Batun onion and the nuances of its cultivation
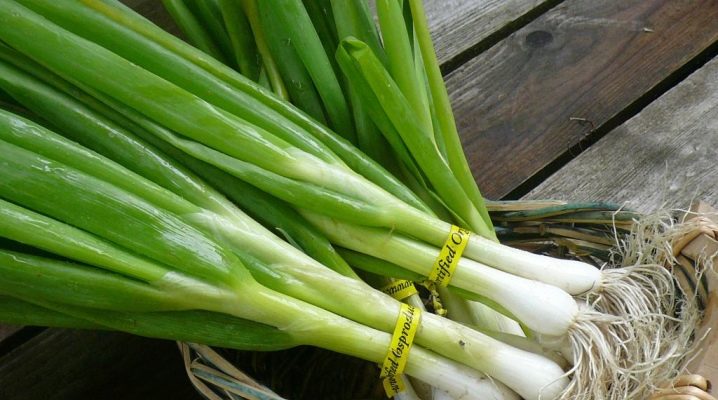

Onion-batun is a perennial, capable of becoming a "sponsor" of chic in terms of the vitamin and mineral composition of greens to the table. Yes, it is not yet the most popular in domestic latitudes, but it is confidently gaining this popularity.
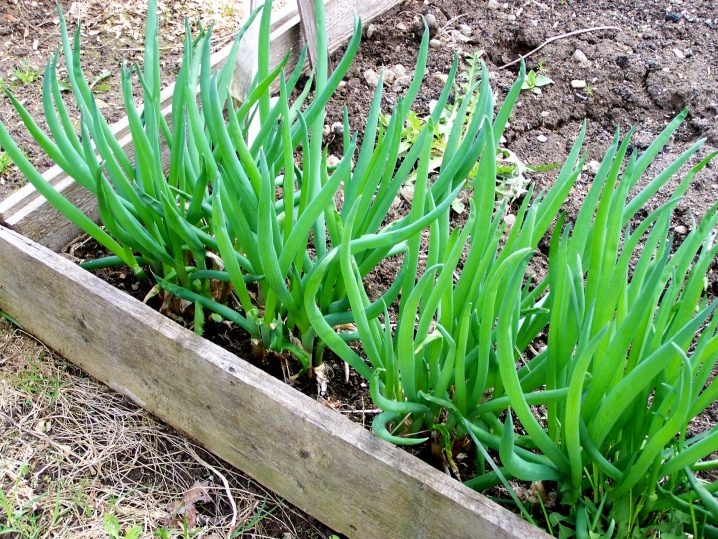

What is especially wonderful about this product is in its undemandingness: once they planted it, and the planting just needs to be renewed, and it is not afraid of even harsh weather conditions.
general description
The onion is considered a herb that can grow for many years without replanting. On the garden bed, it looks about the same as its counterparts: fisty green leaves are not much different from the feathers of other bulbous ones. But only underground this plant does not have that familiar large bulb. The onion of the batun is small, just a little thickening. By the way, you can also eat it, but it is not in demand. Only leaves are eaten by the batun.

What else is important in the characteristics of this plant:
- developed roots grow 40 cm in width and depth;
- the feathers of the plant are thick and powerful, hollow inside;
- if you do not cut feathers in time, they can grow up to a meter in height;
- the vegetable grows very quickly, has a bright color;
- arrows and inflorescences are formed in the second year: they are yellow-green, rounded, there are more than two hundred flowers in the batun;
- flowering occurs in June, and seed ripening - in mid-summer;
- the onion is not afraid of low temperatures (unless this crop will be grown in the Far North);
- in one place the batun grows for 5 years, but if the plantings are very thickened, the onion will become smaller;
- propagated by seeds or by dividing the bush;
- most of the onion is grown in China.


Newbies may have a question about how the batun differs from the leek. Its feather is tougher, the taste is sharper, but you can cut it off earlier. Leek is grown through seedlings, and its white stem is especially valuable (for the sake of it, and they grow). The taste is not as sharp and expressive as that of a batun.
The main thing is to cut off the feathers of the baton in time, because without this they will become tough and tasteless. It will grow on virtually any soil. He will not tolerate completely dry places, but he will not like the wetland either.
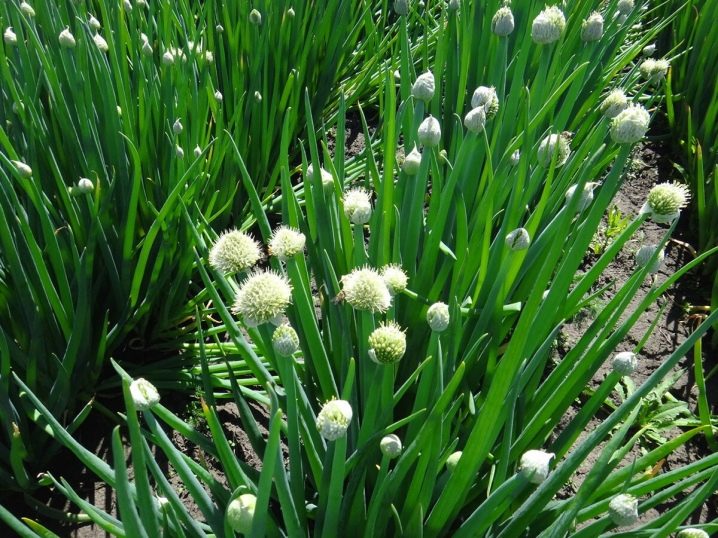

It is better to grow onions in partial shade, under the bright sun, its feathers will dry.
Of the most popular varieties, the following options can be distinguished:
- "April" (early maturing variety, good for salads);
- "Maisky" (resistant to diseases, feathers with a sharp taste);
- Long Tokyo (mid-season, very winter-hardy);
- "Tenderness" (with a mild taste);
- "Seryozha" (early maturing and delicate variety).



Landing
Batun can reproduce both vegetatively and by seed, both ways are simple, both are often used. If the onion is already growing in the garden, the seed method is not used: it is much easier to dig out an existing bush, divide it into smaller shares and plant it. It is also convenient in that weed rhizomes can be removed from the dug out bush. The division of the bush can be carried out at virtually any time, but in August it is more convenient and reliable to do this. The bush is first watered, and then removed from the soil with a clean shovel or garden pitchfork. You can divide it with your hands and with a knife (disinfected).
Seedlings
Seedling cultivation is appropriate when the full cycle (from seed to harvesting with the moment the plants are pulled out) is carried out in one season. That is, it is good if the plant is annual, but perennials are not suitable for seedlings. Seeds are usually sown in April, and at the beginning of summer already decent seedlings are planted on the site. Then, in September, the plant must be dug out without leaving a single bush on the site.
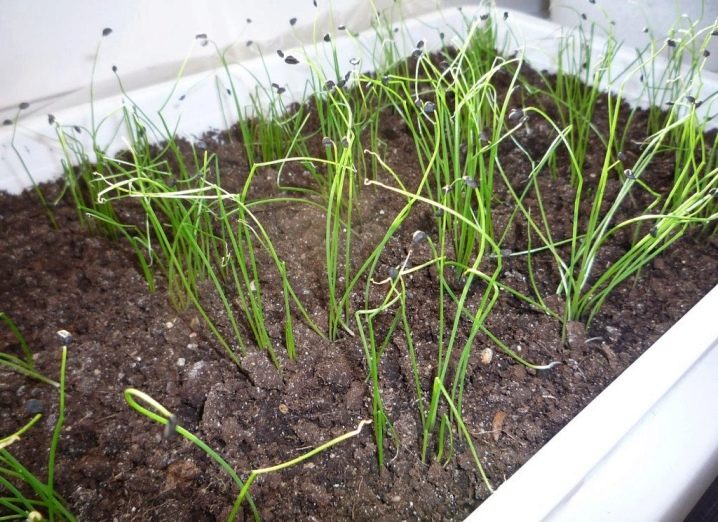

There are some nuances of planting batuna seedlings.
- To accelerate the germination of seeds, they are left in water for 24 hours. Sometimes it is etched for about 25 minutes in a weak manganese solution. They also change the water from time to time, and then the seeds are dried.
- Seeds are planted in special seedling boxes. Sod land is used as a soil, mixed in equal shares with humus. You also need to add 2 glasses of ash there (counting on a bucket of mixture).
- Seeds are sown to a depth of 1 cm, they must go into the pre-moistened grooves in the soil. After the groove is covered with earth, clean sand must also be added there (so that its layer is 2 cm).
- The boxes are covered with glass, and after 2 weeks the first shoots will sprout. Sometimes the time of emergence of seedlings is delayed, this is normal, but there should not be a critical breakdown.
- When the shoots appear, the temperature should be lowered for a week to 10-12 degrees, then raised again. But if the temperature is above 15 degrees, such indicators will become disastrous for the batun. And the backlight is also needed, because the bow loves long daylight hours.
- Watering of seedlings should be moderate, it should not be swamped. It will have to be fed twice: superphosphate and potassium salt. The first feeding is carried out a week after the shoots have appeared, the second - after another two weeks.
- Thickened seedlings must be thinned out, and you should have time to do this in the phase of the first real leaf. The distance between the bushes should be about 3 cm.
- Before planting the seedlings in the ground, they are hardened a week before. And she will be in the garden in the first days of summer (the calculation is taken for the Moscow region and similar climatic regions). The holes in the garden bed are made at intervals of 12 cm.

In general, the seedling method is somewhat troublesome. Seedlings need coolness, and therefore they should grow in a greenhouse or greenhouse: where the temperature in the range of 10-15 degrees can be easily maintained.
Seeds
Still, more often the batun is sown directly to the garden. It is not difficult to collect the seeds of this plant: from the second year of life, arrows-peduncles appear at the batun. They are usually broken out so as not to reduce crop growth. But in this case, these arrows should be left on the bushes, because they will bloom in the middle of summer and seeds will appear in them. Ripe black seeds will still sit firmly in the inflorescences. It is here that the plants are pulled out, collected in bunches and hung down with their heads. This should be done in a dry place, any container is substituted under them, or paper is simply laid out.
The dried seeds will begin to crumble on their own, it will not cost anything to remove them. The seeds are dried a little more, laid out in a thin layer, and then distributed for storage in paper bags. And then you can plant it in the ground. If the batun begins to grow under the film, it is permissible to do so in early spring. You can send seeds to the ground in June, in the year of sowing, the culture will simply strengthen, but it will be possible to cut the leaves only next year. There is also a pre-winter sowing campaign, and it is necessary to make the plantings more thickened, because a certain percentage of the seeds will disappear during the winter period.

What else you need to know about planting a batun onion:
- this culture is not very fond of peatlands and acidic soils;
- on sandy loam and loam, onions give an excellent harvest;
- onion grows with good illumination of the site;
- preparing a bed for planting is elementary: dig up, apply standard doses of fertilizers;
- seeds are sown in grooves spilled with water to a depth of 2.5 cm, row spacing is 30 cm;
- warmed up to at least 5 degrees of soil - a guarantee that the seeds will sprout, it just may take a not always predictable period (from 8 to 20 days);
- after planting, it is better to mulch the bed with humus, the layer should be thin.
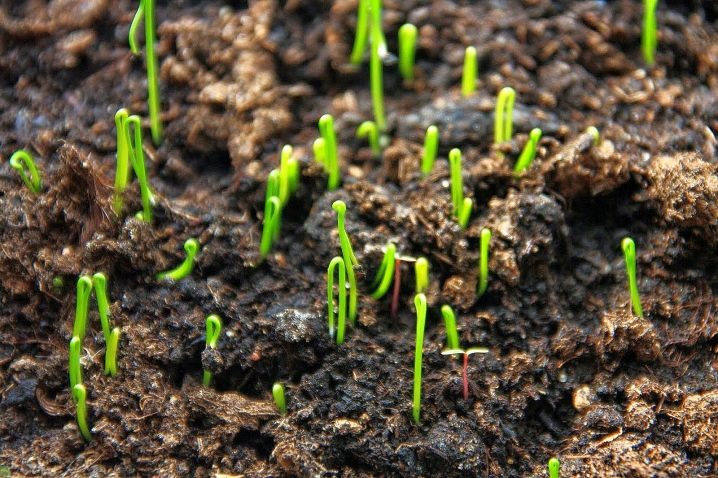

This is how the seed planting looks like, the most characteristic of this onion (however, red and purple are planted in the same way).
Care
There are no special efforts and difficulties in the process of growing a batun. Only at first does he need attention. If the crop is annual, it should be thinned out as little as possible. It is necessary to weed and loosen the bed systematically, here the batun does not differ from other crops.

What else is included in the concept of plant care:
- if the soil in the bed dries up for a short time, the onion will not die, but a prolonged drought is destructive for it: the feather coarsens, loses its taste;
- it is necessary to water the plant once or twice a week, focusing on the condition of the soil, the irrigation consumption is a bucket per square meter;
- a couple of days before the final cut, the onion must be watered abundantly;
- an adult culture will tolerate sprinkling well, but the surface type of irrigation is still not the most preferable, you do not need to flood the feathers too much;
- top dressing is needed after the mass cutting of greens, for the first year it will be an infusion of mullein in proportions of 1 to 10, and after it is absorbed, a glass of wood ash is added per square meter, it must be shallowly embedded in the substrate with a hoe;
- in fertile soil, the batun will grow normally even without additional fertilizing, and the fact that they are needed will be signaled by slow growth and yellowness of the leaves;
- if the onion grows poorly, a weak urea solution can be salutary for it;
- It is not necessary to cut off massively onions in a state of microgreen, but feathers that have already grown to 25-30 cm;
- if the onion is looked after, it will withstand 5 cuts per summer, if not, no more than 3;
- cutting off the leaves until the very frost is not the best idea; the plant must go for the winter with leaves.


Onions are grown at home as well. Since it is not characterized by a state of dormancy, year-round cultivation of a culture as a room is possible. From April to October, onions can grow on the balcony, and if you want a harvest all year round, you need a cool windowsill.
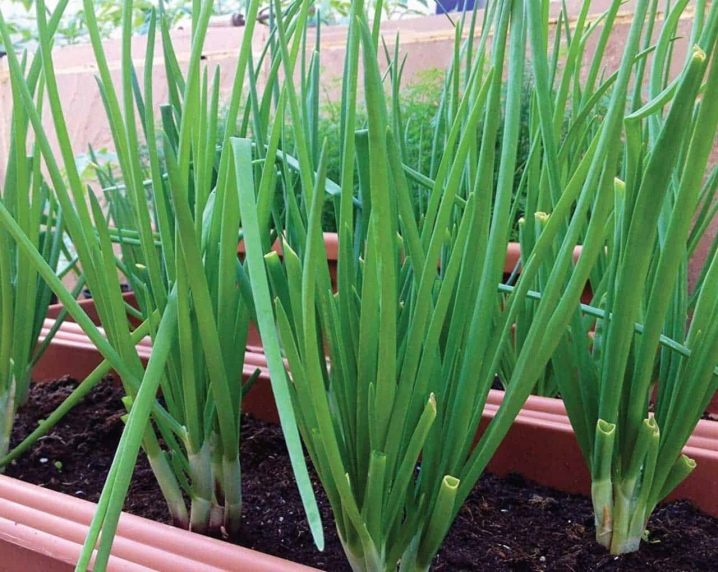

In autumn and spring, homemade onions must be illuminated with phytolamps.
Diseases and pests
Most of the varieties (from "Russian winter" to "April") are resistant to diseases. But still, nothing has ideal immunity on the site. So, a viral mosaic can hit the onion: this is an incurable disease, therefore all seedlings will have to be destroyed, otherwise the disease will occupy neighboring plants. Yellow spots begin to grow over the leaves, the onion immediately stops growing, it cannot be saved.
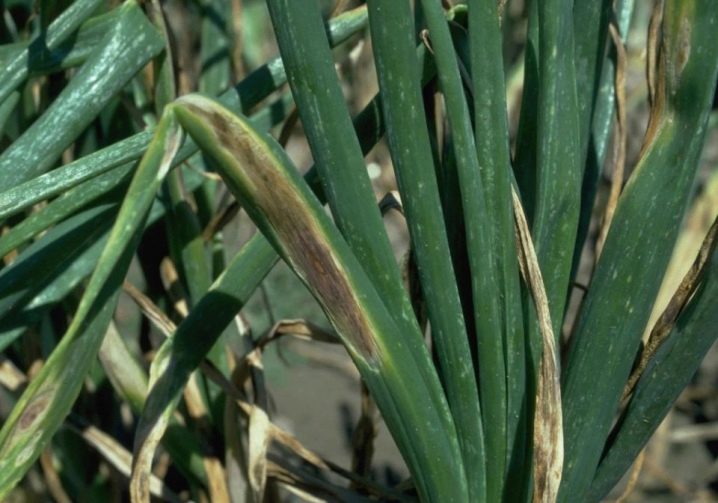

Fungal leaf rust can also overtake the batun: yellow-orange spots will lead to drying of the feathers. Plants that have already been affected by the fungus will have to be cut off, and the whole plants are treated with Fitosporin or Bordeaux liquid. Downy mildew will manifest itself as white spots: diseased plants must be destroyed, healthy plants must be treated with special copper preparations or the same "Fitosporin".
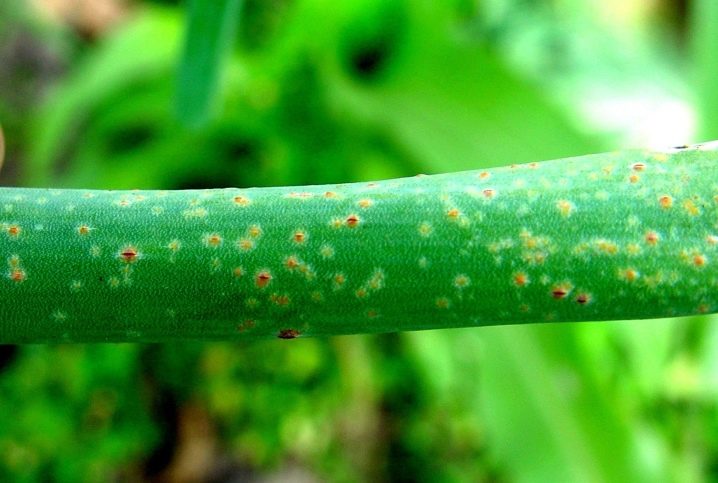
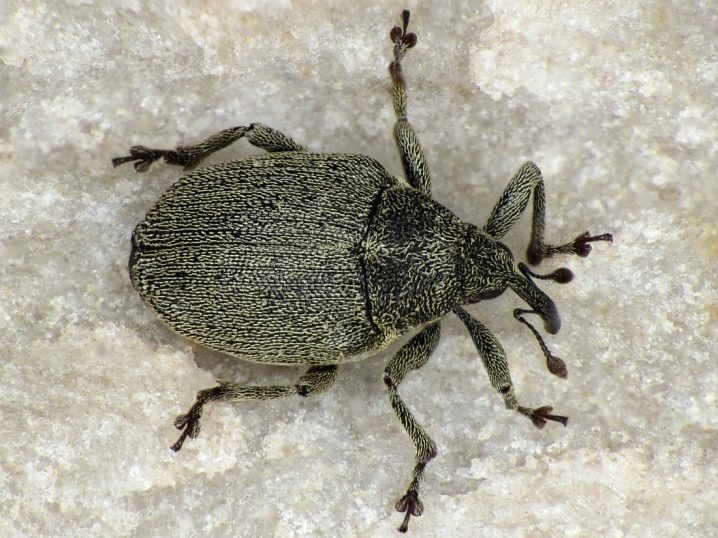
Onion weevil can become dangerous from pests for onions - a dark beetle that gnaws feathers even at the larval stage. Carrots growing in the neighborhood will save from onion flies: the pest cannot stand the smell of carrots. They feed on onion juice and thrips, and usually they attack more than one crop, but try to attack many plantings on the site. Insecticides are used.

Collection and storage
We can say that the frequency of collection is influenced by both the variety and its characteristics. But if you average, then every 3-4 weeks you can harvest onions, that is, completely cut off the leaves. The crop must be cut off completely, and the flower arrows must be broken out (they are left only if seeds are needed). The leaves are usually cut with a sharp knife or scissors and almost at the soil.
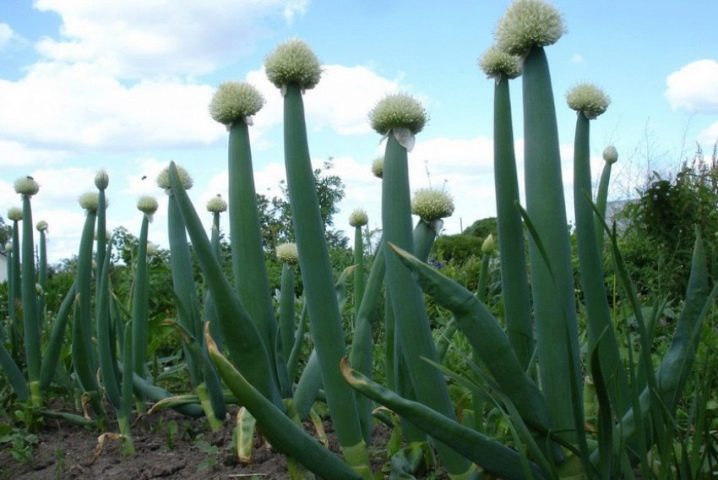

The last cut is made a month before frost.
Green fat-leaved onions are stored in a loosely closed plastic bag in the refrigerator, it is more convenient to stack it in bunches. Fresh foliage will be relevant for only a week, then it deteriorates.But onions can be chopped, packaged in sachets or containers, and frozen. In winter, such a freeze (like microgreens) is great for making soups, main courses and more. By the way, it can also be added to minced meat.
This onion sprouts even in not the most favorable conditions. It is not as beautiful as pink chives, but more tenacious, and the pungent taste of its feathers complements many dishes. Vitamin composition helps to make food even healthier.














The comment was sent successfully.