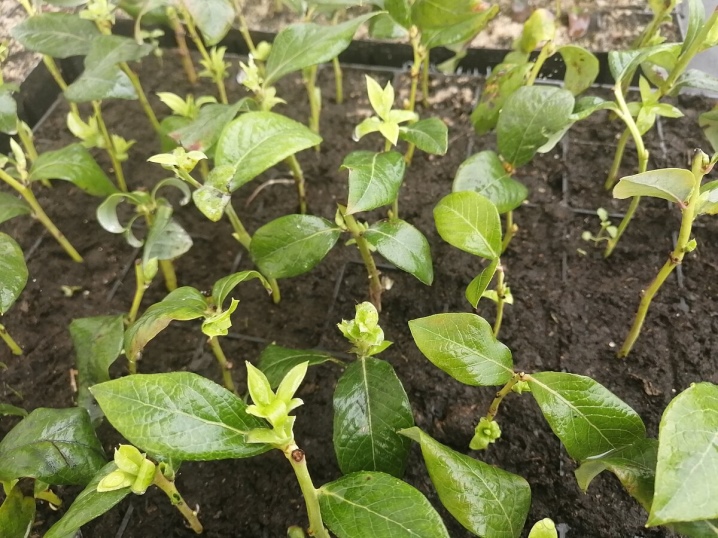

And you can also breed a berry that is unique in its properties and shoots, that is, the so-called green cuttings. Naturally, this method differs significantly from the previous one and has a number of important features. But, regardless of the method of cuttings, it should be remembered that such a propagation process will require certain knowledge, effort and time.
Lignified cuttings
The key task in this case is to preserve the harvested shoots until they are planted in the ground. Cut cuttings are most often tied in bunches and placed in a regular household refrigerator. An alternative can be a special cellar for planting material. In such a situation, the cuttings are laid out in layers, between which a mixture of sawdust and snow is placed.
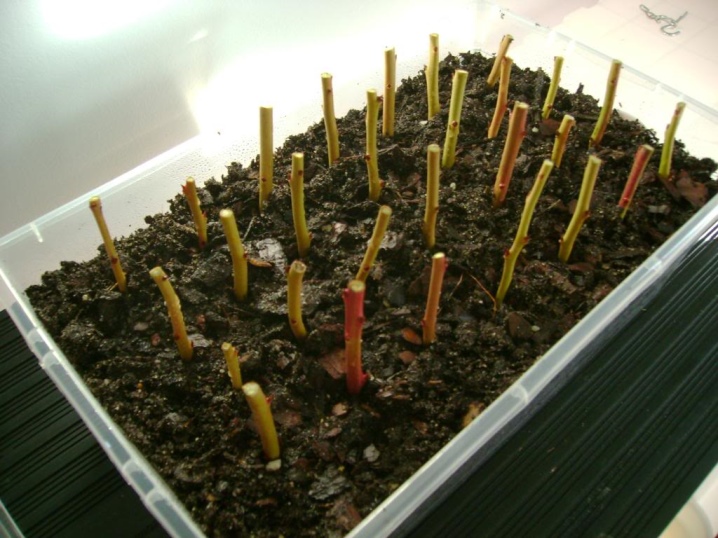

Cuttings are carried out in cold weather, taking into account that there should be no problems with the storage of the material. The optimum temperature for future seedlings is +5 degrees, but it is important to constantly monitor their condition. The main thing is that the harvested shoots do not dry out, but also do not grow moldy. When propagating the garden culture in question in the described way, several key points must be taken into account.
-
Since blueberries are a representative of heather crops, they require an acidic soil. For shoots for this purpose, you will need to prepare a mixture of three parts of peat and part of river sand.
-
Rooting can be done in a separate container (box, container), which will need to be prepared in advance and placed in the greenhouse. It is necessary to make holes in the ground, and replace the extracted soil with the previously prepared mixture.
-
Planting of blanks of future seedlings is carried out about a month after cutting and storage under appropriate conditions. When pruning cuttings, it is important to keep in mind that in situations with tall and undersized blueberries, the length of the shoots should be 15 and 10 cm, respectively. Cut the cuttings at the bottom under the kidney obliquely, and at the top - in a straight line, 2 centimeters above the kidney.
-
It is important to pay attention to the length of time the plants are in the greenhouse. If we are talking about a short stay, then it will be enough to leave 5 cm gaps between the shoots. For longer growing cuttings in greenhouse conditions, the planting interval should be doubled.
-
Future seedlings are placed in the soil prepared in the above way, after which they are abundantly watered and covered with foil. It is highly recommended to provide additional insulation on top of this greenhouse. It is important that the thermometer inside the structure does not fall below 26 degrees. Watering the planted material must be done by sprinkling. It is the high humidity and heat that will allow you to grow strong and healthy seedlings. The main thing is to prevent the appearance of foci of mold and mildew.
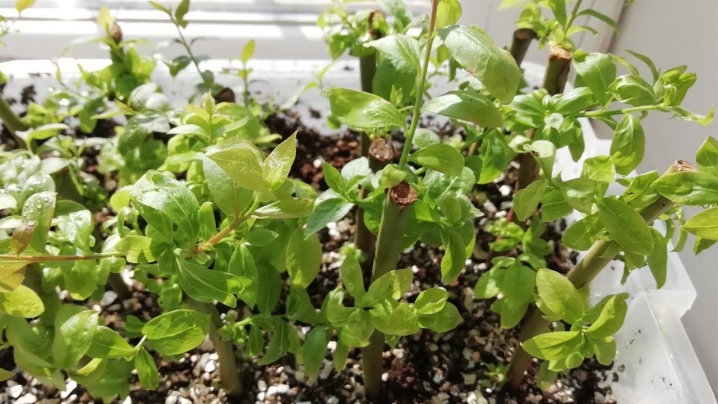

It will take about two months to root lignified cuttings, after which it will be safe to remove the shelter. For the first time after this, it is necessary to abundantly water the already rooted seedlings.
It is also important to pay attention to their handling and airing. By the way, at the site of the first planting, the described plant is able to actively and fully develop for several years. With proper care and prevention of diseases typical for blueberries, the first fruits can be expected in 2-3 years.
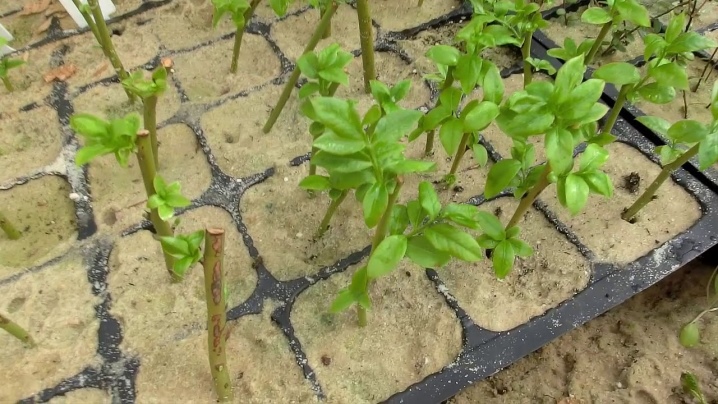

Green material
One of the key features of this method is that the cuttings are harvested in the summer and in the morning. It is important that the future planting material does not dry out. It is necessary to pluck the shoots correctly, since the so-called heel must remain intact. That is why the cuttings are torn off, not cut off. After separating the shoot 10 cm long from the bush, it is required to remove the lower leaves.
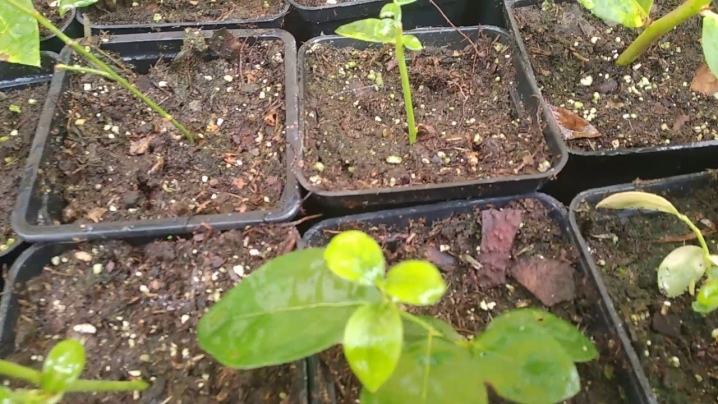

For green cuttings, a mixture of rotted coniferous litter and peat is required. For landing, you can adapt cassettes or individual containers of small volume. They are filled with the prepared soil mixture, and the shoot is located in the center. While observing the spacing between shoots, it is important to take into account that future seedlings should not touch each other with leaves.
As with lignified cuttings, green planting material will require warmth and moisture to root. The leaves on the shoots should always be slightly damp. To do this, they are periodically sprayed.


If we are talking about rooting large plantings in area, then a rational solution would be to use installations for fogging.It is strictly forbidden to water blueberry seedlings with water containing chlorine.
Additional shelter for the greenhouse, unlike the previous method, is not required. If the balance of temperature and humidity is observed, green cuttings will take root in 1-1.5 months. In autumn, the young are covered or transferred to a ventilated room. With the onset of spring, the shoots are transplanted into larger containers or already into the ground, while tightening the bed with a film.
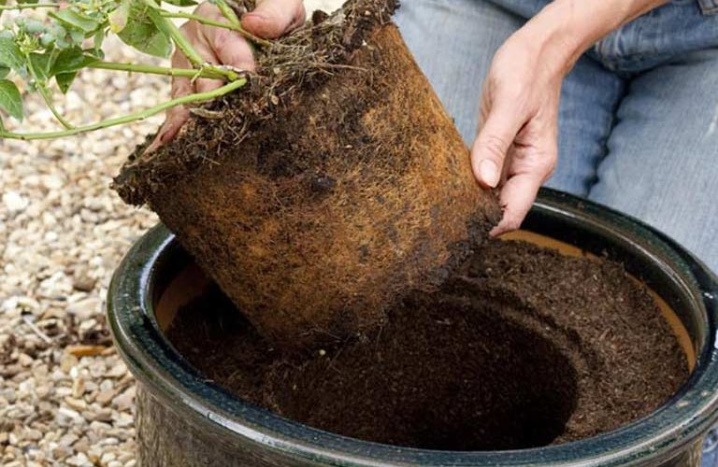

When choosing shoots, preference should be given to developed and strong specimens on which healthy leaves grow. This method is notable for its simplicity, since there are many necessary shoots on the bushes, they are easily torn off, and they do not need to be stored for a long time under certain conditions. At the same time, woody cuttings take root better, but they require longer care.
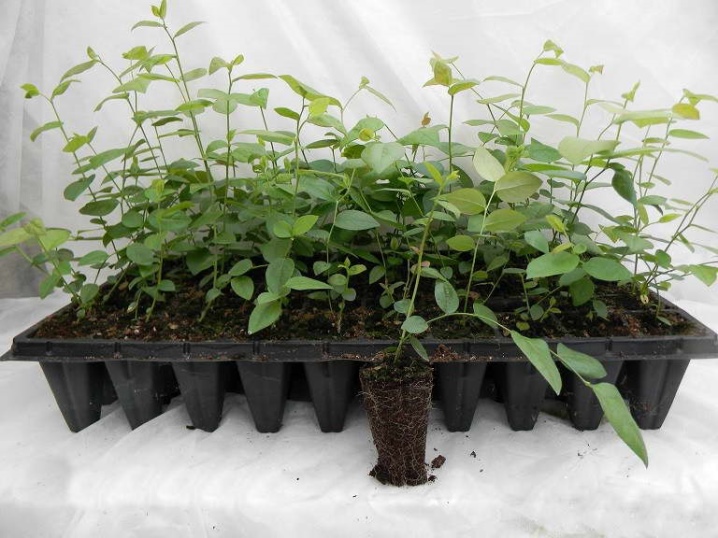

Dividing the bush
This propagation method is relevant for large blueberry bushes with a strong and branched root system. Once the plant has reached the appropriate stage of development, it can be neatly divided into several parts, even with a shovel. This option will be most suitable for low-growing garden plants. It is important to completely dig out the mother bush before dividing without damaging the roots.
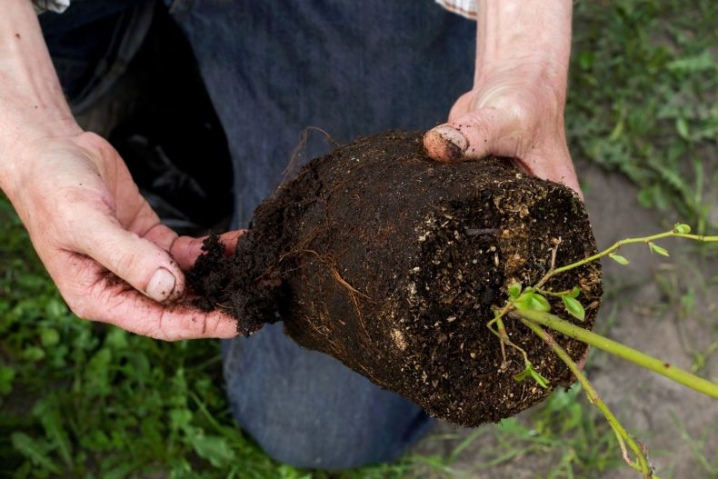

It should be remembered that these manipulations are prohibited during the flowering period, since in this case the plant will not have enough strength to fully recover. After removing the bush, it is required to carefully examine the root system and, if necessary, remove its dry elements.
After removing the plant, there are several steps to follow.
-
Prepare holes for planting.
-
Divide the bush into parts so that a root of at least 5 cm remains on each of the parts.
-
Treat the lower part with disinfecting compounds and rooting stimulants.
-
Place parts of the bush in the holes and spread the roots.
-
Fill the holes with soil.

After planting, the blueberries will need to be watered abundantly. The root zone is mulched in order to prevent rapid evaporation of moisture.
How to propagate by layering?
Initially, it should be noted that this method of breeding blueberries has two important disadvantages. First of all, it requires a significant amount of time. In addition, a small amount of planting material is obtained. At the same time, young animals are distinguished by good development, health and endurance. It is important to take into account that medium and tall plants are propagated by layering.
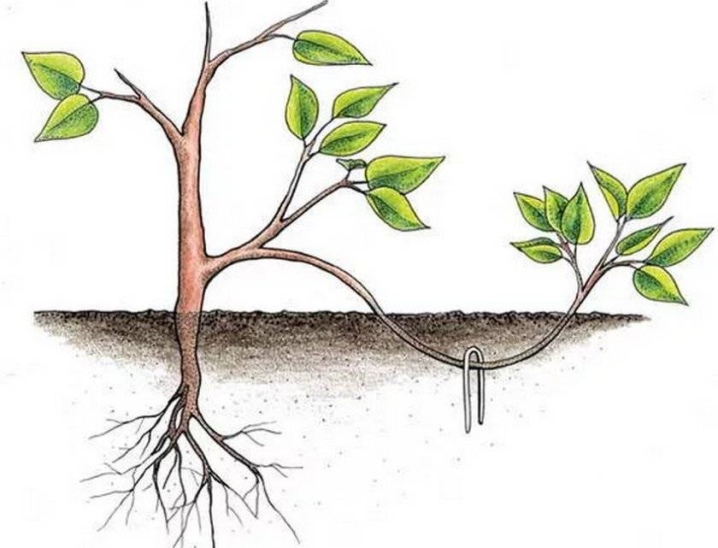
The obvious advantages of the method are reduced to the absence of the need for long-term storage of the material and the creation of greenhouse conditions. It is important to note that the cuttings are not separated from the mother bush. In the sprinkled areas, vertical shoots themselves break through. It is precisely them that will need to be properly looked after. And in this case we are talking about adding soil and watering. It should be remembered that blueberries require acidic soil with the obligatory presence of peat.
Taking into account all the features, propagating a shrub using this method is very simple. But it is important to remember that this process is quite lengthy, and the result may not meet the expectations of novice gardeners. Often, an abundant mass of foliage grows from the layers, but this may not be an indicator of a well-developed root system. Proceeding from this, it is impossible to separate the young from the mother plant, relying solely on the quantity and quality of leaves.
A full-fledged root system of bushes is formed only after 2-3 years. Until this moment, planting young blueberries separately will not work. If everything is done correctly and in a timely manner, then it will be possible to separate the young without harming its own roots. At the next stage, the plant is transferred to a previously prepared hole, which is covered with an acidic substrate. If the place for the permanent residence of the bush has not yet been chosen, then for some time it can be left in the container.
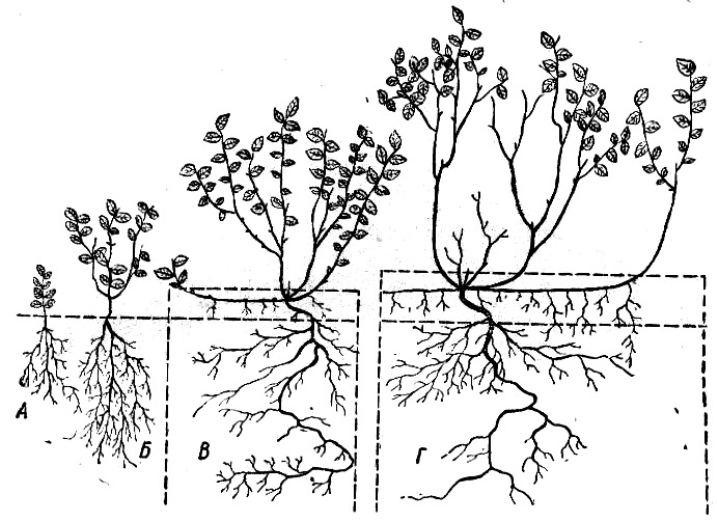
How to grow from seeds?
As noted, the vegetative propagation methods for blueberries are the simplest and most effective. However, such options are not suitable for everyone. We are talking about specialists who concentrate on the development of new varieties. In such situations, they have to use seeds. The latter can be either purchased or assembled with your own hands.
As a rule, experienced gardeners prefer the second option, since when purchasing planting material, one may encounter the following problems:
-
the seeds may belong to a hybrid;
-
varietal qualities remain unknown;
-
with improper storage, germination is significantly reduced.
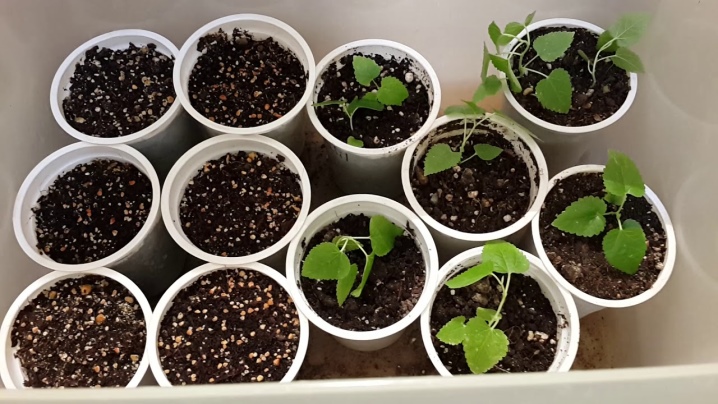

Seeds must be harvested in advance and stratified. By the way, this procedure often lasts for 3 months, based on which the preparation of planting material begins from mid-December. In this case, green sprouts may appear by March. For sowing, peat soil will be required, which will definitely need to be checked for acidity.
Another important condition is the construction of a compact greenhouse to ensure adequate humidity. During the developmental stage, which takes about a year, sprouting blueberries will need to be repotted periodically. At the same time, the quality of the soil is constantly monitored.














The comment was sent successfully.