- Taste: sweet
- The size: large
- Weight: up to 90 g
- Yield rate: high
- Ripening terms: medium
- Appointment: fresh consumption, processing (juice, jam, jam, etc.)
- Description of the bush: high, powerful
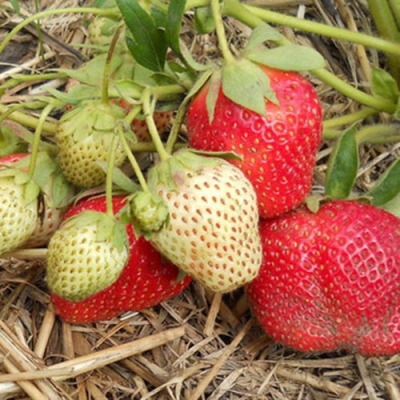
- Berry color: red with glitter
- Winter hardiness: winter hardy
- Berry shape: oklugly
Juan is a US-bred strawberry variety. Juan belongs to very undemanding varieties, so he quickly gained popularity both among private summer residents and in farmer circles. One of the advantages of the variety is the large size of the berries.
Description of the variety
Juan has a tall, powerful shrub with medium-length flower stalks that are set quite high for easy harvesting. Peduncles are able to withstand berries weighing up to 90 g.
Ripening terms
Juan is a medium-ripening cultivar. The fruiting period begins in July.
Yield
It is a high-yielding variety capable of producing up to 2 kg of berries per bush.
Berries and their taste
The fruits have a shiny red color, their weight can reach 90 g. The pulp is juicy, dense, the taste is sweet. This is a versatile variety that can be used both for fresh consumption and for processing into juice, jam, jam and more.
Growing features
The advantage of the Juan strawberry is that it is easy to clean. The variety easily tolerates both frost and drought, and also quickly adapts to new conditions. It is recommended to grow a plant in one place for no more than 4-5 years. It is worth considering that the variety responds well to abundant watering. Growing such strawberries is allowed, including in central Russia.




Site selection and soil preparation
Large-fruited varieties prefer to grow in well-lit areas, so avoid shading with other trees and shrubs. Take advantage of a few more tips from experts in choosing a landing site:
give preference to flat areas;
Juan will grow best if planted in loam, sod-podzolic soil, light loam, black soil;
the soil must be water and air permeable, with neutral acidity in the composition;
choose a cloudy day for planting.
Consider the planting process.
Prepare the soil. To do this, add three buckets of humus for each square meter.
Dig the ridge to a depth of 50 cm and level it.
Dig small holes, fill them with peat and moisten.
Spread the roots of the seedling, and plant it in the hole, cover it with a substrate, tamp the planting site a little.
Water the young sprout liberally and add a layer of mulch. For this, peat, sawdust, spruce branches are suitable.
Follow the 60x60 cm planting pattern between the bushes.

Pollination
The Juan variety adapts well to unfavorable conditions, so it does not need to be grown in a greenhouse. This means that no artificial pollination is required, as the plant will naturally be pollinated by insects and wind.
Top dressing
From the second year of life, the plant should be fed. Typically, there are three types of dressings per season.
- Spring
The first top dressing is applied immediately after the snow melts. During this period, mineral and organic substances are used. Chicken droppings or mullein diluted in water will do.
- Summer
In summer, the culture needs potash fertilizers and trace elements - these substances contribute to the successful formation of peduncles. The variety responds well at this time to complex compositions. In the summer, after adding additional food, it is required to water the bush well. If slow development is observed, then phosphorus and nitrogen may become relevant.
- Autumn
In the fall, you can fertilize strawberries with both organic matter and minerals. Enriching the plant with vitamins will make it easier for it to survive the upcoming cold weather. In mid-September, mullein or chicken droppings are introduced, and at the end of the month, a urea solution or superphosphates can be offered.

One of the important techniques in strawberry care is feeding. Regular fertilization guarantees a rich harvest. There are several different ways to feed strawberries, and each of them is designed for a specific period of plant development. During flowering, fruiting and after it, feeding should be different.
Frost resistance and the need for shelter
It is a frost-hardy variety, but sometimes it needs help to get through the winter. To do this, you should eliminate all old leaves by mid-September, and cover the ridge with spruce branches or non-woven material. When grown in the southern region, the bush does not need shelter.

Diseases and pests
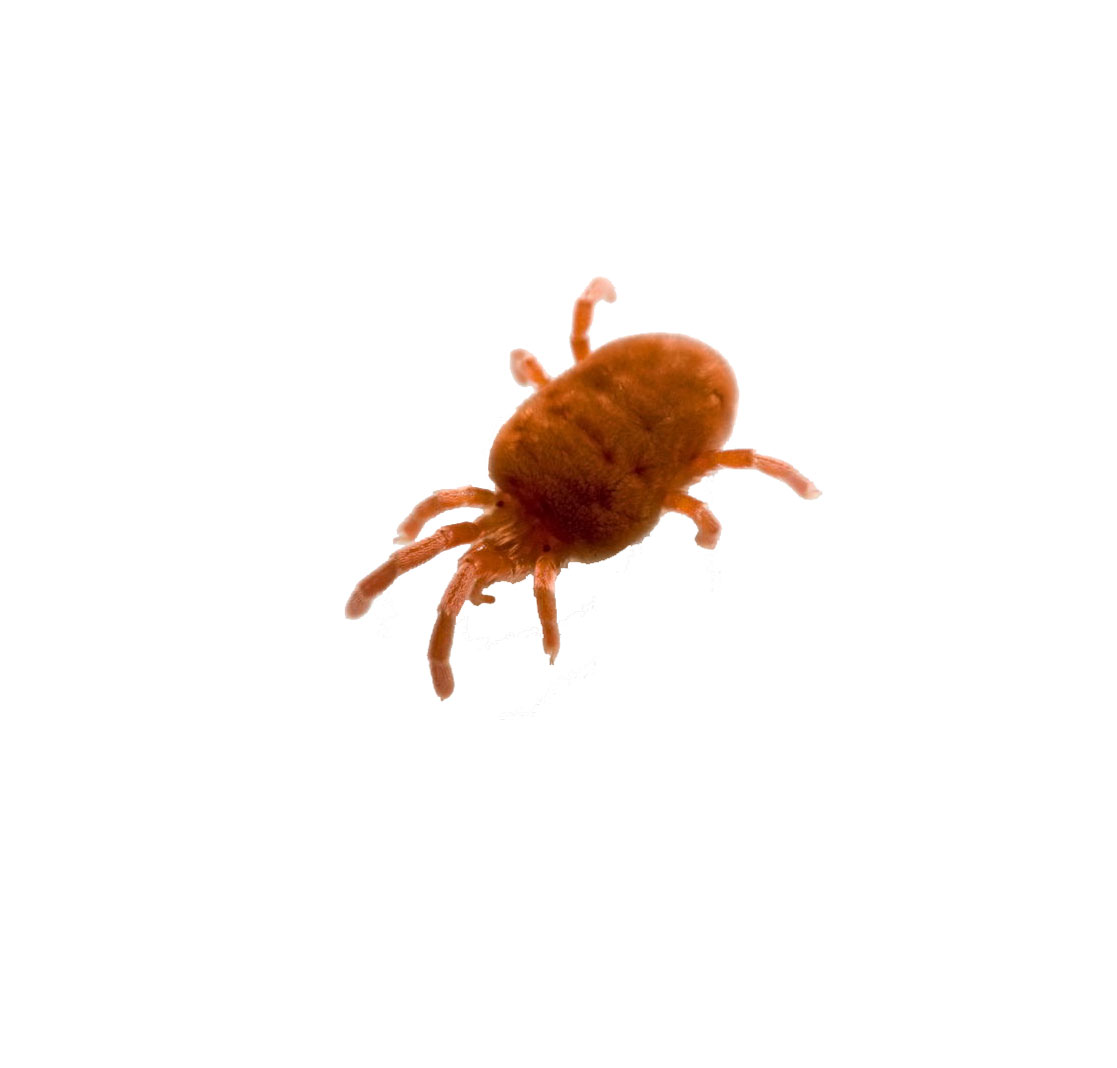
The enemies of the Huang variety are sawfly, weevil, aphids, and among its diseases are common rust, gray rot, spotting, brown rot. For prophylaxis, plants should be periodically examined for lesions. When a sick specimen is identified, it is dug up and destroyed. Conventional insecticide treatments are also relevant.

Strawberries are often subject to many dangerous diseases that can seriously undermine their condition. Among the most common are powdery mildew, gray mold, brown spot, anthracnose, and verticillosis. Before buying a variety, you need to inquire about its disease resistance.
Reproduction
It is permissible to breed such strawberries in the same way as other varieties: seeds, mustache, dividing the bush.