- Name synonyms: Columbus
- Year of approval: 2005
- Ripening terms: mid-early
- Bulb weight, g: 300-400
- Coloring juicy scales: white
- Taste: great
- Disease and pest resistance: tolerant to many diseases and their pathogens
- Appointment: salad, for fresh consumption, for canning
- Yield: high
- Average yield: 3.1 kg / sq.m
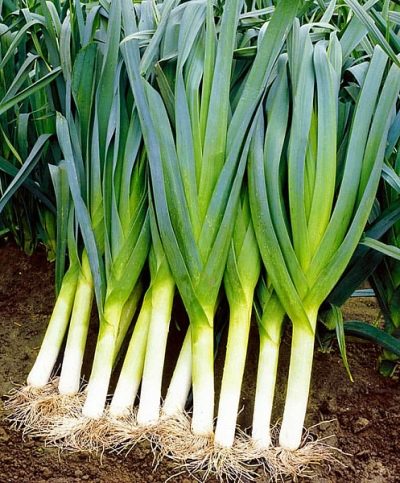
In recent years, leeks, which came to us from Asia, have gained immense popularity among gardeners and farmers. The list of popular varieties includes the medium-early variety Columbus of Dutch selection.
Breeding history
Columbus leeks are the brainchild of Dutch breeders of the agricultural company Bejo Zaden B. V., who developed the crop in 2003. A few years later (in 2005), the vegetable crop was added to the State Register of approved for use on the territory of the Russian Federation. Leeks are cultivated in different regions of the country - from Central to Ural.
Description of the variety
The Dutch leek is a powerful plant with a dense rosette of feathers. The onion is characterized by abundant thickening of long feathers, which extend to a height of 70-80 cm, as well as a developed rhizome. The leaves of the plant are uniformly gray-green or pale green without anthocyanin coloration. On the surfaces of flat onion leaves there is a pronounced waxy bloom. The false stem is endowed with a weakly expressed bulb.
Characteristics of the appearance of plants and bulbs
This variety is valuable for its bulbous bleached leg and thick and fleshy feathers. The snow-white bulb is characterized by a fleshy, tender, moderately dense and juicy consistency. On average, the length of the bulb reaches 20-30 cm, and the diameter is about 4-5 cm. The structure of the bulb is of medium density, consisting of fleshy scales, tightly adjacent to each other. The total weight of the plant is usually 300-400 grams.
Of particular value is the onion pulp, which contains a high content of vitamins of group B, A, E, ascorbic acid, beta-carotene, as well as phytoncides, some proteins and fats. The high iron content is also worth noting.
Cut onions without significant losses transfer transportation over long distances, and can also be stored for a long time. It is characteristic that during transportation the leg does not darken, does not crack. For storage, vegetables are laid out vertically, and then covered with sand.
Purpose and taste
The Dutch onion stands out among its relatives for its excellent taste. Its taste is balanced - low pungency, subtle sweet notes and a light onion aroma are perfectly combined in the snow-white pulp.
Cut onions are versatile varieties. Its bulbs are added to salads, hot and cold dishes. Fleshy and aromatic feathers are widely used in canning and marinade preparation.
Maturation
Columbus leeks represent a class of mid-early varieties. From the moment of mass germination to full ripening of the bulbs, less than 3 months pass - 85 days. Mass harvesting begins between July and September. To carefully remove the onion, you need to make a small dig and pull it out gently. The length of the feathers is kept at the level of 20 cm from the branching, and the rest is cut off.
Yield
This onion species is very productive. An average of 3.1 kg of vegetables is cut from 1 m2.
Planting dates with seeds, seedlings and seedlings
Sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out in February-March, and transplantation to a permanent place of growth is performed after 60-65 days.Onion seeds are sown in open ground exclusively in the southern regions, when the air and soil are sufficiently warmed up - the end of May. Sevkom planting is also carried out in the warm season: late May - early June.
Growing and care
Onions are grown by seedling and seed methods. Seedlings are grown in a greenhouse. The seeds are buried in the prepared substrate by 2 cm. Germination occurs after 2 weeks. The distance between the rows is 4-5 cm. The optimal temperature regime is +20.22 degrees. Bushes ready for transplanting should be strong, with 3-5 true leaves and a false stem diameter of up to 6-8 mm. Landing is carried out in one-line rows or two-line ribbons according to the scheme 25x50 and 30x60 cm.
When planting with sevkom, the scheme of 7-10x50-60 cm is observed. Seeds are planted in open ground in conditions of stable heat. Onion care includes: watering every 3-4 days with warm water, weeding and loosening, applying dressings 2-3 times per season, hilling 2 times in the second half of the growing season to obtain bleached onion legs, prevention of viruses.

Since the onion is an unpretentious and cold-resistant plant, it can be planted both in spring and autumn. It is necessary to properly prepare the planting material, competently prepare the garden bed and determine the timing of planting.

Soil requirements
Onions prefer medium loamy fertile soils with good drainage system and a neutral reaction. The soil is preliminarily well loosened, enriched with nutrients, moisturized.

The bow is not as unpretentious as it seems. For good growth, you need fertile soil, quality care and nutritious fertilizers. Without top dressing, the bulbs will grow small, and the greens will not be lush. At different stages, it should be fed with different substances. The vegetable needs organic and mineral feeding. A good result for fertilizing onions is the use of folk remedies.
Required climatic conditions
Despite the fact that the vegetable crop is endowed with good stress resistance, withstanding sharp temperature fluctuations, short drought and light partial shade, it prefers to grow in sunny areas, where there is a lot of light, heat, and there is also a barrier from drafts.
Disease and pest resistance
The vegetable has good immunity, providing tolerance to many diseases - downy mildew, tobacco mosaic virus, leaf rust. In addition, the variety is resistant to attacks by onion flies and snails. Planting carrots nearby, the aroma of which repels pests, is an excellent tool in the fight against onion flies.

Despite the fact that the onion is a very useful plant, capable of repelling and killing many microbes and bacteria, it itself is often damaged and suffers from various misfortunes. Diseases and pests of onions can significantly reduce the yield. It is necessary to correctly determine the presence of this or that disease and take appropriate measures in time.