How can gooseberries be propagated?

Gooseberry is an undemanding shrub that can grow and develop in many climatic zones of Russia. It is loved for its mouth-watering large berries with a sweet and sour refreshing taste. Gooseberries are delicious as an independent dessert, in the form of jam, compotes, and sometimes sauces for meat.

One of the positive qualities of this plant is its ease of reproduction. There are a number of methods for creating new bushes from old ones. Planting material is obtained by cuttings, dividing and layering. How and at what time to propagate gooseberries by various methods - we will consider further.
Timing
For breeding gooseberries, both spring and autumn are suitable. This largely depends on the chosen method.
Shoots from the bush are taken in early spring. The operation may well be timed to coincide with the next pruning. The main thing is to be in time until the plant begins the phase of intensive vegetation. If the vegetative buds have transformed into green "cones" or have opened altogether, time is wasted. They should only swell a little.
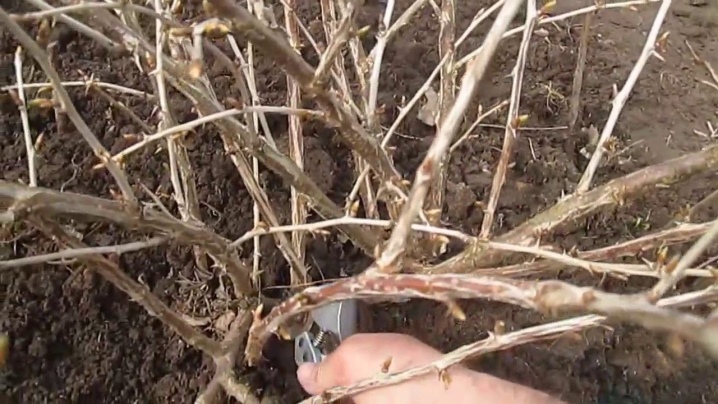

They are also planted early enough. It is necessary to wait until the soil is completely thawed at a depth of 8-10 centimeters, this is quite enough. In zones with mild climatic conditions, this usually happens in mid-April or early May. There are also proven folk signs that can be practiced as a clue - opening leaves on birches or dandelions that have begun to bloom.
Green cuttings are planted in the ground throughout June, woody cuttings - in mid-October. It is not necessary to harvest seedlings in advance in the first option.
You can cut them on the day of disembarkation or 1-2 days before that.

The division of the shrub can be done both in the spring and in the fall. The main thing is that its parts have time to adapt to a new place. Therefore, for warm southern regions, the time from late August to early October is quite suitable. In those places, winter usually comes according to the calendar, which means that you can be somewhat sure that at least 2 months are left before the first cold weather. To divide the shrub in the fall, you must certainly wait for the leaves to fall. Having fallen into a "winter sleep" gooseberry will undergo the operation not so painfully.
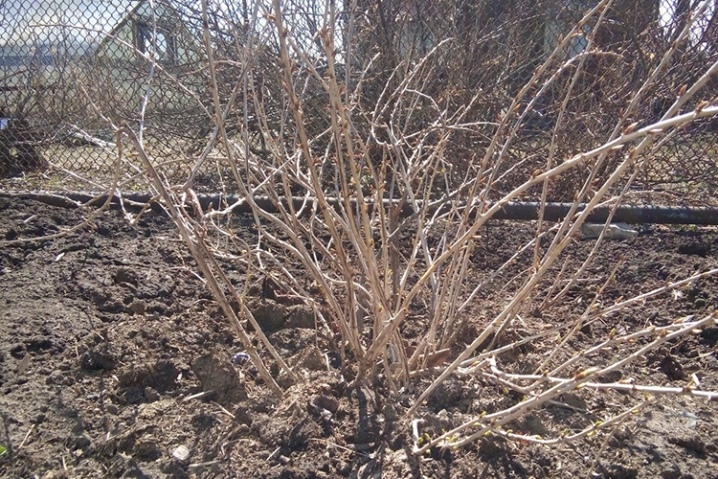

In spring, gooseberry bushes are divided into zones with mild climatic conditions. Over the summer, they will be able to adapt to their new habitat and properly prepare for winter. In this option, you need to be in time before the kidneys begin to swell. Not quite "awakened" bush responds to the operation much less painfully.
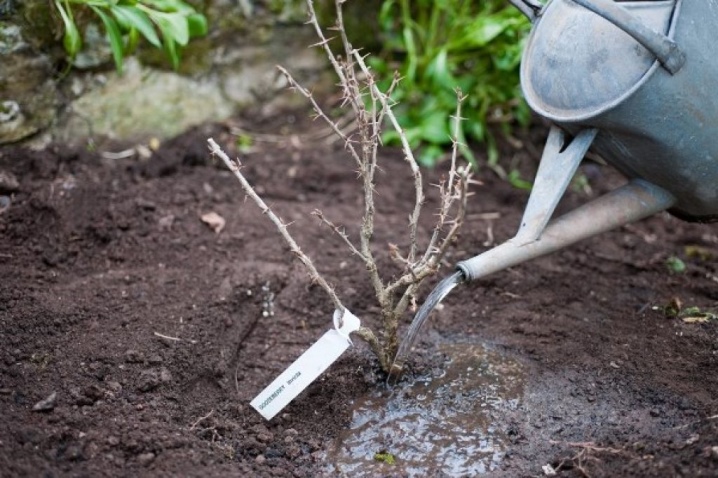

Propagation by cuttings
A single bush, no matter how prolific it is, is not able to provide a large family with berries. You don't have to go to the garden center to get a few more. There are a number of methods for breeding shrubs, and even a novice amateur gardener is able to carry out all the required operations.
Green
The method for root formation and berry growth, leading to the desired results, is performed in the 2nd half of June. The initial seedling is young growths formed this year, which have 5 buds. The procedure is performed in the existing order:
- cuttings are cut into 7-12 cm each;
- are treated with substances that stimulate growth;
- are planted in a mixture that includes peat, earth and sand;
- after root formation, they are planted on a bed at a small angle so that 2 buds are free on the surface;
- the earth around the planted process is compacted, moistened and mulched.
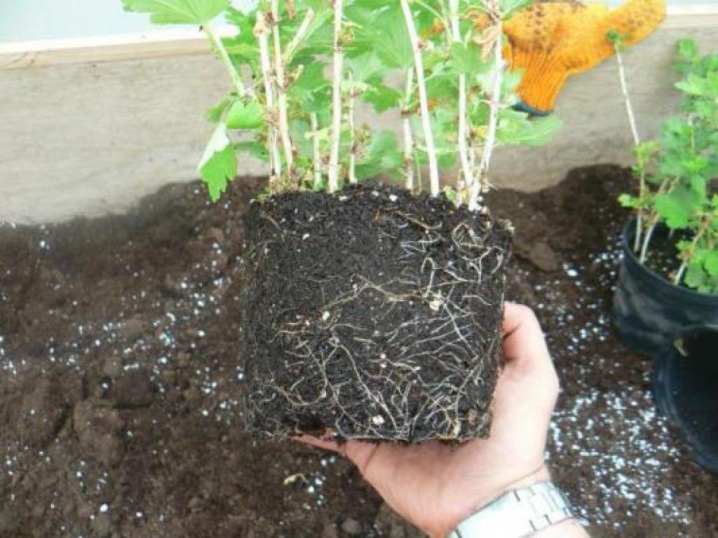

In order for the reproduction of the shrub to give the desired result, it is necessary to ensure constant irrigation and cultivation of the beds. To speed up the formation of shoots, it is necessary to regularly feed them with nutritious fertilizers: ammonium nitrate, potassium salt, phosphate lime. In a proportion of 40 × 20 × 30 grams per 10 liters of water, an excellent top dressing will come out, contributing to the growth of good one-year-old seedlings.
Attention! It must be borne in mind that the cultivation of gooseberries with green cuttings is not suitable for all varieties.
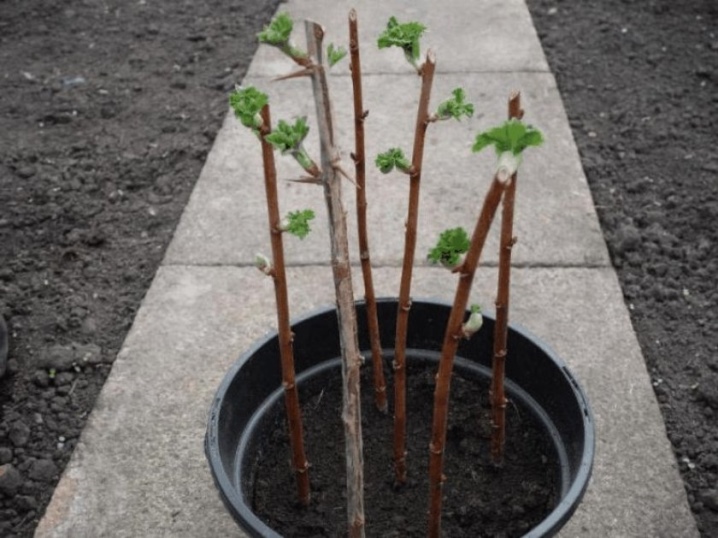

Lignified
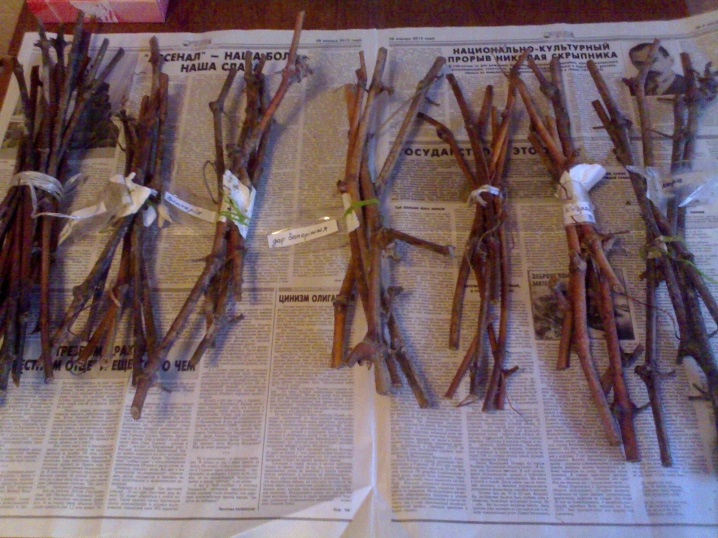
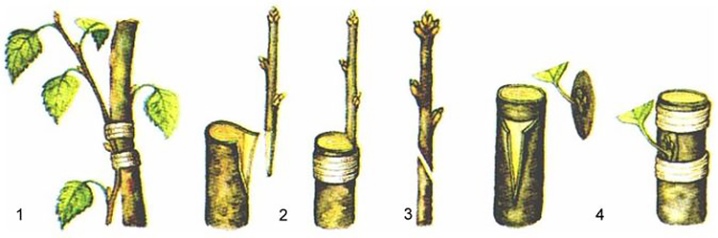
Autumn is a favorable time for the cultivation of gooseberries with lignified cuttings. The ideal time is mid-October, when there is still no extreme cold. It is done in this way.
- Cuttings 15-25 cm long are cut from an adult bush.
- They are cut from above and below at a distance of 2 cm from the lower kidney.
- Rinse in potassium permanganate or other bactericidal solution for disinfection, wash off the composition and wrap it in a cloth or put it in a bag. During the cold season, they are kept in a dark, cool place.
- In February, the cutting is rooted by placing it in water and covering it with a bag.
- When the first roots and leaves appear, the package is removed, and the stalk is planted in a specially prepared mixture, sealing it around the stem. Holes are made in the jar to prevent root decay from excess moisture during watering.
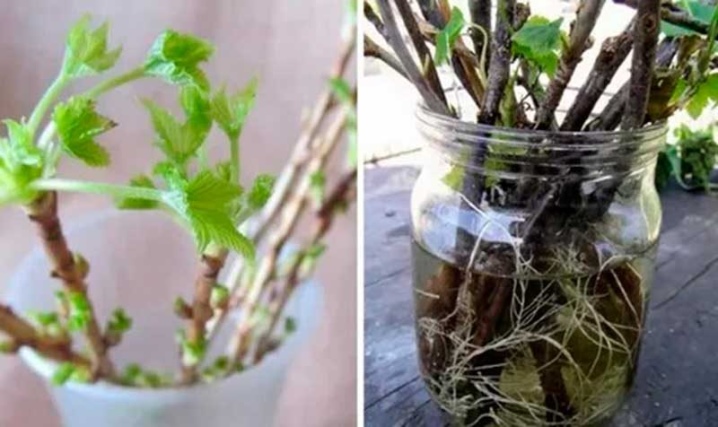

A new shoot is planted in open ground at the end of April. For the successful growth of breeding gooseberries by means of cuttings in the autumn, it is useful and necessary. Seedlings quickly adapt to climatic conditions, easily copes with night temperature fluctuations, with the adverse effects of unstable weather.

Spring. If time has passed, you did not have time to reproduce the shrub in the fall, you can implement the procedure in the spring. The beginning of March is the perfect time to get things done. Scheme of operations:
- cut the cuttings and place them in the refrigerator for 2-3 days in order to adapt to the different temperature parameters of the season;
- prepare the cut material for planting - this event is performed similarly to the propagation of gooseberries in the autumn, excluding planting in a container with earth;
- plant the finished cuttings in open soil.

The preparatory work will take a certain amount of time, during which the right weather will reign for planting cuttings.
Attention! It must be remembered that cutting off the shoots in the spring should be done on time, until the intensive sap flow of the plant begins and the buds swell.

Summer. A good effect is given by cuttings at this time. For the procedure for propagating shrubs using green cuttings in the summer, June or early July is the optimal time. This requires:
- cut a 50-centimeter shoot from the bush;
- remove the leaves from it, keeping the 2 top ones;
- plant it on a fertile, well-lit area, in moist soil with a slight slope;
- cover the shoots with cans to form greenhouse conditions.

In order for the cultivation of shrubs by means of cuttings, hot weather proceeded without any particular difficulties, it is necessary to prevent excessive heating, from time to time open the jars to ventilate the culture.
The shoots overwinter under a warm shelter of dried leaves or rags. They are transplanted to a permanent place in the spring.
Combined
Combined cuttings are the most correct. At the same time, gooseberry stem cuttings give the best results. Seedlings take root quickly and take root well in a permanent place.
The combined method involves the use of planting material obtained from a lignified annual part no more than 3 cm long and a green shoot of this year.
The shrub begins to propagate by the combined method in May and throughout the growing season. There are 3 types of combined planting material.
- With a heel. It is obtained by plucking a green cutting in such a way that a piece of a lignified branch is preserved in its lower part.
- Shank with a crutch. The green shoot is cut with a fragment of last year's branch so that the cut runs along the old shoot.
- With stand. Cut off the branches left over from last year in such a way that the green and lignified shoots are located orthogonally to each other.
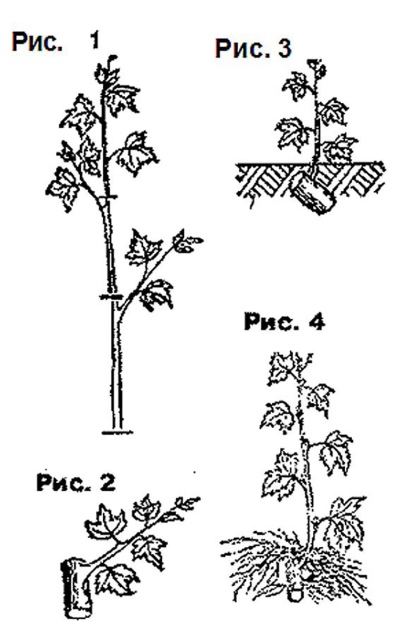
Ready seedlings are soaked for 24 hours in a growth stimulator. Then they are planted, completely deepening the lignified segment and the green shoot by 2-3 cm.
The soil around the seedlings is tamped and covered with mulch, then irrigated with warm water.
How to spread with layering?
A reliable way of growing gooseberries by layering has 3 types, each of which has its own technology.
Horizontal
This is done in October. If it is impossible to implement the process in the autumn, you can transfer it to early spring before bud formation, with well-moistened soil. The procedure is performed according to a strict algorithm:
- a 5- or 6-year-old shrub is selected;
- young branches located at a close distance to the soil are cut off;
- annual increments are cut off by a third;
- the branches are bent to the soil and placed in the grooves made in advance;
- fixed with specialized hooks;
- sprinkled with earth, irrigated and covered with mulch.

After the work done, they must be weeded and fertilized all the time. After some time, the buds on the allotted branches will begin to grow and form vertical processes. The main thing to remember is that when the shoots that have broken through reach 8-10 cm in length, they will begin to need hilling, which should be repeated within 2 weeks.
Reliably rooted shoots in the fall must be separated from the base, dug and cut into segments in proportion to the number of cuttings that have taken root. Plant parts for growing, and plant in open soil in the spring. The method requires some effort and meticulous work.
By the way, it is most suitable for European plant species.
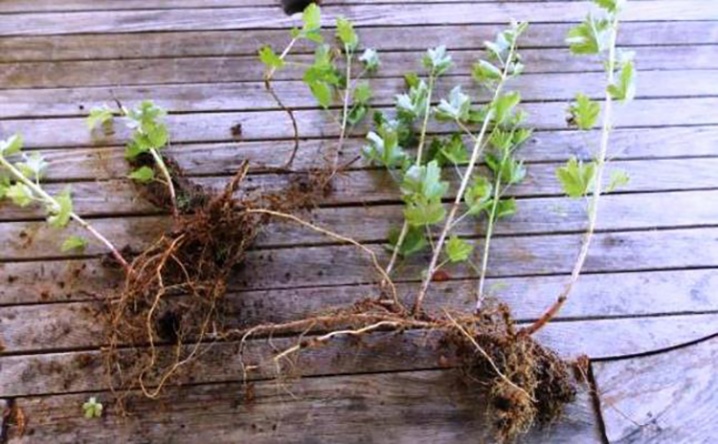

Vertical
When rejuvenating shrubs, the method of vertical layering is practiced. The shrub in the spring during active growth must be dug in with a thin layer of earth.
We irrigate and sprinkle the branches generously. By the fall, many young twigs will form, which are cut off and transplanted to a new place for the development of young bushes.

Arcuate
The formation of roots in arcuate processes often occurs without human intervention. Certain varieties, touching the ground, take root on their own. Such reproduction by bush layering is possible in the summer. The process will be more successful if you help the bush. It is necessary to find the parts that have fallen to the soil, dig a hole under them, fix in it a part of the branch resting in this place, and throw earth with rotted manure.

In the fall, you can dig out the cuttings that have taken root. It is ready to be planted in open soil. Weak sprouts come across. They are sent for growing, and in the spring they are planted in a personal plot.
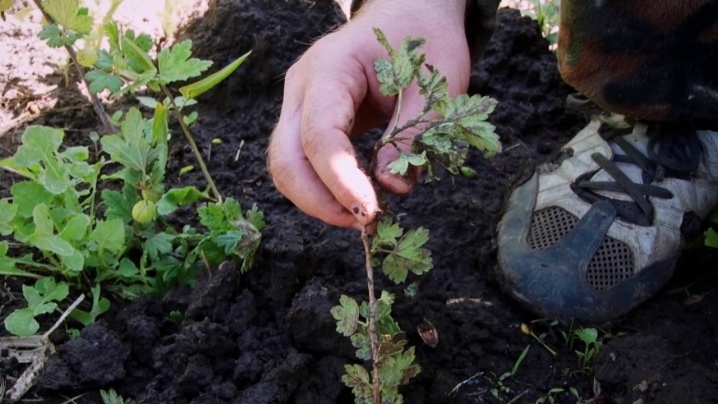
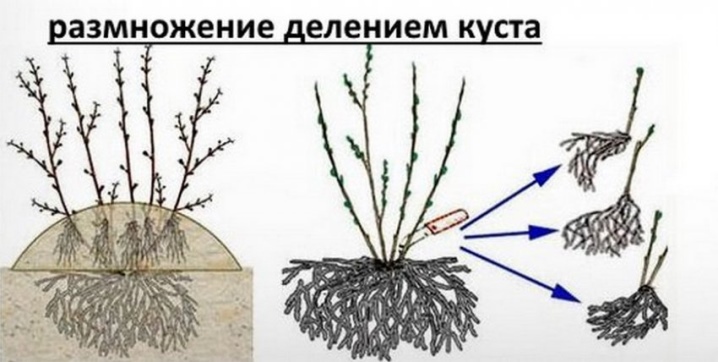
How to plant by dividing a bush?
This method is practiced when it is necessary to change the place of growth of the gooseberry. The branches of the plant, forming, take root near the bush. They turn into planting material.
To create conditions for the normal reproduction of gooseberries through this method, it is necessary in late autumn, when the life process of vegetation freezes, or in early spring, when bud formation is not traced, dig up a bush, divide it,select stronger segments with roots and plant them in loose fertilized soil.
other methods
Graft
Sometimes shrub propagation is used by grafting. Grafted shrubs often produce wild juveniles. With a successful vaccination outcome, a younger generation with improved characteristics can be raised. Gooseberries are usually grafted onto either gold or red currant seedlings.
- Currant seedlings grown by cuttings are planted in pots at the end of the summer season. They are left in the basement for the winter.
- In March, they are brought into a greenhouse and grafted with a copulation technique, which consists in connecting a wedge-shaped cut on a scion with a cone-shaped split on a rootstock and fixing it with soft matter.
- On the gooseberry scion, shoots are born, which are broken off to obtain a dense crown. Shoots also appear on the currant stock, which should be removed.
- The grafted plants are planted in the soil saturated with top dressing.
Seeds
In this way, they seek to create new types of berries. It has a specific sequence:
- the seeds are removed from the unripe brown fruits;
- sprinkle with raw sand and put in a box;
- buried in a hole for the winter;
- in the spring they sow in a greenhouse, sprinkle a bed with a thin layer of peat;
- the appearance of the first leaves means that the plant is ready for transplanting to the garden.

In the summer, they carefully take care of the future berry culture: they often irrigate, fertilize, and loosen the land. In autumn, the bushes that have risen from the seeds are planted in a permanent place.

Finally
The choice of a specific method for breeding gooseberries depends on many conditions - the age of the shrub from which the material for planting is taken, the presence of young 1- or 2-year-old shoots on it, the required number of future seedlings.
Be that as it may, the "donor" plant must be absolutely healthy, without the slightest symptoms of damage by pathogenic fungi, microorganisms, viruses, and insect pests.














The comment was sent successfully.