All about wild strawberries
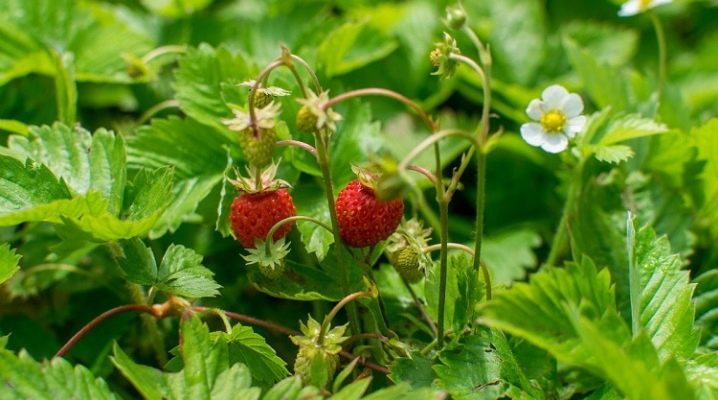

Knowing everything about wild strawberries and the differences between them and strawberries is important not only out of general curiosity - this berry is tasty, and it is useful to imagine how to grow and collect it. Information on how wild strawberries reproduce in the forest and where they grow is relevant. The description of the leaves and the modification of the roots stand apart.


Description
Common wild strawberry is not only a delicious berry, but also one of the most remarkable representatives of the forest flora of the northern hemisphere. It belongs to the dicotyledonous class and the Rosaceae family, and therefore its relatives can be considered:
- meadowsweet;
- mountain ash;
- bird cherry;
- spirea;
- cinquefoil;
- raspberries;
- pear;
- apricot.
The forest plant forms perennial bushes. The root system includes short rhizomes. The height can vary from 0.05 to 0.3 m. Leaves grow on different types of strawberries:
- from vegetative shoots - ternary type;
- in warm seasons - with long petioles;
- with the approach of cold weather with shortened petioles.
The basic leaf arrangement is a rosette near the root. The stomata can be seen only at the lower edges. The upper edge of the leaf is colored in a dark green tone and is almost devoid of any cannon, the lower one is transitional from gray to green, with soft pubescence. Stipules of the lanceolate type are present at the base of the leaves.
Speaking about the modification of the roots (shoots), it should be emphasized that the strawberry rhizome is a perennial transformed stem.


In total, the parts of the stem located above and in the ground reach a length of 10 cm. Surface shoots are divided into 3 categories:
- short annuals (better known as horns);
- antennae (they tend to creep along the ground);
- peduncles formed in mid-spring from generative buds.
In the botanical characteristics of wild strawberry, there is no unified approach to the description of its life form. So, according to the Raunkier system, it is described as a rosette hemicryptophyte. There are also classifications of Zazulin, Smirnova and Serebryakov, and in each of them this plant is defined differently. To understand more clearly what a strawberry looks like, you need to take into account its other characteristics:
- petioled leaf type with a serrated edge;
- cirro-reticulate venation;
- white flowers;
- development of whiskers from the axils of the basal foliage;
- erect stems with a good level of leafiness;
- elongated pedicels;
- fruits of the achene format;
- inflorescence low-flowered, corymbose type.
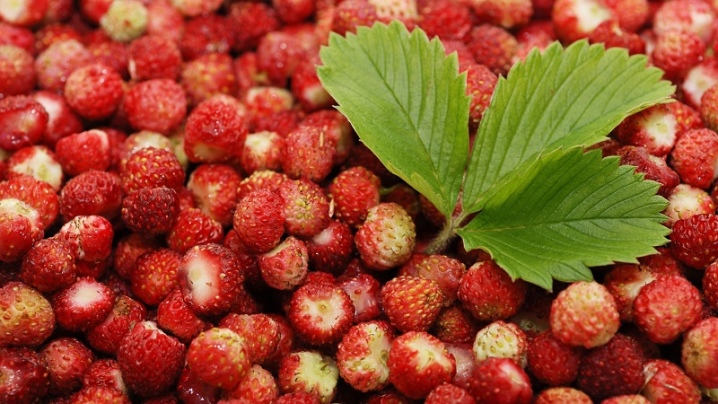

Spreading
The habitat of wild strawberries covers almost all areas in Russia up to the Urals. The only exceptions are:
- regions of the Far North;
- Black Sea steppes;
- Volga lower reaches.
Moreover, the places of growth of this type include additionally:
- south of Siberia;
- Belarus;
- part of the Ukrainian steppes;
- Central Asian forest zone.
This berry grows in the forest in light sparse areas and edges, in glades. You can see it in a forest meadow, and among dense bushes, and even in old burnt-out areas. Although the strawberry spreads very widely, it is unable to form large thickets.
The main reason is the overwhelming effect of the grass cover. On recently felled areas, this light-loving species develops actively, but it almost never occurs in old clearings, and its productivity is rapidly decreasing. Within 1-2 years, the renewal of the forest and herbaceous rivals leads to the displacement of strawberries.Therefore, an important measure for the cultivation of thickets is the maximum disposal of competing plants - the main thing is that it does not cause major damage to the ecosystem. Some sources claim that wild strawberries grow on any continent of the Earth, except for Antarctica, but this species is most common in Eurasia. Such a shrub grows not only in wild forests, but also in forest belts.
The middle zone of Russia is rich in strawberries. Sometimes they can even be seen in the fields. In the Moscow region, the berries of this species are large in size. Strawberries gravitate mainly towards deciduous rather than coniferous forests. Among all deciduous trees, she especially "adores" aspen and birch. At the beginning of the fruit season, strawberries can be found on the southern edges. Then the berry "goes" into the depths of the forest. In the last part of the season, it is worth looking for it on the northern edges and in remote shaded areas. On the floodplain area and on the gentle slopes of ravines, there are also quite a few chances.
In addition to the European part of Russia, you can go for berries to the Caucasus, to the Tien Shan mountains, in the forest-steppe.


How is it different from strawberry?
These two berries are relatively similar, but there are significant differences between them. The taste of strawberry fruits is much sweeter, and their shape is closer to a full circle. The ripe strawberry crop takes on a rich red, sometimes burgundy color. The cup does not clasp the fetus, but slightly turns away from it. There are other significant differences:
- strawberries are bisexual, strawberries always form unisexual bushes;
- strawberry berries are dark red on the outside, white inside, and even the flesh of strawberries is completely red;
- strawberries are sour, strawberries are devoid of such a note (despite their less pronounced sweetness) and have an extremely strong pleasant aroma;
- strawberries are soft, strawberries better preserve their shape and are comfortable during transportation;
- strawberries have more whiskers and higher biological productivity.
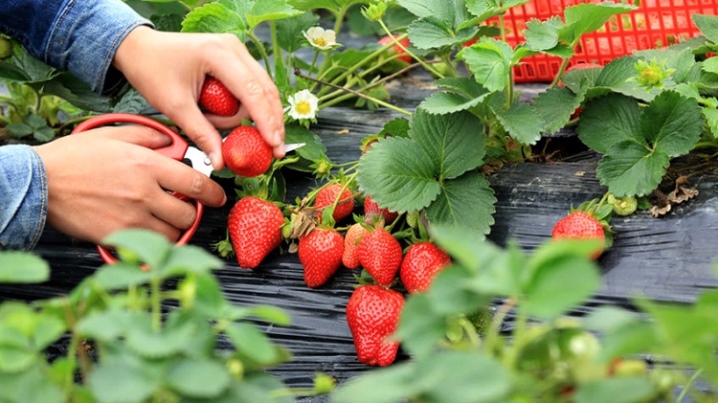

Landing
From the very beginning, it should be emphasized that planting small and large strawberries nearby can be completely calm. These are dissimilar species with different levels of ploidy, and therefore crossing is completely impossible. As in nature, it is more correct to plant wild strawberries in sunny areas. For this work, a relatively cool moment is chosen and it is imperative to check how well the earth is moistened. It is advisable to sprinkle the planted plants with sand.
Predictably, it is better to buy seedlings from proven nurseries with a good reputation (although you can grow such a crop yourself). It is planted in open areas in the first decade of May. In well-developed shrubs, the foliage is completely green and does not have any red spots. It is also worth making sure that the roots are well developed, there are no dried or rotted areas on them. Sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out in the first half of February, it is usually preceded by soaking for 48 hours in warm water.
Seedling containers are filled with universal soil. The seeds themselves are mixed with a certain amount of sand before being laid out on the surface. Water the seedlings with a small amount of water. The correct and safest way is to use a sprayer. The containers are covered with plastic wrap and kept in a cool, dark corner for 48 hours. Then the containers must be placed in a warm corner with good lighting. In this case, it should be monitored so that direct sunlight does not fall on the plants. Seedlings of wild strawberry are usually watered with a syringe. It is much easier for them to give a thin stream that does not fall on the foliage.
A pick for individual containers is made when the 2nd true sheet appears.


The hardening of these plants begins in the last decade of April. They are initially kept outdoors for 1/2 hour. This time is gradually increased. Seedlings are usually ready for transplanting outdoors in May. To make the procedure more successful, the earth is moistened and loosened.
It is also useful to introduce:
- compost;
- ash;
- sand.
Strawberries are planted in strips, with row spacing of 30 cm. The gap between the holes should be 10-15 cm. Plants should not be planted deeply - the leaf rosette should remain in the open air. There will be no more special agrotechnical subtleties in the process itself. You just need to take into account that the hills and open places for planting strawberries are not very suitable, if you plant them there, you will then have to take care of snow retention.
Additional recommendations:
- in the fall, dig up a site for 1 shovel bayonet;
- in the spring to loosen the ground with a rake, simultaneously getting rid of weed roots;
- when planting in the fall, dig up and loosen the site in 15-20 days;
- before digging, apply 10 kg of manure, 0.05 kg of superphosphate and 0.03 kg of potassium sulfate per 1 m2;
- thoroughly spread the roots and sprinkle them with soil.


Care
The correct cultivation of wild strawberries in the garden or in the vegetable garden implies:
- weed control;
- regular irrigation;
- loosening the earth;
- introduction of nutrients.
After the formation of a solid carpet, it will become easier to care for. Weeds have almost no chance of germinating where it has formed. Loosening can also be stopped. Growing strawberries at home or in a summer cottage, you will need to get rid of dry leaves and mustaches in the spring. They are cut off with a knife and then burned in a safe place.
The advantage of wild strawberries over garden strawberries is that they do not require film protection against temperature changes in spring. In the spring months, it is necessary to loosen the ground to a depth of 2-3 cm next to the bush. On row spacings, this figure reaches 10 - 12 cm. Old bushes are supposed to be covered with productive soil. You need to water the plants in the country:
- when they fade;
- when each harvest wave ends;
- when fruiting ends;
- in mid-September (the moment the flower buds are laid).


Transplanting in the fall can be done quite calmly. It differs little in technology from the transshipment of young seedlings in spring. In any case, wild strawberries need regular fertilization. For the first time they feed her at the end of April or in the first May decade. The feeding solution is formed as follows:
- dilute 0.5 kg of cow dung 6 times;
- pour 10 liters of water into a container;
- add 0.06 kg of superphosphate and the same amount of wood ash.
The second time, fertilizer is applied just before flowering. 0.09 kg of wood ash and 0.06 kg of superphosphate are placed on a regular 10-liter bucket. The third dressing is done when the crop is harvested. First, the earth must be watered. Then evenly distribute (in terms of 1 sq. M) 0.01 kg of ammonium nitrate.
You can replace it with 0.02 kg of ammonium sulfate. Instead of mineral fertilizers, slurry is often used. It is diluted exactly 6 times. Such a composition is used in an amount of 3-5 liters per 1 sq. m. At the junction of summer and autumn, it is necessary to use exclusively mineral dressings - 0.05 kg of superphosphate and 0.025 kg of potassium salt.


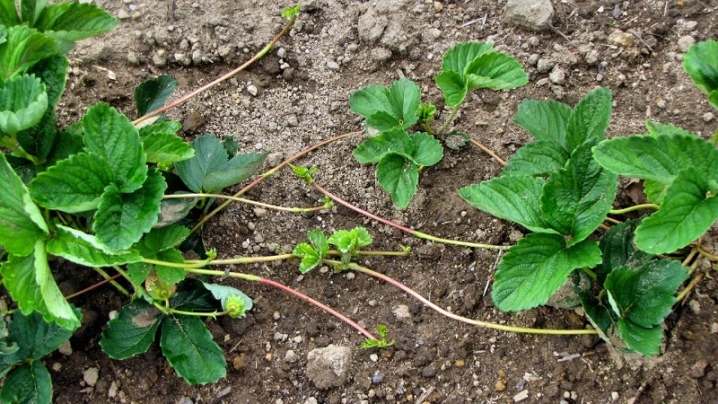
Reproduction
Mustache
This method works especially well for bushes of the first and second years of development. Just at this time, the formation of the mustache is especially effective. The bushes will have to be dug out in late July, early August. But you can also do this at the junction of May and June. Landing on a personal plot is carried out in shaded areas.
In order for the green mass to form more actively, 45-60 days before the transplant, they lay in the chosen place:
- 8-10 kg of organic matter;
- 0.012 kg of phosphate fertilizers;
- 0.015 kg of potash mixtures.
When the formation of whiskers begins, the ground is mulched with peat. Its optimal layer is 4-5 cm. The rosettes, spreading the mustache, are pinned or sprinkled with soil. Intensive watering is required. This technique allows you to work out from 1 bush brought from the forest to 20 outlets. For your information: wild strawberries reproduce in nature just with a mustache. Therefore, this method turns out to be the best choice from the point of view of botany.
Seed propagation is also possible.But it is more laborious and is suitable mainly for those who are fond of selection. A mustache is a much more suitable solution for the average gardener.

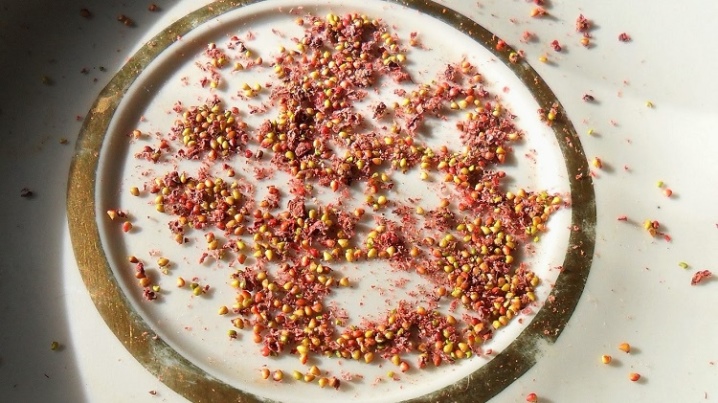
Seeds
Sequence of work:
- selection of ripe berries;
- cutting seeds with a sharp blade;
- drying them on thick paper;
- storage until early spring;
- in the first decade of March - saturation of containers with light garden soil;
- leveling the surface;
- abundant watering;
- dusting the decomposed seeds with a millimeter layer of sand;
- covering crops with glass, which is removed only for spraying from a spray bottle;
- removal of glass in the event of seedlings;
- dive of seedlings when 1-2 true leaves appear;
- transshipment into open ground at the onset of stable warm weather.

Diseases and pests
White mold is a dangerous disease of wild strawberries. It is fundamentally incurable. This ailment is suppressed in only one way: they get rid of the affected bushes and treat problem areas with chemicals. Raspberry-strawberry weevil can be scared away with tansy broth, to which laundry soap is added. When this insect attacks during budding use "Intavir", and when the fruits are removed - "Actellik".
To avoid tick damage, strawberry bushes are treated with onion peel infusion before flowering. If the ticks attack after the harvest, the leaves will have to be mown. The plants themselves are treated with fufanon diluted to a concentration of 0.1%. Protection against slugs is provided by sprinkling the earth:
- slaked lime;
- a homogeneous mixture of wood ash and tobacco dust;
- superphosphate.
Spraying with soap-soda or soap-vitriol solution helps to prevent damage by powdery mildew before flowering. If in previous years the strawberry has already suffered greatly from such an infection, its leaves are treated with Topaz or an 8% solution of colloidal sulfur. To reduce the risk of fungal infection, straw is laid out and plastic is laid. To suppress the causative agent of gray rot, preemptive spraying with garlic solution helps. They resort to it during active budding.


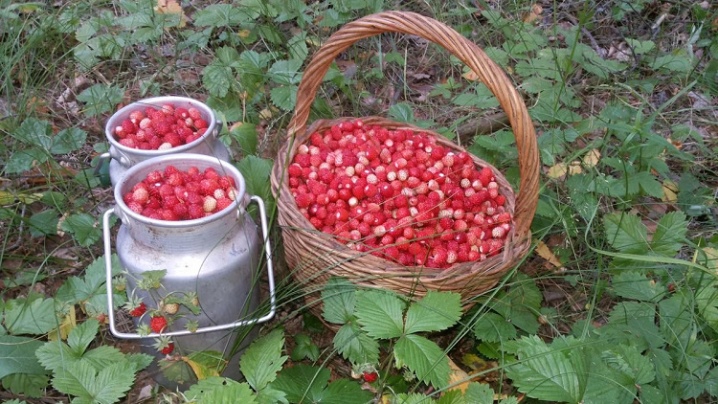
Collection and storage of fruits
Usually wild strawberries ripen at the end of June and in the second third of summer. But this is typical only for the middle lane. In the southern regions of Russia, it sometimes ripens already at the junction of spring and summer. In a particular year, the situation can change dramatically. It is necessary to pick berries either in the morning, when the dew evaporates, or at the very end of the day.
Wet strawberries, like those harvested in hot moments, quickly deteriorate. This is also typical for an overripe, mashed crop. The berries need to be dried a little (or outdoors during daylight hours, go in the dryer for 4-5 hours). Then they are dried at 45-65 degrees, achieving flowability, but excluding the appearance of mold.
It will be possible to store the fruits for up to 24 months.

Interesting Facts
It is worth pointing out right away that the real fruits of strawberries are small nuts, and what is usually eaten is just a false fruit. At the same time, they began to grow it artificially later than they created firearms and discovered America. Previously, people were satisfied with what grew in nature by itself. In Brazilian culture, strawberries are a symbol of well-being and family prosperity - it is not for nothing that they are very fond of scattering them around themselves at carnivals.
Contrary to popular belief, in Russia this shrub bears fruit for a long time - from mid-May to mid-July. Even in the distant past, in our country there was a custom to feed all relatives and neighbors with the first strawberry harvest, but not to touch the crop ourselves. It was believed that this would ensure a stable collection in the future. The influence of wild strawberries on the human body is contradictory. On the one hand, it helps fight headaches and activates collagen production, on the other hand, it is distinguished by pronounced allergic activity.
Until the very beginning of the 19th century, this plant was not at all on the island of Bourbon. However, as soon as only 5 bushes were brought there, they multiplied and grew enormously. During the ripening of the crop, the banks in many places are completely red. According to experts, the earliest forms of strawberries appeared at the turn of the Cretaceous and Paleogene periods. And in our country, this berry became widely popular only in the 18th century, before other shrubs were of much greater interest.
There are some more unusual facts:
- wild strawberry - one of the most widespread plants in the world;
- its leaves are extremely useful;
- this species does not live in one place for more than 5 years in a row, even in artificial conditions;
- the unofficial strawberry capital of the world is the city of Vepion (Belgium).















The comment was sent successfully.