- Authors: Institute for Selection of Fruit and Vegetable Crops, Wageningen (Holland)
- Name synonyms: Fragaria Korona
- Taste: sweet
- The size: average
- Weight: 15-30 g
- Yield rate: high
- Yield: up to 12 t / ha
- Repairability: No
- Ripening terms: mid-late
- disadvantages: difficult separation of the stalk from the berries
Strawberry Corona is a Dutch variety grown both in summer cottages and on large plantations. The high frost resistance of the plant made it popular in many countries of the world, including in the northern regions. The variety attracts gardeners with its unsurpassed taste and ease of care.
Description of the variety
Strawberry Crown has small, spreading bushes. The leaves are large, with a rough covering and a serrated edge. The roots are voluminous, grow to the sides. The stems are slender but strong, capable of supporting the weight of the fruit. The variety is characterized by a large number of peduncles, as well as medium formation.
Ripening terms
The Korona variety has a medium early ripening period. Fruiting begins in late May or early June. Lasts 2-3 weeks.
Growing regions
Strawberry Crown is excellent for growing in central Russia with warm summers and snowy winters. In the northern regions, it is grown in closed greenhouses - this is how strawberries tolerate up to -22 degrees Celsius.
Yield
During the fruiting period, up to 1.5 kg of berries can be harvested from each plant. Strawberries bear fruit within 3-4 years, but for a high yield, it is recommended to renew the bushes every 2 years. This is due to the fact that the size of the berries and their number are significantly reduced every year.
Berries and their taste
Fruits are even, conical, bright red in color. Darken as they ripen. During the first harvest, the weight of the berry can reach 30 g, in subsequent ones - about 15 g.
The fruits have a fleshy pulp with a sweet taste. Suitable for dishes made from fresh berries. Not recommended for freezing or long-term transportation. The downside is the difficult separation of the berry from the stalk.
Growing features
Before planting, choose the strongest plants with 3-5 rosettes. The roots should not be less than 5 cm. Too long are cut and soaked in a preparation that promotes the healing of the slices. It is recommended to plant strawberries on rainy days or in the evening.
You need to water the variety regularly, at least 2 times a week, preferably by drip. Each bush needs about 0.5 liters of water. After each watering, the soil is loosened, providing the roots with access to oxygen. The moistened soil is mulched with sawdust or straw.
In the spring, dead leaves are cut off without touching the core. In the fall, immediately after harvest, the mustache is removed. After each pruning, the plants are treated with organic fertilizers.




Site selection and soil preparation
Well-lit beds that are not blown by northern winds are suitable for Korona strawberries. The soil is chosen rich in humus, permeable to air and moisture, of any acidity. A year before planting, it is recommended to plant green manure in the garden bed.
Strawberries are planted in late summer or early autumn. Before that, wood ash and superphosphate are introduced into the soil, they are well moistened. Saplings are placed at a distance of 50 cm from each other, in a checkerboard pattern. The depth of the holes is 10 cm. It is important to remember that the apical bud of the plant must be left on the surface. If it goes underground as it grows, the soil around is cleared.

Pollination
In the open field, pollination takes place with the help of insects and wind. When grown in a greenhouse, a fan is used for large plantations and a manual method for small ones.
Top dressing
Fertilization will help to get a good harvest, to strengthen the bushes.
In the first days of spring, the soil is watered with a urea solution or infusion of weeds.
During the beginning of flowering, the soil is fertilized with humus and wood ash (1 tbsp. L. For each plant).
During harvesting, leaves and stems are sprayed with Cytovit fertilizer. At the end, liquid manure is introduced into the soil.

One of the important techniques in strawberry care is feeding. Regular fertilization guarantees a rich harvest. There are several different ways to feed strawberries, and each of them is designed for a specific period of plant development. During flowering, fruiting and after it, feeding should be different.
Frost resistance and the need for shelter
The Korona variety can do without shelter at low temperatures. For reinsurance, the plants are covered with a layer of humus. At the end of August, the obligatory pruning of leaves and whiskers is performed, the bushes are treated with Bordeaux liquid.

Diseases and pests
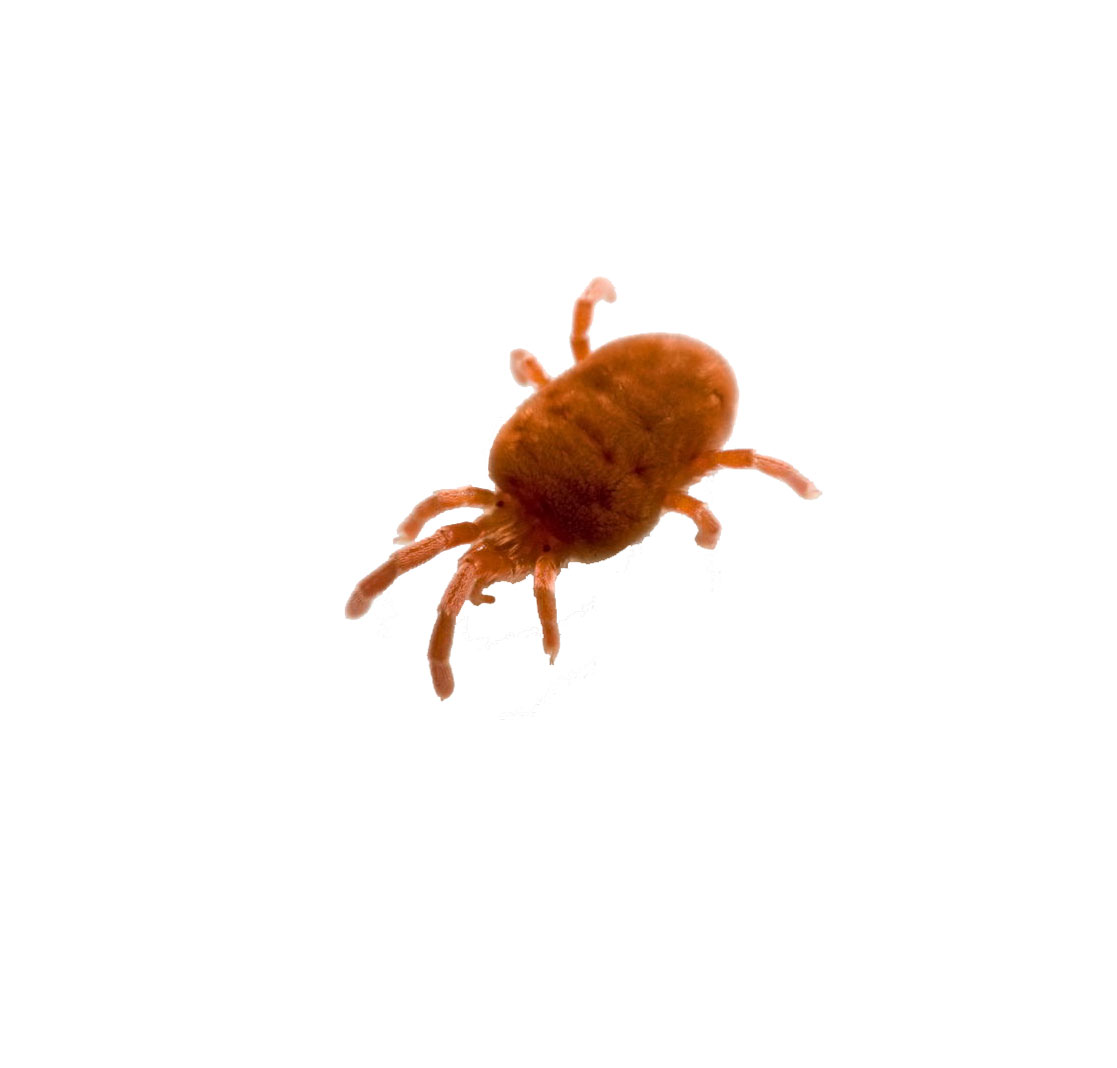
Strawberries are not prone to fungal attack, but often suffer from gray mold or white spot. The most dangerous insects are: nematode, leafhopper, weevil. Pest control is carried out in a variety of ways.
Gray rot on leaves and stems is treated with 5% iodine solution.
White spotting is prevented by using Bordeaux liquid. The bush is processed before flowering and 2 weeks after the end of fruiting.
Weevil is destroyed by special means "Aktara" and "Fitoverm".
From leafhoppers use a solution of potassium permanganate.
Plants affected by a nematode are dug up and destroyed.
When planting strawberries, be sure to keep the distance between the bushes. During the care process, they do not allow excessive soil moisture.

Strawberries are often subject to many dangerous diseases that can seriously undermine their condition. Among the most common are powdery mildew, gray mold, brown spot, anthracnose, and verticillosis. Before buying a variety, you need to inquire about its disease resistance.
Reproduction
Reproduction is carried out in several ways.
1. Mustache
The most common method. Rosettes from the strongest bush are dug into the soil until the leaves appear. Next, the mustache is cut off from the mother plant, carefully dug up and transplanted to the garden bed.
2. By dividing the plant
An adult, healthy shrub with the highest yield is chosen. They are dug out, then divided into parts so that each has a socket and a root. The resulting seedlings are transferred to the garden bed and watered abundantly.
3. Seeds
A rare breeding method due to the low percentage of seed germination. They begin to sow at the beginning of spring, having previously aged 1-1.5 months. The material is planted in a container, tightened with a film and placed in a warm place with direct sunlight. The film is removed before the formation of sprouts only when watering. When several leaves appear, the plants are transplanted into separate containers. Strawberries are moved into open ground if there are 4 leaves on a seedling.
Seed propagation does not guarantee the similarity of seedlings with parent bushes. Dividing the strawberry is not suitable for creating a large number of new plants.
The Korona variety has earned popularity among summer residents for its high yield and unpretentiousness. With proper care and timely prevention of diseases, healthy bushes with an abundance of juicy berries can be grown on the site.