All about mint and its cultivation
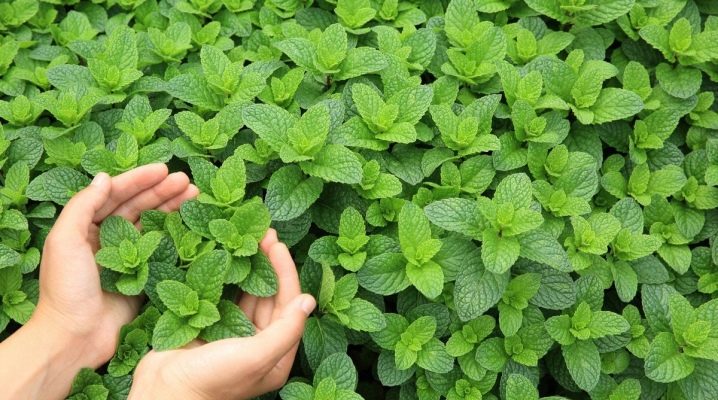

Mint is not only a beautiful but also a very useful plant. Therefore, people are happy to grow it both in the garden or in the garden, and on the windowsill.

Description
Mint is a perennial herb. She belongs to the Lamiaceae family. The plant grows well in both cold regions and warm ones. It is considered to be quite unpretentious. Therefore, even novice gardeners can plant it on their site.
Mint has a voluminous branchy rhizome. It grows rapidly. Therefore, mint often captures large territories, displacing its neighbors. The stem of such plants is hollow, covered with short down on top. In height, mint grows up to 40-60 centimeters. The leaves of the plant are elongated. Their front side is darker and the back is lighter.
The plant blooms throughout the summer. At this time, mint looks especially beautiful. Its inflorescences are composed of small lilac flowers. After the end of flowering, fruits appear on the plants.

Views
There are several main varieties of mint in nature. Each of them has its own characteristics.
- Garden. Such plants grow up to a meter in height. Branched and large bushes look beautiful anywhere. The fermented garden mint foliage is suitable for making non-alcoholic cocktails and teas. Drinks from such raw materials are aromatic and pleasant to the taste.

- Curly. This plant has good frost resistance. Therefore, it is often planted in cold regions. It is very easy to recognize such a mint: its foliage is curly and very bright. It is actively used in cooking and traditional medicine.
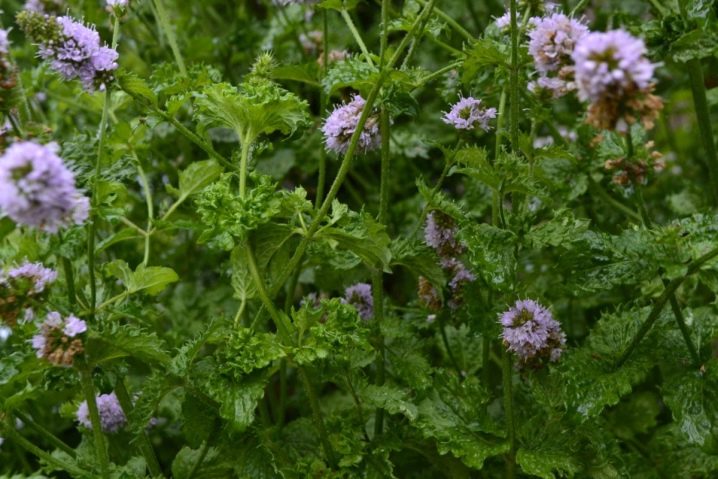

- Apple. Perennial apple mint has a small bush size. Its foliage is velvety and not very fragrant. It can be used to prepare drinks and desserts as well as main courses.
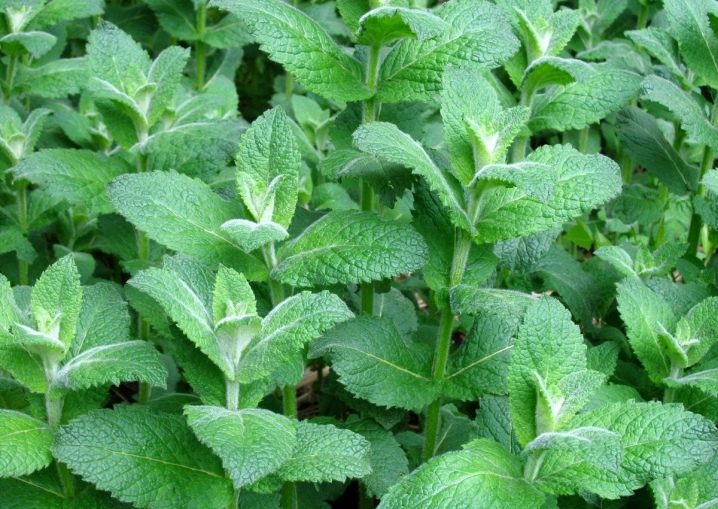

- Long-leaved. This plant grows up to one and a half meters in height. The color of the leaf blades is dark green. Their smell is delicate and very light. Long-leaved mint leaves can be added to the marinade when preserving vegetables.
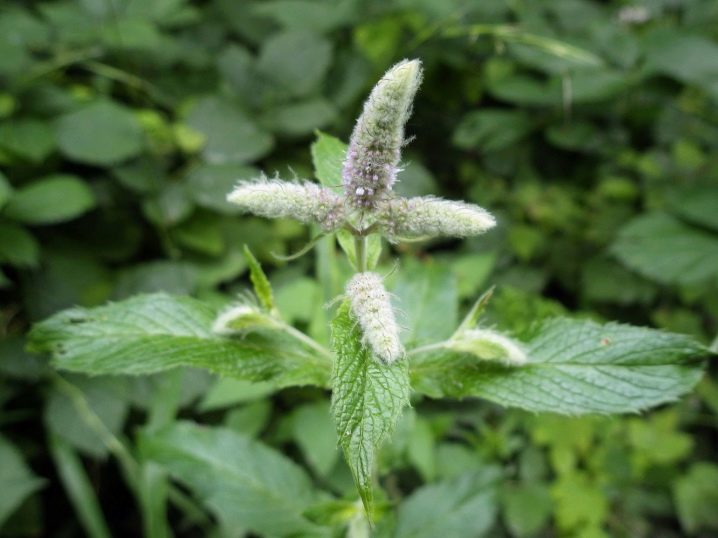

- Field. This type of mint is also called deaf or wild. The plant is common in nature. The foliage of such mint does not have a strong aroma. In dried form, it is used for cooking dishes and decoctions.
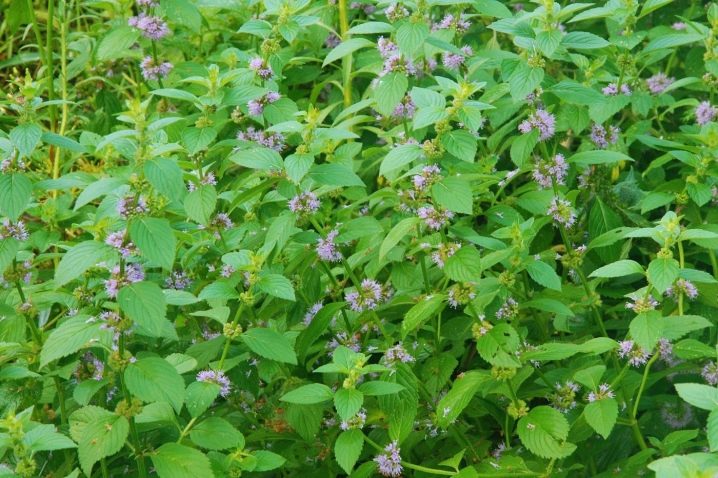

- Lemon. This mint is very often grown on windowsills. This plant variety is also called lemon balm. Mint has neat, rounded leaves. Their front surface is dark green, and the wrong side is lighter. The smell of such leaves is mint-lemon.
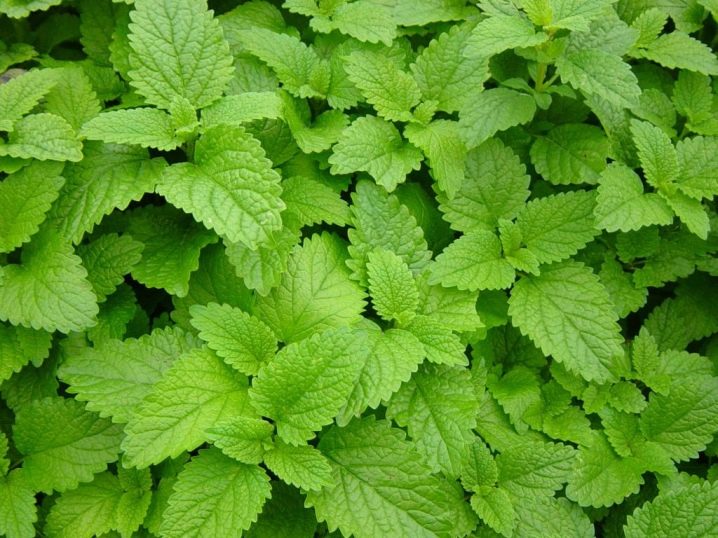

- Fragrant. This variety of mint can grow up to 40-80 centimeters in height. She has wrinkled leaf plates of a dark green color. The edges of the sheets are light colored. All parts of the plant are characterized by a light and unobtrusive aroma.
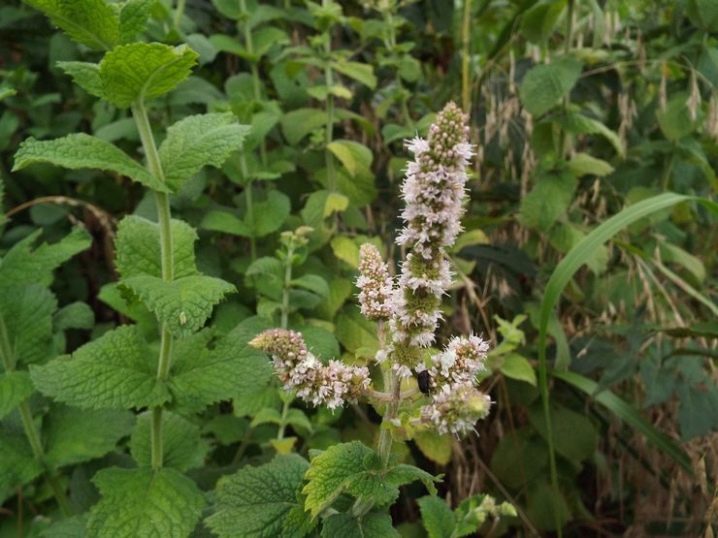

- Pepper. This is the most common type of mint. It is grown on an industrial scale and is actively used for the preparation of various dishes, as well as the manufacture of cosmetics.
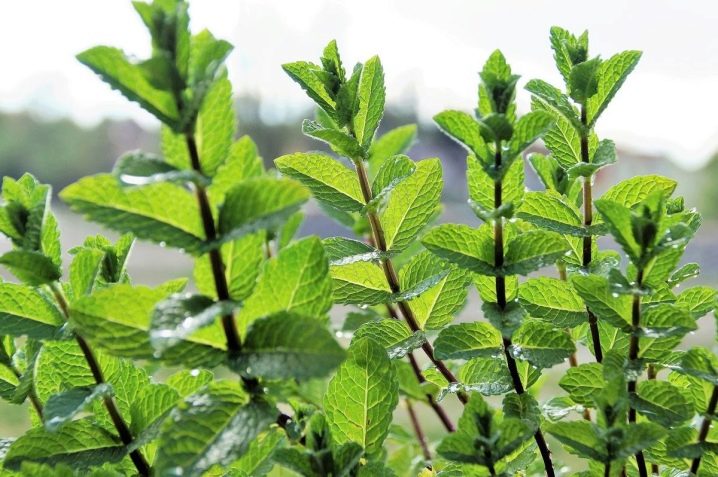

Several different types of mint can be grown in the same area. They go well with each other.
Landing
You can plant mint in both spring and summer. Potted plants can be found at most gardening stores. It is worth choosing healthy specimens without dried or damaged foliage.
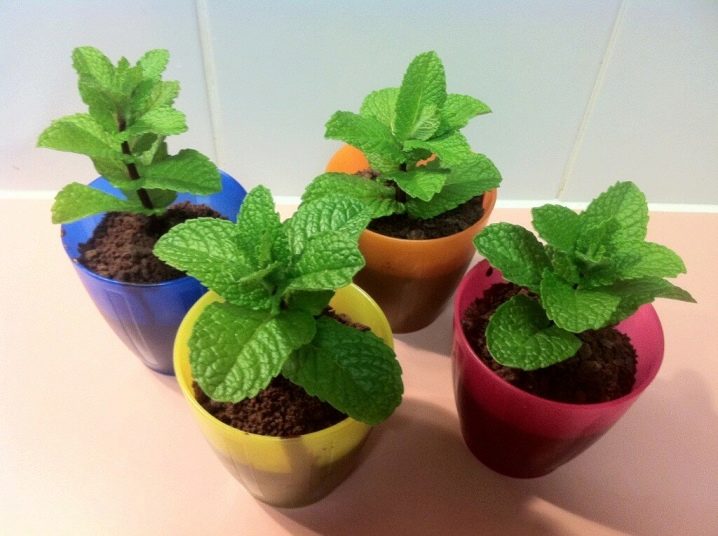

When transplanting plants into open ground, the following points should be considered.
- Soil quality. Mint grows best in areas with loose, moist soil. Acidic and swampy soil is not suitable for planting green plants: the bushes on it will grow small and weak.
- Illumination. It is recommended to grow mint in the sun. It is in open areas that it grows fastest. If you can't find a suitable place in the country, the seedlings can be placed in the shade. Mint grows well next to apple, pear and other fruit trees.
- Neighborhood. The aromatic perennial mint works best with other herbs. The main thing is that the plants have already had time to take root by the time the young seedlings are planted. Otherwise, it will crowd out its neighbors. Mint beds can also be placed next to cabbage or tomatoes.
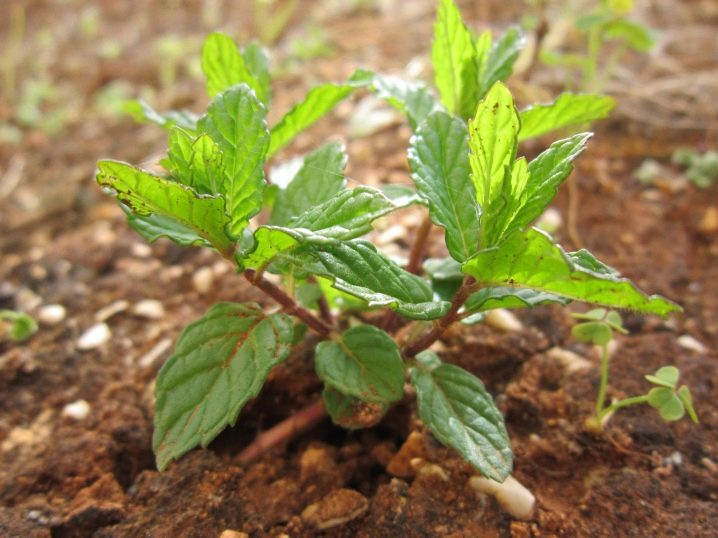

It is recommended to plant plants in rows. The distance between them should be within 30 centimeters. It is also worth leaving spaces between individual plants. Mint grows very quickly. Therefore, the free space will soon be filled with greenery.
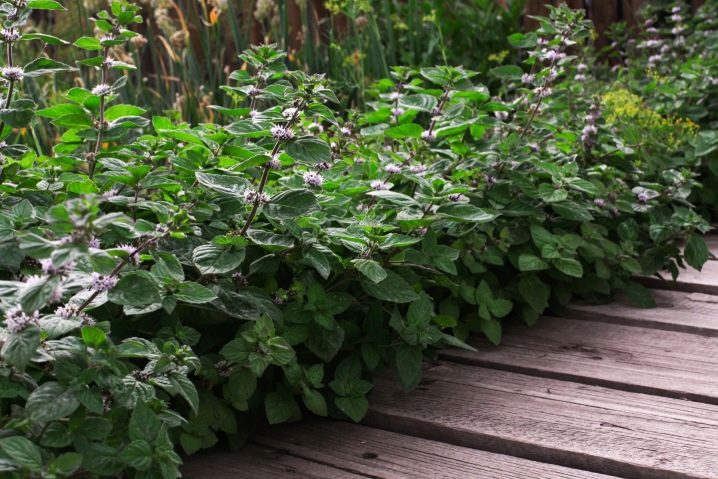

About two weeks after planting the plants in open ground, the gardener can pinch their tops. In this case, the bushes will grow short and dense.
Care
Growing mint on your property is a fairly simple process.
Watering
Only young seedlings or plants that have recently been transplanted to another place need regular watering. Adult mint is watered only in the heat.
For irrigation of the bushes, it is worth using warm, settled water. It is recommended to water the plants in the evening. After this agrotechnical measure, it is recommended to loosen the soil next to the stems. In this case, a dense crust will not form on the site. It is also important to remove all weeds in the process, because they take a lot of nutrients from the soil.

Top dressing
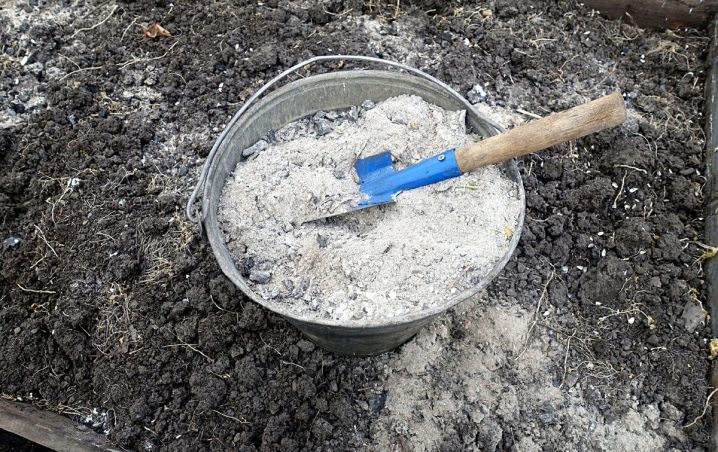
Fragrant mint is fed only once a season. They do it in the spring. At this time, wood ash is usually embedded in the soil. Instead, the soil next to the plant stems can be covered with a layer of compost or peat. This mulch will protect plants from weeds. Besides, peppermint will get its nutrients from organic produce over time.
Bushes that do not grow in the garden, but on the windowsill, are also recommended to be fed in the spring. You need to use complex mineral fertilizers for this purpose. It is worth adding them to the soil in liquid form. Top dressing of room mint is usually combined with watering.

Reproduction
There are three main breeding methods for mint.
Seeds
This method is suitable for non-hybrid varieties. The seeds can be planted both in open ground and in containers. The second method is most often used by residents of cold regions. The process of growing seedlings consists of the following steps.
- To begin with, the seeds collected at home must be sorted out. They must be healthy. Specimens with traces of mold or rot must be disposed of.
- The planting material is placed in a container with a substrate. Sprinkle the seeds on top with a thin layer of soil.
- Next, the ground is gently sprayed with warm water. After that, the containers are covered with a transparent film and sent to a warm and well-lit place.
- After the first seedlings appear, the shelter must be removed. When the mint grows a little, it can be transplanted to a permanent place in the vegetable garden or garden.
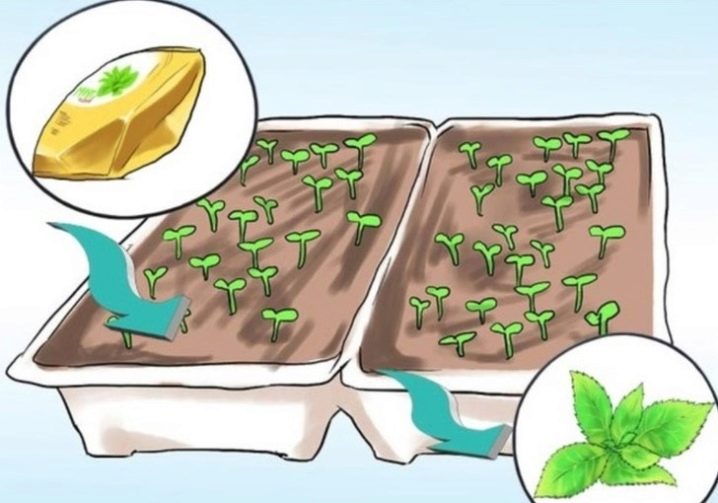
Plants are planted in open ground in mid-spring. You can grow fragrant healthy mint from seedlings in a couple of weeks.
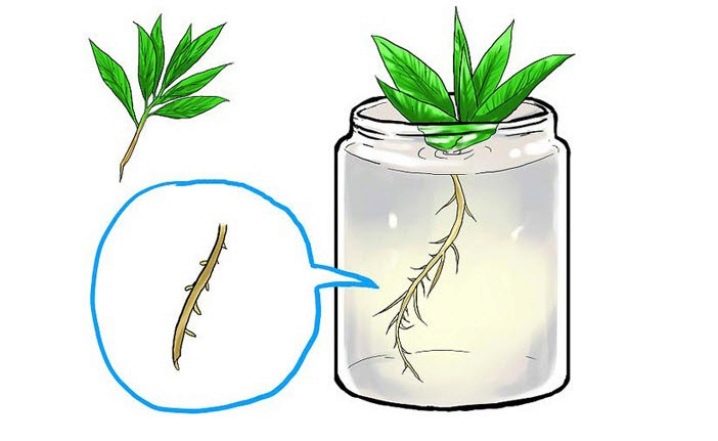
Cuttings
A more popular breeding method for mint is cuttings. For plant breeding, the bushes must be carefully trimmed with sharp scissors. Each of the cuttings should have about 5 sheets.
The cut off shoots are placed in jars of water. Each stalk should be in a separate container. After a week, short roots will appear at the edge of each shoot. At this stage, the plants can be rooted.
Prepared cuttings are planted at a distance of 20-30 centimeters.They are looked after in the same way as for ordinary young seedlings.
For propagation of mint by cuttings, you can even use shoots bought in the supermarket or on the market. The main thing is that they are fresh and healthy.
By dividing the bush
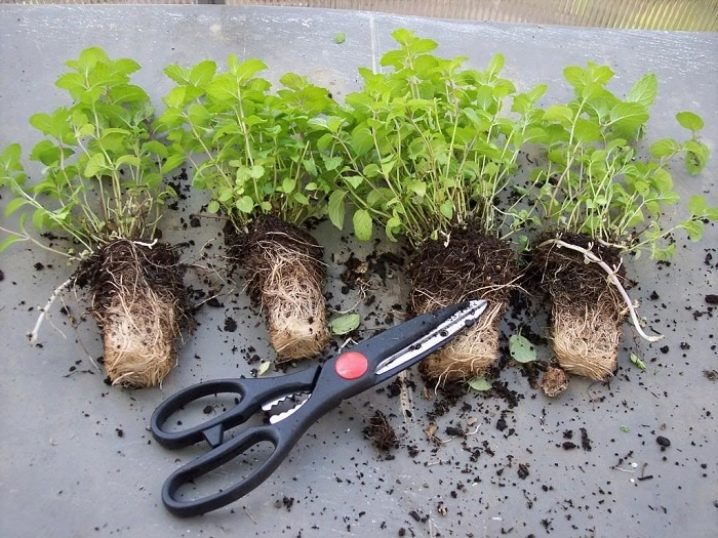
Mint propagates by dividing the bush. This method is suitable for plants over three years old. It is necessary to deal with dividing the bush in the second half of spring.
The plant must be dug out, being careful not to damage the rhizome. Then the bush must be divided into several parts. Separate bushes need to be planted. Usually delenki are located on different sides of the site. You need to take care of them in the same way as for ordinary adult plants.
In general, it is quite easy to breed mint on your site. The plant takes root very quickly and easily captures new territory.

Diseases and pests
Mint is one of those plants that do not get sick very often. But if the conditions for growing the bushes were not very suitable, then gardeners may face the following diseases.
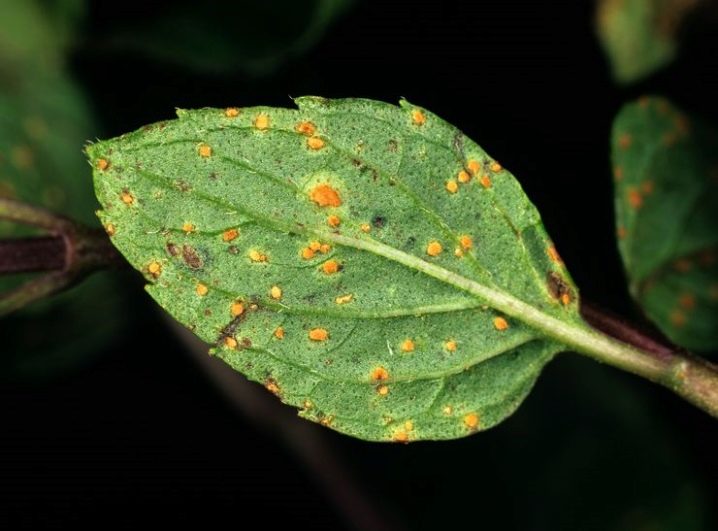
- Rust. This is the most dangerous disease that affects mint. It develops in conditions of high humidity and sudden changes in temperature. The foliage of the affected plants from the inside is covered with voluminous auburn spots. Over time, the bushes weaken, and then completely die. Diseased plants must be dug up and destroyed. After that, the site should be treated with herbicides.

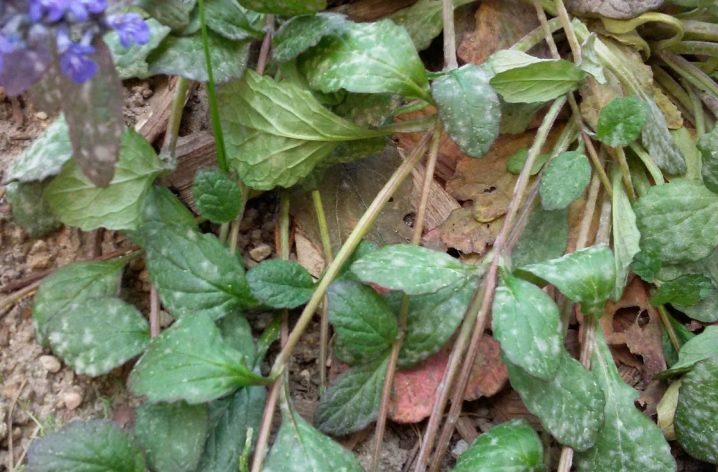
- Powdery mildew. This disease affects green bushes in the second half of summer. The foliage of diseased plants is covered with a whitish bloom. Usually, the development of this ailment is provoked by cold and high humidity. For its treatment it is worth using "Vitaros" or similar drugs.

- Dry rot. This fungal disease develops in dry and hot weather. The lower part of the stem darkens. At the same time, the mint dries up and stops growing. At the first signs of the disease, the bushes must be treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
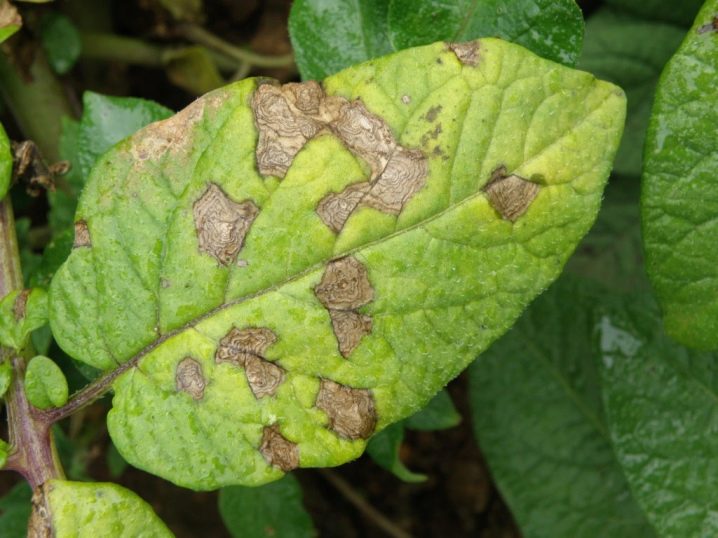

- Brown spotting. This disease is also fungal. Infected plants become covered with brownish spots, which further only increase in size. Proven fungicides are used to combat brown spotting.
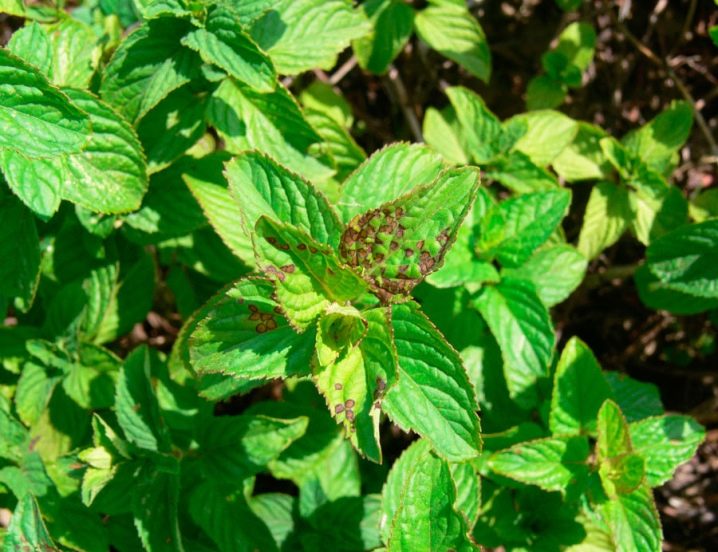

- White spot. This disease is also called septoria. A sign of its development is light-colored spots that can be seen on the lower leaves of the mint. To combat spotting, a drug called "Energy" is used.

It is necessary to process not only plants, but also the soil around them.
Often, mint is also affected by various pests.
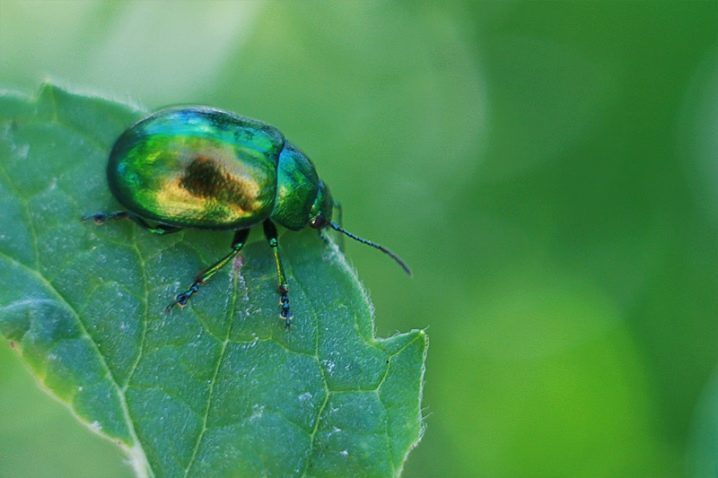
- Mint flea. These small bugs with a yellow body color are very difficult to spot. They gnaw neat round holes in the foliage. They are most commonly found on mint foliage in the spring.

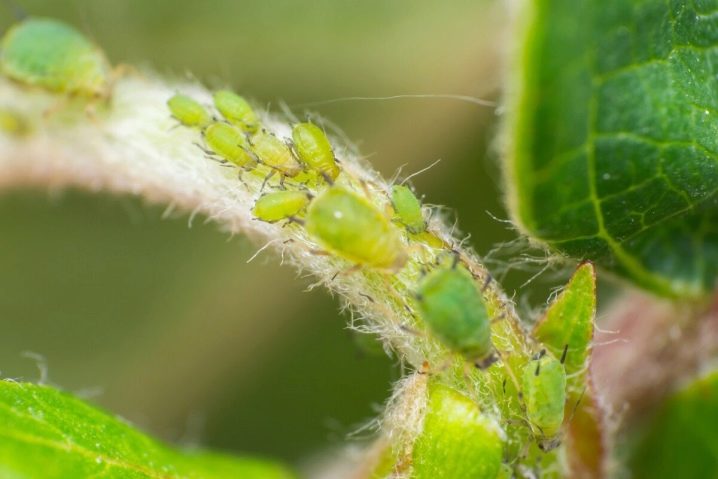
- Aphid. This pest is dangerous to almost all plants in the garden and in the garden. Insects suck sap from foliage. This leads to a slowdown in the growth and development of the bushes. In addition, aphids are the spread of many viral diseases. Therefore, having noticed small insects on the surface of the leaves, you must immediately get rid of them.

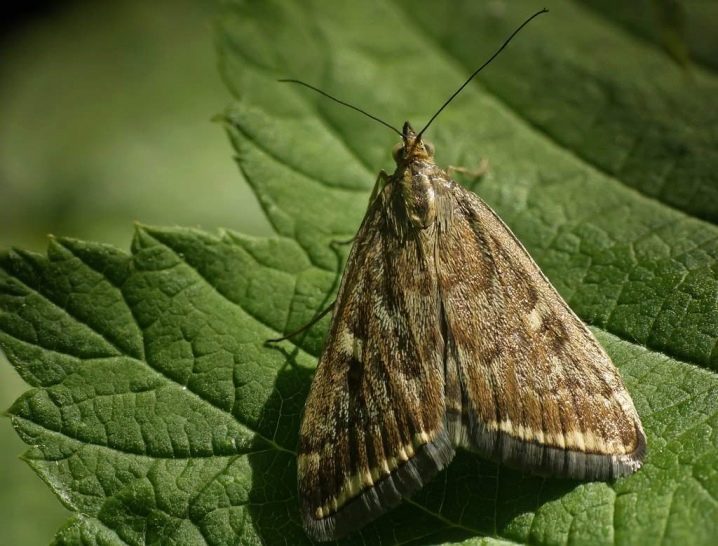
- Meadow moth. A group of such insects can completely destroy the mint bush. Such pests are activated at the end of the summer period. It is rather difficult to notice them. Therefore, you need to pay attention to the general condition of the plants. If the foliage is covered with small holes and seems lethargic, then the bush has been affected by pests.

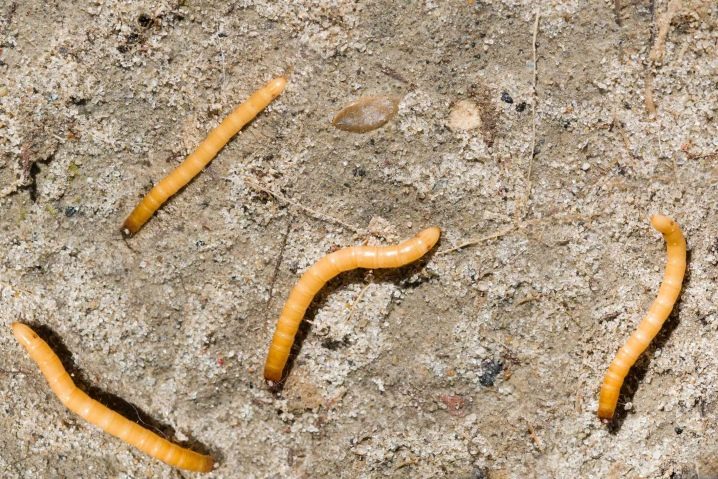
- Wireworm. If the mint beds are next to potatoes, wireworms can attack the greens. Such pests gnaw at the roots of plants. This leads to their rapid death. You can notice the wireworm while loosening the soil.

To prevent all these pests from attacking mint bushes, gardeners need to observe crop rotation. In the fall, the site must be cleared of plant debris and dug up. If the pests still covet the mint bushes, you should try to get rid of them using folk methods.For the treatment of plants, an infusion of celandine or other aromatic plants is usually used.
If a natural remedy doesn't work, use a proven insecticide to spray the mint. This should only be done if the foliage of green plants will not be used in cooking.

In general, if properly cared for, mint will adorn the chosen area for many years. Therefore, it is quite profitable to grow it near the house.













The comment was sent successfully.