What does Ginnal's maple look like and how to grow it?
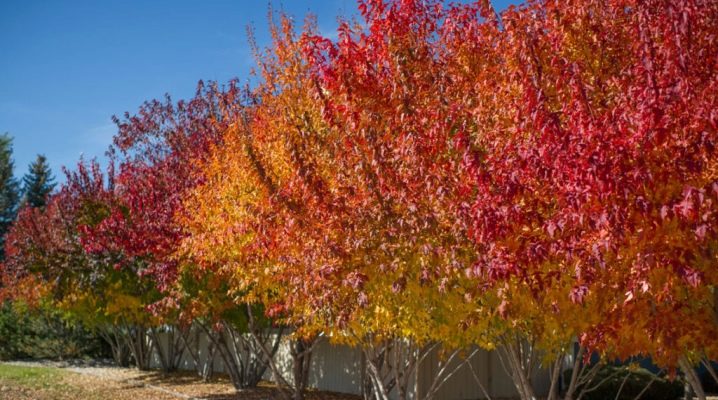

Often they try to choose a tree for a personal plot, which is highly decorative and requires minimal care. Ginnal's maple belongs to such varieties of garden trees. Experts note the high frost resistance of the species, it tolerates drought and heat well, feels great on any type of soil.
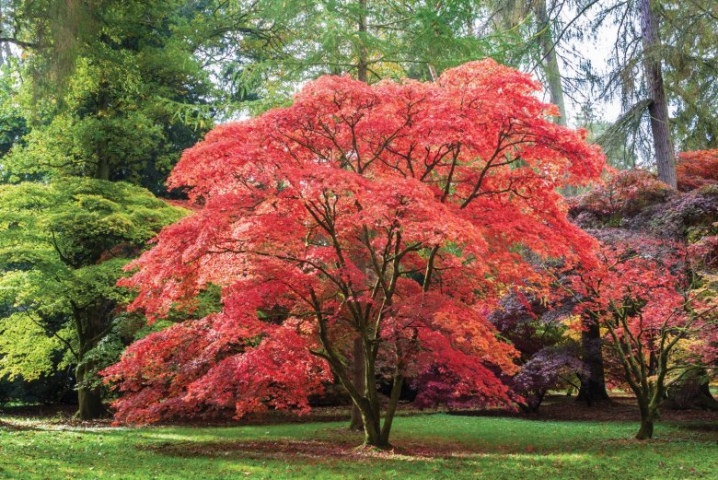

Description
Ginnal's maple is another name for riverine maple. A shrub plant of the sapindaceae family appeared in Russia in the middle of the 19th century. The first samples were brought to the St. Petersburg Botanical Garden from the Far East.
Related to the Tatar maple, sometimes they are referred to the same subspecies.
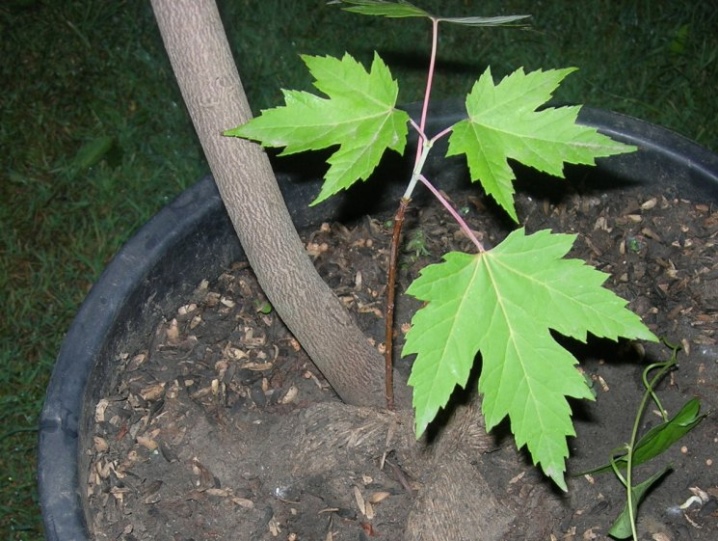
The Ginnal maple is a small deciduous tree that grows from 3 to 10 m in height, its trunk is short, 20-40 cm in circumference, the branches are straight and thin. The roots of the tree are located close to the surface, very branched and dense, giving abundant growth. The bark is brown with a grayish tinge, in young plants it is thin and smooth, and darkens with age, shallow cracks appear on it. The crown is in the form of a tent, near low bushes it almost touches the ground. The crown diameter is about 6 m.


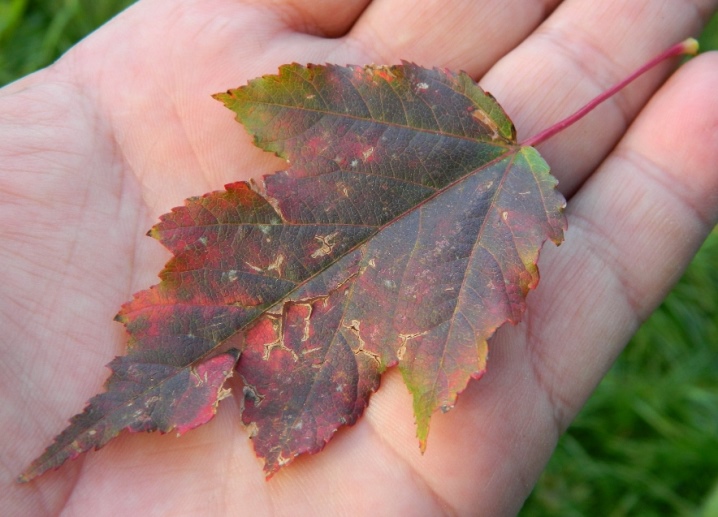
The leaves are arranged in pairs at each node, simple in structure, 4-10 cm long, 3-6 wide, strongly cut fan-shaped with 3-5 serrated lobes, pink petioles. The surface of the leaf is glossy, emerald green in color, turns yellow or scarlet in October.
It blooms in spring (at the end of May) after the leaves open, the flowers are small yellow-green and fragrant, 0.5-0.8 cm in size, collected in inflorescences of 15-20 pieces. Flowering lasts 2-3 weeks. The variety is considered an excellent honey plant. In a warm year, one bee colony collects 8-12 kg of high-quality honey from a plant. Creamy honey with almond flavor and delicate aroma.


At the beginning of autumn, at the place of inflorescences, fruits ripen: the fruit is a small seed with a blade of about 2 cm, located in pairs on one petiole. At the beginning of autumn, the blades with seeds have a bright red hue, then turn brown.
The species grows one at a time or in small groups near rivers, streams, in wet meadows or on low hills, but not in the mountains. Prefers well-moistened soil, is frost-resistant. Propagated by seeds, root processes and overgrowth from the stump. It grows quickly, very young plants are distinguished by a high growth rate, they add 30 cm per year.
Trees are considered centenarians - they grow in one place from 100 to 250 years.


Spreading
Under natural conditions, it grows in eastern Asia: from the east of Mongolia to Korea and Japan, in the north - to the valley of the Amur River, in the west - to its tributaries: Zeya and Selemdzhi. In the east, it grows in Primorye and Amur region.
They are planted in decorative form in northern Europe and North America. In Japan, it is very often used to create bonsai.
On the territory of Russia, it is grown everywhere, including in the Leningrad, Tula, Sverdlovsk, Omsk, Novosibirsk, Irkutsk regions, in Buryatia.

Landing
Planted in the fall at the end of September or in the spring in April. The species prefers a sunny place without close groundwater. Will grow in an area that is shaded for several hours during the day or in partial shade.The Ginnala maple is not very picky about the composition of the soil, but it does not tolerate saline soils and nearby groundwater, as well as swampy areas. It grows best on slightly acidic and neutral soil. In soils with a high lime content, it is recommended to use peat as mulch.
Seedlings can be purchased from the nursery. These are small trees 2 years old, placed in a container with soil, which is convenient for transportation. It is convenient to plant them even in summer.
You can cut a maple shoot and root it yourself, or grow seedlings from seeds.

Planting pits or trenches are prepared in advance 2 weeks or even 1 month before disembarkation: the earth should be compacted and not sink. Humus, peat, river sand and mineral compounds must be added to the removed soil. The area of the planting pit should be 3 times the size of the tree's root system.
Both a shrub and a tree can be grown from a Ginnal maple sapling. The result will depend on how the root system and crown initially begin to form.
For a single planting, the seedling is placed at a distance of 2-4 meters from other plants. With a close location of groundwater, drainage is installed. A layer of crushed stone about 20 cm is poured into the pit for planting at the bottom, then fertile soil with organic and mineral additives. A seedling is placed vertically, the roots are spread over the surface of the soil. The root collar is positioned flush with the soil surface. Sprinkle with a layer of earth, lightly ram, watered abundantly and mulched with sawdust or peat.
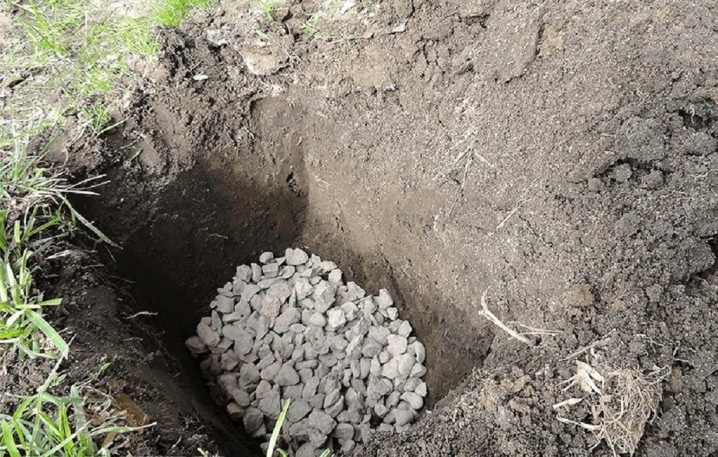

After planting 2 months, the seedlings are watered every week. When creating a hedge, the shrub is planted quite densely with an interval of 1-1.5 meters; for a curb, the distance is reduced to 0.5 m.
To plant a decorative hedge, a trench is dug 50 cm deep and wide, a mixture of humus, sand and leafy earth is poured onto the bottom, per 1 sq. m add 100 g of superphosphate. The seedlings are placed in a recess, covered with soil, watered, mulched with peat.
Young trees are tied to pegs, for the first time they are covered with an agricultural canvas for protection from direct sunlight. The first 3 years of the year requires additional care.
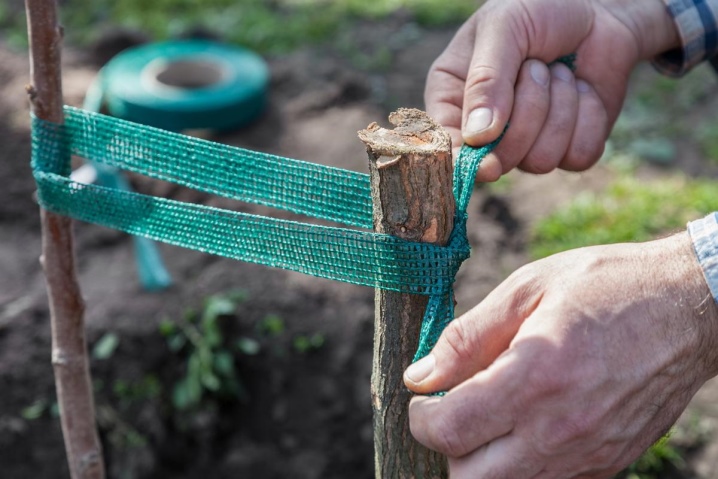

Care
As an adult, it practically does not need care. During the period of active growth, it is recommended to water, loosen, remove weeds, and feed. The variety is wind-resistant, tolerates urban gas pollution, smog, heat well.
Young trees in open ground in the first 2-3 years after planting need a special shelter. Ginnal maples grown on a trunk are the most vulnerable to frost. In the fall, the roots and trunk of young trees must be covered.
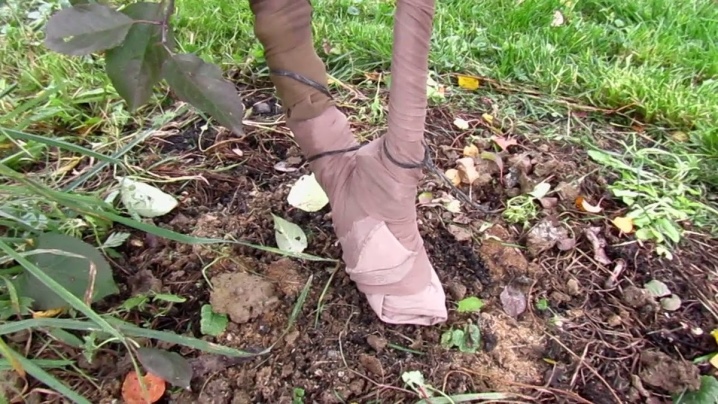

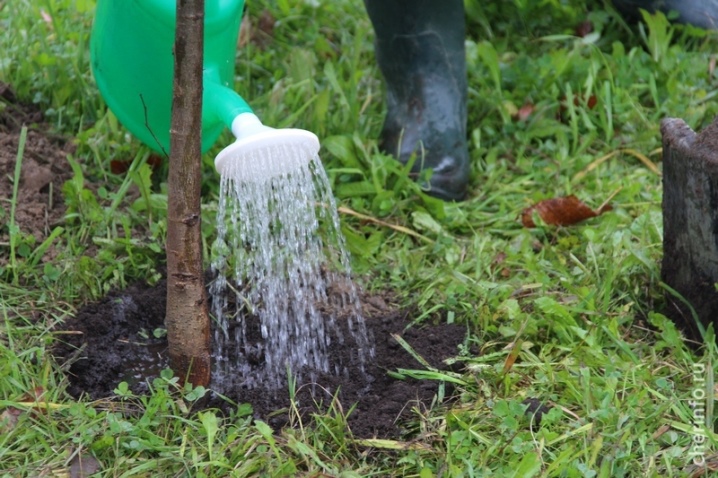
Watering
The variety prefers moist soils: an adult plant in the fall and spring is watered once a month with about 15-20 liters of water. An adult tree tolerates drought well, but with regular watering, the crown becomes lush, and the leaves are green and large.
In summer, especially in hot weather, watering is increased up to 1-2 times a week. With optimal watering, the soil is moistened by half a meter. The regularity of watering depends on the composition of the soil; in looser and sandy soils, they are irrigated more often.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that moisture does not stagnate in the ground - an excess of it has a bad effect on the tree.
Additionally, gardeners are advised to water not only the roots, but also the crown and trunk. This is done early in the morning so that the bright sun does not leave burns.

Top dressing
If, when planting, fertilizing was introduced into the ground, then you can not fertilize it during the first year. The next season is fertilized in May or early June.
For this, the following compositions are suitable:
- superphosphate - 40 g per 1 sq. m;
- urea - 40 g per 1 sq. m;
- potassium salt - 20 g per sq. m.
In the summer, complex mineral compositions are used, for example, "Kemira-universal". In the fall, while digging a plot, humus or compost is poured under the trees, per 1 sq.m make 4 kg.


Weeding
After watering, weeds are weeded out under the trees and removed, the soil is carefully loosened.
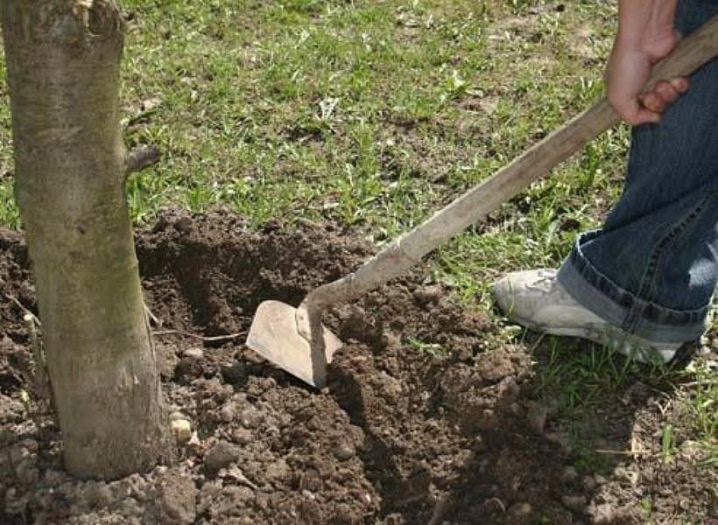

Loosening
The area of the near-trunk circle is loosened from time to time, since a hard crust forms on the surface of the earth after rain or watering. The procedure is carried out carefully, deepening no more than 5-7 cm, so as not to damage the roots that lie close to the surface.
The trunk circle is mulched, and lawn grass can be planted around the tree.

Pruning
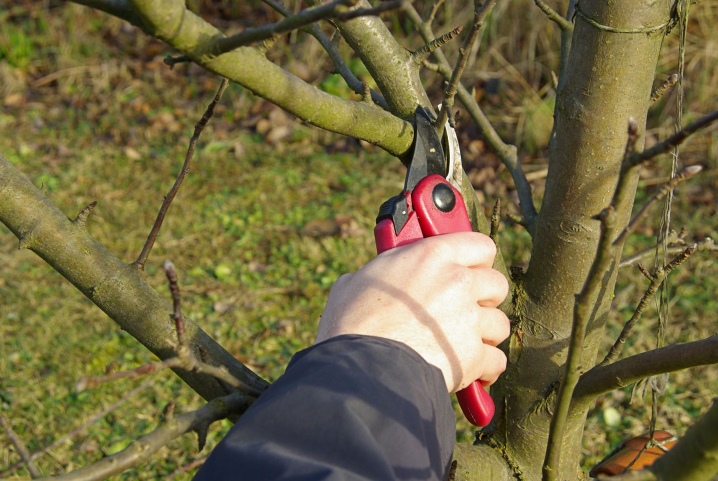
Depending on the cultivation technique, you can get a tree or shrub. The desired shape is given by trimming. An adult plant is recommended to be pruned once or twice a year. After that, new branches and leaves begin to grow. It is carried out in the warm season: in the spring before the awakening of the buds or in the fall after the foliage turns red.
The first time they are pruned the next year after planting - this stimulates the growth of new branches. Special scissors are used for the procedure. The branches are cut at a slight angle, a few millimeters are left between the bud and the cut, shortened by about half or one third.

Haircut options are as follows.
- Classic with a spherical crown on the trunk. The trunk is completely freed from vegetation, and the side branches are directed to grow at an angle of 45 degrees. Young shoots are pinched once a month, after which they begin to branch. Branches growing straight up are also cut off.
- Natural in the form of a tent. The plant is formed on a straight stem or several lateral branches are left, all root shoots are removed. The lower part of the crown is trimmed more intensively. In the crown itself, long branches and too thickened areas are cut off - this is usually about 35% of last year's undergrowth.
- Hedge. To form a denser and denser hedge, plants are recommended to be cut several times during the season: in the spring before bud break, in the summer after the emergence of young shoots and in the fall after the leaves fall. To achieve the desired height of the bush when cutting, leave no more than 7-10 cm of growth. I often form it in a trapezoidal shape.
- Border... To create such a planting, the maple bush should not exceed half a meter in height. Often, an inclined method is used so that the lower part of the shrub does not become exposed. In addition, sanitary pruning must be carried out in the spring, removing weak, dry, diseased shoots.
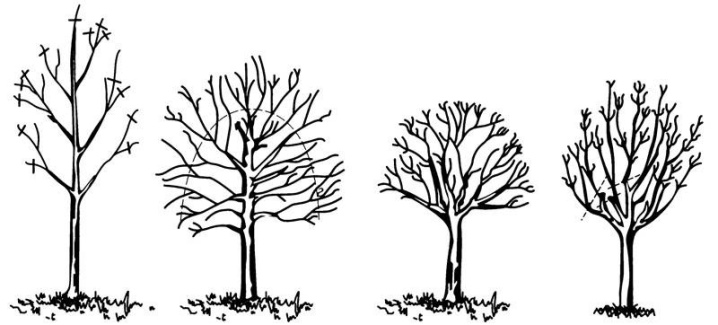
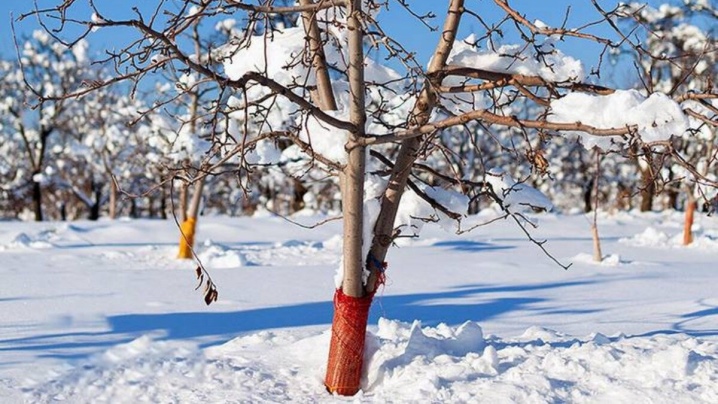
Wintering
Young trees are recommended to be insulated for the winter - especially the root system, to mulch the soil around the trunk circle with sawdust, leaves and spruce branches, in snowless winters it is better to cover the entire root system. The trunk and root collar, especially in the standard varieties, are wrapped with agrofibre or burlap.
Mature trees have a high degree of frost resistance, withstanding temperatures down to -40 degrees.

Reproduction
The Ginnal maple is propagated by seeds and cuttings. The seeds are harvested in the fall, they dry up and turn brown. At the end of October, the seeds are buried in fertile soil to a depth of 5 cm. In the spring, stronger plants will sprout. If the seeds are planted only in spring, they are placed in a container with wet sand and refrigerated for 3 months. In April-May, they are transferred to open ground.
During the first year, the shoots are stretched to a height of 40 cm. The shoots must be regularly watered, loosened, and weeds removed. In the heat, the seedlings are shaded from the direct rays of the sun. After 3 years, they can be transplanted to a permanent place.
Propagated by cuttings in the spring immediately after flowering. A strong shoot is chosen and cut off with a length of about 20 cm; it must have axillary buds on it. The leaves are removed, the cut site is treated with a growth stimulant. The stalk is immersed in wet sand, covered with a jar or plastic bottle, and left to take root until the buds wake up. They are transplanted to a permanent place only after a year or two.

Diseases and pests
Most often, the first signs of the disease appear on the leaves: they begin to turn black in the summer, dry and crumble, multi-colored spots fall on them. This means that the tree is sick or attacked by pests.
Types of diseases.
-
Powdery mildew - has the appearance of a small flour-like plaque on the sheet. The plant is treated with ground sulfur, mixed with lime in a 2 to 1 ratio.
-
Coral spot - appears as red spots on the bark. The diseased areas must be removed, the sections are lubricated with garden varnish, and the tree is sprayed with copper sulfate.
-
White spot - the disease usually appears at the end of summer, many small white spots form on the leaves, there is a black dot in the central part of each spot - this is the place where the fungal infection spreads. Bordeaux liquid is used for treatment.
-
Black spot - black spots with a characteristic yellowish rim begin to appear on the leaves. They are sprayed with preparations: "Hom", "Fundazol", "Fitosporin-M".

Of the pests, they are more often attacked: whitefly, weevil, mealybug. When the first signs of pests appear, the fallen leaves and branches must be collected and burned. The crown and the trunk circle are sprayed.
Whitefly hides on the lower part of the leaf, feeds on the juice of young shoots. The foliage dries up and begins to fall off in any season, if there are a lot of insects, all affected leaves begin to turn yellow. Whitefly is sprayed with insecticides: Aktellikom, Aktaroy, Amphos... The near-trunk circle is sprayed several times with dinotefuan or imidacloprid - the agent enters the tree sap through the roots, which the insects feed on.
The leaf weevil is more harmful to young trees; it nibbles flowers, buds and upper shoots. The external decorative effect of the crown is lost. Drugs help well Chlorofos and Fitoferm.
The mealybug, a close relative of the scale insect, sucks the juice from the leaves and buds, thereby slowing down the growth of the tree. White shreds of fluff appear on the branches and leaves on the back side, young shoots twist. Before the kidneys open, they are treated with "Nitrafen", and in the summer - "Karbofos".

Application
Very often, the Ginnal maple is used to create different options for garden compositions in landscape design. The view has several advantages:
-
beautiful carved bright green foliage, which turns crimson in autumn;
-
tolerates a haircut well, it can be given almost any shape and height;
-
undemanding in care and goes well with different types of plants.
They are used for single plantings near the house or on the lawn, creating a hedge, a border in one or more rows, for group compositions. Often planted in combination with conifers, barberry, magnolia, lilac, dog rose, dogwood, snowberry. Often placed on the banks of a pond or river, here the most favorable growing conditions are created for the species.
Ginnal's maple perfectly replaces the more heat-loving Japanese in oriental-style landscape compositions... It is used to create alpine slides and rockeries. In autumn it looks beautiful against the background of juniper and spruce. It goes well with alpine meadow grass. Pay attention to the fact that the variety cannot get along with the fir.





































































The comment was sent successfully.