- Authors: Germany, 1954
- Taste: sweet and sour
- The size: large
- Weight: 9-10 gr
- Yield rate: high
- Yield: up to 1.5 kg per bush, 5-7 t / ha
- Repairability: No
- Ripening terms: late
- Appointment: fresh consumption, processing (juice, jam, jam, etc.)
- Description of the bush: tall, compact
Zenga Zengana garden strawberry is a unique variety. Many consider it the standard among strawberries, since the culture is unpretentious and has a good yield.
Breeding history of the variety
The Senga Sengana strawberry was first grown by breeder Reinhold von Sengbusch in Hamburg. The professor crossed two species - Marche and Sieger, to get a berry, which could later be deeply frozen. The main task was to create a new culture that perfectly adapts to a variety of climatic conditions and is suitable for growing in different areas.
Crossbreeding work began in 1942, and the variety went on sale in 1952. The culture was brought to the Soviet Union in 1969, but officially entered the market after all tests only in 1972.
Description of the variety
Zenga Zengana strawberry is a late ripening variety. Bushes are erect, small. The leaves are dark green in color, medium in size, rounded with jagged edges. The flowers are white and are found directly under the leaves.
At the time of the creation of this culture, the main feature was the ability to freeze it. Nowadays, many varieties are distinguished by this ability. But Zenga has a number of other advantages:
high productivity;
large berries;
great taste;
transportability;
the ability to grow in any soil;
the ability to bear fruit even with a small amount of light.
This species can withstand extreme heat, drought and even frost without any problems. Disadvantages include the need for pollinators and a tendency to disease.
Ripening terms
The culture ripens late, belongs to the category of late-ripening varieties. Flowering begins towards the end of May, and the first fruits appear somewhere in June. It acts as a representative of a short daylight hours, therefore it is not repairable. The culture bears fruit only once a season. There are few antennae on the bush, the main task of the plant is the formation of new fruits.
Yield
Zenga Zengana strawberries are considered to be high-yielding. A distinctive feature of the variety is the simultaneous flowering, and then ripening, that is, about 7-14 days pass between the set of color and fruiting. On one bush, more than 30, or even 50 berries can grow and ripen, from which it turns out that on average one small bush can bring up to 0.5 kg, and a larger bush up to 1-1.5 kg of berries. By the end of the season, the fruits on the bush ripen smaller, that is, the first berries can weigh up to 30 g, and the subsequent ones - on average up to 10 g. With age, the fruiting of the bushes becomes worse, and the number of berries becomes smaller.
Berries and their taste
The berries are large, with an average size of 10 g, the very first ones, of course, weigh more - 30-40 g. The shape of the fruit is broad-conical, angular, without a neck. The rind is a juicy red or dark red, shine is present. The berry is dense, juicy, and the pulp is homogeneous. The seeds are deeply planted.
The taste is sweet and sour, directly dependent on the amount of sun received, as well as the color.
Growing features
Saplings are needed to breed a crop. The stem should be firm and bright green, and the root collar should be 5 cm in diameter. The roots must be in order for the plant to take root.
Seedlings in regions with a temperate climate are planted in the spring, they can be planted in summer and even autumn, but in this case, the harvest will need to be expected only for the next season.
You should not plant the plant in places where raspberries or gooseberries previously grew, since these plants suffer from the same diseases, you should also avoid neighboring with them.
Many people know that Zenga strawberries are unpretentious in choosing the soil, but this is not entirely true. The variety has certain preferences that should be taken into account when planting. This crop grows best on loose soil, such as loam.




Site selection and soil preparation
Strawberry bushes are compact, therefore, when planting seedlings in one row, it is necessary to maintain a distance of 25 cm between them, and the distance between rows is about 35 cm, no less.
The soil should be mulched, and you can also use a dark film or any other material, but not fabric. This is necessary so that the soil does not warm up too much during the hot season. You can put straw on top.
Moisture should be maintained using an irrigation system.
The site should be well lit by the sun, not only the color of the berries depends on this, but also its taste. Water should not stagnate in the soil, because then it will dry out badly, and this can affect the root system or the berries, which will soak and rot in such an environment.
On the ridges, holes are dug, equal to the number of seedlings, with a depth of 20 cm. In each hole there should be a small mound of the ground. The seedling is immersed in the hole, the roots are straightened so that they do not break. Next, the roots are covered with earth, the earth is tamped around the stalk so that it does not tilt. Each bush should be spilled with warm water, you can mulch with humus or sawdust. Do not use moss or leaves for mulch. In the case of using black film, you can mulch later.

Pollination
One of the disadvantages of strawberries is that they cannot self-pollinate, since they only have female flowers. Therefore, in order to pollinate the plant, gardeners select pollinating varieties that bloom at the same time as Zenga, that is, towards the end of May.

One of the important techniques in strawberry care is feeding. Regular fertilization guarantees a rich harvest. There are several different ways to feed strawberries, and each of them is designed for a specific period of plant development. During flowering, fruiting and after it, feeding should be different.

Diseases and pests
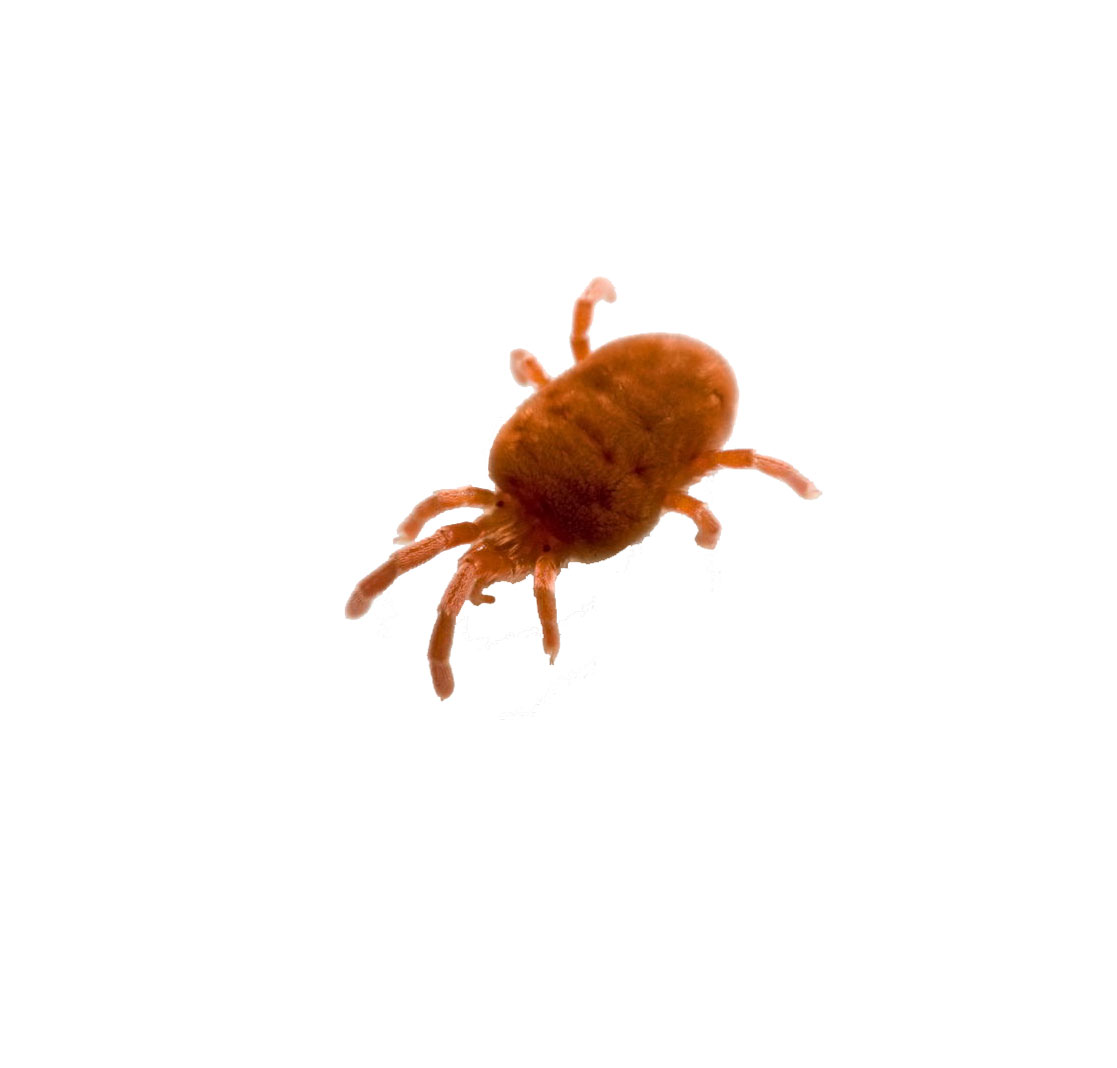
Like any variety, strawberries are prone to being attacked by a number of diseases and pests. One of the main enemies is the strawberry mite. It is located in the very rosette of the plant, in its core, and it is rather difficult to understand that it is there, since the mite is small and transparent.
An indicator that the plant is suffering from a tick is the fact that new leaves grow with a non-uniform cover, in places as if with "blisters". They curl quickly and look very dry. The growth of berries slows down, as does the bush itself, as it ceases to receive the necessary components, which the tick "eats". To fight the strawberry mite, the bush should be treated with a pest preparation, for example, "Iskra M".
The second disease that Zenga Zengana strawberries suffer from is a gray rot fungal infection - it can ruin up to 90% of the crop. In this case, the berries suffer, they are covered with a dark bloom, which resembles mold, only with hairiness. And subsequently the berries begin to rot. To fight the infection, the bushes should be pollinated with chemicals.

Strawberries are often subject to many dangerous diseases that can seriously undermine their condition. Among the most common are powdery mildew, gray mold, brown spot, anthracnose, and verticillosis. Before buying a variety, you need to inquire about its disease resistance.
Reproduction
The most common way of breeding strawberries among gardeners is by dividing. To do this, you need to choose a large bush, a 4-year-old is best suited. It should be dug out, dry foliage removed, the roots should be lowered in water, allowed to soak a little. And then divide by a convenient amount.
It makes no sense to share this species with antennae, since the strawberry Zenge gives out too little whiskers during the fruiting period. Usually this division occurs naturally. A new tendril grows in the ground, forming a new rosette. The gardener should only loosen the soil around the new bush and water it.