When and how to transplant raspberries to a new location?

Over the years, raspberry bushes cease to delight their owners with high yields. For a while, fertilizers solve the problem, but then there is only one way out - the plant needs to be transplanted to a new place. It is not difficult to cope with this task: it is enough to know when and how it is performed correctly.


The need for a procedure
Many gardeners believe that over the years raspberries bear fruit successfully without changing their "place of residence". They admit their mistake rather quickly - after 4-6 years from the moment of planting, when the yield of the bush is noticeably reduced. With good care, anxiety symptoms appear later, but they are inevitable anyway. Over time, the berries become smaller, their taste and aroma become less pronounced, and the number of fruits decreases steadily.
Let's consider the main reasons for these problems.
- Gradual depletion of the soil. For full-fledged fruiting, raspberries need useful and nutritious components that it receives from the soil.
- Lack of space for root development. The natural result is a decrease in the number of new shoots, the bush ceases to rejuvenate properly.
- Lack of proper care most often leads to excessive thickening of the plantings, when the branches begin to interfere with each other. Other misfortunes are also possible - pests and pathogenic microflora, which gradually accumulate in the soil.
- Change in soil acidity. As a rule, it arises due to improper conduct of agrotechnical measures.
In addition to the age of the bush, a raspberry transplant can be provoked by:
- lack of lighting;
- excess moisture;
- being in a draft.
Experience shows that most often the described procedure is carried out every 5 years. With the late onset of anxiety symptoms, it is performed 1.5-2 times less often.


When is the best time to transplant?
In the case of raspberries, the event in question can be held in both spring and autumn. Both options have their obvious advantages, and therefore the success of the procedure primarily depends not on the season, but on strict adherence to the established schemes and rules.
- Spring transplant - a guarantee of the rapid development of the bush in the warm season. The summer length of the day, combined with high temperatures, makes the raspberry more robust, accelerating the development of the plant's root system. Such a culture will survive the winter without problems - one of the main threats to the shrub. Another plus of transplanting raspberries in the spring is the ability to timely solve emerging problems (for example, the appearance of pests).
- Carrying out the procedure in the fall has its undeniable advantages. In such cases, the plant does not need a lot of useful and nutritious substances, and with the arrival of spring, it enters a phase of active growth immediately - without adaptation. At the same time, the gardener can accurately identify the shoots affected by frost and remove them (if any).
An equally important factor in determining the timing of transplanting raspberries will be the region where the crop is grown. For the middle lane and southern regions, autumn is the best option, and in areas with a more severe climate, the procedure is best done in spring. The last point is explained by the fact that a young plant must take root before the onset of cold weather.
The main condition for a successful raspberry transplant in the spring is the procedure before bud break.


Depending on the region, the optimal time to complete the work differs significantly:
- the middle lane (including the Moscow region) - the last decade of April;
- Siberia, Ural, northwestern regions - the first decade of May;
- Kuban, Rostov region and other southern regions - the last decade of March.
As for the autumn raspberry transplant, it is performed 4 weeks before the arrival of real frosts. Bushes with lignified young shoots that have several replacement buds are considered ready for such a procedure. As in the case of the spring transplant, the timing of the work is determined by the specifics of the region:
- areas with a cold climate - immediately after harvesting (from the last decade of August to mid-September);
- middle band - from early September to mid-October;
- areas with mild climatic conditions - from early October to the second decade of November.
Special attention should be paid to the variety of bushes to be transplanted. If in a certain region, raspberries with an early ripening period are transferred in mid-September, then representatives of late varieties are disturbed only after 2-3 weeks.

Choosing a new location
In order to get the maximum effect from transplanting raspberries, the gardener should also take into account the new location of the bush, the choice of which is determined by various factors.
- Good lighting. The culture should not suffer from a lack of sunlight, but ideally, light shading at lunchtime is desirable. If there is not enough light, raspberry shoots stretch out, and yield decreases.
- Wind protection. The greatest danger to the plant is represented by cold air currents, and therefore it is justified to plant it from the south side of the building or fence.
- Suitable soil. First of all, the soil on the site should be fertile and belong to the sandy loam or loamy type. The pH indicator is also important: any of its values from 5.8 to 7.0 are allowed (reaction from slightly acidic to neutral).
- Waterlogging protection. Raspberries should not grow in areas that periodically suffer from flooding (first of all, lowlands should be avoided). It is also worth checking the groundwater level (permissible values are 1 m or more).
It is necessary to take into account the crops that grew in the selected area earlier. The best option is the land that has been “resting” from plants for the last 5 years.

If there is no such place in the garden, you need to find a site that did not grow:
- raspberries (ever);
- potatoes (6 years old);
- currants, strawberries and strawberries (5 years);
- gooseberry (4 years old).
As for the predecessors recommended for raspberries, first of all, these include siderates, also called "green fertilizers". They noticeably improve the structure of the soil, saturate it with nitrogen and slow down the development of most weeds.
An equally important point is the plants located in the neighborhood. First of all, stone fruit crops are among the unsuitable options:
- apricot;
- peach;
- plum and cherry plum;
- cherry and sweet cherry.
Other unwanted neighbors are walnuts and most berry crops (strawberries, wild strawberries, blueberries, grapes, gooseberries, sea buckthorn, currants).
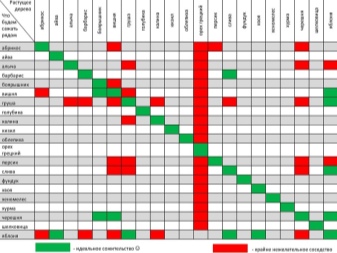

Selection of planting material
The choice of seedlings for new raspberry bushes is determined by the season. For the spring period, mature plants with strong roots and a fairly thick trunk (at least 10 mm), covered with a large number of buds, are suitable. Experts note that such bushes can be divided into several parts, following a simple algorithm:
- moisten the soil well above the roots;
- carefully dig in the raspberry tree from all sides (the shovel must be held at right angles to the ground - this method is the least dangerous for the underground part of the plant);
- slowly remove the bush from the ground;
- divide the plant into parts with a pruner.
An alternative solution is to use root cuttings. They should be harvested in the fall, choosing specimens 10-15 cm long and about 3 mm thick.The selected material hibernates in a basement or other cool place, and you need to plant it with the onset of spring.
As for the autumn raspberry transplant, lignified young shoots are best suited for it. The second significant point is the length of the plant roots: it is desirable that it be 15-20 cm. And it is also worth paying attention to the health of the planting material: it should not have traces of pests and / or pathogenic microflora. There is little sense from diseased seedlings - they do not take root in the vast majority of cases.
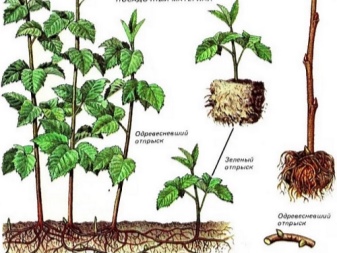
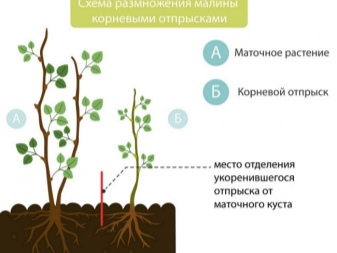
Preparation
A new place for a raspberry bush should be prepared a month before transplanting. This procedure involves digging the soil to a depth of 25-35 cm, removing stones and weed residues from it. Further, the soil gradually settles and compresses.
If the soil does not meet the optimal criteria mentioned earlier, certain steps may be required from the grower.
- Elimination of excess acidity (pH below 5.8). It is carried out by adding slaked lime or dolomite flour to the soil.
- Arrangement of effective drainage. As the latter, you can use broken brick or gravel. This is most often true for areas with heavy soil, the basis of which is clay.
- Creation of a cushion to retain moisture. It is required in areas with a predominance of sandy soil, which allows water to pass through too quickly, and represents the arrangement of a clay layer.
And also for the purpose of prevention, the soil can be treated with a broad-spectrum insecticide. The procedure is performed 3-5 days before the scheduled transplant. The latter is carried out in pre-prepared pits.
- Wells. The width and depth of such pits is about 35 cm, the distance between them is 60 cm. If several rows are provided, then they should be done at a distance of 1.5-2 m from each other.
- Trenches. The width and depth of the ditch is 35 cm, as is the case with the holes. As a rule, the length of one trench is 2 m, which is enough for comfortable placement of 3 bushes. The recommended distance between the moats (if several are planned) is 2 m.

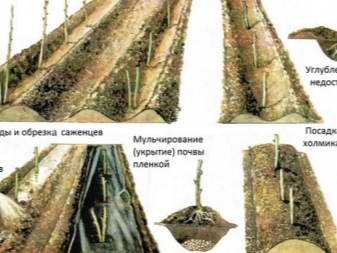
In the process of preparing pits, special attention should be paid to the top layer of the soil. It is the most fertile, and therefore it is laid aside and used when planting young plants. And also at the bottom of the recesses, it is advisable to equip a double layer of organic matter. First, you should put the cut pieces of bark and branches, and then dry grass and leaves. Next, the holes or trenches are filled with a mixture, which includes:
- sod land and compost (in equal proportions);
- charcoal (370-380 g per 1 sq. m);
- superphosphate (in the region of 90 g per 1 sq. m);
- potassium sulfate (40-50 g per 1 sq. m).
Fertilizers should be applied to the soil, mixing them thoroughly. Ignoring this recommendation can lead to uneven distribution of nutrients and burns to the roots of the plant. At the end of the work, the recess must be covered with a material that does not transmit light to avoid weed germination.
The last significant point is the correct pruning of the raspberry bush. This procedure allows the plant to more easily endure stress after transplanting, shifting the emphasis of its development towards rooting. As a rule, the shoots are cut by 50 cm - this is enough to slow down the growth of the green mass.


How to transplant correctly?
Depending on the specifics of the plant, the described procedure may have its own characteristic features. Considering them, the gardener will achieve the desired result with the least investment of time and effort.
Mature bush
Let's analyze the procedure for transplanting an old raspberry bush.
- Remove the plant from the ground. Digging in the bush is performed at a safe distance from the trunk. The shovel should enter the soil at right angles, with the least risk to the main roots.
- Transfer the raspberries from the old place to the new one. This should be done without delay, while maintaining an earthen coma around the roots.If the transfer involves long-term transportation, the seedling is thoroughly moistened, wrapped with a thick cloth and placed in a bag.
- Place the bush together with the earthen clod in the planting hole. In a situation with plant division, each specimen is carefully straightened the roots. They should be positioned evenly and neatly, without bending upwards.
- Check the level of the root collar. Ideally, it should be flush with the ground.
- Fill the hole with fertile soil, which was set aside during the preparation process. Next, the soil should be compacted and watered (for each raspberry bush you need 5-6 liters of water). If, after a few hours, the soil settles, it is necessary to add it to the previous level and moisten it again.
- Drive in a peg near the planted plant, being careful not to catch the roots. The raspberry garter is done with twine, the tension of which should be moderate.
The final stage is covering the soil with a layer of mulch 5-7 cm thick. Sawdust, shavings, cut grass, humus and other natural materials are suitable for solving this problem.


Root shoots
Such planting material is represented by young shoots growing at a distance of 30-70 cm from the middle of the bush. Their appearance is possible due to the adventitious buds, which are formed on the roots with a horizontal orientation.
Shoot transplantation is most often carried out in the spring. This period is preferable to the autumn period, since the soil is richer in moisture throughout its entire length. To solve the problem under consideration, it is necessary:
- select a suitable material for planting - healthy shoots 20-25 cm high;
- carefully dig up young plants;
- carry out the transfer according to the standard algorithm.
During the first decade from the moment of transplantation, plants should be protected from the scorching rays of the sun. A dense fabric fixed on temporary supports allows you to achieve what you want.


Replacement shoots
This planting material develops from the buds located in the root collar of the plant. The average height of the replacement shoot is 50 cm, and its main function is the regular rejuvenation of the raspberry bush. The transplant of such material is carried out in the spring. The place for the plant is prepared according to the previously discussed scheme, starting in the fall. The transfer procedure itself provides 7 main points:
- remove old plant stems and root suckers, leaving no more than two replacement shoots (the event is carried out after harvesting);
- drive in pegs and securely tie shoots to them;
- spud the plant in a timely manner (before the first frost);
- with the onset of spring, cut off the shoots by 10 cm;
- remove hilling when the length of the leaves reaches 15 mm;
- chop off the roots at a distance of 20 cm from the center of the bush;
- carefully remove the plant and transfer it to a new place according to the standard algorithm.
At the end of the procedure, it remains to thoroughly water the raspberries, and mulch the soil.


Follow-up care
In order for the transplanted raspberry to take root faster, experts advise pouring it with a root formation stimulant, following the instructions for the drug used. In the future, it is worth considering a few more recommendations.
- Water the plant regularly, but in moderation. The average frequency of the procedure is once a week (the specific value is determined by the amount of precipitation). The main thing is that the soil around the bush never dries out.
- No less important conditions are timely removal of weeds and loosening of the soil. Thanks to these measures, the raspberry roots are not afraid of a deficiency of nutrients and oxygen.
- A month after the spring transplant, it is advisable to feed the culture. To solve this problem, complex mineral preparations are used. Alternatively, the bush can be fertilized with nitroammophos.
- Before the onset of frost, the soil is mulched with a thick layer (15-20 cm). Agrofibre is used as an additional protection for young plants.
Following the listed recommendations, you can achieve excellent survival of the transplanted culture.The natural result of this will be bountiful harvests that will delight the gardener over the next few years.












Where can I find a plot, in a vegetable garden or in a country house, where nothing has grown for 6 years?
The comment was sent successfully.