How to propagate sea buckthorn?
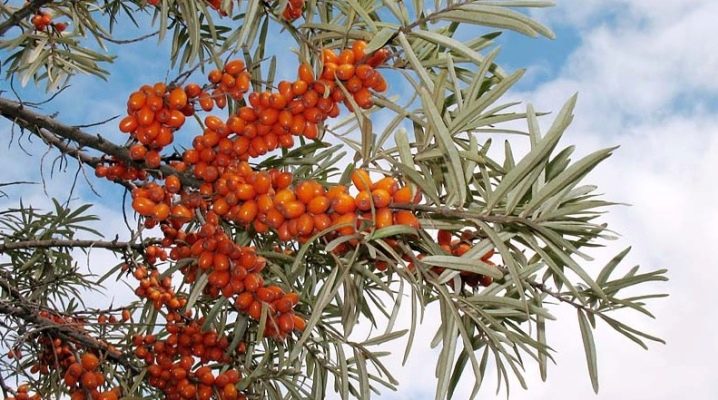

Due to its beneficial properties, sea buckthorn has long gained popularity among gardeners. And breeders are breeding all new varieties of culture. Each gardener can choose a variety based on the characteristics of the soil and climatic conditions in his area. To increase the number of trees on the site, gardeners do not have to buy seedlings at a nursery at high prices; sea buckthorn can be propagated independently using one of the popular methods.

Dividing the bush
It is better to propagate sea buckthorn by dividing the mother bush in early spring, until the trees begin to actively grow. Another option is mid-autumn, after harvest. But you need to be in time before the fall frosts and give enough time for the seedlings to grow stronger before the first wintering.
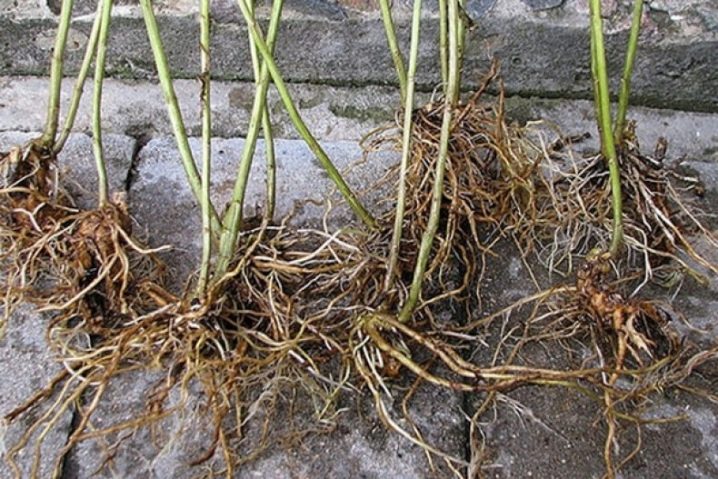

Reproduction by dividing the root system is often used when transplanting an adult sea buckthorn or for tree rejuvenation. The sea buckthorn bush is dug out, carefully freeing the roots from the soil. All old, damaged branches are removed. The root system is also rejuvenated by cutting off old roots. It is best to divide the bush into several parts with a sharp garden pruner or knife.
Each new seedling should have sufficiently developed healthy roots, while young and healthy ones need to be cut and trimmed a little, old and damaged ones must be removed.

Cuttings
To preserve all the qualities of the mother tree during propagation, the propagation method is used. But this method requires patience and certain skills from gardeners. It is often difficult for beginners to comply with all the nuances of cuttings, and the result is zero. Achieving good results from gardeners requires attention to detail, a lot of effort and time.
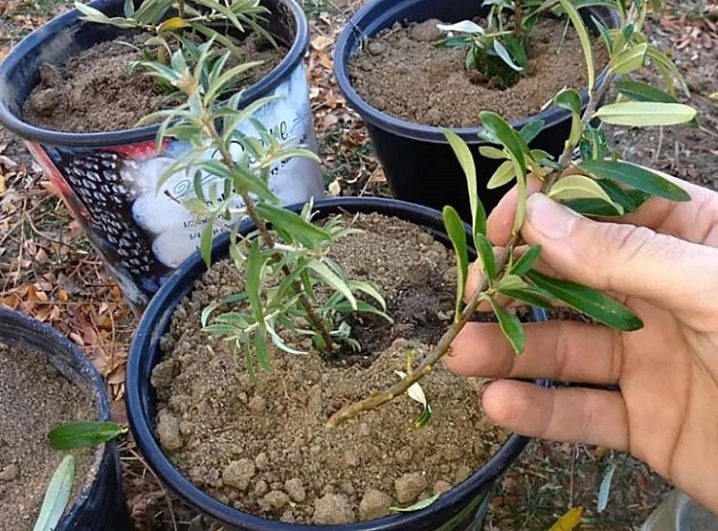

There are two methods of propagation by cuttings: using woody cuttings or green cuttings. Both options are quite effective, provided that the grafting technology is performed correctly.
Lignified cuttings are cut at the end of autumn from healthy mature bushes. The shoots are wrapped in paper or cloth and put away for the winter in a basement, cellar or refrigerator. In spring, the shoots are cut into cuttings 20 cm long. Before planting, the cuttings are placed in a solution with stimulators of growth and formation of the root system. A week later, the buds will begin to swell on the cuttings and the first roots will form. You need to plant the cuttings so that 2-3 buds remain on the surface. After that, they are watered abundantly, and the soil around is sprinkled with peat. Next year, the seedlings will be ready for transplanting to a permanent place.

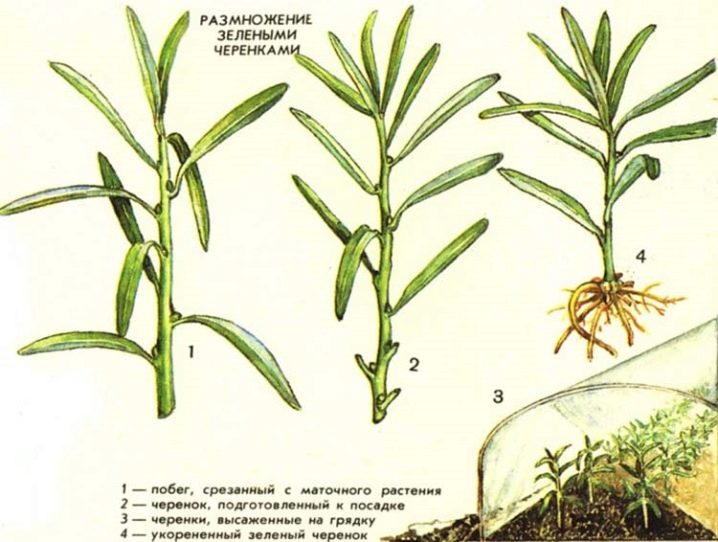
Green cuttings are cut in late spring or even summer, before early July. For cuttings, slightly lignified shoots are suitable (not green, even though this is the name of the cuttings method). Cut the cuttings to a length of a little more than 10 cm. The lower leaves on the cuttings must be removed. The workpieces are placed in a jar or bucket of water (growth stimulants can be added) for 3-4 days. Cuttings are planted in a garden bed at a distance of 6-7 cm from each other. They are grown under a film, often watered and loosened the soil. During the day, the film can be slightly opened for airing.
After it turned out to root the cuttings, the film can be removed. For the winter, young seedlings are covered with fallen leaves and sawdust. In the spring, they can be seated in permanent places. Before planting, it is recommended to treat green cuttings with a solution of potassium permanganate to destroy pathogenic bacteria and fungi (for example, black leg).
Reproduction by green cuttings allows you to preserve the qualities of the mother tree almost completely. But this method is considered more laborious, young seedlings require more attention and care. The seedlings must grow stronger before the onset of cold weather in order to survive the winter.
Propagation by root shoots
This breeding method is suitable for those who want to get a quick result. Young shoots are obtained as a result of trauma to the root system of an adult tree. Often this is done on purpose, inflicting shallow wounds with a shovel blade. Sometimes this happens unintentionally, the sea buckthorn has an extensive root system that takes up a lot of space.
During the growth of the young growth in the first summer, it is necessary to provide appropriate care. The soil should be moistened, and the sprouts should be hilled regularly, providing support for the thin, fragile trunk.
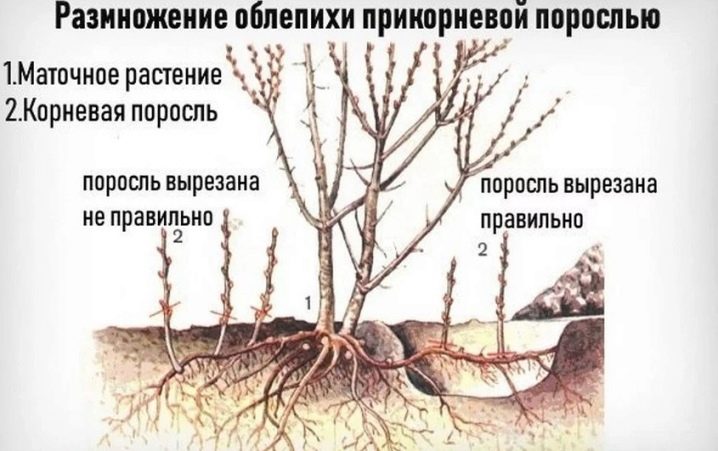
In the second year of life, the shoots can already be separated from the mother tree. The covered roots must be carefully excavated, it is better to do this with your hands. Then release the root system of the young offspring. By the second year of growth, it should form its own small root system. The root coming from the mother bush must be cut with a sharp knife in one motion. It is necessary to separate the root system very carefully so as not to damage the young soft roots. An earthen lump around young roots must be preserved. Now the offspring can be transplanted to a new place. After transplanting, young trees require care, regular watering and feeding.
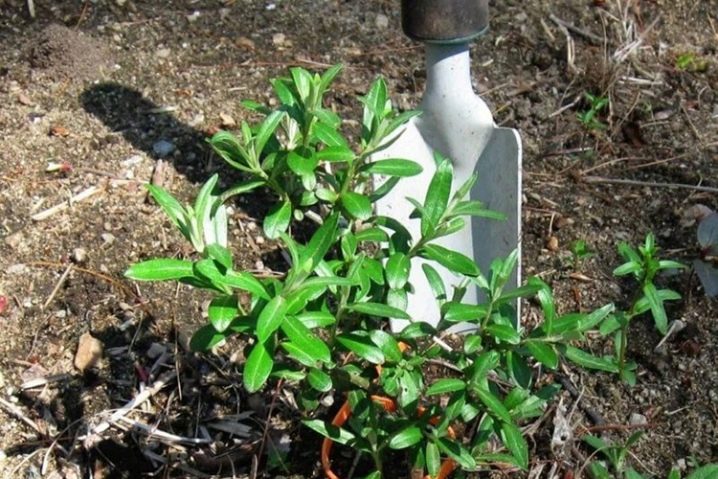

The site for transplanting shoots must be prepared in advance. In the fall, it is necessary to enrich the selected place with humus and dig up the soil. In the spring, they dig it up again before planting seedlings.
The offspring do not always receive all the qualities of the mother tree. And if the parent bush was grown from a grafted cuttings, then the roots may turn out to be an offspring of a completely different variety. Another significant drawback of this propagation method is damage to the vegetative system of the parent bush. To inflict the least damage on a tree, shoots are formed at a distance of more than 1 meter from it. The root system of sea buckthorn is extensive, so choosing the best place at a sufficient distance is not difficult.
It should be borne in mind that some varieties (especially artificially bred ones) do not give growth, and the method of reproduction by offspring is impossible.
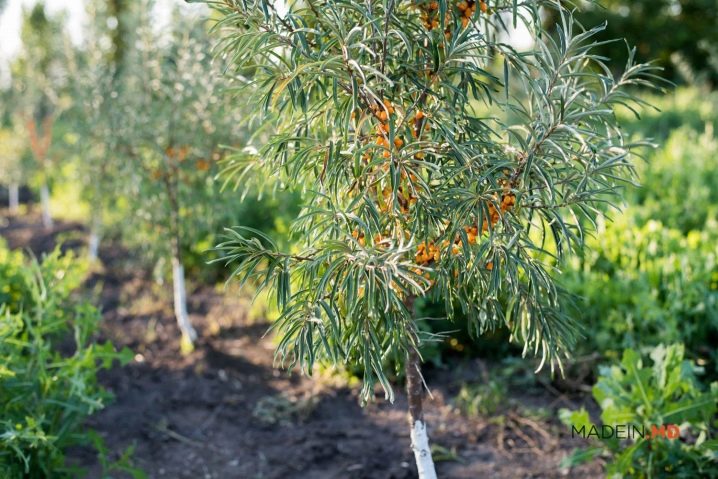

other methods
There are other breeding methods for sea buckthorn. They are suitable for both beginners and experienced gardeners. When breeding, do not forget that sea buckthorn is a dioecious crop; there should be at least two trees on the site (male and female). Only female bushes bear fruit. It is possible to find out the floor of a seedling only for 4-5 years, when it begins to bloom. When propagating, it is necessary to take this factor into account and propagate trees of both sexes. The following two methods are suitable for almost all known sea buckthorn varieties.
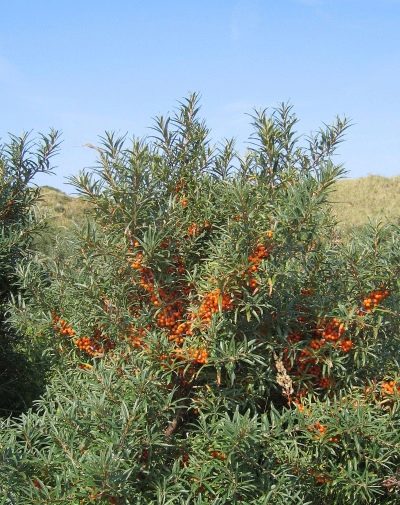

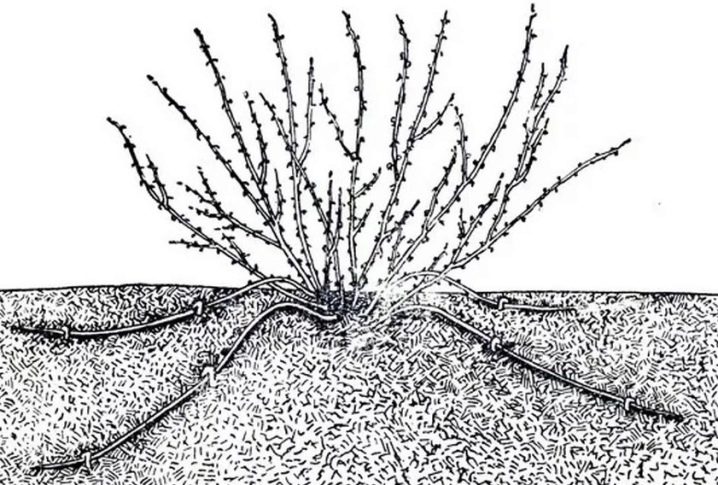
Layers
With this method of reproduction, the new tree receives all the qualitative characteristics of the mother bush. This method requires a young, healthy shrub with young flexible shoots. First, you need to dig up the soil around it, shed well and fertilize. Then the lower flexible shoots are tilted and pinned to the ground with a wire, leaving the tip free. Shoots are buried in earth with humus and watered abundantly.
All summer you need to make sure that the soil is moistened. By the fall, the cuttings will form their own root system. For the winter, they need to be covered with fallen leaves or sawdust. In the spring, the layers are separated from the mother tree and transplanted to a permanent place. It is necessary to transplant layers very carefully so as not to damage only the formed root system.
This method has one significant drawback - the exposure of the lower part of the mother bush.
Seeds
With seed propagation, new trees do not inherit all the qualities of the mother variety, but maternal diseases are not transmitted through seeds either. This method takes a long time, and the result may not be what you expect. One cannot be sure exactly which variety will grow from a seed. The berries may be small or too sour. Or the branches will be covered with long sharp thorns, and the berries will be impossible to pick. But sometimes seed propagation is the only option for getting new trees.
There are sea buckthorn varieties that do not reproduce by offspring and layering, and only sufficiently mature healthy trees can be divided. Cutting is also not always possible, so the seed propagation method may be the only one.
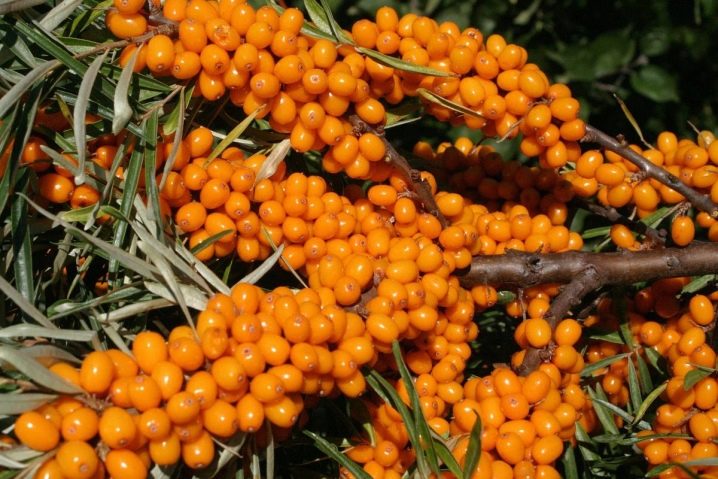

Seed material for growing sea buckthorn can be purchased in specialized stores or collected by yourself. To do this, ripe berries are rubbed through a sieve, freeing the seeds from pulp and juice. Then they are thoroughly washed with running water and dried. You need to store ready-made dry seeds in a cloth (canvas) or paper bag. In a dry, dark and warm place, they are stored for up to 3 years, retaining their germination capacity.
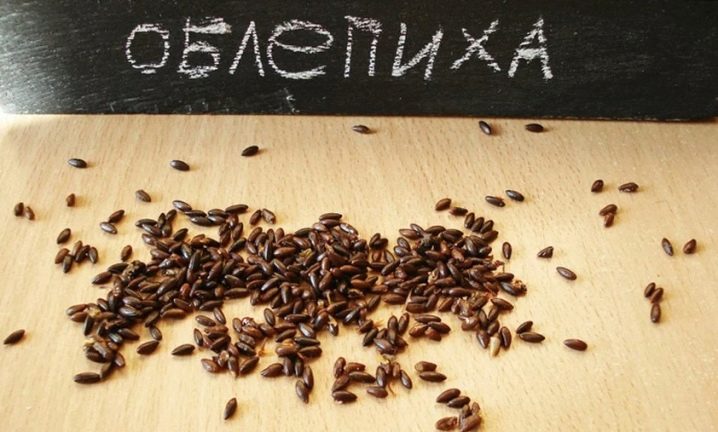

Before sowing, the seeds are usually soaked for 3-4 days in hot water, then dried. On the 5-6th day, they should germinate, if this has not happened, most likely the seeds are spoiled. Some gardeners sow dry seeds in wet sand, place a container with sand in the refrigerator. It is necessary to ensure that the sand always remains wet, every two weeks the sand with seeds is mixed. The first shoots should appear in a month.
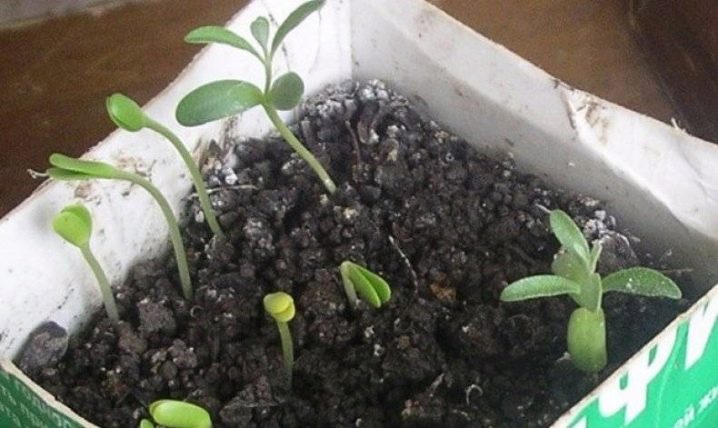

Sprouted seeds are planted in the ground in spring, when the soil has already warmed up. The first month the garden bed should be watered abundantly. During this period, the first seedlings should appear. For better growth, you can use a greenhouse or cover the seedlings with separate containers, periodically airing the bed.
Sea buckthorn seeds can be sown in late autumn, late October - early November. The first shoots will appear in early April.
Sowing at an earlier date is not recommended, the seeds may begin to germinate before the onset of cold weather and die.
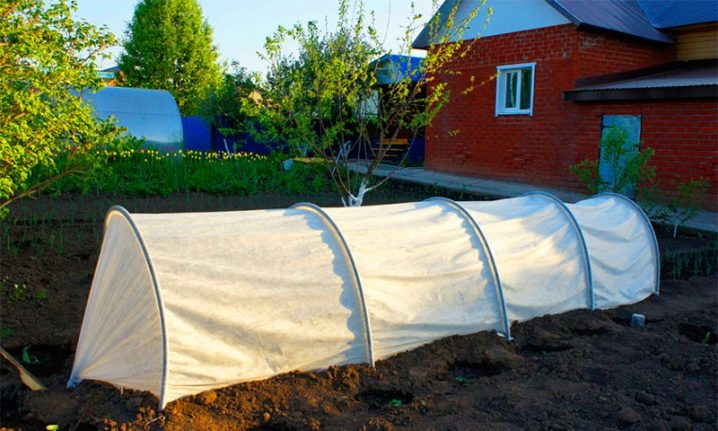

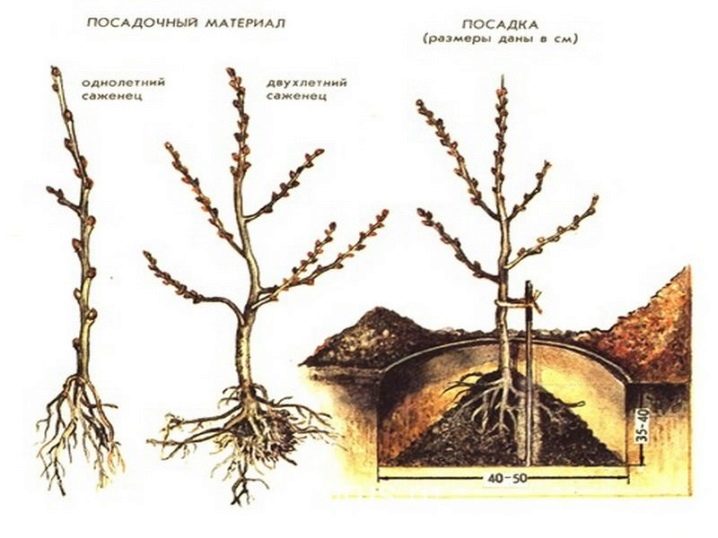
After the appearance of the first 2-3 leaves, it is necessary to thin out, leaving about 3-4 cm between the shoots. After the appearance of the 5th pair of leaves, thinning is repeated, leaving about 10 cm between the plants. After that, you can make a dive, only once, in the future it will not be required. So sea buckthorn seedlings will grow for 2 years. In summer, in hot weather, they require abundant and regular watering, and in the spring - feeding with organic fertilizers. During this time, they should reach 40-50 cm in height, and the trunk should be at least 5 mm in thickness. They are now ready to be transplanted to their permanent location.
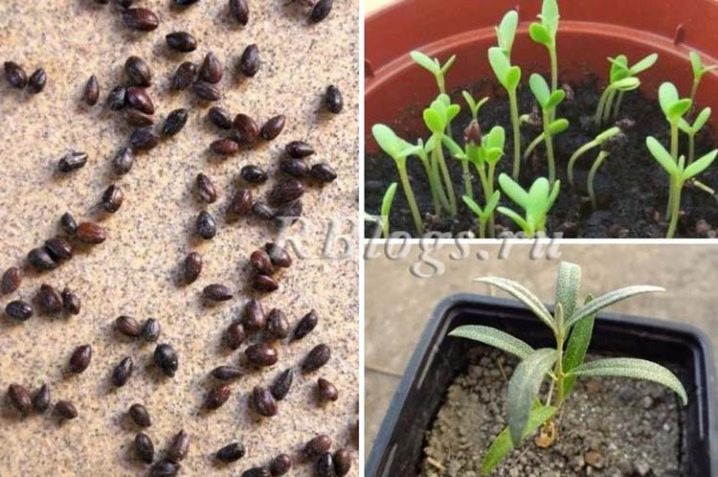

Seedlings are transplanted both in spring and autumn. In either case, the hole must be prepared in advance. In a hole about 50 cm deep, sand and compost are poured in equal parts and sprinkled with a fertile layer of soil. If desired, you can add ash and superphosphate in small amounts. Seedlings are transplanted with a clod of earth around the root system. The seedling is covered with soil so that the root collar looks out 5-7 cm from the ground. After planting, the seedlings are watered abundantly, then the soil is mulched.
After planting, the first 3 years of seedlings require regular watering, the soil should be slightly moist. But don't let the water stagnate. You do not need to fertilize the seedlings. Pests love to feast on young foliage and shoots, trees must be sprayed for preventive purposes. For this, both special chemicals and folk recipes are suitable. In spring and autumn, they must be pruned, form the correct beautiful crown. At 4 years old, the tree should begin to bear fruit.











The comment was sent successfully.