What does powdery mildew look like on roses and how to treat it?
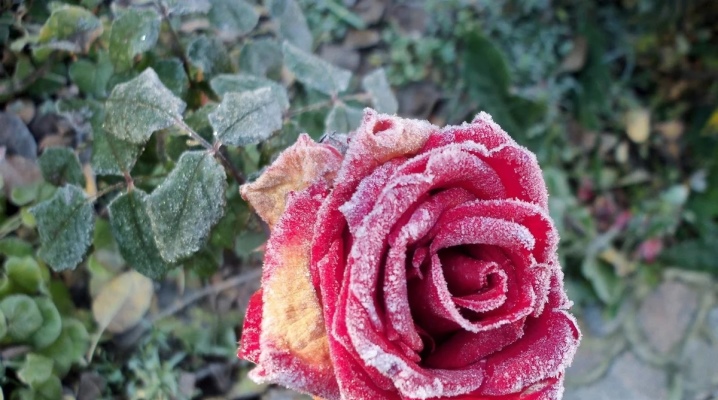

Powdery mildew, also called "linen", "ash", is a fungal disease that gardeners and lovers of indoor plants are familiar with firsthand. It never goes away on its own - it is necessary to take measures to eliminate it, and the faster the better, since the infected plant withers and dies very quickly.
Today we will talk about what powdery mildew looks like on roses, where it comes from and how to get rid of it.
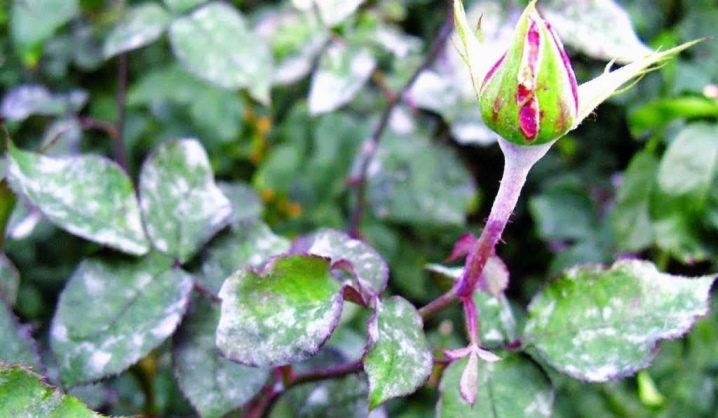

Description
The appearance of powdery mildew on plants is associated with the parasitization of microscopic ectoparasitic fungi from the order of Erysiphase, or powdery mildew (Erysiphales). The rose, which this ailment has chosen as its victim, looks like this:
- stems and shoots stop developing;
- the leaves become coarse and black;
- the buds are deprived of their decorative properties, they are deformed.
In addition to losing its attractive appearance, the rose also loses its immunity, it ceases to normally perceive and tolerate temperature fluctuations - the overwhelming majority of flowers, being infected with ash, die immediately when cold weather sets in, and there is no question of normal wintering.
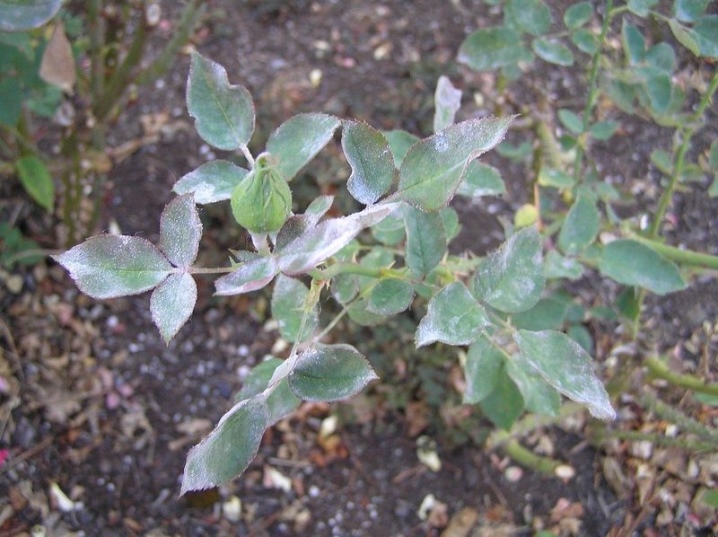

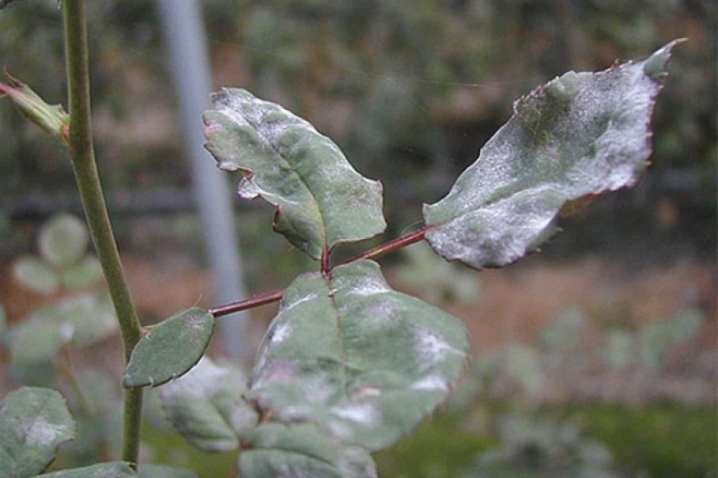
It is quite easy to recognize powdery mildew on roses. If you see that the plant seems to cover a dirty gray coating, similar to flour, you should know that this is the very powdery mildew. In the process of maturation of the spores, it looks like this, and after that small droplets of moisture (dew) appear on them. If an ailment struck a rose in June, then in the absence of proper treatment by the end of August, it will be completely covered with ripe brown spores and will die in the fall.
I would like to note one important thing: the same diseases are characteristic of the climbing rose, and for the bush garden, and for the room. Species with more delicate foliage - tea and hybrid tea - are especially affected.

How does powdery mildew affect the plant?
Plaque resulting from the growth of mycelium covers the stems, peduncles, buds, petals and leaves, hiding them from ultraviolet radiation and interfering with photosynthesis. A rose that is sick ceases to accumulate nutrients, its growth slows down, and then stops altogether.
All affected parts are bent, deformed, disfiguring a beautiful flower.

Reasons for the appearance
The most important cause of powdery mildew on a rose is the overwintering of fungal spores around the plant. Here's where they tend to hide:
- in the soil;
- in plant remains;
- on diseased seedlings;
- on dirty garden tools;
- in neighboring areas.
In the spring, the spores of the fungus are released and infect the plants again.
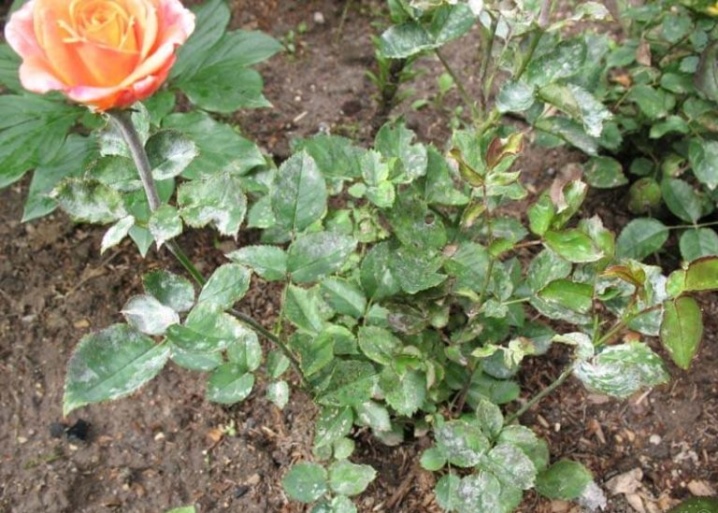

There are also some natural factors that contribute to the spread of this disease.
- High air humidity (60–80% in the absence of precipitation). The underlying cause of the appearance, growth and spread of a pathogenic fungus.
- Sharp jumps in day and night air temperature... In general, temperatures from +5 to +28 degrees Celsius are favorable for the formation of conidia, but mass development occurs at + 20 ° C.
- Cold summer rain can provoke the emergence of more than just ash, but also other fungal diseases.
- Excess nitrogen in the soil, because of which the rose does not have time to grow and strengthen its immune system, but only grows, forming young shoots. The latter, due to its vulnerability, is quickly affected by powdery mildew.
- Wrong irrigation schedule: their excess or lack.
- Density of plantings. Well, everything is very clear here: if the rose bushes grow side by side, and one of them gets sick, then don't go to the fortuneteller - soon the whole plot will get sick.
- If you do not huddle the soil around the plants and do not weed out, it also becomes a risk factor for contamination of crops with powdery mildew.

Control measures
It is possible and necessary to deal with the ashes on the roses, but it is better to do this when the first signs of the disease are detected.
It is useless to treat a plant completely covered with ripe spores.
Chemicals
The most effective treatment is to treat rose bushes with chemicals, namely fungicides, which suppress and destroy fungal infections. You can save the plant with the following drugs.
- "Triadimefon" ("Bayleton") Is a systemic fungicide, the action of which is aimed at protecting the flower, as well as at its treatment. With its help, it is possible to suppress an incipient disease, to stop a fully developed disease.

- "But" - a one-component fungicidal preparation, which contains trifloxystrobin, which fixes the agent on the surface of leaves, buds and stems of the plant. Rose protection continues even in bad weather. The active substance of the drug by suppressing the mitochondrial respiration of the fungus leads to a cessation of its development and death.

- "Quadris"... It is highly effective in the fight against powdery mildew due to deep penetration into the tissues of leaves and stems - this helps to extend the exposure time and reduce dependence on the vagaries of the weather. Destroys fungal spores.
- "Rayok" - systemic fungicidal preparation of prolonged action. Its active ingredient, difenoconazole, disrupts the biosynthesis of sterols in the body of fungi. Because of this, the processes of elongation of growth tubes, cell division are suppressed and the growth of the mycelium stops.
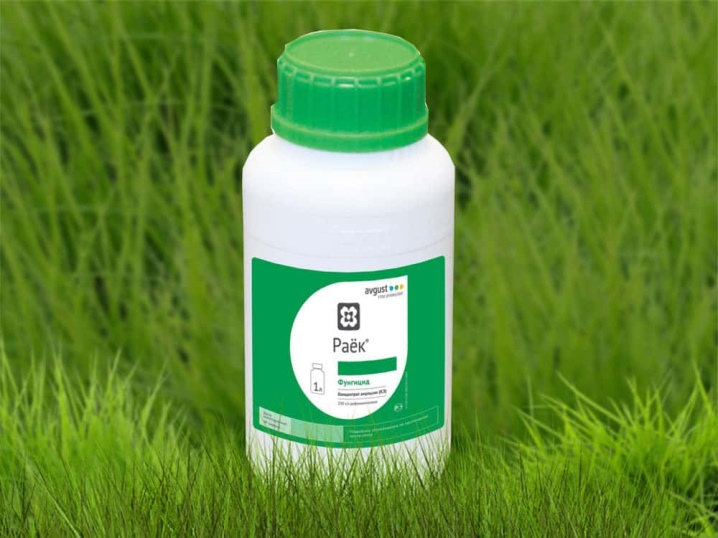

- "Speed"... It is intended for the prevention and treatment of powdery mildew on many plants, both garden and indoor. However, if you see already ripe spores, do not use this drug - here it will be powerless.

- Tilt. Refers to systemic fungicidal agents with prolonged action. Used to protect and prevent disease. Stops the further development of pathogenic microorganisms by suppressing the formation of spores.

- "Topaz". It is used for the prevention and treatment of powdery mildew on roses. It helps to stop the growth of mycelium within a couple of hours after processing the bush.
Penetrates deep into the plant, eliminating the risk of washing away in inclement weather.

- "Tiovit Jet"... Fungicide-acaricide. Its active ingredient is sulfur, due to which the vital processes of harmful microorganisms are disrupted. The drug is perfect for soil disinfection.

- Fundazim. Broad spectrum fungicide. Heals, protects and heals plants. Resistant to water washout.

- Fundazol. Fungicidal agent of systemic contact action. It affects the fungus in the following way: it disrupts the division of cell nuclei, due to which the reproductive function of the microorganism is suspended. "Fundazol" can be used to treat seed material, foliage and rose stems.

- Fitosporin. Natural biofungicidal preparation. The main active substance is the live spore-forming bacteria Bacillus subtilis strain 26D. They are activated after application of the product and begin to actively eat, releasing waste products and thereby suppressing the spores of the harmful fungus. Plant immunity increases. "Fitosporin", enriched with humic bioactive fertilizer GUMI (this is indicated on the package of the preparation), saturates plantings with useful humic acids.

Which remedy is the best is hard to say. However, experienced gardeners advise not to dwell on one thing, but to alternate preparations so that the pathogenic fungus does not develop resistance.
Folk remedies
If you don't feel like using chemicals to get rid of powdery mildew, you can treat your rose garden with your own products. Remember only that such compositions are good only at the initial stage of the disease and as a preventive measure - it is impossible to remove the fungus with them even a week ago.
- Soda solution... To prepare it, take 1 tablespoon of regular baking soda or soda ash, half a teaspoon of liquid soap and 4 liters of warm water. Mix the ingredients. Cool the mixture. Spray rose bushes with it 2-3 times in clear dry weather, observing an interval of 7 days.

- Ash infusion. You will need 10 liters of water per kilogram of wood ash. It is necessary to infuse the mixture for 3-5 days, stirring it periodically. Further, the tincture should be filtered, add half a teaspoon of liquid soap and spray the roses with this composition. An ash residue will remain on the bottom - there you can add another 10 liters of water and pour it over the rose bushes.

- Mustard solution. To prepare a mustard-based powdery mildew composition, you need to take 2 tablespoons of dry mustard powder, 10 liters of water, mix, cool, and then sprinkle the plants and water them at the root.

- Onion peel... Pour 100 grams of onion husks with 5 liters of hot water, leave for 24-48 hours. Next, the broth should be filtered and you can use it for spraying.

- Weed tincture... Take half a bucket of any garden weeds (it is important that they are without signs of any diseases), chop them finely, fill the bucket to the top with boiling water, stir, leave for several days. Strain through cheesecloth, use to irrigate rose bushes.

- Milk... Dilute ordinary cow's milk with water in a ratio of 1: 10 and sprinkle roses with it at the first sign of powdery mildew infection or as a preventive measure. The procedure should be repeated every 5-7 days.

- Garlic tincture. You will need 30 grams of chopped garlic and 1 liter of water. The composition must be infused within 24 hours. Then it should be filtered and applied to irrigate rose bushes with a spray bottle.

- Potassium permanganate solution. Take 3 grams of the substance (in powder form) and 10 liters of water. Dilute. You can spray them with roses, as well as water.

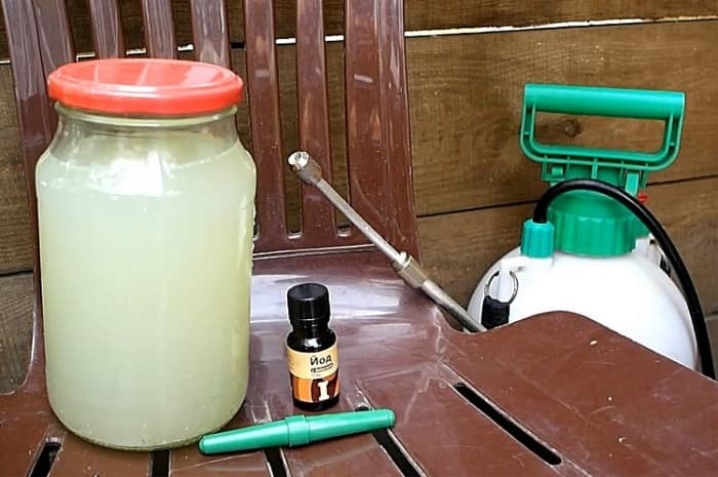
- Serum solution. You will need 1 liter of milk whey, 10 liters of water, 10 drops of iodine. The components are mixed, the solution is used to spray the leaves and stems 2 times with an interval of 7-10 days.

- Infusion of rotted cow dung... The fertilizer is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 3. It is necessary to let the composition brew (about 3 days). The resulting concentrated substance is diluted with water (1: 2) and irrigated with rose bushes.

- Decoction of horsetail (field). You will need 100 grams of freshly picked horsetail. Grind it, pour 1 liter of water, leave for 24 hours, then boil for an hour. Strain the resulting broth, cool it, dilute with clean water (1: 5) and use to spray roses.
You can store the concentrated broth for 7 days by choosing a dry and cool place.

- Tar soap solution. Half a piece of soap should be grated and diluted in a bucket of warm water. Water the rose bushes abundantly.

We will give some tips regarding the treatment of roses with folk remedies:
- it is recommended to spray the plantings only in the evening to avoid the appearance of burns on the leaves;
- each time it is necessary to prepare a new solution, only concentrates can be stored for some time (this, as a rule, is indicated in the recipe);
- the minimum number of sprays is 2;
- before processing, it is required to remove and destroy (burn) all infected parts of the plant (leaves, buds, flowers).

Prevention
Of course, the best protection of plants from any disease is the timely adoption of preventive measures.If we are talking about roses, it is important for us to preserve their decorativeness and attractiveness, and also to prevent the disease from spreading from diseased specimens to other cultivated plants. Therefore, this is what needs to be done annually.
- Choose varieties that are resistant to powdery mildew for growing. These include: "Floribunda Leonardo Da Vinci", "Pullman Orient Express", "Nostalgie", "Monica Bellucci", "Rococo" scrub, "Ascot", climbing rose "Elf", "Crown Princess Margaret", "Sahara" scrub "," Wallerton Old Hall ".
- Plant roses keeping spacing between them... It depends on the type of plant: miniature varieties are recommended to be planted at a distance of 30-40 cm, hybrid tea - 60-70 cm, climbing and park - 80-100 cm.
- Powdery mildew, as you remember, likes high humidity.... Therefore, when choosing places for planting, it is recommended to avoid waterlogged and periodically flooded soils.
- Take care of the winter protection of roses: bury and cover them.
- Stop fertilizing at the end of summer (especially nitrogen-containing).
- Have a sense of proportion when watering, do not fill the planting.
- Improve the immunity of roses with special preparations ("Trichodermin", "Gamair").
- Use fungicides one at a timeso that pathogenic fungi do not develop addiction to a specific active substance.
- Remember to remove all affected plants from the site and destroy them.

For information on how to deal with powdery mildew, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.