Varieties of futoroks and the rules for their selection
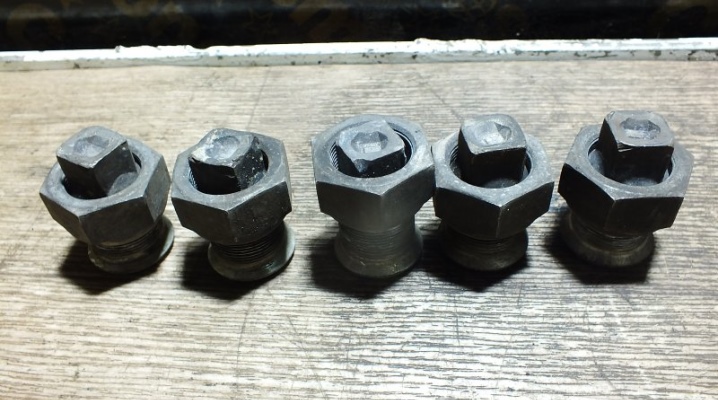

In order to achieve the desired functionality of the threaded connection, you may need special adapters - fittings. One of the most common is the futorka. Depending on the tasks, universal and specialized models are produced. In this article, we will consider what kind of fittings are and how to choose the right part so that it can cope with the task and withstand the load.



What it is?
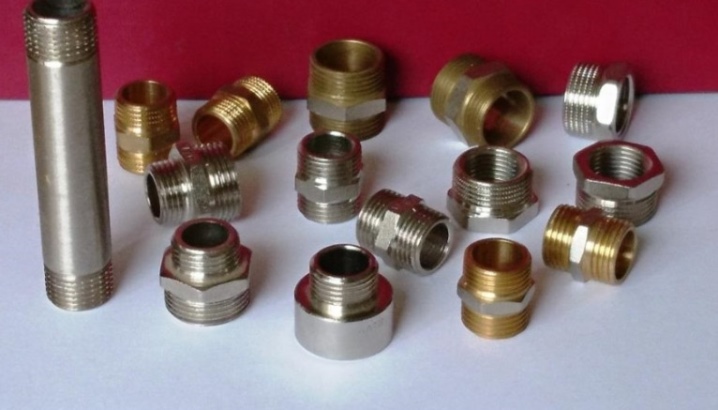
Futorka - a type of threaded adapter (fitting), which is used to connect parts of circular cross-section, transition from one thread to another. In appearance, it resembles a cylinder with a threaded through hole and threads on the outer surface. The diameter of the outer thread is usually larger than the inner thread, but there are also reverse threads. The internal thread of the case is usually called a nut, the external thread is a fitting.
External and internal threads can be of the same type and differ only in diameter, or they can be of different types (for example, internal metric, external - inch).


Such a connection is capable of withstanding large mechanical loads, it is sufficiently tight, it can be disassembled and assembled an unlimited number of times.
The installation of the foot is quite simple and in most cases does not require special skills and tools (you need a hexagon or a gas wrench).

Each product, depending on the field of application, can be of different sizes, have its own diameter and thread parameters. Typical characteristics are regulated by GOST, DIN, ISO standards. Non-standard models are also available.

Description of species
The futorka is characterized by the following parameters.
- Thread direction - left, right. Parts with right-hand threads are screwed in clockwise, left-hand ones counterclockwise.
- Installation method - threaded, without external thread (driven).
- Thread type - all types of metric, pipe, inch threads are used.
- View - transitional, plug. The transitional (pass-through) foot creates a transition from one diameter to another, has a through hole. The plug looks the same as a transitional sleeve, only from the outer end it is hermetically sealed or closed and allows you to block the pipe section, put on the radiator.
- Straight or reverse foot. For straight foot, the outer thread diameter is larger than the inner thread. But there are also details of a non-standard design - the opposite. They are equipped with a special thickening at one end (flange), on the inside of which there is a thread of a larger diameter than the diameter of the thread on the outside of the fitting.

Products can have:
- a spacer mechanism (most often a spacer ball);
- hex head or gas wrench;
- flange.



Furniture fittings can be supplied with fixing clamps, spikes. Spring-loaded repair fittings - a tongue that facilitates installation.


Plumbing
In plumbing, transitional fittings are most often used - for connecting pipes, various devices, radiators. For these purposes, along with straight lines, reverse fittings are often used. Also, plugs are in great demand, which are used to seal the lines, are placed on the battery. To connect the radiator to the pipelines, special radiator fittings are used. They are often sold in a 4-piece assembly kit (two left-handed and two right-handed).
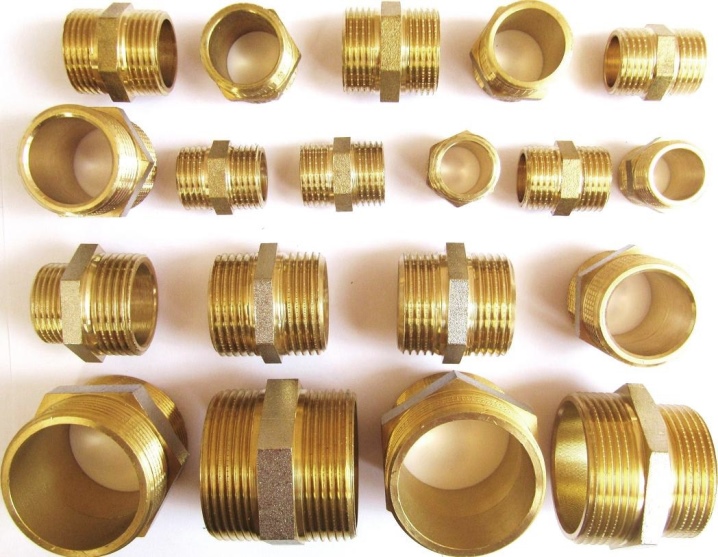

Plumbing fittings usually have a pipe or inch thread, it can be left or right.
Right-hand thread is more common, it is used on most pipes and connecting pipes of various equipment (water heaters, pumps, filters). The left-hand thread is used on pipes that connect to the radiator on the left side. Metric threads for the pipes themselves are usually not used, but can be used to connect various devices - for example, pressure gauges or reducers.

The most popular sizes are those that correspond to the most common pipe diameters: these are universal products that comply with GOST. Typical plumbing fittings have thread diameters ranging from ½ "to 2" (8-50 mm). For pipes with a larger cross-section, threaded fittings are rarely used. The length of the thread is from 13 to 28.5 mm, the total length of the product is from 17.5 to 39.5 mm.

Repair
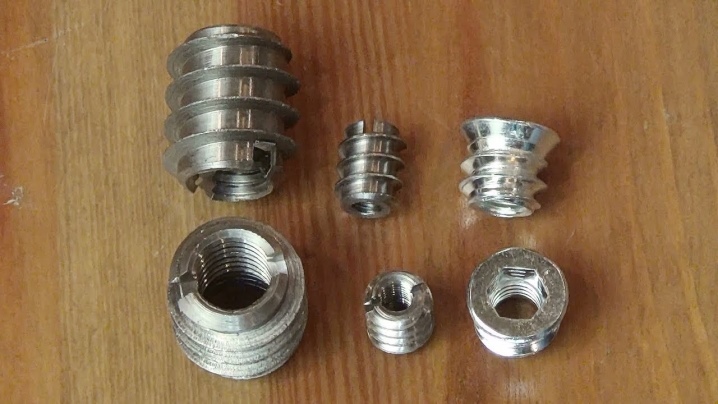
The main type of repair fittings are threaded spiral (spring) inserts. Outwardly, such a part is a springy spiral made of diamond-shaped steel wire, provided with a projection or tongue on one side. The tongue is necessary to facilitate installation; after installing the footwear, it is bitten off.
Specifications:
- are made of corrosion-resistant steel, can be used in aggressive environments;
- the restored thread is more resistant to mechanical damage, the insert has no effect of "biting" damaged hardware;
- loads are evenly distributed and amortized along the entire length of the connection, and not only due to 2-3 upper turns;
- the connection becomes 2-4 times stronger and lasts longer.



Due to its unique qualities, such an insert is used not only for repairing damaged threads, but also for reinforcing rigid threads in places of important highly loaded joints in aviation and space technology, nuclear reactors, and medical equipment.
In everyday life, they are used to repair stripped threads on pipes and on various mechanisms - for example, to restore the spark plug thread of an automobile engine.
The parameters of spiral inserts for general industrial use and the most common in everyday life usually correspond to the DIN 8140 standard. The length of such an insert is made a multiple of its diameter in the assembled state. Standardly it is 1D, 1.5D, 2D, 2.5D, 3D, where D is the diameter.

Furniture
The furniture shoe is used not as a fitting, but as a fastener, with which you can make a socket for attaching a countermeasure to a surface made of wood, wood board, or plastic. That is, it works like a nut immersed in the material.
The difference between furniture fittings and other types (plumbing, repair) is that only metric threads are used.
Along with parts of a standard type (with external and internal threads), a special type of foot is used for furniture fasteners, in which the thread is applied only on the inside of the hole, and on the outside, instead of the thread, a notch-retainer and spikes are used to adhere to the material.
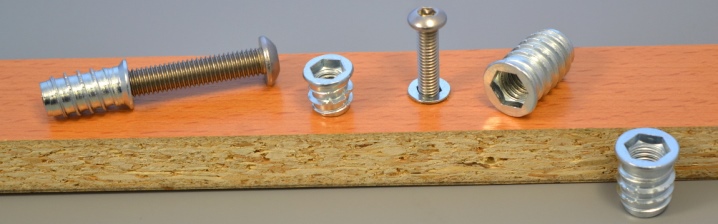
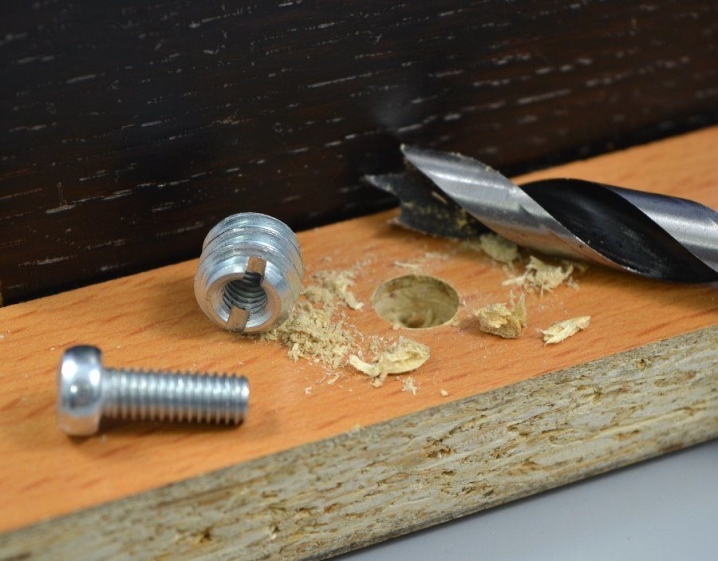
The outer part of the shoe is screwed or hammered into the material, where a hole of the required diameter is pre-drilled. When installing a part with an external thread, it itself cuts the threads in the material, since chipboard, wood and similar materials have a relatively soft structure. The hammer-in case (without external thread) is simply hammered in with a hammer. Some are equipped with a spacer mechanism.
The internal thread serves to install the hardware, which is used to attach the second part. Due to this, it is possible to create various types of furniture fasteners - both simple screw ones, consisting only of the footboard itself and a counter screw, and more complex ones, where the footboard is used as part of a complex mechanism - for example, eccentric couplers, door fasteners, folding and sliding structures.

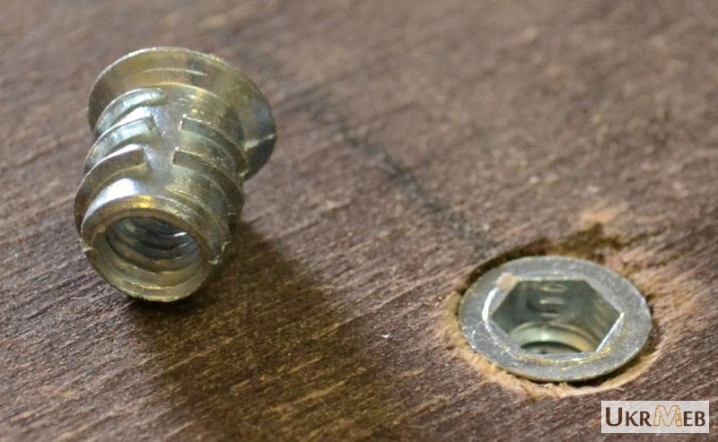
The futorka is mounted discreetly, does not spoil the furniture design.
At the same time, the connection is very reliable, it allows you to cushion the impact on the material, therefore it is applicable not only for hard wood species, but also for soft, crumbling materials (chipboard, plywood), plastics, for which not every type of fastener is suitable. In addition to the furniture itself, this type of fastener is used for a wide variety of wooden and plastic structures. With its help, for example, fastenings for balusters, handrails are created, handrails of the required length are assembled. It can also be used for facing works - for fixing wooden panels.

Furniture fittings are made of metal and plastic, they are made for various counter hardware (screws, screws, self-tapping screws, pins) and plastic fasteners. The manufacture of furniture fasteners is not strictly regulated by GOST, it is often non-standard. Nevertheless, the most popular are universal footwear, which can be used for furniture assembly and for a wide range of household tasks - for a standard GOST / DIN screw from M4 to M20.
Their typical sizes:
- inner diameter from 4 to 20 mm (M4 to M20);
- external - from 6 to 29 mm;
- thread pitch - from 0.5 to 1.5 mm;
- height - from 8 to 20 mm.

Materials (edit)
Fittings are made of plastic and metal. Small plastic footboards are used for furniture fixings. They are lighter in weight, more resilient than metal, and do not corrode. Where the weight of the fastening itself is critical or hard metal hardware cannot be used due to the specifics of the material (a thin sheet of chipboard, plywood), such parts are indispensable. Some plumbing fittings are also made of plastic, which are used in the installation of household plumbing systems.
In particular, fittings for aluminum heating radiators are made of polypropylene - such an adapter prevents the formation of a galvanic pair between the radiator and the steel pipe.


For critical connections that must withstand high mechanical loads, be exposed to high temperatures, pressure, aggressive environments, only metal fittings will be used. They are cast iron, steel, copper, brass, sometimes bronze.
- Cast iron footwear used for cast-iron radiators and pipes, withstand pressures up to 25 bar and temperatures up to 175 degrees.
- Brass foot - a good connector for household and most industrial engineering systems. This material is durable, chemically inert, and safe. But in terms of strength, brass is inferior to cast iron and is used for systems with an operating pressure of no more than 16 Bar.
- Steel - are made of high-strength, corrosion-resistant carbon steel, additionally coated with a protective zinc or nickel coating. They are suitable for aggressive environments, can withstand high mechanical loads, pressures up to 16 bar and temperatures up to 110 degrees. Such fittings are used for critical connections in industrial and utility pipelines. Fittings of small dimensions for creating reliable connections (furniture, spring inserts) are also made of stainless steel.



Features of choice
When choosing a footwear, it is necessary to determine which type of footwear is needed, what dimensions and characteristics it should have, what loads to withstand and what material it should be made of. It is especially important to choose the right size of external and internal threads and their type (metric, inch, pipe; right or left). To do this, you need to carefully study the characteristics of the mating thread on which the futorka will be mounted.
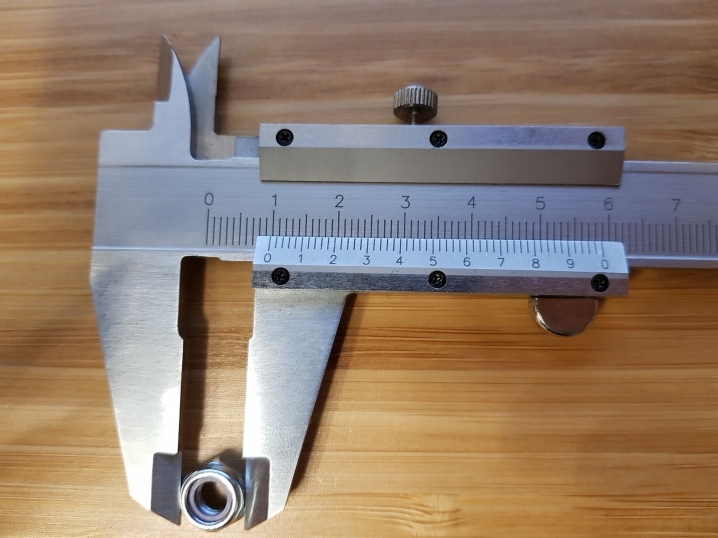
Using a vernier caliper or ruler, determine the pitch of this thread (the number of turns per inch or millimeter) and use the table of thread standards to determine which type it corresponds to.
It can be difficult for a non-professional to determine the type of thread in this way, so it is worth resorting to the accompanying documentation for the equipment for which the footwear is being selected, or using the advice of an experienced craftsman.

Here are some tips to help you when choosing different types of footwear.
- If we are talking about the installation of water or heat supply systems, then all the elements of the installed system, including fittings, are best bought in a set, from one line of a certain manufacturer. This ensures maximum hardware compatibility.
- For pipes made of some metals, not all adapters are suitable (even if they fit on the thread), but only from the appropriate materials. So, for copper pipes only copper fittings with brass elements are suitable, for cast-iron radiators and pipes - only cast-iron ones. For plastic pipes, steel and cast iron fittings will be too heavy, plastic, brass or combined adapters are used here. But fittings from any materials are combined with steel pipes.
- In the catalogs of manufacturers for a metal pipe with a thread, the diameter is indicated, measured along the inner side of the pipe (excluding the thickness of the pipe itself), and for plastic pipes, along the outer (taking into account the thickness of the pipe). This must be borne in mind in order to correctly select the bore diameter and join pipes made of different materials.
- The repair spring sleeve must sink ¼ of the thread pitch into the hole. It must be selected based on the fact that in a free state, the length is slightly less than after installation. When designating such fittings according to the DIN standard, this feature is taken into account, and the final size is indicated (for example, an M8 2D insert in the installed state and with a broken shank will be a length equal to two diameters, that is, 16 mm). But when it comes to non-standard models, manufacturers can use their designations, and you need to be especially careful when choosing.
- When installing the furniture footboard, the edge of the hole and the upper edge of the footboard must exactly match, and the length should be selected so that at least ½ thread pitch remains from the bottom edge of the footboard to the surface (the hole is usually not through).

In any case, it is better to choose universal parts made according to GOST / DIN standards. They do not require special tools to install, they are compatible with other typical equipment. What mechanical loads a part can withstand, in what environmental conditions it can be used and other important characteristics can also be learned from the relevant standard.

When buying, you need to make sure that the thread is smooth, and there are no cracks or damage on the body of the part. To ensure the quality of the threads, you can “test drive” the fitting by connecting it to a suitable mating thread.


The following video provides an overview of the stainless transitional outer case.













The comment was sent successfully.