Mansard roofs: types and design features

Surely, sooner or later, every owner of a private house comes up with the idea of arranging an attic roof - the so-called attic. It allows you to expand the building space, thereby preserving the cherished meters of the site itself. In addition, if you show a little imagination during the construction and decoration of this part of the house, then the non-standard and attractive view will delight not only guests, but also ordinary passers-by. You can learn how to competently combine all the safety requirements for construction and an individual design idea from this article.



What it is?
Many people associate the image of the attic with the bohemian creative life of Paris, whose representatives - writers, musicians and artists, lived on the uppermost dimly lit and unheated floors. In the literal sense, these were utility premises that only the poor could afford.
Today, the presence and design of a mansard roof speaks of the well-being and sense of taste of the owner. The architectural geometry of the roof, unusual combinations of window openings and balconies will not only distinguish a private house from others, but also functionally increase the living space, excluding the cost of one more floor.


Also, the room can affect the reduction of the heat loss of the building. Officially, according to all standards, the attic must have a height of at least 2.5 m from the floor level, otherwise it will be considered an attic.
When building an attic roof in Russia, one should remember about the peculiarities of natural conditions - rather frosty winters with frequent temperature drops require special attention to the quality of insulation of the attic room.


Features of the device
The design features of the attic oblige you to adhere to some rules:
- soundproofing;
- reliable insulation and vapor barrier;
- lack of stretch marks and bevels;
- ventilation gap;
- functional and aesthetic combination with the general exterior of the house.



At the same time, compliance with all the rules does not limit the choice of the option of all kinds of designs of the structure itself: single-pitched, gable, broken, two-level, conical roofs, with or without a balcony, mid-pivot or balcony skylights. There are many variations. For reliability and safety, it is important to choose the type of roof, calculate the dimensions, the amount of insulation and roofing materials.
Comfortable living in the attic directly depends on thermal insulationwhich will allow you to enjoy the light coolness in summer and keep warm in winter. Consider the method of laying the "pie" of the attic roof, which will serve not only as a heater and the base of the roof, but also as protection against the insulation of the room, all surfaces inside the attic floor - ceiling, floor and walls - are subject to insulation. It is important to preliminarily draw up a plan of the attic with all communications and an indication of the thermal conductivity of the materials from which the building and load-bearing coatings were erected. Only after this is the selection and calculation of the insulation made.
Particular attention should be paid to the indispensable presence and exact sequence of each layer of the "pie" of the attic insulation:
- vapor barrier layer;
- insulation;
- ventilation gap;
- waterproofing material;
- roof covering.
In this list, the layer of insulation and ventilation is especially important.The following materials can be used as insulation.
Styrofoam
A modern, demanded material with a low density, but at the same time high strength. Differs in soundproofing, does not give in to corrosion and does not attract dust. However, a significant disadvantage is the high flammability and the release of toxic substances. If you dwell on this insulation, then the foam layer should be fenced with at least 3 cm of a flame-retardant structure, for example, with a two-layer drywall. In addition, the foam is susceptible to rodents.



Mineral wool
The most common material for attic insulation. Among its characteristic features are resistance to temperature extremes, fire safety, high sound and thermal insulation, and environmental friendliness. It can be purchased in the form of a roll, plate or mat. The latter is recommended as a heater for the attic. The material certainly needs good ventilation.


Polyurethane foam
The main advantages are strength, long-term use, not susceptible to moisture, mold, suitable for any surfaces, non-toxic. But behind all the advantages, there is a high cost and the work of exclusively specialists with the equipment.


It must be remembered that the thickness of the insulation layer is determined depending on the climatic zone.
To insulate the attic you will need:
- waterproofing film;
- insulation material;
- vapor barrier;
- mounting tape;
- cord (nylon);
- nails;
- hammer;
- pliers;
- sharp knife.



Thermal insulation of a room is directly related to the quality, type and size of roof windows; their structures are usually placed between the roof rafters in order to avoid costly renovations. Therefore, in choosing it is important to focus on the available dimensions. Among other things, you need to take into account the height of the slopes, the total area and the purpose of the room.
The standard dimensions of roof windows are considered to be 78x118, 78x140, 78x160 cm and more enlarged - 94x140, 114x118 and 114x140 cm.




In the event that the rafters are installed closer to the established frame standards, it is likely that a custom-made window will be required, which, of course, will affect costs.
By the way of opening, roof windows are divided into:
- mid-pivot structures;
- with lateral axis;
- raised axis of rotation;
- with a lower axis;
- a combined axis that allows the sash to be rotated 180º.
The most popular option among Russian summer residents is with a central pivot axis. The advantages are ease of use (such windows are easy to clean).


A separate type is represented by remote-controlled windows, which will be convenient if the location does not allow you to reach them on your own. They are often equipped with rain sensors.

Several types of windows can be selected depending on the model.
- Vertical. They are mounted in a special so-called "nesting box" attic, because of which it is necessary to slightly change the structure of the roof. However, a large amount of light is guaranteed.
- Balcony attic. They are two sashes, when opened, one rises, the lower one moves forward, forming a miniature parapet. As well as the previous model, they are expensive.


It should be noted that if the load-bearing walls are possible, a hanging balcony can also be made, which can either be located on the columns that serve as decoration in front of the entrance, or move the pediment (part of the end wall between the roof slopes and the cornice) of the attic floor from the load-bearing wall, and the roof of the ledge done by extending the roof to the level of the outer wall.



- Extensions. Decorative upper window elements. They fit perfectly into the design and most often have a round, semicircular or triangular shape.

- Light tunnel. It combines a reflective tunnel into the room and a ceiling lamp directly in the room itself, which evenly diffuses the light.
- Cornice models. Placed at right angles between the wall and the roof.
- Glazed bay window. Quite an exotic and expensive glazing model. The structure extends beyond the plane of the wall.



Leading Russian manufacturers of high-quality roof windows - Velux, Fakro, Roto. Velux models are slightly more expensive. For example, a window with a size of 78 cm will cost 21-24 thousand rubles, wider - from 26 thousand.

Also, do not forget about some additional useful accessories:
- blackout curtains;
- roller shutters, blinds;
- heat absorbing mesh;
- mosquito nets.



According to the established standards, the glazed area must be at least 10% of the floor area.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the attic floor can rightfully be considered:
- Profitability. The attic allows you to reduce the cost of heating the room. The air space between the floor and the ceiling of the attic prevents the generated heat from escaping through the roof. The low thermal conductivity of the air allows more heat to be stored on the ground floor.
- Savings on completing one more floor or increasing living space by expanding the foundation are also obvious. The attic allows you to obtain additional constructive space at minimal cost.
- Aesthetic appeal. Undoubtedly, the attic with the complexity and expressiveness of the roof gives the building a harmonious, architectural and finished look.
- Construction speed. Such an extension will not last for several years, as is often the case with the expansion of the foundation. Installation can be completed within a week.


Besides the pros, there are also disadvantages.
- Saving on heating and replacing the second floor with an attic will subsequently result in a pretty penny. The room provides for the installation of specialized windows, which are much more expensive than conventional ones.
- Sloped ceilings reduce the height of the walls.



- The vulnerability of the structure is due to the fact that the attic takes on all the main "blows" of nature, and therefore requires increased attention and periodic inspection. If it is necessary to repair or replace the insulation, damage to the finish along with the vapor barrier cannot be avoided.
- A complex charcoal roof results in difficult-to-ventilate areas, which negatively affects the quality of the roof.
- Individual requirements for hydro and thermal insulation.

Problems that can be encountered when building an attic:
- the use of lumber untreated with fire retardants and antiseptics can lead to rotting of the tree and the appearance of parasites;
- leakage of one layer of the "pie" before laying the next;
- too light and unsuitable overlap;
- equipment of an attic with an already installed roof;
- poor-quality steam and waterproofing can cause rotting of window slopes or the inner lining of the attic.
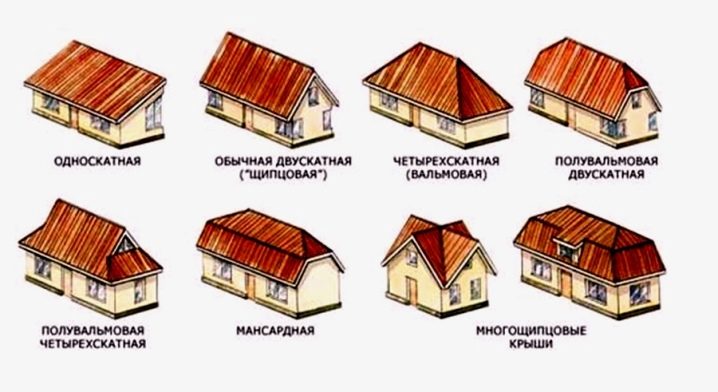
Varieties of designs
Undoubtedly, the ideal option for an attic would be to include it in the project drawing even before the start of construction work on the house. But often the idea of an attic comes with the need to expand a useful living space after a certain time of use. In this case, one has to deal with the choice of the type of construction. There are such types of attic roofs.

Mono-pitched
An ordinary uncomplicated attic with one roof corner and one full-fledged wall, which allows you to expand the area. The most successful angle of inclination in this variant is in the region of 35 ° -45 °. Otherwise, it can lead to the accumulation of a large amount of snow. The slope is placed on the windy side. In this case, window frames can be positioned both on an inclined roof surface and on the main vertical wall.However, this design is not used so often, since due to the norms of wall heights of more than 2.5 m, the slope turns out to be very steep. And this requires strengthening the frame of the rafters and, therefore, extra costs. However, such a roof looks rather unusual.



Gable
A more rational and optimal option due to the uniform rise of the ceiling, in contrast to the single-slope model. The two roof slopes are at the same angle to the walls. For a rational distribution of space, 45 ° is enough. It is also subdivided into subspecies: symmetrical with a ridge over the middle of the house and asymmetric with an offset from the center. The gables in this version are straight, and the room takes the shape of a trapezoid. Such an attic can be equipped with a balcony at the end, and the very design of the structure allows you to get rid of the typical "cubism" for a house. However, this also seems to be a significant disadvantage, limiting the area of the attic space on the sides. As an exit, this space can be provided for pantries or cabinets.



Broken line
The most common type in the construction of an attic without the involvement of specialists. In fact, the same gable structure, but built from two parts at different slopes. The advantage of the broken shape can be considered the ability to avoid the formation of unsuitable for habitation "dead" zones at the junction of the walls and ceiling, as in a gable structure. By reducing the angle of inclination, the height of the walls increases. And the presence of two slopes allows you to reduce the load on the roof.

When choosing this option, it is important to pay attention to the special breaking rafter system.
With outboard consoles
This design provides for the displacement of the vertical wall of the attic to the edge of the facade of the house or beyond. This feature allows you to significantly expand the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe room. The rafters are reinforced with struts and rest on floor beams that protrude beyond the load-bearing walls. The vertical wall provides flight for imagination in the choice of window designs.


Two-tier
This type of attic is designed exclusively together with the dwelling and is considered the most complex structure. It represents several rooms at different levels and is not some isolated part of the structure, but a full-fledged room in the structure of the whole house. With such a structure, it turns out not a one-story attic, but two additional mini-floors. A preliminary calculation of the load on the walls and the rafter system requires special attention.


Multi-gable roof
The intricacy of the design is expressed in a whole complex of angular protrusions. The non-standard appearance, the strength of the rafter structure and the absence of accumulation of precipitation are more priority than the difficulties of designing and increasing the calculations. However, such characteristics require the work of exclusively specialized personnel. And the cost of such a mansard roof significantly exceeds the prices for other types of structures.


Chetyrekhskatnaya
This roof structure is considered the most attractive. In addition, it is very easy to maintain - precipitation hardly accumulates on it, and due to the inclined structure, the wind does not carry a large load, as a result of which such a roof will last longer. However, during construction, you will have to significantly spend money on insulation of such an attic. But there won't be much usable living space due to the sloping ceiling on all four sides.



Hip
They are a typical version of the four-pitched roof type. A comfortable and spacious space is obtained by increasing the area of two facade slopes of the house, made in the form of a trapezoid. Hips are the slopes from the end of the building in the form of triangles. The half-hip design is made of slopes that do not extend from the ridge to the cornice. This type of roof is rarely used, since the rafter system is one of the most expensive and complex.


Tent
Suitable option for a square-shaped house.The roof in such a structure is slopes of the same parameters and requires arrangement by specialists. Among the options are 4 or more slopes, in the form of a dome or pyramid.

Asymmetrical
It is obtained as a result of lengthening one of the roof surfaces. This attic looks both outside and inside very unusual. The seemingly simplicity of roof displacement hides a detailed calculation of the load parameters on each wall. The living space in such a room will be unevenly distributed depending on the side and angle of the roof.



With a "cuckoo"
"Cuckoos" in this case are called small protrusions in the shape of a triangle, where windows are most often located. Moreover, on one slope there can be several such structures with individual rafter systems. The shape of the structure can be completely different, both one- and four-slope.



L-shaped
Quite an inexpensive roof option with a non-standard look. Most often, two gable roofs are used for this, docking with each other at right angles, which is the most difficult structural unit. Of course, such models are mainly used in buildings of the same shape.


Having listed the main forms of attic structures, it should be added that combinations of such roofs are also possible. For example, a lean-to can be built as a broken line. The most important thing here is to comply with all operational and design requirements during construction.
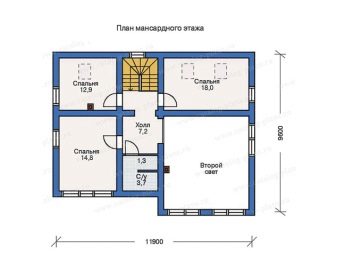
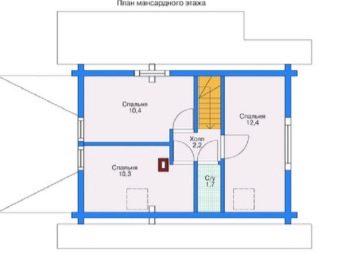
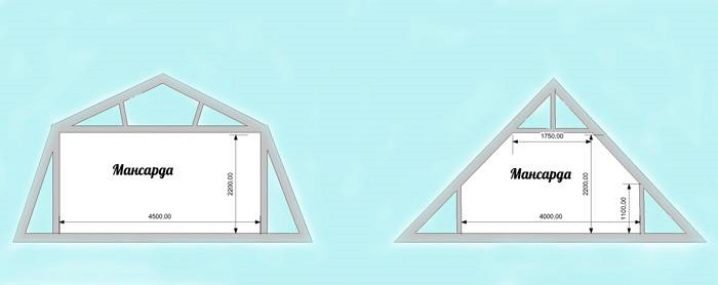
Shapes and sizes
The construction of the attic floor also has variability in terms of the embodiment of various architectural forms of the room itself. The geometry of the attic room can be either triangular or broken, cubic or L-shaped, symmetrical or asymmetrical, one-story or two-level, occupy the entire space of the house, only part of it, or even with the extension outside the bearing walls, supported by columns. There are many alternatives. A complex structure requires correct calculations of dimensions and drawing up a construction plan.


Calculating the exact parameters of the attic floor area involves a number of preliminary calculations. To draw up a project, it is required to schematically divide the space into simple geometric shapes: trapezoids, rectangles, parallelograms, squares, triangles and, having calculated the area of each of them, add the results obtained. This principle applies to almost all attic structures. And if all the norms for the height (at least 2.5 m) of the attic are met, then the floor area should be at least 16 m².
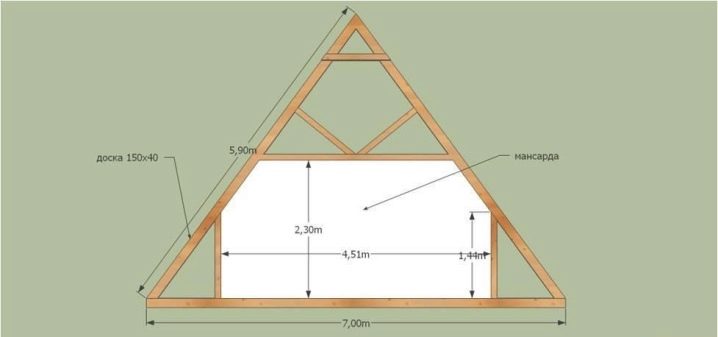
It should be noted that in addition to the established parameters of the height, where such calculations are possible, there are attics of other sizes:
- attic in the range from 0.8 to 1.5 m;
- half-attic less than 0.8 m.
In such cases, or when the slope of the roof is quite significant, the following formula applies:
P = AxL + 2Bx0.7L
P = L (A + 1.4B),
where P is the area;
L is the length of the attic plane;
A - floor width for walls above 1.1 m;
B - floor width for walls above 0.8 m.
The useful living area is calculated from the points on the ceiling 90 cm perpendicular to the floor. The rest is considered a "dead" zone.
Such formulas allow both to calculate the strength and weight of a structure, and to determine the amount and type of material used.
Thanks to modern technologies, today it is quite possible to carry out calculations of the parameters of the attic roof online. To do this, you will need to enter data on the type of attic, the scheme of the rafter frame, the material of the roof and insulation.

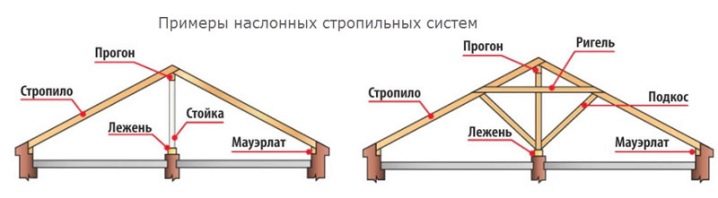
Rafter system
The transformed rafter system is the key differentiator of roof roofs from others. This already heavy structure can withstand the weight of the roof, floor beams, the load of the attic floor, and precipitation. Therefore, only one that is made in compliance with all requirements can be considered a reliable and durable system.


One of the basic rules is that the system must provide for an even distribution of pressure on the base and load-bearing walls.
Only high-quality, well-dried and treated with an antiseptic wood is used. The optimal parameters of the rafters are 100 × 100 mm in cross section, they will create a structure resistant to weather conditions.


Inserting a tree into the lower crown is strictly prohibited. The slope of the rafters is in the range from 30 ° –60 °. To secure them, exclusively rigid metal materials (corners, staples, nails) are used.
Particularly carefully calculate the step of the rafters, since the choice of the width of the insulation and the size of the windows located between the two rafters depend on this. It should be added that the width of the step between them should be less than the width of the insulation by 3 cm to reduce waste.
All of the above requirements are met regardless of the choice of one of the types of construction of the rafter system, which is of the following types.
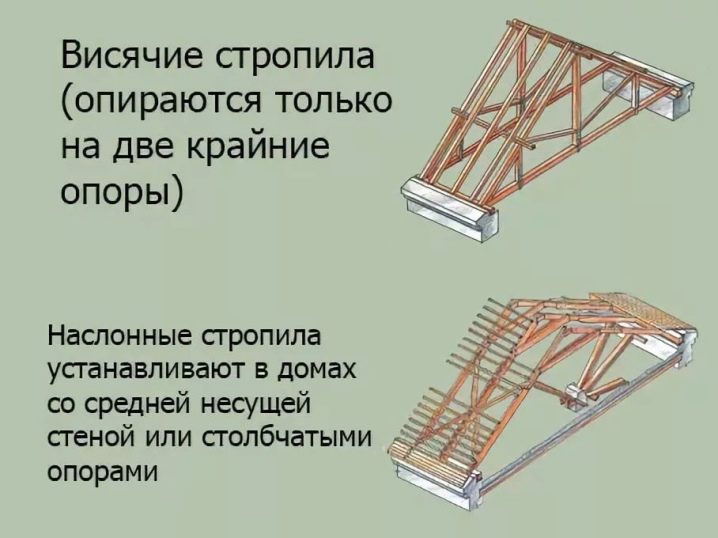
Hanging
Differs in economy and practicality. Such a structure rests on the side walls of the structure, and the rafter legs are fastened with horizontal bridges for rigidity - crossbars, which also serve as the basis for the ceiling. The advantage is the location of the main elements of the system outside the used part of the room, which allows you to expand the usable space.
When installing such a system, you should pay attention to the fact that:
- the supports of the roof overhang should not fall on the bottom, brought out of the load-bearing walls, rafter legs;
- for the rigidity of the roof, a wind board should be nailed between the ridge and the Mauerlat;
- the moisture content of the rafter tree should not be more than 15%. Otherwise, the system may become unstable. If, nevertheless, such material is used, then it is better to connect it with the help of bolts, which, if necessary, can be tightened.
Naslonnaya
It is used in attics with a load-bearing partition in the center of the room, which is an additional support. Most often, such a system is used for large areas of the house and heavy roofing materials. The principle of construction consists in the flooring on the inner walls of the bed, which protrudes instead of the Mauerlat, and the installation of a special rack to support the ridge girder.
Features of the arrangement of the layered system:
- thickness of each element - from 5 cm;
- all nodes are smooth and located exclusively in the right places according to the design;
- the connection of the Mauerlat and the rafter leg is strictly horizontal;
- symmetry in the position of the struts and struts;
- reliable and high-quality ventilation;
- waterproofing at the junction of nodes and masonry;
- the length of the rafter leg without support - up to 4.5 m.

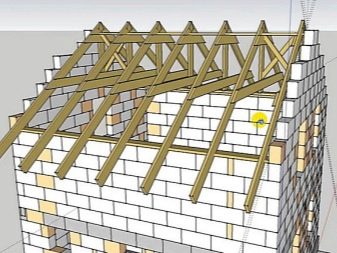
The independent design of the rafter system provides for the fulfillment of a certain order and requirements:
- Fastening the Mauerlat (the base of the rafter system over the area of the house). The strength of the attachment with the lower slings will protect against "breaking the roof" in the literal sense of this expression. The material used is dry processed beams with a section of 150x100 mm. Mauerlat transfers some of the load of the rafter system to the walls.
- The base of the beams is laid horizontally, always using a level. Attaches to walls with bolts or brackets.
- The waterproofing layer is located on the crowns, columns of the frame building or on the brickwork. You can use roofing felt, roofing felt, bitumen.



- Frame racks. Perfectly flat vertical and horizontal racks are fastened with brackets or nails to long beams, insulation is laid between the vertical ones. Before proceeding with the work, it is imperative to check the racks for mobility - they should not loosen. Otherwise, they are strengthened with braces or ties.
- The girders hold the rafter legs together. Above is a ridge run, on the side - side ones. If the length of the rafter legs is less than 8 m, it is not necessary to install the ridge.The element that performs its functions can serve as stretch marks that secure the ceiling of the attic.
- The last stage in the construction of the system is the fastening of the lathing.
The crate is of undoubted importance for the roofing system, which takes on all its load.
It represents the bars laid perpendicularly on the legs of the rafters. Moreover, various materials are used here, depending on the type of coating: boards, timber, plywood, tes. Although usually used for this edged board 40-50 mm. Soft types of cover suggest a continuous crate, and with harder materials, a distance between the boards of 25-40 cm is provided.


All rafters are connected at the highest point of the roof - the ridge. The ridge gives the whole structure rigidity and stability. Therefore, it is obvious that the duration of operation of the entire roof depends on the reliability of this part of the system.
The connection of the rafters, and, therefore, the formation of the ridge, takes place using the following fasteners:
- an overlap is formed by laying the rafters on top of each other and connecting through fasteners;
- a cut in half a tree as a result of overlapping rafters, in which half the thickness and fastening are selected at the edges;
- trimming the end sides of the beams involves overlapping rafters and trimming in a mirror image at one angle.



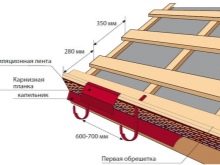
In the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe ridge, the rafters are fastened with overlays of plates made of wood or metal, metal corners, staples, staples, wooden wedges, nail plates. During the construction of the truss system, such an important part of the house as the cornice is being installed. To do this, either the length of the rafters is increased, or a filly is used.
Among his primary tasks:
- protection of walls from moisture and dirt;
- partially eliminates the ingress of water and snow from the roof onto the foundation of the building, preventing blurring;
- harmonious and complete look of the overall structure of the roof of the house.



Construction requirements
The design of the attic floor assumes the fulfillment of the following requirements:
- the interconnection of communications between the attic and the whole house;
- the selected material for the attic must be technically and harmoniously combined with the building material;

- compliance of the additional floor plan with the building project;
- compliance with safety rules when carrying out work with the presence of people in a residential area;
- strict adherence to fire safety rules;
- compliance of the light-transparent fence with the general concept of the building style.
Installation technology
The assembly of all elements of the attic space occurs in the following order:
- it is better to calculate the strength of a building with the involvement of specialists;
- preparation of the attic and roof project can also take place with the participation of qualified people or on the basis of a ready-made version;
- dismantling the old roof if it is not a new building that is being rebuilt;


- the manufacture of a rafter wooden frame is one of the most difficult points in the construction of an attic;
- it is necessary to make sure that the erection is accurate using a cord stretched between the arches, which ideally should be in a horizontal position;
- fixing arches with each other with nail plates or stamping corners;
- vapor barrier material on the inside of the rafter system, secured with construction brackets;
- a layer of insulation tightly attached to the rafters;
- installation of the lathing on the insulation material is carried out using wooden blocks;
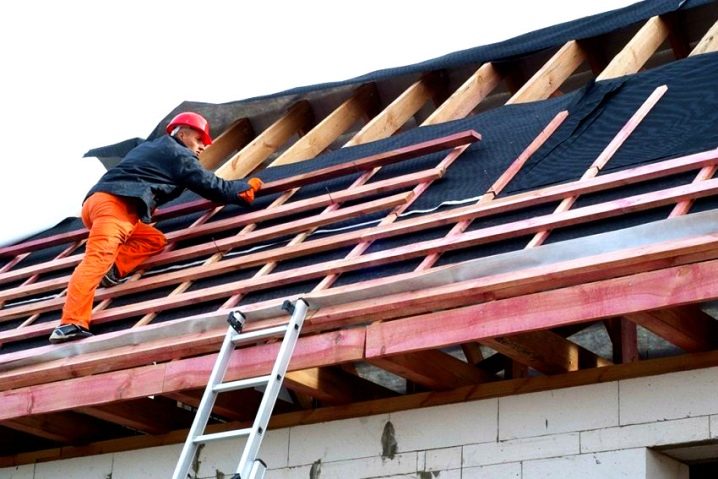

- waterproofing is laid on the outside of the rafter system - often polyethylene film is used for this, and another layer of boards is stuffed on top of this layer;


- for natural ventilation of the space under the roof, special cavities are arranged between the hydro- and heat-insulating layers in the cornice area, which are displayed in the upper part of the ridge;
- overlapping the frame with roofing material, depending on the preferences of the owner of the house.
Among the options for the finish coat, you can consider the following options:
- Metal tiles are used not only because of their attractive appearance. This material is excellent value for money. Durable, easy to install and lightweight. It reliably transfers blows, but at the same time it transfers all sounds well, which is the main drawback.



- Roofs covered with corrugated board are quite durable. Such a roof has additional polymer protection and is inexpensive. Despite its flexibility, the material is quite durable, but just like metal tiles, it suffers from the effects of noise.
- Ondulin is lightweight, environmentally friendly, resistant to moisture, quiet, can carry loads of more than 900 kg and is not expensive enough, but is exposed to sunlight - it quickly fades and emits an unpleasant odor. It is also flammable.


- Slate is an economical and durable option. Non-flammable and easy to handle. Behind these advantages lies fragility and the presence of asbestos harmful to humans.
- Shingles - longevity up to 70 years, looks rich and stands within reason, is quiet and does not allow corrosion to develop. But it is sensitive to weather conditions: in the cold it is fragile, in the heat it melts and gives off a pungent odor. Highly flammable.


Design
Many consider the attic a second-class room and seriously think about how it will look only from the outside, but modern solutions allow you to make an atmospheric and colorful room inside the room, which will be to the taste of all residents of the house.






The arrangement of this room is not an easy question. When choosing furniture, it is worth remembering the inclined walls of the attic. For the rational arrangement of the attic space, designers recommend:
- you can visually increase the low ceiling due to low furniture - low tables, pedestals, ottomans, beds without legs;


The head of the bed is installed against a low wall opposite or next to the window; if the space is completely limited, then it is better to place it along the wall;
- regardless of the functional purpose of the attic, there must be a place for storing things, be it cabinets or cabinets, which are usually located in the "dead" area of the attic to save space and free movement;


- it is important to pay attention to the quality of lighting;



- think over what items are really needed in this room, and not litter it with anything;
- the attic can serve as both a bedroom and a living room, an office, a nursery, a dressing room, a billiard room, a cinema or a gym, and even a bathroom can be placed within it.





Often, the interior of the attic is decorated with natural materials and adheres to a certain style.
The attic in the Scandinavian style is spacious, discreet and cozy. Subdued soft tones concentrate all attention on minimal decorations. On the walls - either light wallpaper, or paint, or wood. The floor is covered exclusively with parquet boards, darker than the shade of the walls.


Ecostyle assumes forest, sea, floral or mountain themes. Furniture is selected only from natural materials. For a complete reunification with nature, designers offer transparent roof inserts. Delicate and light colors are used.



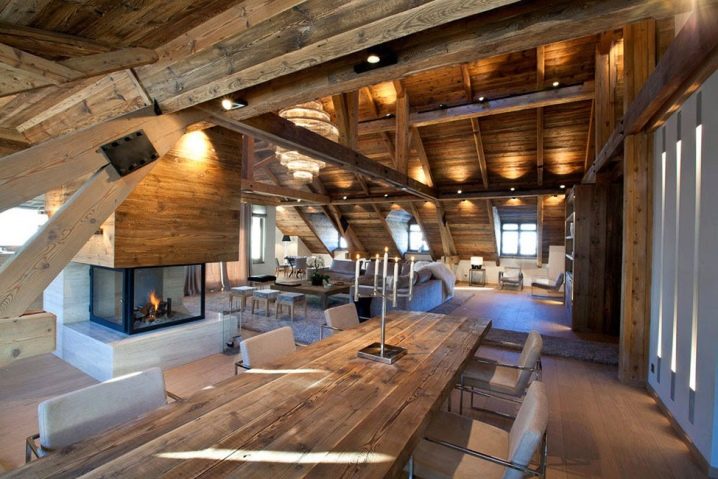
The very name of the style - chalet, suggests that the design of the attic will be presented in the form of a kind of hunting lodge with massive ceiling wooden beams and leather furniture. An attractive fireplace and hunting souvenirs fit into such an interior. The color scheme is in muted tones.

One of the most popular styles today, both for the attic and for any other premises, is the loft. Its distinctive features are concrete or brick finish, display of communications, massive floor-to-ceiling windows without curtains and curtains, a minimum amount of furniture. Unusual rare items can be used as attributes.

The Provence style is characterized by an abundance of textiles, floral, checkered or striped patterns. The furniture is usually a little dated and quite large.For example, a bed can be made of wrought iron or wood, and for volume, it has a large number of bedspreads and pillows.





Beautiful examples
Attic with a conical roof.


Multilevel roof slopes give the attic an original look.
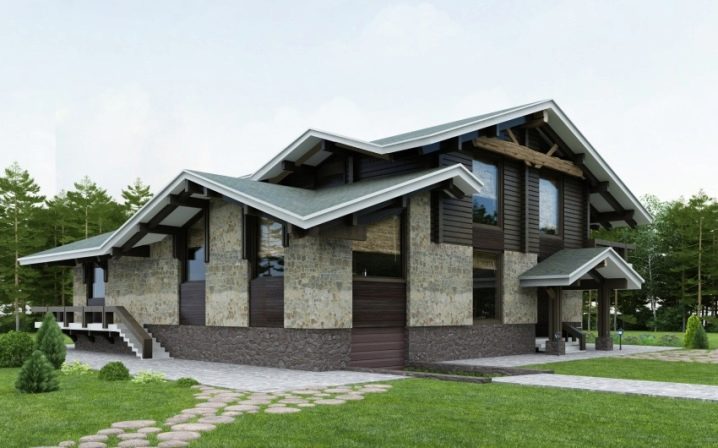

The construction of such a roof allows you to build a covered terrace.
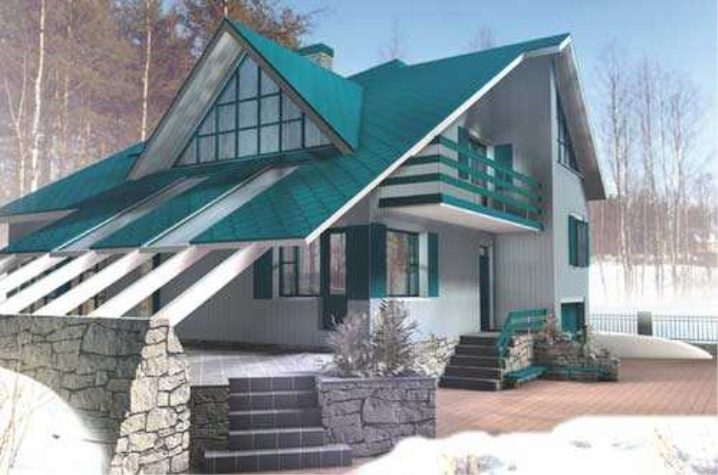

Fashionable European attic architecture design.


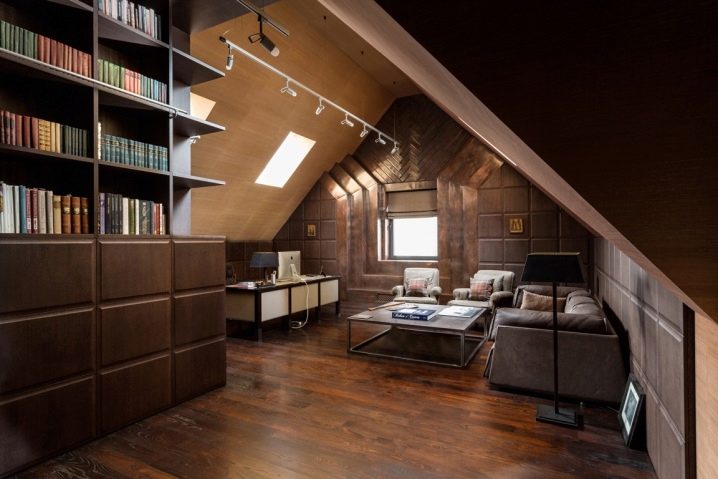
Attic cabinet interior.

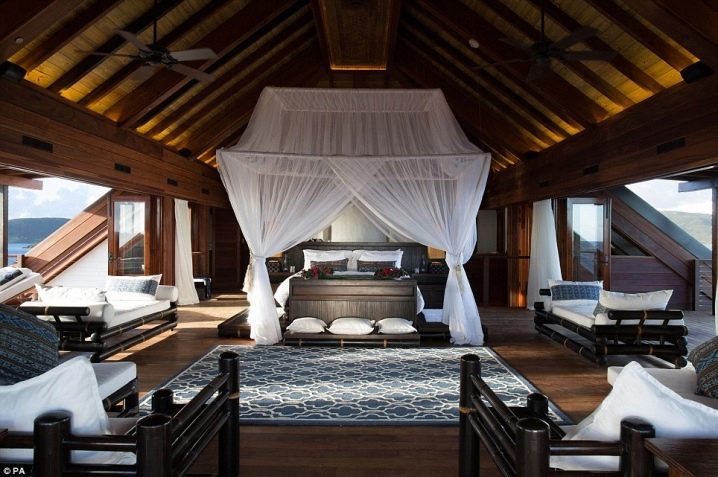
An attic bedroom design in a resort hotel.

The project of a children's room located in the attic of the house.

The following video shows the installation of a mansard roof.













The comment was sent successfully.