Aphids on indoor plants: what does it look like and how to get rid of it?

Ornamental indoor plants can be attacked by harmful insects. Aphids, which can kill a plant in a short time, are considered one of the most common and dangerous pests.
Reasons for the appearance
The warm and dry atmosphere of the premises is a favorable environment for the existence of insects, and many reasons contribute to the appearance of aphids on indoor plants.
- Often, when transplanting plants, aphids appear from contaminated soil if it has not been previously disinfected.
- A newly acquired plant may be infested with insect larvae, from which adults subsequently emerge.
- Infection with winged aphids can occur through uncovered balconies and windows.
- The appearance of ants indoors also contributes to its spread. Feeding on the sweet secretions of aphids, they are at the same time its carriers.
- Pets can bring aphids on their paws and fur.
- The source of aphid infestation can be brought bouquets containing infested flowers.
If an aphid attacked one indoor flower, then in a short time it is able to infect all plants, since it multiplies very quickly and then it will be extremely difficult to fight it.

Views
Aphids are an unusual group of insects in terms of biology, species diversity and the danger they pose as a pest. They usually form large colonies both on the aerial part of the plant and on the roots. With its vital activity, aphids generate pathological changes in the affected areas, which are manifested in foliage coagulation, deformation of the endings of the appendages, the formation of galls - growths that are hollow inside.
The result of the life of aphids is the formation of sticky secretions (honeydew), which serves as food for ants, contributing to the spread of insects.
Aphids have a complex cyclical development. The most typical cycle is with fertilized larvae overwintering in the ground or on the root parts of plants. In the spring, wingless females appear, capable of reproducing without fertilization. In addition to these females, each aphid species also has a winged female, whose role is to spread the species and change the host plant. Males have wings.
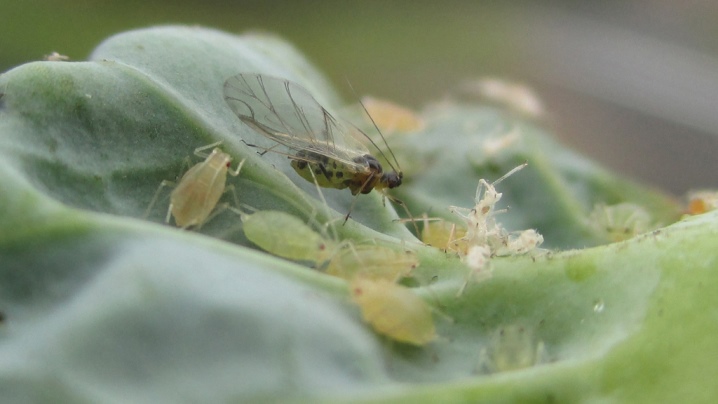

The aphid is a small insect with a length of 1 to 7 mmhaving a jelly-like body of oval, round or elongated shape with a delicate cover. The head has antennae, eyes and proboscis, with the help of the latter, the pest bites through the surface of the leaves. With the help of long legs (there are only 6 of them), the insect is able to move and jump.
The species diversity of the pest is distinguished by a huge number - about 5 thousand species.
They vary in size and color. There are species in which the development cycle occurs on a specific plant. It is a monovalent species.
Others develop on a variety of plants. This is a polyphagous species of aphids. The pest is distinguished by fertility: during the season 1 female lays up to 100 eggs with a frequency of 10 days.
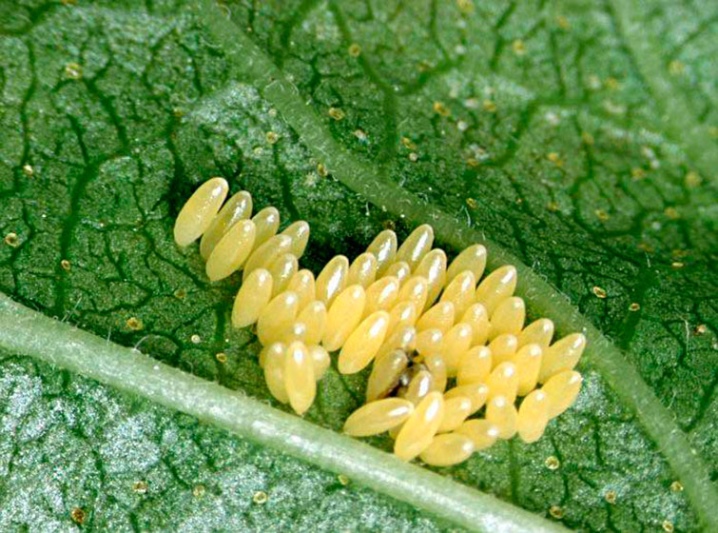

Household plants are mainly parasitized by these types of flower aphids.
- Aphids are white or hairy. The oval body is light brown in color with bristles on the sides, covered with a white fluffy bloom, so the affected plant looks like it is covered with frost. The stems are deformed, foliage and flower ovaries dry and crumble.
- Black or cherry aphids. The wingless female has a wide pear-shaped body with a length of 2 to 2.4 mm. The shiny back is black, the abdomen is brown. The winged female also has a shiny black body about 2.4 mm long. Prefers stone fruit crops, but can also settle on home flowers.


Consider other varieties of aphids that can also infect indoor plants.
Green peach or greenhouse
The body of the pest is oblong-ovoid, up to 2.5 mm in size. The covers of the body have a color that depends on the plant on which the pest lives, and are light green, yellow-green, pink. With a massive defeat, buds and foliage wither and crumble. This species can parasitize on 50 types of plants: vegetables, fruit, greenhouse crops, home flowers.
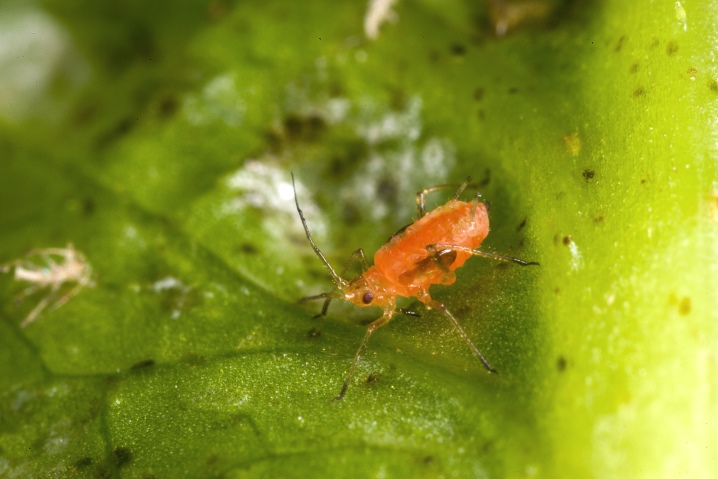

Melon or cotton
This is a polyphagous species of insect. The body of the aphid is elongated-oval in shape, pointed at the rear, has a length of 1.2 to 1.9 mm and is colored yellow, deep green or black-green. The legs and antennae are dark brown or black in color. The winged female has a black head and breast. A characteristic feature of this species is the ability to form dense colonies on both foliage and buds, as well as on shoots. It can affect vegetable and berry crops, citrus fruits, fruit trees, ornamental flowers, including greenhouse crops.
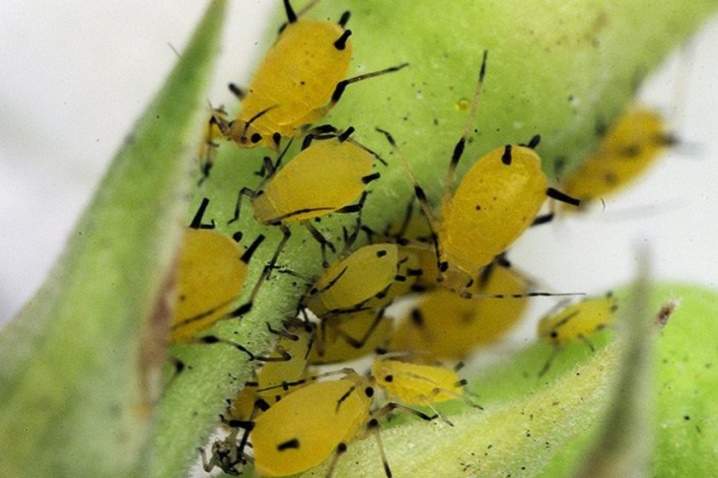

Legumes (beet)
It is a migratory insect. The pest has an oval body, slightly widened from the sides, 1.7-2.7 mm long. Body color is varied - from different shades of green to brown and even black. In an insect, the breast is black, and the abdomen is usually lighter in color. The tarsi and antennae are light with a black top. The winged female is similar to the wingless, but the breast and head have a glossy black cover.
The legume aphid affects various legumes, nightshades, pumpkin, asteraceous species of garden crops, as well as weeds and ornamental flowers.
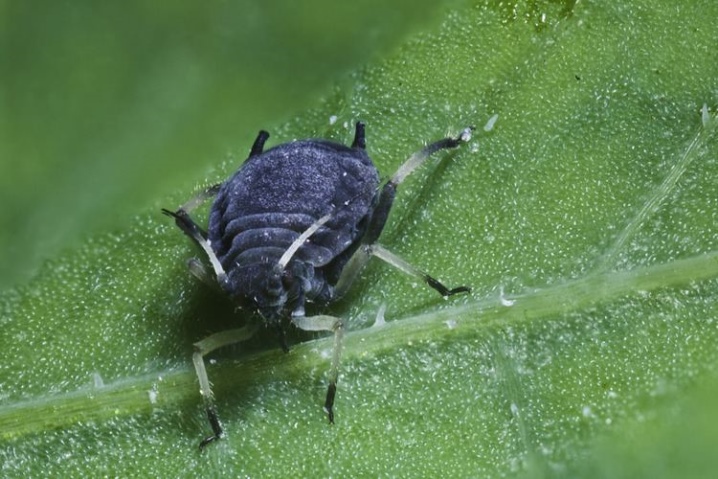

Large potato
The large body of the insect is spindle-shaped and can reach a size of 4 mm. The covers of the body are green or red. The winged female is somewhat smaller - from 2.3 to 3.4 mm. It is colored light green, and the antennae and legs are brown.
The wingless female can hibernate in the ground, and in the spring she moves to the plant. Aphids harm garden crops (potatoes and cabbage, beets and tomatoes) and many ornamental indoor and greenhouse plants.
The main harm caused by aphids is the spread of about 50 types of viral infections.

What plants are affected?
Despite the fact that many species of aphids are polyphagous, the pest does not settle on all types of indoor crops. Since their food is plant sap, they prefer flowers that have soft, fleshy leaves. For example, palms and dracaena with their tough, dense foliage do not attract pests, and they avoid settling on them.
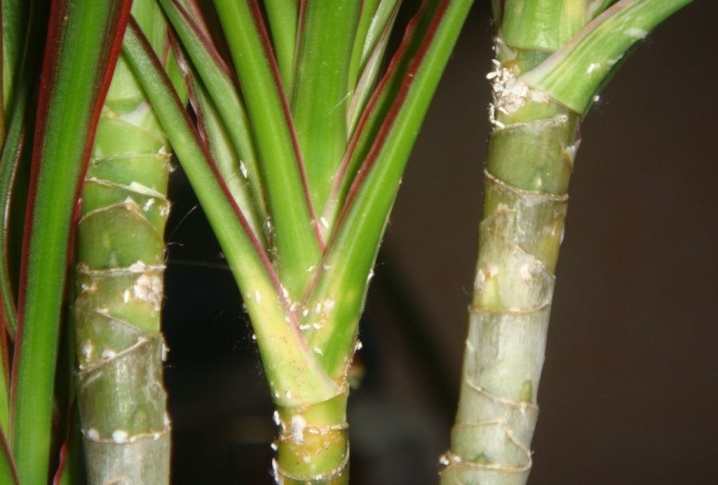

Usually insects infect these types of decorative flowers.
- Kalanchoe. The plant with large leaves, juicy branches and a trunk attracts black and green aphids. Colonies form on the inner surface of the leaf. The honeydew, covering the surface of the leaves, clogs the leaf stomata, and as a result, the process of photosynthesis is disrupted.
- Ficus. Adult specimens of the plant with a dense leaf and trunk surface do not attract aphids. Only young shoots of dwarf and small-leaved varieties of ficus are attacked. Leaves, deprived of juice, become deformed, turn yellow and crumble. The pest causes such a dangerous disease as a sooty mushroom. Without treatment, the plant dies.
- Azalea. The conditions for keeping the flower (dry air, absence of drafts and direct sunlight) are also favorable for the life of the insect. The affected plant slows down its development, the buds do not bloom.
- Hibiscus (Chinese rose) also attracts pests. All parts of the diseased flower are covered with a sticky bloom, the leaves fall off, the buds wither.
- Cyclamen. On this flower, the aphid prefers to infect the buds. Subsequently blossoming flowers have a deformed shape. Honey honeydew contributes to the formation of sooty fungus, anthracnose and wet rot. The plant gradually withers and dies.
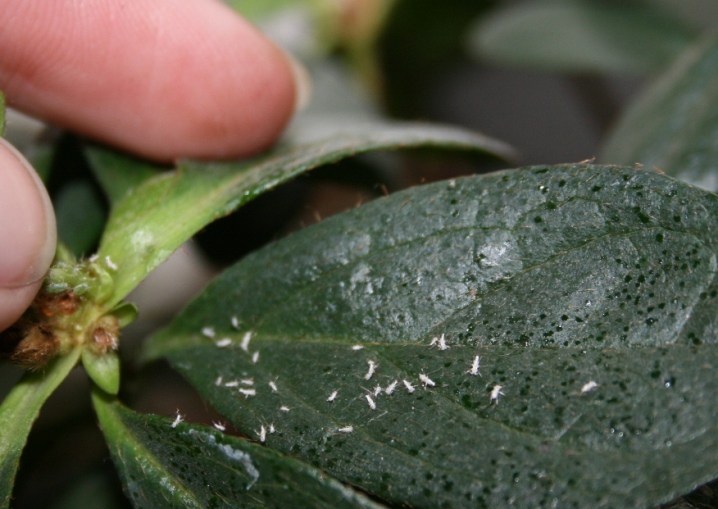

Aphids also affect other indoor flowers:
- spathiphyllum, balsam and poinsettia, in which the stem and twigs become crooked;
- anthurium, in which the leaves curl up into a tube, the decorative appearance disappears;
- begonia, in which affected buds fall off, there is no flowering.

How to fight?
The defeat of aphids leads to serious consequences. The rapidly growing and expanding colonies are finding new places to live in different colors. Therefore, it is so important to start the fight at the very first symptoms of defeat. If single colonies of aphids are found, it is quite possible to quickly eliminate it with your own hands, if you follow these steps step by step:
- remove the top layer of soil in a pot and add fresh soil;
- then the plant must be washed with running water and wiped with a soft swab;
- wipe the flower with a soapy or water solution of methyl alcohol, let the plant dry;
- in the last place, the flower itself and the soil are sprayed with an insecticidal preparation.

There are several ways to get rid of white and other types of aphids at home.
Chemicals
You can destroy pests by treating flowers with insecticides. Chemicals work quickly and efficiently. They belong to the preparations of contact and intestinal effects, which are able to penetrate both through the integument of insects and through the digestive system. Houseplants can be treated with such versatile remedies that can be applied to all types of plants.
- Aktara. The drug is used to treat the plant itself and the soil. It begins to act very quickly - within 30 minutes. To remove the surviving pests, a second one is done 3 weeks after the first treatment.
- Actellik. The tool kills almost all varieties of aphids, both on the plant itself and in the ground. In addition to spraying, you also need to wipe the inside of the leaf and the stem with the agent. In case of extensive infestation, the treatment is repeated after 14 days. In order to avoid the addiction of pests to the drug, the concentration of the solution must not be reduced. The drug is very toxic, so the procedure should be carried out outdoors.

In addition to these universal ones, there are special preparations for certain plants:
- for violets - "Aktofit" and "Intavir";
- for Kalanchoe - "Intavir" and "Calypso";
- for hibiscus - "Decis" and nicotine sulfate;
- for chrysanthemums - "Metaphos" and "Karbofos";
- for azaleas - "Ambush" and "Karbofos".
Working solutions of all drugs must be prepared strictly following the instructions.

Biological methods
The difference between biological drugs and chemical drugs is that they are less toxic and therefore harmless to humans and animals. Bioinsecticides contain microorganisms (various groups of fungi, living bacteria), which, entering the digestive tract of insects, cause their death. They work for 10-20 days, therefore, processing is required every 10 days. Working solutions of all drugs are also prepared strictly according to the instructions.
The most famous are such funds.
- Fitoverm. The infected flower must be sprayed with a solution of the product. On the first day after treatment, adult parasites die. 6 days later, the procedure must be repeated to destroy the juveniles. In case of mass defeat, it is recommended to wipe the affected areas with a sponge dipped in a solution.
- "Bitoxibacillin". Helps to remove pests in almost a week.
- Akarin. The action of the remedy occurs within 8-16 hours after application.Pests begin to die within 1-2 days, but Akarin has the most active effect on the 5-6th day.
- "Entobacterin". The drug is produced in the form of a powder containing spores of live bacteria. The efficiency of the treatment depends on the temperature, the best result is achieved at + 25- + 26 degrees.



There are also natural exterminators of aphids - these are ladybugs and lacewings: they feed on insect larvae. In summer they can be used to control aphids.

Traditional methods
The most popular among flower growers are folk methods of pest control proven in practice. Such means are used.
- Laundry soap. Soapy solution is used to wipe those parts of plants where aphid colonies are located. The working solution is prepared as follows: 300 g of soap shavings are placed in 10 liters of water. The composition stands until the soap is completely dissolved.
- Soap-oil solution. In this case, soap and sunflower oil are taken in equal quantities - for a bucket of water, 1 glass of oil and soap shavings.
- Soap and soda solution. For 2 liters of water, you need to take 40 g of soap solution and 2 tablespoons of l. soda.
- Soap solution with the addition of kerosene. 5 liters of water requires 100 g of soap shavings and 20 ml of kerosene. Potassium permanganate is often used as an addition to soap solution.
- 9% vinegar. Add 30 ml of vinegar to 1 liter of water.
- Soda... 0.5 l of water and 15 g of soda.
- Hydrogen peroxide... Dissolve 25 ml of a 3% preparation in 0.5 l of water.

You can also prepare decoctions and infusions from different plants.
- Celandine. The tops of flowering celandine (100 g) are placed in water (1 l) and boiled for 30 minutes. After cooling, the plant is sprayed with infusion.
- Tobacco. It is poured with boiling water and insisted for a day.
- Citrus peels (orange and lemon). Boiling water (1 l) and zest (1 glass) are placed in a thermos and insisted overnight.
- Tomato tops. The working solution is prepared from 1 liter of water, 400 g of tops. The mixture is boiled for half an hour. Straining, add 1 table l. soap shavings. After the soap is completely dissolved, the mixture is ready for use. It is used to wipe the leaves and trunk of plants, and you need to spray it with infusion diluted with water.
- Bitter pepper. 2-3 crushed pods are boiled in 200 g of water and allowed to brew for 24 hours. After straining, add water to a volume of 1 liter. You can use it once every 14 days, but not more often.




Garlic infusions, decoctions of onion husks, pine needles and flowers (marigolds, dandelions) are also widely used. Essential oils (mint, rosemary, cloves) are used to destroy small clusters of aphids - 5 drops of oil are required for 200 g of water. At the initial stage of the lesion, small colonies can be washed off with plain water. The procedure should be carried out daily until the absolute extermination of parasites.

Prevention measures
Such preventive measures will help prevent the appearance of aphids.
- Inspect flowers weekly.
- When the first colonies of aphids are detected, the plants should be treated urgently in any way.
- Newly acquired flowers need to be isolated and quarantined for about a week.
- Observe all the rules of agricultural technology and timely water and fertilize, transplant and replace soil.
- In summer, mint leaves can be placed near flower bowls, the smell of which aphids do not like. In winter, geranium is used instead of mint.
Aphids prefer a dry environment, so it is important to monitor the humidity in the room and avoid excessive dryness.

In the next video, you will learn how to get rid of aphids in brugmansia.































The comment was sent successfully.