What does powdery mildew look like on cucumbers and how to treat it?
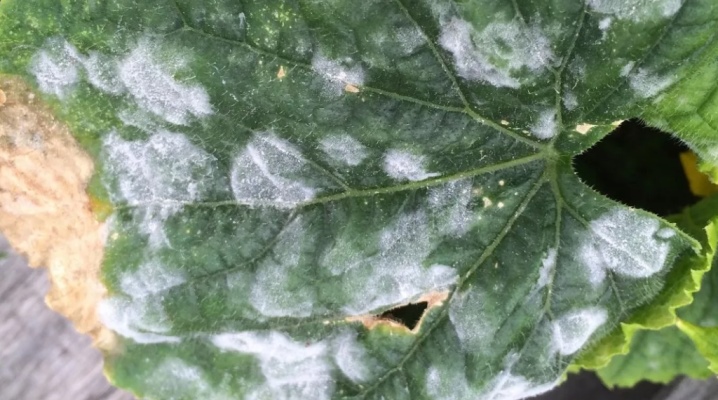

Powdery mildew often affects cucumbers growing both in the greenhouse and in the open field. To preserve the harvest, it is important not only to fight the fungus in a timely manner, but also not to forget about preventive measures.
Description of the disease
Powdery mildew, also known as ash, appears on cucumbers due to the activity of the fungus Oidium erysiphoides, the microorganisms of which travel by airborne droplets. In the greenhouse, the first signs of the disease, as a rule, appear on the bushes located near the vents, broken glass or loose doors. In the open field, on the contrary, specimens planted in shady, moist and thickened places first get sick. The disease can manifest itself in any month of the "active" season, that is, from May to September, although the greatest risk is observed in the middle of summer. In most cases, this happens a few days after heavy rainfall. The optimal conditions for the development of the fungus are air temperature from 20 to 27 degrees and humidity equal to 50%.


A plant in the first stage of the disease looks like its leaves are lightly sprinkled with white flour. By the way, the first signs appear somewhere in 4-5 days after infection. In the future, the amount of plaque increases, and the whiteness "creeps" to other plates and even stems. The top of the leaves is covered with small white specks, and the bottom is covered with a loose layer of the same color. If you carefully examine the leaf, then on the plaque you can see dark balls - the receptacle of mushroom spores. After they ripen, droplets of liquid resembling dew are found in this place. The diseased plant soon becomes covered with rusty spots. Gradually, their area increases, the plates curl, dry up and crumble.
The disease develops "from the bottom up", that is, the lower leaves suffer first, and then the plant is absorbed entirely. If powdery mildew is not noticed by the gardener in time, then even the fruits themselves may die: due to a violation of the supply of nutrients, they stop growing, and the taste becomes bitter. The pathogen fungus hibernates well in the soil, and is even able to survive on plant waste for about 7 years, so it is extremely important to carry out preventive measures aimed at destroying the focus of infection.

It is worth mentioning that true powdery mildew must be distinguished from false. Downy mildew is caused by the fungus Peronospora. The disease is also triggered by high humidity, as in the rainy season, but also requires low temperatures. Symptoms of downy mildew differ from the true one: on the outside, yellow-green spots appear on the leaf blades, later becoming brown oily, and their turnover is covered with a gray-purple bloom. This disease affects only the leaves and shoots of the crop, which, however, also leads to a reduction in yield.
Reasons for the appearance
Powdery mildew on cucumbers usually appears due to weather conditions: after prolonged rains, temperature jumps or fog. Low light also contributes to a decrease in plant immunity, as a result of which even disease-resistant varieties can get sick. However, it is useful to add that improper care and even the initial planting can aggravate the situation and make infection more likely.So, powdery mildew is "enhanced" by plant thickening, frequent irrigation with cold water, weeds and oversaturation of the soil with nitrogen. Failure to comply with the rules of agricultural technology and the lack of potassium-phosphorus fertilizing also contribute.
By the way, non-observance of the rules of crop rotation, that is, growing cucumbers in the same place for several years, negatively affects their immunity.

Control measures
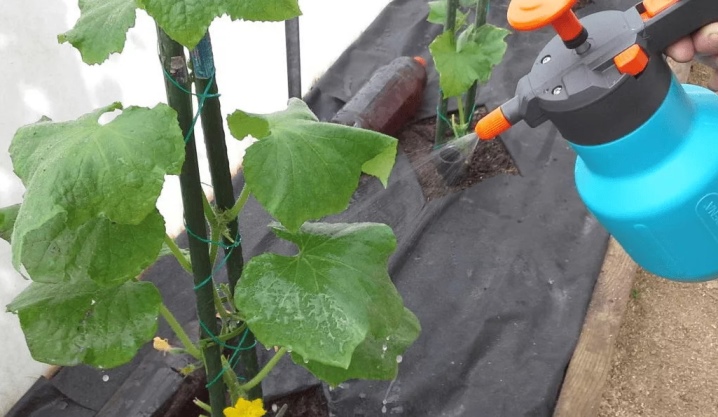
It is customary to treat powdery mildew with the help of folk remedies or use purchased biological or chemical preparations. Experts recommend treating with chemistry only in extreme cases, since a significant part of it can remain in the fruits, which will then be used. In order to take action on time, it is important to regularly inspect the plantings, remembering that the early stage of the lesion is best treated.
Having found a fungus, it is necessary to stop watering and feeding the culture. All infected parts are trimmed and burned, after which the plantings are weeded.


Chemicals
Chemicals should be used when most of the plantings have already fallen victim to powdery mildew. When working with toxic substances, it is important to wear a respirator, gloves and protective clothing. As a rule, sprinkling the cucumbers once is sufficient to kill fungal spores. Against powdery mildew, you can use "Baylon", which provides the plant with two months of protection from re-infection, and starting to act after 4 hours, "Topaz" is less effective: plantings remain healthy for only a couple of weeks. It contains penconazole, which is dangerous to living beings.
Gardeners also use Tiovit Jet, which contains sulfur, as well as Skor, which further increases the bushiness of plantings. Of course, Fundazol can help, as its benomyl prevents the growth of fungi. You can also treat infected beds with a twenty percent solution of colloidal sulfur. Such processing should be carried out on a non-sunny day at an air temperature of 20 to 30 degrees.
It is important to remember that sulfur is not suitable for the treatment of cucumbers in a greenhouse, as even a standard concentration in such conditions causes dangerous burns.

Treatment of plantings with toxic copper sulfate can also lead to the desired results. Typically, 75 grams of the substance is supplemented with 100 grams of baking soda and then diluted with 10 liters of water.
Whatever chemical is used, it will need to be diluted with clean water to the indicated concentration. This should be done in a container that is not intended for food. The plantings should be sprayed abundantly - the liquid should drain from the leaf blades, as if after rain. To prevent the culture from becoming addictive, the means should be alternated. After using chemicals, even ripe vegetables should not be eaten for about 20 days.


Biological agents
To save cucumbers from powdery mildew, you must first remove the damaged parts of the bush, and then spray the plant with biological products. The substances included in their composition do not inhibit the surrounding microflora, therefore, the culture is restored quickly, and after a short time, new healthy ones appear in the place of the cut off diseased leaves. Biological agents are most effective in the early stages of infection. "Albit" will help not only get rid of the fungus, but also stimulate the emergence of new shoots and strengthen the immunity of cucumbers. Treatment with Alirin-B, which is able to restore the microbiological composition of the soil, is useful for the culture.
Gamair shows itself well: it helps to fight against powdery mildew, provides the necessary prophylaxis, strengthens the plant's immunity and makes the soil fertile. The most effective biological product is "Baktofit", however, after using it, the fruits must be washed with clean water.Finally, The universal remedy "Fitosporin-M", which is sold in the form of a paste, powder or suspension, will also help to cope with the disease.
All of the above preparations are environmentally friendly, they can be used at any stage of plant development. However, for the complete destruction of the fungus, cucumbers have to be processed several times.


Traditional methods
Not all gardeners run the risk of processing cucumbers with chemicals, and therefore prefer to use folk methods - cheap and safe. Using baking soda or mullein, of course, you can be sure that no toxins will be found in the crop, but whether the fight against powdery mildew will be effective is not so clear. Quite often, the leaves are sprayed with cow dung diluted with clean water in a ratio of 1 to 4. This substance is first infused for a couple of days, and then diluted again in the same proportions. The processing of the culture with a mullein is allowed to be carried out twice a month.
A solution of marigolds is also popular. Half a ten-liter bucket is filled with crushed flowers, after which the other half is filled with warm water. After two days of infusion, 50 grams of soap shavings are added to the solution. This remedy is suitable for spraying plantings already suffering from brown spots. A manganese solution is prepared from 5 grams of potassium permanganate and 10 liters of chilled water. The prepared liquid is used for spraying from a spray bottle after irrigation of the plantings. She can also water the bushes at the root, counting on 500 milliliters of funds for each cucumber lash.


A preparation is quickly prepared from laundry soap and wood ash. Somewhere 50 grams of shavings and 1.2-1.4 kilograms of powder are diluted in 10 liters of water. After mixing the mixture until smooth, it can be used for watering the beds. Another recipe involves the use of 2 tablespoons of mustard powder and 10 liters of water heated to 50-60 degrees. The resulting liquid can be used both for root processing and for spraying.
A fairly effective drug is obtained if 60 grams of baking soda and 50 grams of soap shavings are diluted in 10 liters of water. It can be used once every 7 days, but not more often than three treatments for the entire growing season. It makes sense to treat cucumber tops with 10 milliliters of an alcohol solution of iodine, diluted in 10 liters of water.
By the way, it is allowed to combine soap, iodine and milk in one recipe. In this case, 20 grams of shavings and 25 drops of iodine are mixed in a liter of milk.

To combat powdery mildew, universal horsetail infusion is also suitable. To prepare it, a kilogram of fresh green mass is poured with 10 liters of hot water. Exactly a day, the product will have to be infused, and then it will have to be boiled for about 2 hours. After straining, the infusion is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 5. It can be used every 5 days, but no more than 3 times during the growing season. For daily processing, weed infusion is suitable. The cut grass should be poured with water in a ratio of 1 to 1, insisted for three days and filtered.
You can spray the plantings with kefir or whey diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 10. By the way, it's a good idea to add 30-40 milliliters of ammonia to them. Ammonia will reduce the acidity of the dairy product and form ammonium lactate, which, in turn, will contribute to the formation of conditions for "competitors" of the powdery mildew fungus. Before starting treatment, diseased leaf plates will need to be removed from the bush. The solution is first watered at the root, using the near-stem zone, so that each plant has from 0.5 to 1 liter. Further, there is abundant spraying of the entire bush, from the ground to the top.


Prophylaxis
One of the important preventive measures is the processing of the greenhouse after harvest, especially if the cucumbers in it have been ill in the summer. The easiest way is to fumigate the space with a sulfur stick, or use preparations containing copper. Sulfurous anhydride-secreting checkers are effective against fungi and bacteria, but also render the soil unfertile. The same can be said about copper-containing preparations. In principle, given that the causative agents of the disease rarely live in the greenhouse itself, it will be sufficient to wash it with a mop with plain water with a small amount of manganese. The soil should be watered with biological products capable of destroying pathogenic microorganisms, but not depleting the soil. If mulch was present in the greenhouse, then it should be burned.
In addition, it is necessary to carry out a number of other activities. At the beginning of the season, the seed must be soaked in potassium permanganate or a solution of fungicides for about 30 minutes. For irrigation of cucumbers, warm water must be used, and the temperature in the greenhouse cannot fall below 20 degrees. It is important to follow the rules of crop rotation (in the same area, the crop is located at intervals of 4 years), annually change the top layer of the soil and control the introduction of nitrogen-containing dressings. If the cucumbers will grow in the open field, then before planting the seedlings, all the soil should be removed from the surface and the soil should be poured with boiling water.

The seedlings should be positioned in such a way that no thickening occurs in the future. It is necessary to weed out weeds in a timely manner, disinfect the soil with potassium permanganate in the fall, do not spray on the leaves and stems during irrigation, and also do not plant cucumbers in shaded low-lying places.
Which varieties are resistant?
Another preventive measure is the acquisition of powdery mildew-resistant cucumber varieties. Parthenocarpic hybrids are most effective in this matter, capable of withstanding sudden temperature changes, not requiring pollination and ready to grow both in a greenhouse and in open ground. For example, suitable for landings "German", "Cupid", "Artist", "Arina F1" and "Regina-plus F1". Of the bee-pollinated hybrids, Phoenix Plus, Competitor, Delikatesny, Natalie and Murashka F1 are deservedly popular.

For methods of dealing with powdery mildew, see below.













The comment was sent successfully.