All about the indoor Tydea flower
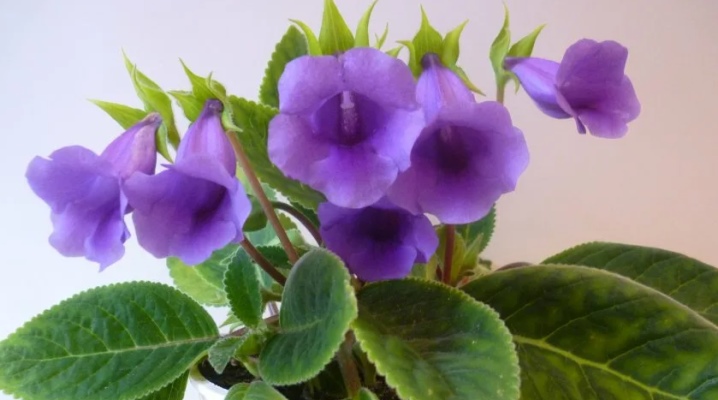

The houseplant tydea is considered a favorite of many flower growers due to its unique appearance. During flowering, the bush is covered with a large number of buds, and the variety of colors allows you to choose the ideal option for each interior. Caring for thisa has certain characteristics that must be taken into account for the growth of a healthy and charming plant.

Description of the plant
This indoor flower belongs to the Gesneriev family. It is a compact perennial plant that grows in South America (rainforests), and Brazil is considered its homeland. Tydea is found in two species: a herbaceous plant and a semi-shrub, which reaches a height of about 50 centimeters. Varieties that are grown at home grow no more than 30 centimeters.
Shoots can be straight or drooping, the root system of the flower is tuberous. Large leaves are ovoid and grow on long petioles. The color of the plant mass is rich green. The leaf plates are covered with a light light fluff. During the flowering period, tydea is covered with small flowers in the form of bells.


The following plant features are distinguished:
- easy growing that even a beginner can handle;
- the flowering period begins at the end of spring and lasts until the first days of autumn;
- the growth rate is low.
This indoor flower is often confused with koleria and gloxinia, but these are three completely different representatives of the flora. They differ in the shape and color of the buds. Only house tydea is capable of blooming pink or purple flowers, the other two plants above do not have these shades. Gloxinia also differs in the cupped shape of the buds.



Types and varieties
The following sub-varieties are distinguished, which have a number of characteristic features.
- "American girl". This type is chosen due to its charming tenderness and lightness. The flowers are very large - from 10 to 12 centimeters. Each petal has an unusual color that combines two colors. The edges are pink and the middle is white.


- "Russian girl". The variety is very similar to the "American". Differs in gradient color of petals. The snow-white middle passes to a bright blue edge with a purple tint.
If the flower grows in a cool room, the color loses its saturation and becomes paler, but the decorative qualities remain at their best.


- "Cockatoo". The unusual color of the flowers noticeably distinguishes this subspecies from the rest. Pale pink petals cover blotches of red, contrasting against the background of the main color. The edges are corrugated, wavy, which makes the flowers look voluminous and lush. The petals, like the leaves, are terry. With proper cultivation and care, the plant blooms for a long time and abundantly.
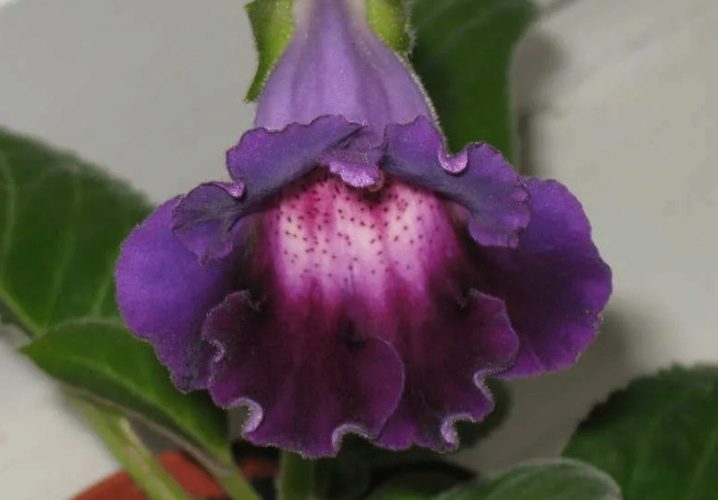

- "Anyuta". The next variety blooms with white buds, which are also covered with small red dots. The edges are wavy. The flowers are similar in shape to gramophones.

- Lavinia. An amazingly delicate and attractive plant. White petals are covered with pink dusting. In the area of their junction, the additional color is more pronounced. The ribbed edges make the flowers look like a fringe. Up to 50 buds can form on one plant at the same time, which will appear and bloom one after another.

Also, all existing types are divided into three main categories.
- Mini. This includes indoor species, but flowers can be up to 6 centimeters long.The color of the corolla is varied, as is the texture of the petals.
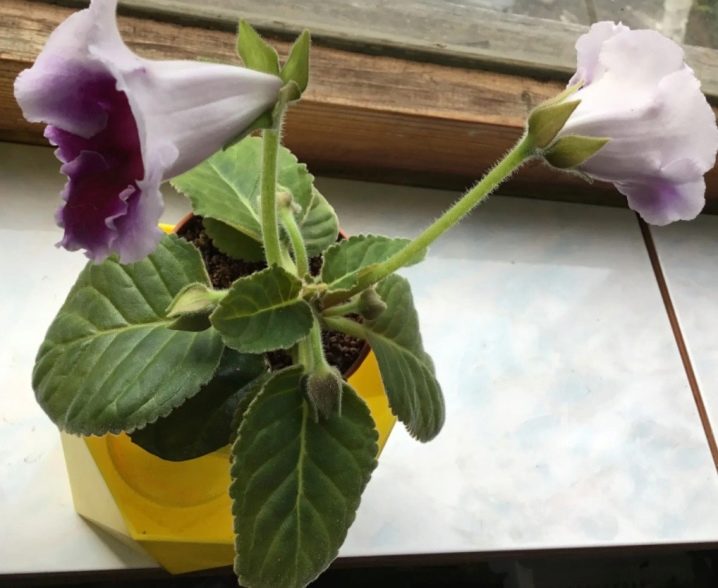

- Standard. This category includes larger bushes, but the size of the flowers remains the same (up to 6 centimeters). Plants from this group can boast of unpretentiousness. There are buds of different colors and shades.
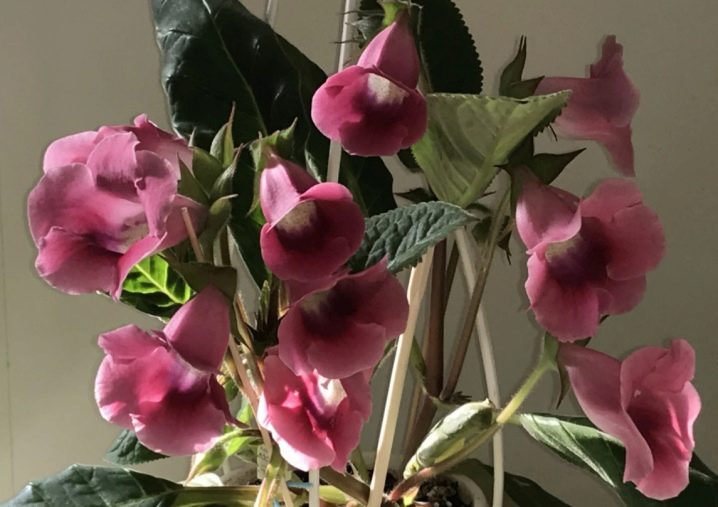

- Multibells. A group of plants with compact rosettes, but large flowers (about 10 centimeters). During the flowering period, corollas open wide. The edges of the petals are jagged. Terry species in this category are very rare.

Note: some growers talk about yellow tydea, but this plant is sinningia, the second name is gloxinia. The appearance of these species is so similar that even experienced gardeners often confuse them.
Growing conditions
Caring for the idea at home is not difficult. The main task is to create comfortable conditions and periodically rejuvenate the plant. The indoor flower does not have a rapid growth rate, and a pronounced dormant period may be absent altogether.
Location
Growing begins with choosing a suitable place. Thidea is very fond of sunlight, so the place for her placement should be well lit. Despite this characteristic, you need to protect the flower from direct sunlight, which will only harm it. A window sill on the east or west side is ideal. When installing the pot on the south side, the plant is shaded with a cloth or paper.
Lack of natural lighting negatively affects the condition of the flower. Shoots weaken and stretch. Flowering may also be completely absent.


The soil
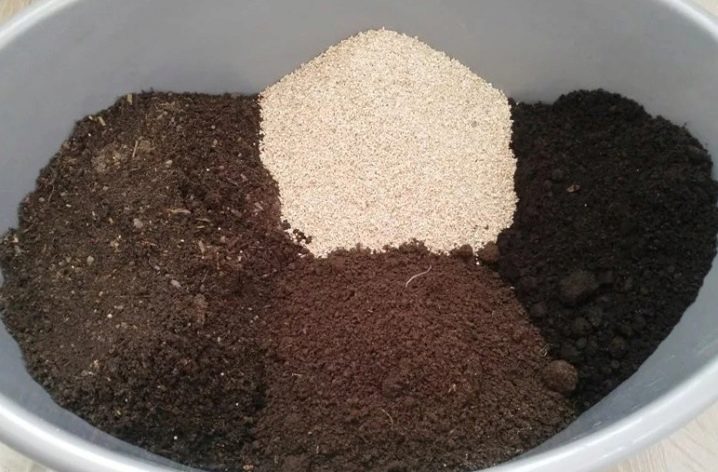
Lightweight, loose and breathable soil is considered ideal. The acidity should be low or neutral. A special substrate designed for growing home violets is perfect.
You can prepare a suitable tidea soil yourself. The mixture includes a double slice of leafy soil with peat, humus and sand. Perlite can be used instead of the last component. To make the soil more fertile, a small portion of bone meal or charcoal is mixed into it.

Landing
Before planting, you need to prepare in advance not only a suitable soil mixture, but also a container. A drainage layer 2-3 centimeters thick is laid on the bottom. Next, about two-thirds of the pot is filled with earth, in which the young shoot is placed.
Once the plant is fixed, the container is filled with the remaining soil. The earth is moistened and rammed. If necessary, you can add some more soil.


Watering
Only soft water at room temperature can be used for irrigation. It may also be a little warm. Rain or river water is considered ideal, so if possible, it should be stocked up. In winter, melted snow is often used, which is heated to room temperature. The flower responds well to distilled water. If water for irrigation is taken from the tap, it must be passed through a filter, boiled and defended for two days.
Watering is done carefully so that the liquid does not get on the leaves and stems of the flower. Bottom watering is great for tedea, in which the flower pot is placed in a container of water. So the liquid penetrates into the soil and nourishes it measuredly. After 20 minutes of such watering, excess water is poured out so as not to overmoisten the soil. The procedure should be performed with an interval of 3 days. This time is enough for the soil to dry out. For such irrigation, there must be holes in the bottom of the pot.
With the onset of autumn, watering is gradually reduced to once a week. If the plant has entered a dormant state, which can happen in winter, it is transferred to a cool room for comfortable wintering. At this time, the flower is hardly watered. But the earthen lump should not dry out completely.


Top dressing
During active growth, tydea must be fertilized. It lasts from mid-spring to September. Nutrient formulations are dissolved in water and added together with watering (regularity - one top dressing once a day of the week). Universal complex formulations will be effective, but they should be used in a dosage reduced by half. The plant will tolerate a small deficiency of nutrients much easier than an excessive amount of them.
The regularity of using fertilizers depends on whether the flower goes to rest or not. During the rest period, the plant cannot be fed, as this will negatively affect its flowering in the next season. When the flower retains its green mass (that is, does not retire), stimulating formulations, together with a lack of lighting, will lead to stretching of the shoots. To restore the teidea's attractive appearance and neat shape, you need to trim it.
A flower that goes into a dormant state accumulates much more energy. It will be needed for growth and flowering next year. Also, thanks to this feature, the need for feeding is significantly reduced.


Pruning
From time to time, it is recommended to perform formative pruning, with the help of which the decorative qualities of the flower will remain at their best. This procedure is optional, but experienced florists advise you to spend a little time on it. During work, remove deformed plant matter (broken shoots, limp leaves and flowers).

Reproduction
You can grow tydea from seeds. The process is performed in winter. The best time to sow is January or February. Seeds are gently spread over the surface of the moistened soil. For germination, a soil consisting of sand and leafy earth is used. The seed is not deepened.
To create a greenhouse effect, the crops are covered with a thick film or glass. Every day you need to remove the shelter for ventilation. The first shoots will form in about a few weeks. As soon as each sprout has two true leaves, a pick is made.


The second method is grafting (the cutting is part of the stem, leaf or root). Cuttings are harvested in autumn or spring. The cuttings are placed in water and after about 2 weeks, roots will appear on them. As soon as the root system reaches at least one centimeter, the cuttings can be transplanted into the ground. To form a lush plant, 2 sprouts are planted in one pot.
Dividing the rhizome is considered a simple and effective method of reproduction. The procedure is performed in the spring during the transplantation process. Long rhizomes are cut into equal parts in lengths from 3 centimeters. Remember that individual parts of the bush must be formed for further development.


Before planting plant parts in separate containers, the cut sites are treated with coal powder and dried. In a humid and warm microclimate, rhizomes will quickly begin to develop. Before the emergence of shoots, the soil must be watered measuredly. With this method of reproduction, the tydea will begin to bloom already in the first season.
Beginners choose the method of dividing an adult bush. Each individual part must have its own roots and shoots. The division is performed in the spring. The resulting parts are immediately planted in separate pots. Small plants are not suitable for this method of reproduction, since they do not take root well.
When propagating adult bushes, tuber division is practiced, which is combined with a flower transplant. The massive tuber is carefully divided into several parts. Each of them must have at least one growth point and formed roots. Germinate the plant in loose and fertile soil.































The comment was sent successfully.