- Authors: Wageningen (Netherlands), Plant Research international, Bert Meulenbrock.
- Taste: sweet, with a slight delicate sourness
- The size: medium and large
- Weight: 25-50 gr
- Yield rate: high
- Yield: 1.5 kg per bush
- Repairability: No
- Ripening terms: mid-early
- Advantages: Does not darken after collection and storage. Prolonged rains do not spoil the taste of the fruit
- Appointment: universal
The Sonata variety has become widespread both in Europe and in Russia. Sweet and juicy berries are eaten fresh and used to make drinks, jams and various desserts.
Breeding history of the variety
The Sonata strawberry variety belongs to the non-renovated garden strawberry varieties. It appeared in the Netherlands in 1998. It was created by specialists from the foreign company Plant Research International. A group of specialists have been working on a new variety for fourteen years. The result is a very special variety that has been praised by gardeners around the world.
Description of the variety
You can determine the variety by erect and furry bushes. Leaves are wrinkled, saturated green. Despite the powerful green mass and high growth, the plant is compact in size, its branches are slightly spreading. The variety belongs to the universal. The harvested fruits can be stored for a long time without loss of taste.
Ripening terms
This variety belongs to the mid-early strawberry varieties. Bushes bear fruit once. This period occurs at the end of the first summer month.
Yield
With proper care, the variety boasts a high yield. Under industrial conditions, up to 1.5 kg of berries are harvested from one bush. Under conditions of home cultivation, such indicators are difficult to achieve, so from one plant you can collect from 300 to 500 grams of strawberries.
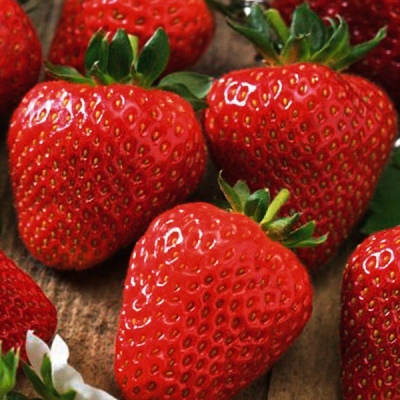
Berries and their taste
Ripe fruits acquire a deep red color, have a shiny coating. Berries can be large or medium, depending on weather conditions, fertilization and watering. Their shape is wide-conical, correct, there is no neck. The mass of one berry is from 25 to 50 grams.
Experts describe the taste as sweet, with an unobtrusive sourness. The aroma is pronounced, but not saturated. There is no emptiness in the pulp, the color is delicate pink. The berries are juicy but not tough.
Growing features
When growing strawberries, you need to take into account that the variety grows remarkably well in greenhouse conditions. Antennae are present in small numbers. High resistance to drought and frost is noted. In one place, the bushes can be grown for 3 years, after that you need to change the location in order to maintain a high and stable yield. Fruiting is also affected by the correct adherence to agricultural technology.




Site selection and soil preparation
Nutrient soil is the best choice for this variety. Before you start planting a plant, you must first prepare the site. The territory is carefully dug up, bringing in nutrients. It is desirable to fertilize the soil with organic matter. Work is performed about six months before planting.
The planting site should be carefully lit by the sun, since berries do not grow in the shade. If the land is located next to tall buildings or trees, the harvest will be significantly affected. Also, locations where cucumbers, tomatoes and potatoes were grown are not suitable for cultivating strawberries. The soil on which carrots, peas or beans were cultivated is ideal.

Pollination
The flowers of this strawberry variety are bisexual, so the plant does not need pollinators to get a stable and high-quality crop. The flowers are white, large in size. Peduncles are located at the same level with foliage, they are tall and strong. Ripe berries do not touch the ground, which prevents rotting.
Top dressing
Nutrients are used 3-4 times in one season.
The fertilization scheme is as follows.
- The first time feeding is added at the beginning of spring, after the plant leaves sleep. Experts advise using organic, chicken manure or mullein-based infusion. It is simple to prepare it: a kilogram of the substance is dissolved in one bucket of water.
- The second time feeding is used in the process of forming ovaries. During this period, the berries need potassium and phosphorus compounds.
- Organic fertilizers are added to the soil after harvesting the fruits. Fertilizer helps the plant to withstand the winter cold, and also gives the berries a lot of nutrients.

One of the important techniques in strawberry care is feeding. Regular fertilization guarantees a rich harvest. There are several different ways to feed strawberries, and each of them is designed for a specific period of plant development. During flowering, fruiting and after it, feeding should be different.
Frost resistance and the need for shelter
During the preparation of the plant for wintering (carried out in August), the bushes are cleared of leaves. Weeds are removed on the site. The soil is fed with nutrients. Before the frost begins, the beds need to be covered with agrofibre or straw. Part of the green mass must be left. It is advisable to cover the plant every year, despite the weather conditions in the region.

Diseases and pests
The European variety has a strong innate immunity, which makes it immune to gray mold and powdery mildew. In this case, the variety often suffers from rotting of the root system. If the bushes are not properly cared for, the plant becomes susceptible to other diseases and infections.
To get a stable and high-quality crop, you must adhere to the following recommendations.
- Adequate space must be left between the seedlings. The thickening of the planting will negatively affect fruiting. If you place the bushes too close to each other, the risk of fungal diseases increases significantly.
- Damaged branches and dry leaves must be removed periodically so that the plant does not waste energy on them.
- Do not flood the strawberries with water; the soil should be moderately moist.
- It is recommended to treat the root system of seedlings with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. This will strengthen the plant's immunity.
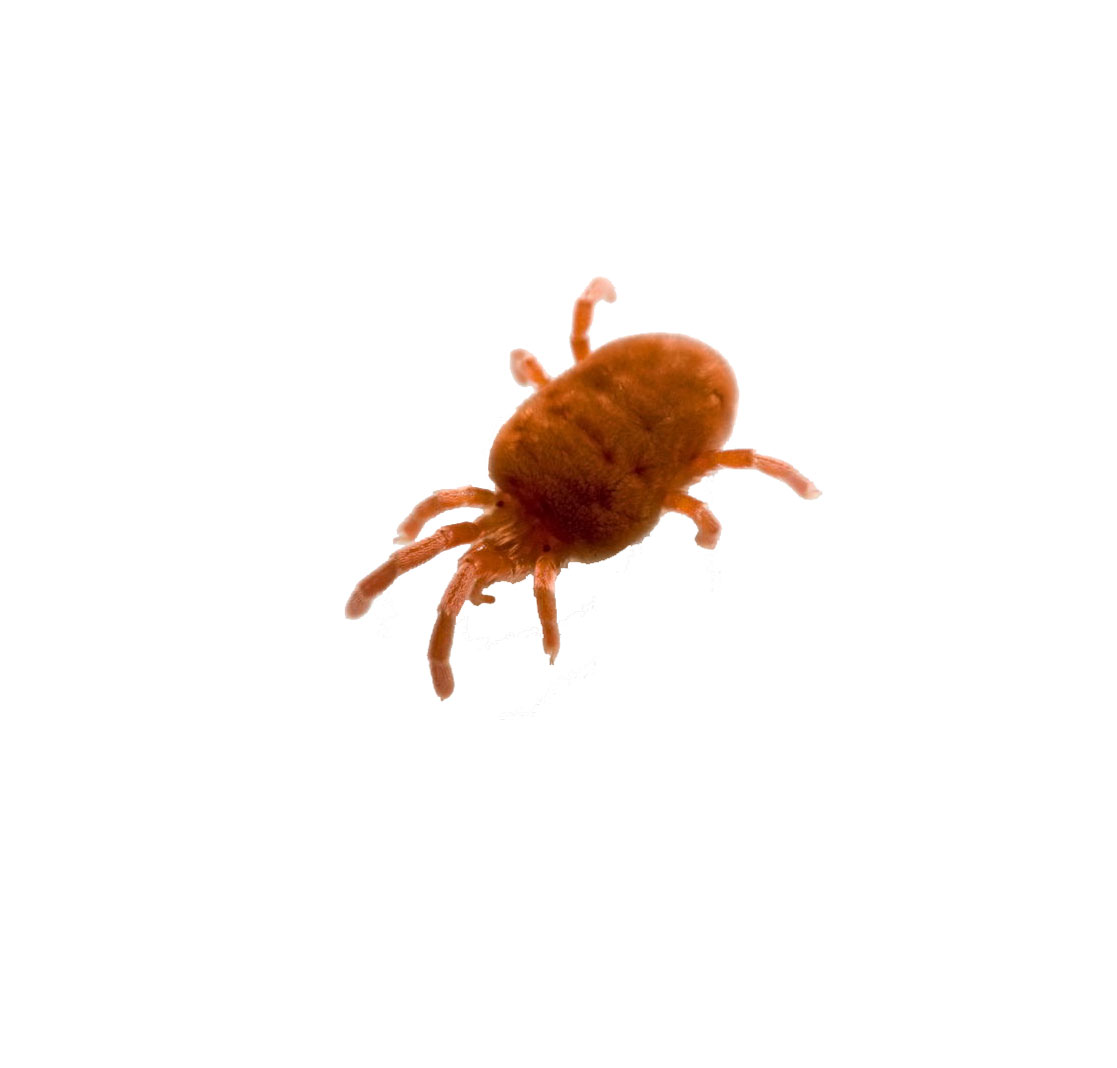
Important: sometimes garden strawberries are attacked by strawberry mites. To protect against this parasite, you can use special formulations that are sold at any gardening store.

Strawberries are often subject to many dangerous diseases that can seriously undermine its condition. Among the most common are powdery mildew, gray mold, brown spot, anthracnose, and verticillosis. Before buying a variety, you need to inquire about its disease resistance.
Reproduction
This strawberry variety produces an average number of vegetative shoots. The plant can be propagated using outlets. Sprouts are rooted only from the best specimens. Sockets can be put in the second row in the garden or transplanted into pots. Rooted shoots are cut off immediately after 3-4 full-fledged leaves appear on them. It is recommended to rejuvenate the plantation before the bushes are 4 years old.
The maximum number of whiskers is observed in annual plants. Then their number is significantly reduced from year to year. A large number of antennae should not be expected from bushes that are already 4-5 years old.
Another common breeding method for garden strawberries is division. The work should be done in early spring or after picking berries. Healthy plants at the age of 3 years are suitable for division. The bushes must be carefully divided into horns. Old plants are not suitable for reproduction by division.
From one mother bush, you can get up to 10 full-fledged horns, quickly increasing the strawberry plantations. Seedlings should be planted in pre-prepared and fertilized soil. Despite the convenience and simplicity of this method, the survival rate of horns is low, so division is rarely used.
It is impractical to grow this variety with the help of seeds. In this case, all varietal characteristics of the garden crop will be lost, and the crop will lose all the qualities of the mother plant.