All about watering cucumbers in a greenhouse

Cucumber, like all pumpkin crops, requires a lot of water for irrigation. If you neglect this rule, then the fruits will be small and bitter. In addition, the cucumber is a kind of vine: like, say, a vineyard, the plant rushes upward during most of the season, trying to give more harvest.


Water quantity and temperature
All pumpkin seeds, including cucumber, do not tolerate excess cold, as well as excessive heat. The minimum temperature of water and soil at which a cucumber crop grows is +16 degrees. The optimum is 20-30, the maximum is 35. The temperature of the soil and water seeped into it, under +40 degrees and more, will surely lead to wilting of the growth, loss of yield. For this purpose, cucumber seedlings are placed in a greenhouse. In principle, the month of planting does not play any role if the greenhouse is brought to the level of an all-weather greenhouse, in which + 18 ... 20 on the thermometer is maintained. The land and water that you water cannot cool below +16.
Before the onset of the flowering period, cucumbers are watered at the rate of 5 l / m2 of cucumber thickets per day... After the appearance of embryonic inflorescences, the cucumber shoots are watered twice or three times with plenty of water, but do not allow the soil to become waterlogged. This rule is about the same for a greenhouse-greenhouse, and for overgrowth in the open field. If a warm wind has risen, contributing to increased evaporation, then the number of irrigations from one to two or three.
For a garden bed closed in a greenhouse or greenhouse, the amount of water per day per 1 m2 of cucumber growth remains unchanged.


Frequency
It is not recommended to water cucumbers too often: excess water will displace air from the soil, and the roots will begin to suffocate, causing the plants to rot, stopping growth. With jet-sprinkler irrigation, the optimal frequency is a couple of times a day: in the morning and in the evening.
The amount of water by volume should not be exceeded, the irrigation method does not change the total amount of moisture received by the cucumber vegetation. Observe the regime - depending on the month and specific dates in the year: you need to water at sunset and before sunrise. This rule is the same for seedlings and adult plants.
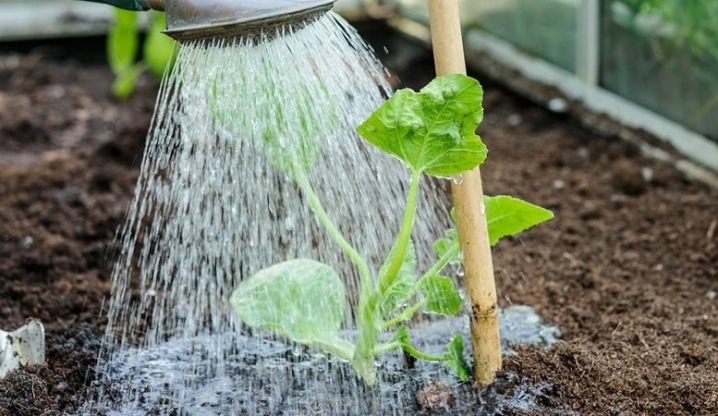

Is it better to water in the morning or evening?
Cucumbers should be watered exclusively in the evening only during the period of the year when you are sure that the pre-morning (before dawn, at dawn) temperature will not drop below +16... Cucumber is a thermophilic plant: like all pumpkin plants, it does not forgive noticeable violations of the temperature regime of growth. In the summer months, when the weather is hot, watering the cucumbers is mandatory - twice a day, and you don't have to choose whether you water the cucumber beds in the morning or in the evening.
Watering in a greenhouse also does not play a big role - it all depends on the weather. When it comes to the spring months, cucumbers are watered once a day - in the morning, since it is still quite warm during the day, but in the morning the temperature often drops below the same border mark of +16 Celsius. In the summer months, greenhouse watering is also performed once every day - a greenhouse or a closed greenhouse is placed mainly to prevent the soil from drying out quickly, and nothing should prevent the plants from absorbing the right amount of moisture necessary to successfully bloom and form an abundant amount of ovaries, as well as to ensure the growth of "set" cucumbers.

Make sure there is enough natural light in your greenhouse or greenhouse. Use a white or colorless matte material for the roof and walls of the greenhouse: it scatters direct sunlight, preventing the plants from burning in the summer heat. If this is not possible - the greenhouse is opaque - then take care of bright LED lighting, giving "cold" and "warm" light. You cannot use colored or black material for the greenhouse - overheated walls in the heat will turn into a kind of oven, and on the very first day of May your seedlings will burn.
Cucumber "drinks" a lot of water, and also likes to "sunbathe", provided that there is enough moisture in the soil. Provide him with both. Cucumbers that have already formed are not afraid of direct sunlight. This cannot be said about seedlings that have not yet grown enough to give flowers and form fruits from them.
Weigh both of these factors to get a good harvest on time and on time.

Overview of methods
Watering cucumbers in a polycarbonate or plastic greenhouse requires a thorough approach. Watering the beds correctly means preventing erosion of the near-surface soil layers, which can expose the adventitious and main roots of the cucumber shoot... It is advisable to water it at the root. Cucumbers also "love" irrigation from above (sprinkling), but only if cloudy weather is observed: direct sunlight, concentrating on leaves and stems through the thickness of water droplets, play the role of short-focus collecting lenses (clear water is transparent), capable of causing multiple microburns to the green cover.
And this means one thing: any garden shoots are watered by sprinkling only in cloudy weather, when the sunlight is significantly diffused. Nature has already taken care of this - and when it rains, it will often not make such mistakes, if the rain is not "blind", and the sun has not deviated far from the "zenith" position - although such annoying mistakes do occur. But a person (gardener) makes this violation much more often.
If you continue to "sprinkle" cucumbers in the heat, on a hot afternoon, over and over again, the foliage will burn out, and you can forget about the harvest.



Manual
Manual irrigation is called any irrigation system in which the main character is a person: the work is done manually... In the simplest case, hoses with a "shower", watering cans, and all kinds of nozzles are used that create a directed "rain" (but not a jet that beats into the distance with force). The scheme of actions is as follows: the watering can is filled with water, and the gardener goes to water the garden, then the cycle repeats. Using a hose makes it possible not to go back and forth unnecessarily, but to water all the beds without leaving the greenhouse. The disadvantage is that the summer resident is not free at these moments, as he must bring the watering to the end.
As water, either tap water is used, if its temperature has not dropped below +20 degrees, or pre-collected from a well or well, settled and heated. Rainwater does not need to be heated - all these actions have already been done by nature itself. In addition, precipitation is softened water, almost distilled, maximally useful and enriched with oxygen. After rain, as a rule, any vegetation grows at an accelerated rate.


Auto
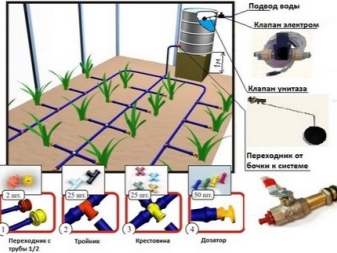
The primitive irrigation system is not fully automated, but only mechanical. Watering through plastic bottles or droppers is referred to as drip irrigation. These reservoirs can be filled both by the summer resident himself daily and by the pump. The latter method is the most attractive. The drip irrigation system, made from bottles, allows you to minimize not only water consumption, but also the cost of installation and commissioning. Plastic bottles can be found anywhere, even in a landfill, provided that their integrity is not compromised and holes are punctured in the corks. Any containers with a cut-off bottom are suitable as blanks; you can use both 2- and 19-liter containers. The best option is that capillary tubes, through which water from bottles enters, are dug into the ground to a depth of about 20 cm: the water entering there is concentrated in the deepest layers, on the underlying roots of cucumber plants. This allows you to abandon loosening, more frequent weeding of beds from weeds.
An automated drip irrigation system provides for the use of a piping system with holes in the locations of the beds, and a pump. It is enough just to open the main tap - and the water will flow to the beds, saturating, saturating the soil with moisture. Disadvantage - with a small pressure, the lack of which is observed at the height of the summer cottage and garden season, watering the entire greenhouse of cucumbers is a problem. The pressure may simply not be enough for all pipelines: they will need to be grouped, which will entail forced opening and closing of taps.
If you often leave for other business, it makes sense to entrust the automation with the installation of water flow sensors, electromechanical valves and a program unit that controls this periphery on a schedule or remotely on the pipeline.

The nuances of watering at different periods
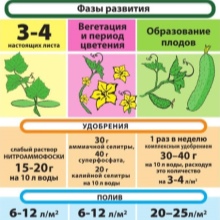
After planting, the seedlings only need a small amount of water - no more than 3 liters per 1 m2 of cucumber growth. Watering is carried out using a drip system - a constant humidity mode is maintained here. During flowering, watering reaches 6 l / m2. When fruiting, more water is used - up to 12 l / m2 of beds. The larger the formed cucumbers become, the more water they will need, up to the maximum mark: a cucumber is 90% water.
A decrease in the amount of water will immediately lead to unripe cucumbers, the fruits will become small, bitter and wrinkled, most of them will simply burn out from the heat, or the plants will dry out. The irrigation scheme does not change, it is only important to make sure that the relative humidity close to 100% has not formed in the greenhouse or greenhouse: excess moisture leads to the appearance of diseases, for example, to the damage of fruits by mold or fungus. After harvesting, cucumber seedlings do not need to be watered. Cucumber is an annual crop, and after the end of the ripening of cucumbers, there is no point in watering these plants.


Combination with top dressing
Top dressing of cucumbers is needed to obtain the maximum possible yield from each square meter of the beds. The minimum number of feeding sessions is at least four. Initial feeding is done during the third leaf phase, when two-leaved seedlings indicate a tendency for new leaves to form on the seedlings. Nitrogen, potash and phosphate fertilizers are applied in the form of a weakly concentrated solution - up to 10 g per bucket of water. Organic - cow dung and poultry manure - are diluted 7 and 12 times, respectively. Wood ash - no more than 2 glasses per bucket of water (10 L). The resulting solutions are poured into 1.5-2 liters for each plant after normal watering.
Urea is also diluted no more than 15-20 times. It is unacceptable to use concentrated urine - that, in turn, will burn all the growth. Mineral fertilizers are applied in the form of complex additives: they contain both potassium salts and phosphorus-containing compounds. Top dressing is carried out in the rain, or after watering. It is not allowed to pour nutrient solutions on dry soil: the soil must be sufficiently moistened. After the first feeding, at least 15 days should pass, or better - 20: the slightest oversaturation will lead to not quite correct growth and development of vegetation, and the cucumber harvest may shift in time, or turn out to be far from your expectations. The second top dressing may include ammonium nitrate diluted in the same amount of 10 g per bucket of water.


The following drugs are used to protect against diseases:
- potassium permanganate - until a crimson shade of the solution is obtained;
- urea - 10 g of anhydrous urea per bucket of water;
- iodine - no more than 15 drops per bucket of water;
- boric acid - up to 3 g per bucket.
Processing with these compounds - any, of your choice - produced every 15 days. They must not be poured under the root, but sprayed on the leaves and stems. Irrigation of the aboveground part of the cucumber shoot is carried out at any period other than the flowering period: otherwise you will wash off the pollen from the flowers, and pollination, and with it the harvest, will not happen. This method is called foliar feeding - potassium permanganate refers to a source of potassium. One-time foliar feeding is also done with the help of micronutrients, for example, ammonium nitrate, superphosphate and potassium sulfate. All substances are mixed, respectively - in dosages of 5, 10 and 10 g per bucket of water.

Possible problems
Do not feed during the day when the soil temperature drops to +16: in cold soil, some compounds are extremely difficult to assimilate. Do not water the cucumbers less than once every 1 to 2 days. Dry weather will dry out the soil, even when you've loosened it up. Don't neglect mulching. The starting material will be the already obsolete cucumber "tops", which no longer bring crops, as well as any residues from vegetables, fruits, berries and even weeds. Mulch inhibits the evaporation of moisture from the soil - in this respect, it resembles the effect obtained from loosening the beds. Do not use compost that has not fermented for three years (plant residues, human, dog and cat waste, cow dung, chicken and goose droppings, urine, etc.).
It must undergo anaerobic (airless) decomposition to the required stage - high-molecular organic matter is extremely difficult to assimilate by plants; the compounds must undergo splitting into simpler substances, including dissolved gases. Do not overuse organic fertilizing: oversaturated soil will lead to the fact that nothing but some weeds will grow on it. The frequency of fertilizing the soil with solid organic matter is once a year, preferably in the fall. Do not get carried away: brute force is not needed. Do not use the contents of a septic tank as fertilizer containing residues of household chemicals - washing powders, scented soap, shampoo, detergents.
They usually contain ammonia, formaldehyde, silicates, liquid polymers, chlorinol and other harmful compounds. Those, in turn, can get into plants and then with cucumbers into your body.















The comment was sent successfully.