- Authors: Germany, Otto Schindler
- Name synonyms: Frau Mice Schindler
- Taste: sweet
- The size: average
- Weight: 10-20 gr
- Yield: 0.8-1 kg / m²
- Repairability: No
- Ripening terms: late
- Appointment: fresh consumption
- Description of the bush: low
Strawberries are the queen of summer cottages. The modern market offers many different varieties with different ripening times and taste qualities of the crop, but most gardeners prefer the German variety Miese Schindler.
Description of the variety
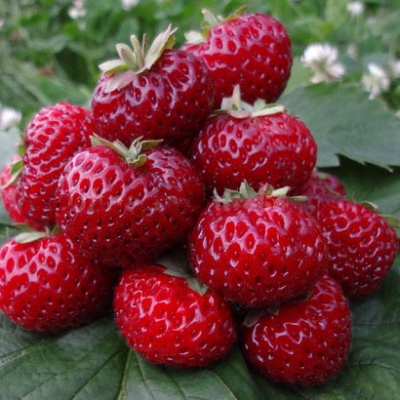
Mice Schindler is a non-refurbished garden strawberry variety. It was bred in 1933 in Germany, crossing the cultures of Lucid Perfect and Johann Moller. The berry was created by the breeder Schindler. The name of the variety is synonymous with Frau Mice Schindler. Quite often, the culture is called Kitty Schindler, and in Russia, strawberries have another name - Malinka. It characterizes the rich taste and aroma of the berry.
Strawberry Mice Schindler is characterized by low and spreading bushes, which have a large number of whiskers and very little foliage. The leaves themselves are distinguished by a rich dark green color on top, while the lower part has a silvery tint. The leaf plates are medium in size, with a ribbed surface and short petioles.
Ripening terms
Mice Schindler is a late-ripening culture. Fruiting occurs in July. The plant easily adapts to any weather conditions and care, so the yield will be uniform regardless of growing conditions.
Yield
The crop is distinguished by a low level of yield - about 0.8-1 kg of berries ripen per 1 square meter. The plant is more suitable for home breeding. The fruits are consumed fresh or processed (preserves, jams, compotes), it is not recommended to freeze them, since after thawing they lose their original appearance and spread into gruel. Mice Schindler is fragile, wrinkles during assembly and transportation, which is why she is not grown for sale.
Berries and their taste
The fruits are rather small. At the first assembly, the weight varies from 15 to 20 grams, subsequent ones weigh from 10 to 12 grams. They have a rounded shape and a red hue, which, as it ripens, becomes a rich cherry. The seeds on the surface of the berries are strongly depressed. The pulp is juicy, has a rich aroma and raspberry color.
Mice Schindler's strawberry tastes very high. The sweet taste of the berries will appeal to both children and adults.
Growing features
The ideal time for planting seedlings is spring, from April to May, and can also be planted from mid-July to September. If all the necessary and favorable conditions were created for the seedlings, then full rooting will occur in three weeks. When planting in spring, you should not wait for a full harvest, fruiting will be partial. The distance between the rows should be at least 60 cm, and between the bushes - 20 cm.
Saplings must have:
- branched root system;
- at least 3-4 young leaves.
There should be no rot or plaque on the planting material, all parts of the bush should be intact.




Site selection and soil preparation
The planting site plays an important role in the growth and yield of Mice Schindler. Too wet, waterlogged and clayey soil is not suitable for growing crops. The strawberry plot must meet the following standards:
- Smooth surface;
- good lighting, as the culture does not like shade;
- the site should be open, but protected from wind and draft;
- the soil is suitable light and fertile with an acidity of no higher than 5-6.
Before planting, the holes must be filled with humus and ash.
Neighboring plants play an equally important role in the development of strawberries. Legumes, radishes, spinach, radishes, beets, marigolds and jasmine have a beneficial effect on the culture. Cabbage, sunflowers, horseradish, Jerusalem artichoke and nightshade will be fatal for Mice Schindler.

Pollination
The flowers of the culture are unisexual, that is, they do not have stamens, so they need pollination. The varieties Korona, Ostara and Cambridge are suitable as pollinators, as they, like Mitze Schindler, are late crops.
Top dressing
During the period of active leaf growth, the plant needs nitrogen fertilizers. Top dressing is carried out through watering or scattering substances over the surface of the beds. Ammonium nitrate is diluted for irrigation in the amount of 1 tablespoon per bucket of water. Urea is spread on the soil in the amount of 20 grams per 1 square meter.
Humus is suitable as an organic feed and can be used 10 days after nitrogen fertilization. With its help, the soil surface under the strawberry bushes is mulched, buckets are enough for a square meter. A glass of wood ash per 1 square meter of soil compensates for the lack of potassium and fluoride. In addition, you can prepare an infusion of nettle. To do this, the plant must be cut and tightly packed in a plastic bag, then left in the sun. When the nettle goes into a state of a homogeneous slurry, the tincture can be considered ready. Then it is diluted at the rate of 1 spoonful of tincture for 10 tablespoons of water.

One of the important techniques in strawberry care is feeding. Regular fertilization guarantees a rich harvest. There are several different ways to feed strawberries, and each of them is designed for a specific period of plant development. During flowering, fruiting and after it, feeding should be different.
Frost resistance and the need for shelter
The Mice Schindler variety has a fairly high frost resistance. The need for shelter is needed only in regions with extremely low temperatures and little snow. In places with northern climates, the culture also needs shelter. To do this, after the last feeding and removal of the whiskers, when the air temperature has reached zero degrees, the ridge is covered with a layer of straw or dry grass. In addition, polyethylene can be laid on top, on which holes are made in advance.

Diseases and pests
Unfavorable weather conditions and non-compliance with the cultivation technique can provoke the appearance of diseases in the crop.
Gray rot mainly spreads to the fruits of the plant. The plant is moderately resistant to this disease. Rot appears due to rains that have been going on for quite a long time. The disease can spread to almost the entire crop (up to 90%). A characteristic feature is a gray bloom. For the fight use substances such as "Horus", "Switch", "Strobi", "Fitosporin" and "Trichodermin".
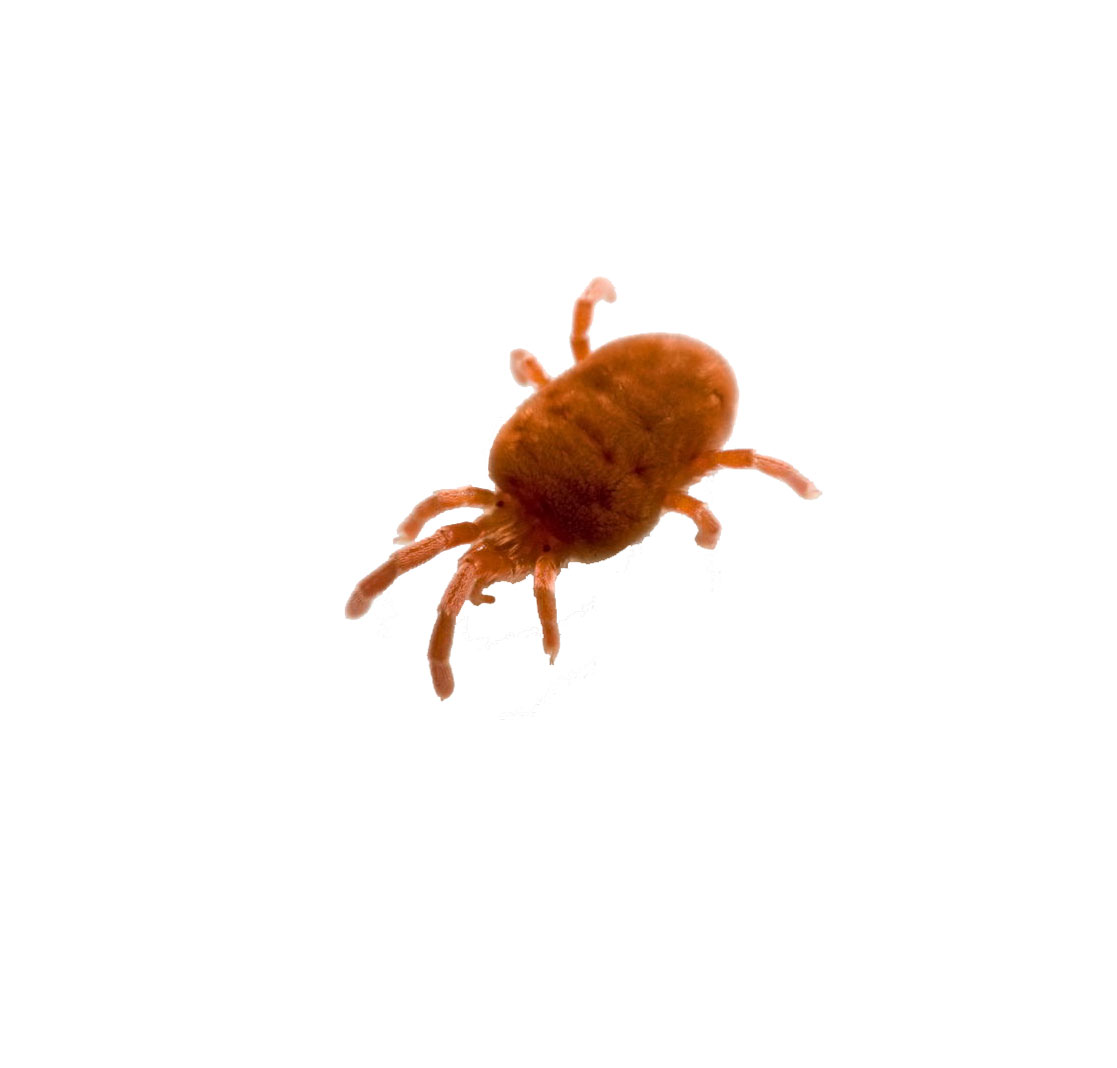
As for powdery mildew, here the plant also has average resistance. Often, strawberries of the described variety are also affected by the strawberry mite. To prevent this from happening, it is recommended to regularly carry out preventive measures. Insecticides are used to combat.

Strawberries are often subject to many dangerous diseases that can seriously undermine their condition. Among the most common are powdery mildew, gray mold, brown spot, anthracnose, and verticillosis. Before buying a variety, you need to inquire about its disease resistance.
Reproduction
The Mice Schindler variety can be grown on the same plot for more than 4-5 years, after which the yield begins to decline. To get new seedlings, pure-bred uterine bushes are used. The whiskers that form on them are not removed, but allowed to take root. After that, they are transplanted to a new bed. Up to 3 new plants can be obtained in one season. The old plantation is not recommended for further use. It is better to plow it up, and the next year to start improving the soil.