All about clematis

Unusual plants with bright, often fragrant flowers on shoots climbing along the fence and arbor are clematis. For the combination of bright greenery and beautiful flowers, they are loved by owners of gardens and backyards.
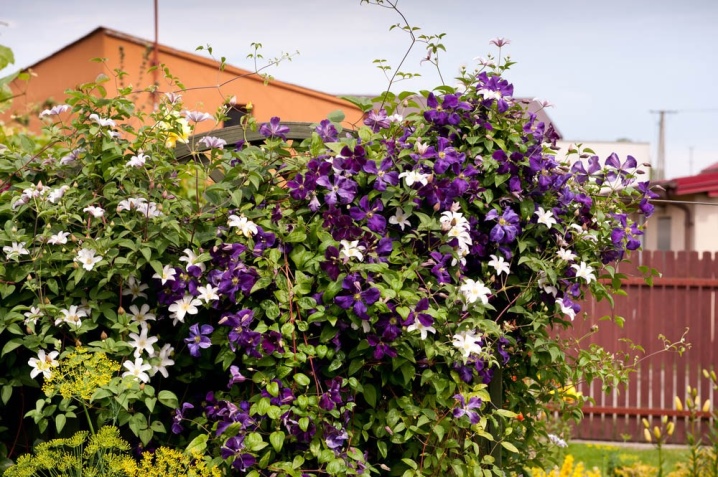

Description
Clematis is a perennial plant that belongs to the buttercup family. From the Greek language it is translated as "a branch of a vine", and in another way - "a shoot of grapes." Also known under the names clematis, warthog, wart. Found all over the world, except for the North and South Poles. Clematis are very popular among gardeners in many European countries, America, Australia, Japan, a classic English courtyard will not do without clematis. In Russia, these plants are not so well known, although now more and more flower growers prefer clematis.






Advantages:
- undemanding to the composition of soils;
- resistance to low temperatures and drought;
- fast growth;
- lush and dense greenery;
- abundant and long flowering;
- resistance to fungal diseases;
- takes up a minimum of space when landing.




All types of perennial clematis, shedding plant leaves for the winter, there are evergreen varieties. Not a single variety of clematis is annual. They can grow from 20 to 50 years and even longer, much depends on the environmental conditions and the species characteristics of the plant.
Escapes
Most of them are liana (or loach), clinging to leaves that twist their petioles around the supports. They grow up to 3 meters in length, some species up to 8 meters (grape-leaved, mountain clematis). There are climbing bushes that almost do not cling, but lean on supports, reaching from 1 to 2.5 meters in length (Manchurian, grade "Alyonushka"). There are standing straight and not clinging to the leaves, grow up to 90 cm, often more than a meter (whole-leaved, hogweed). Distinguish with herbaceous stems that dry out in winter (forest, straight), and with woody, which tolerate winter well (purple, grape-leaved).


Leaves
- simple (dissected or whole);


complex (trifoliate, dvazhdytroychaty, imparipinnate).



They are located on the stem on the opposite side in pairs, but there is a triple arrangement of leaves. Many species have mixed leaf shapes, for example, Jacqueman's clematis has pinnate foliage, but the tops are covered with simple leaves. The foliage is also colored in different ways, from dark green (shrub) and deep green (paniculate) to gray, and sometimes burgundy, for example, in Clematis Balearic in winter, and in spring - the blossoming leaves of purple-flowered and Armand.
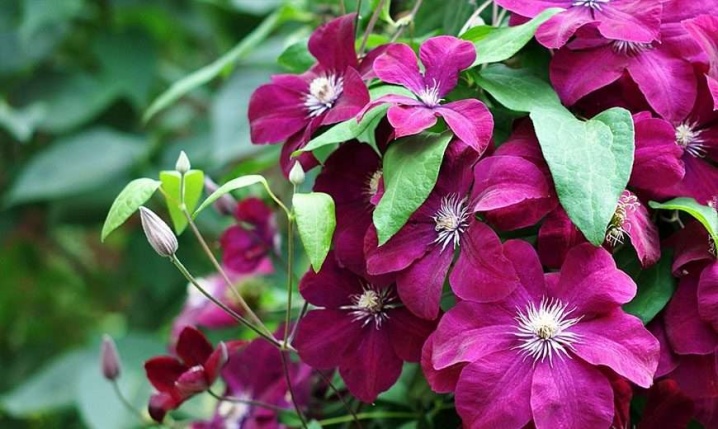

Flowers
There are solitary and collected in inflorescences with a huge number of stamens. The clematis flower has no petals, what are considered petals are sepals of different shapes and colors. Forms of flowers in large-flowered:
- star;


- cross;


- disk;


- bell.


The size of large flowers is from 10 to 20 cm in diameter (sometimes more), often in the spring-summer period they are larger than at the end of the season. Medium-sized flowers grow from 4 to 10 cm, and small-flowered - from 2 to 4 cm, often form inflorescences or panicles.
Small-flowered forms:
- cupped;
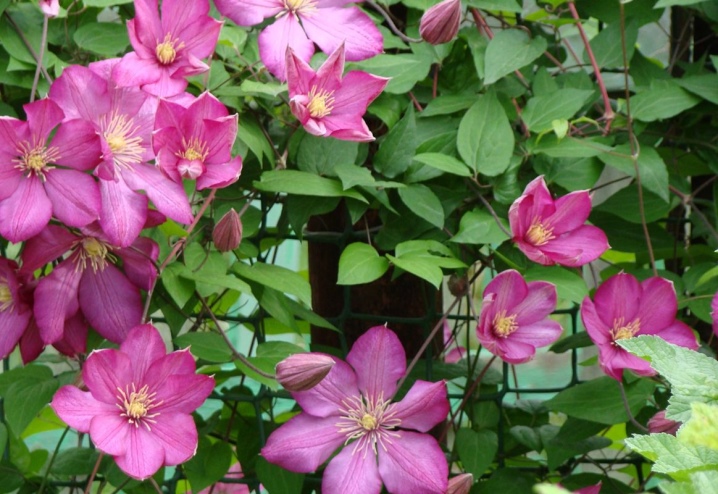

- bell-shaped;
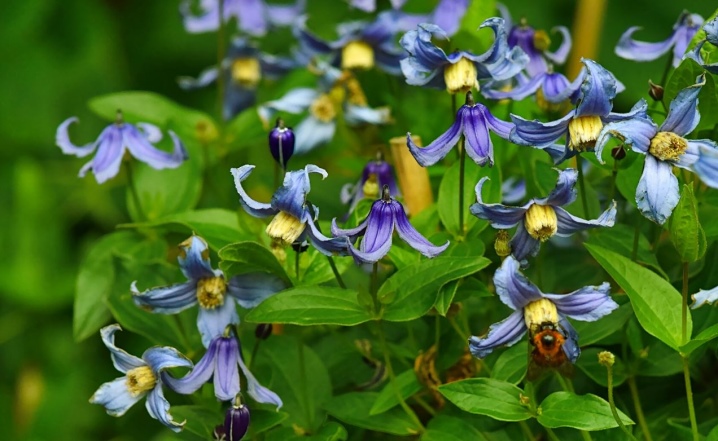

- pitcher;
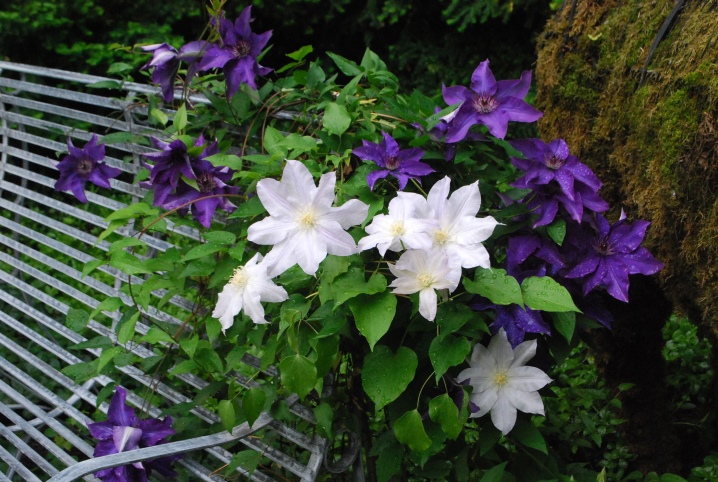

- tubular.


Coloring of flowering clematis:
- white;
- yellow;
- pink;
- carmine;
- purple;
- purple;
- blue;
- blue.
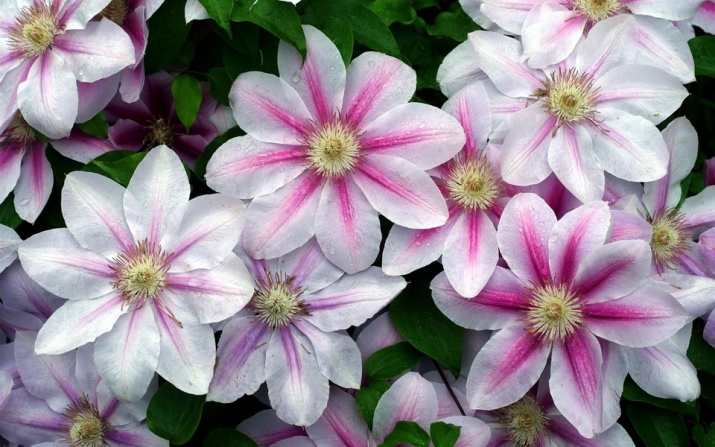






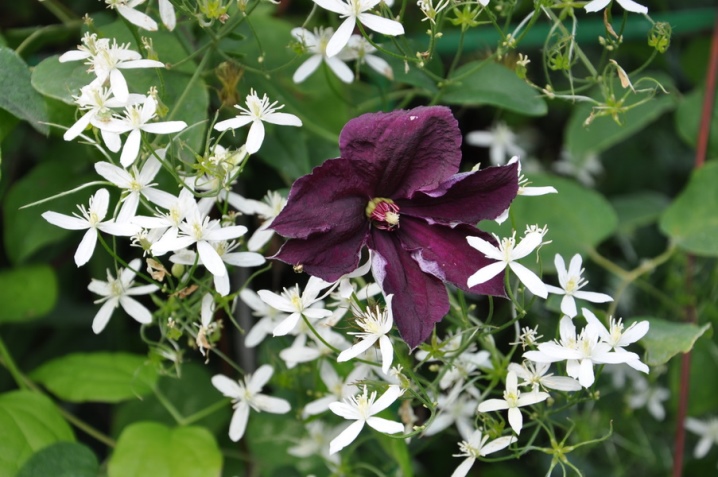
Some varieties have a stripe in the center of the petal. Hybrid varieties are multicolored, rich in shades and many stripes (Wildfire, Akeshi, Royalty, Josephine, Piilu, Andromeda).
Flowers smell nice:
- almond aroma (Sweet Summer Love, pungent, Rubromarginata);


- citrus (recta, "Blue Bird");

- jasmine (Manchu, paniculate).

In place of the inflorescences, seeds are formed. They are similar in shape to an arcuate rod with villi and are assembled into heads. Seeds that are not ripe and pubescent, ready for propagation, look decorative. The root system of clematis is:
- superficial - fibrous, not deeper than 45 cm, but very extensive, up to 200 roots (burning, Texas, purple);


- deeper - pivotal up to a meter, about 45 roots in one bush (grape-leaved, Tangut, eastern).


Plants with pivotal roots do not like transplants, they are planted immediately in a permanent place.
Views
The genus of these perennial plants is very diverse, there are about 300 species around the globe. On the territory of the former USSR, 18 wild varieties of clematis grow. For convenience, all varieties and varieties obtained with the participation of these species are divided into climbing and bush. In addition, there are:
- large-flowered (Zhakmana, Florida);


- mid-flowered ("Carmencita", "Alexander");


- small-flowered (burning, Manchurian).


There is a generally accepted garden classification, according to which there are:
- large-flowered climbing species (Vititsella, Zhakmana, Lanuginoza, Patens);




- large-flowered bush species (Integrifolia);
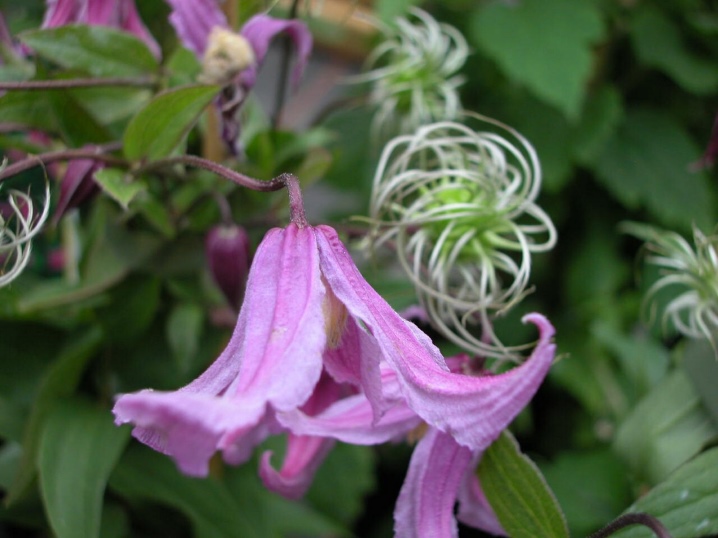

- small-flowered and mid-flowered (Hexapetala, Heracleifolia, Montana).



Large-flowered varieties and hybrids are grouped by origin from a particular variety.
Viticella Group
Bred with the participation of purple clematis. This is a bush loach up to 3.5 meters. It has compound feathery leaves, 5–7 per branch. Flower cups up to 12 cm in circumference with 4–6 petals. The colors range from pink to purple. Blooms profusely in summer on new shoots. Pruning is needed in the fall.
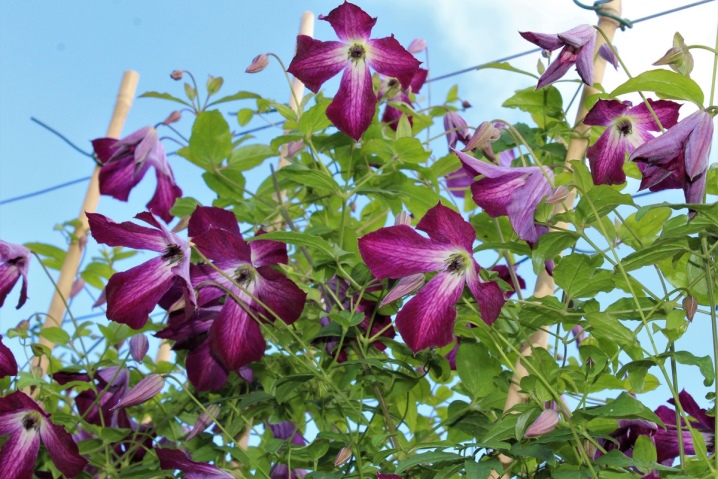

Jacquemann's group
It includes hybrids bred from Clematis Zhakman. Shrub vines up to 4 meters. Leaves are compound pinnate, from 3 to 5 on the stem. Flowers up to 20 cm in size can have up to 6 sepals, colors vary from blue to purple. Flowering time: mid-summer to early fall. Autumn pruning.
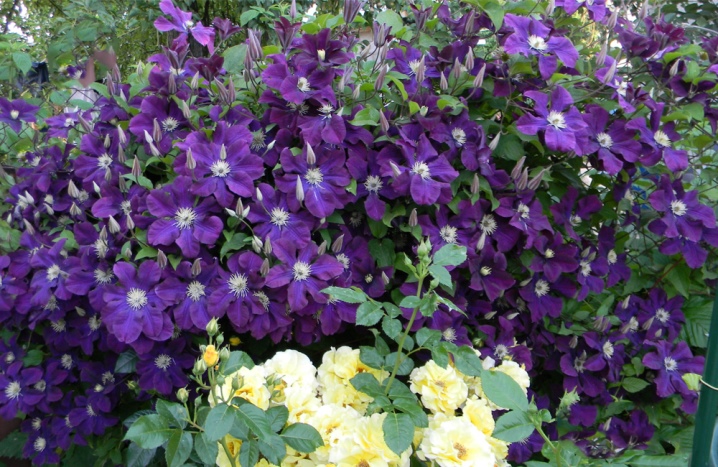

Lanuginoza group
When crossing white woolly clematis, shrub vines up to 2.5 meters in length were obtained. Simple or trifoliate leaves are slightly pubescent. Large flowers up to 25 cm with 6-8 petals. Light colors: white, blue, pink. It blooms in spring and summer on last year's shoots, in August - on new ones, but not abundantly. Do not cut off shoots before wintering, on which buds will appear next spring.
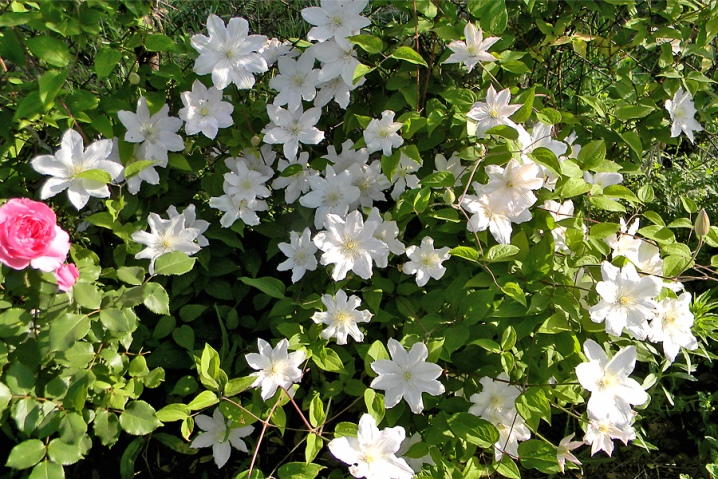

Patens Group
Formed with the participation of sprawling clematis. Shrub vines up to 3.5 meters. Leaves are compound pinnate, up to 3-5 on the stem. The calyx of the flower is up to 18 cm, open, often in the form of a star. Up to 8 petals in blue, violet, purple and lighter shades. Terry forms are not uncommon. It blooms on last year's vines in May, sometimes on new vines in August. Pruned and covered in autumn.
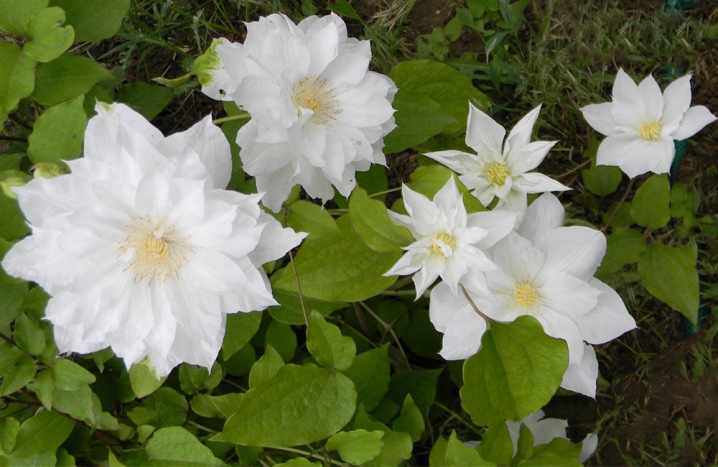

Florida group
Obtained with flowering clematis. Shrub vine up to 3 meters long. The leaves are trifoliate and dvazhdytrychatye. The size of the cup is up to 17 cm, with 6 petals, there are terry species. Light-colored are common, but there are also dark combinations. Last year's vines bloom in May and June: double or semi-double flowers, new ones - simple flowers appear. In the fall, cut to half the length of the plant and cover.
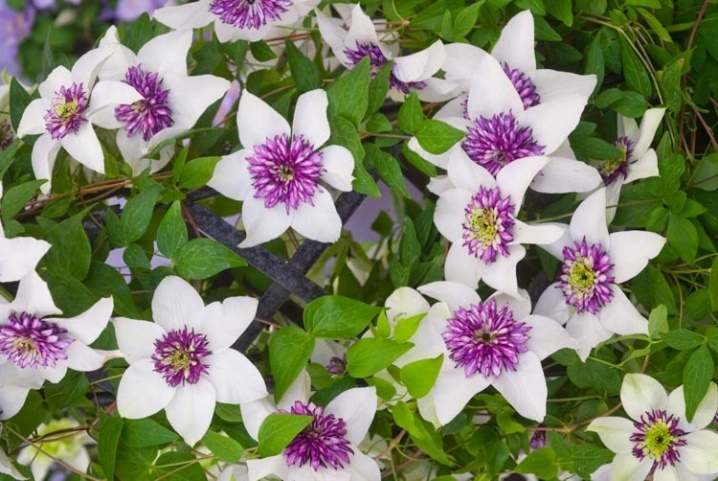

Integrifolia Group
Whole-leaved clematis forms the basis of the varieties in this group. It is a climbing shrub up to 1.5-2.5 meters, which clings a little to the fence. Leaves can be simple or complex.The cups are half open, bell-shaped up to 12 cm. From 4 to 8 petals of the most varied colors, drooping buds. Abundant flowering on new shoots. Pruned in the fall.
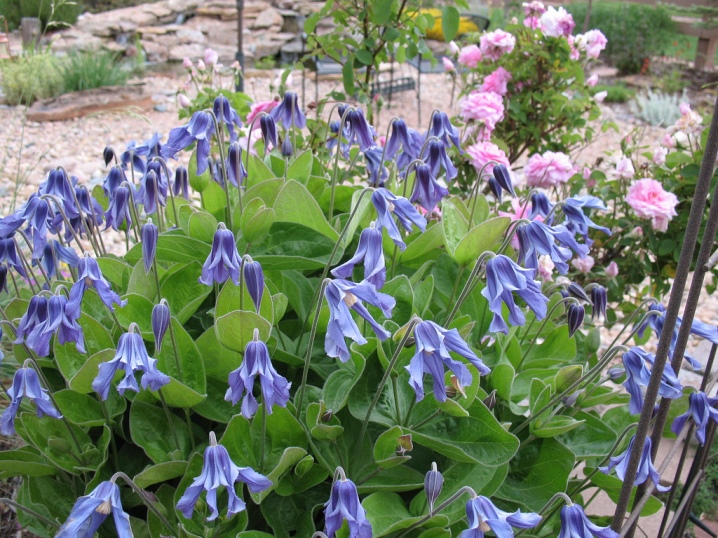

Small and medium-flowered varieties:
- Alpina (prince, "Alpina Blue");

- Armandi (Armanda);

- Fargesioides (Paul Fargez);
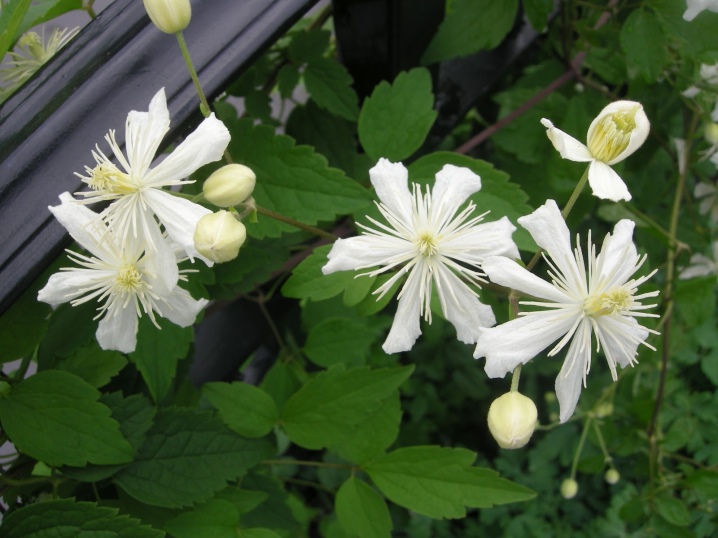

- Heracleifolia (hogweed, New Love, Crepuscule, Pink Dwarf, I am Stanislaus, Mrs Robert Brydon);
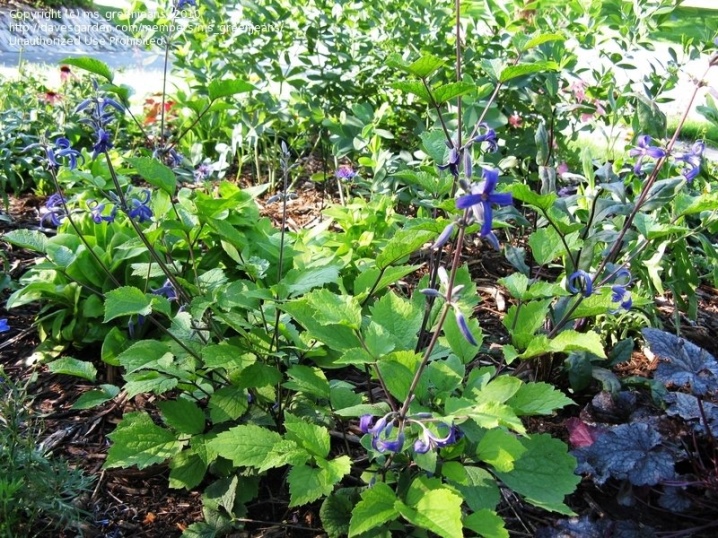

- Hexapetala ("Moonlight", "Zvezdograd");
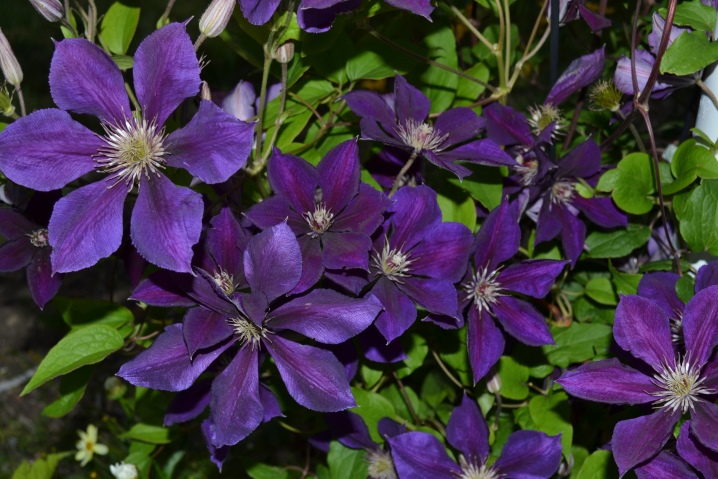

- Montana (Rubens, Grandiflora);
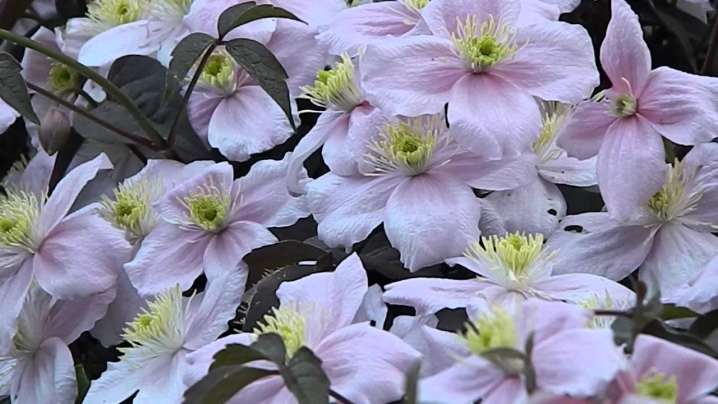

- Rekta (straight grassy);
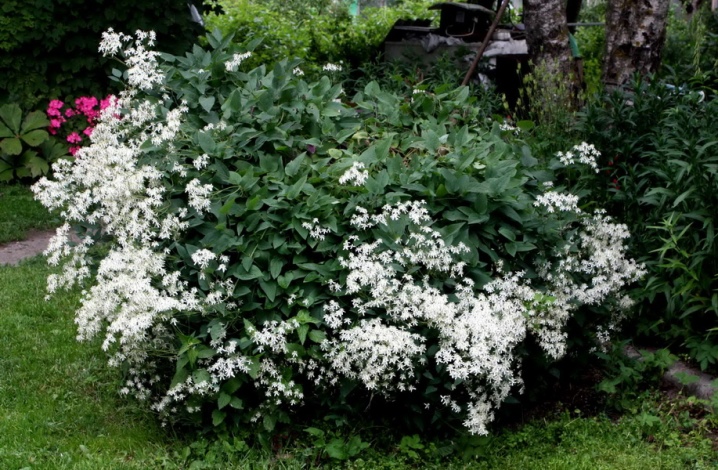

- Texensis (Princess Diana, Duchess of Albany).
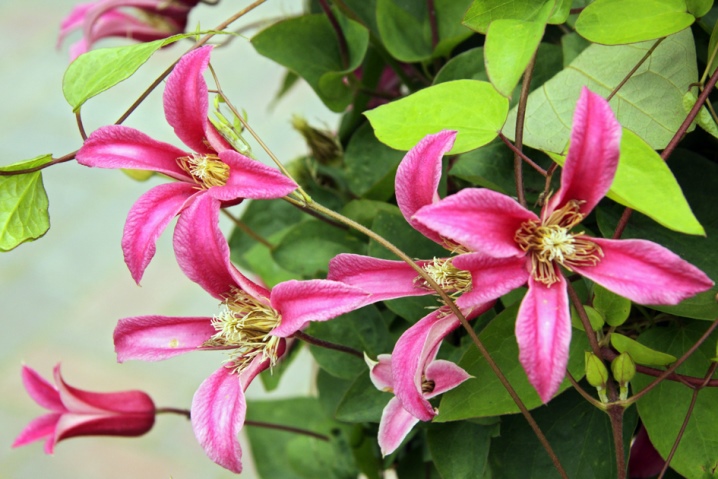

Large-flowered clematis Vititsella, Zhakmana, Integrifolia, Lanuginoza, Patens winter open and slightly covered in the Krasnodar Territory, Moldova, Ukraine. With regular shelter in winter, these unpretentious species are well suited for cultivation in non-chernozem areas of the central part of Russia, northwestern and southeastern, as well as in Siberia and the Far East. A low-growing bush type of clematis is grown without sheltering from frost even in the northernmost regions.



For most regions, the following types of clematis are recommended:
- hogweed and varieties derived from it;
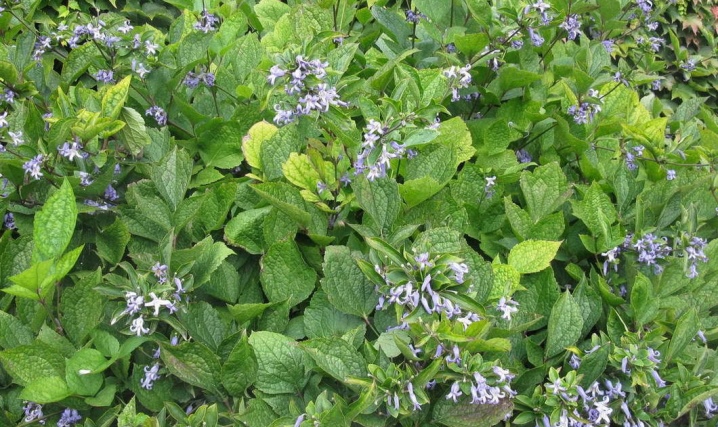

- Virginia;
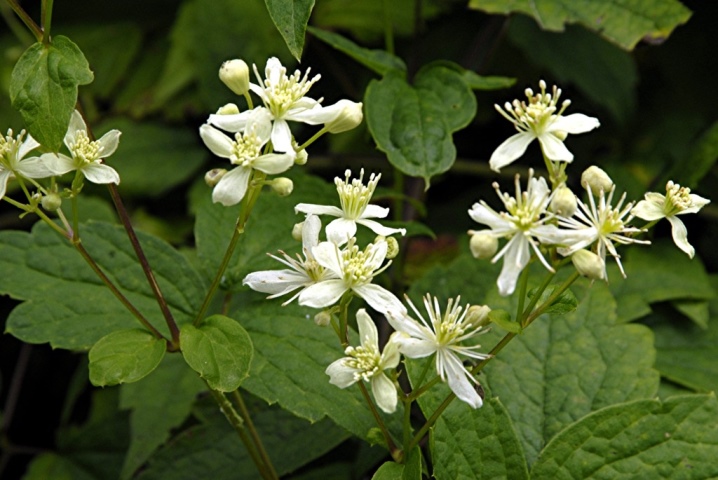

- Oriental;
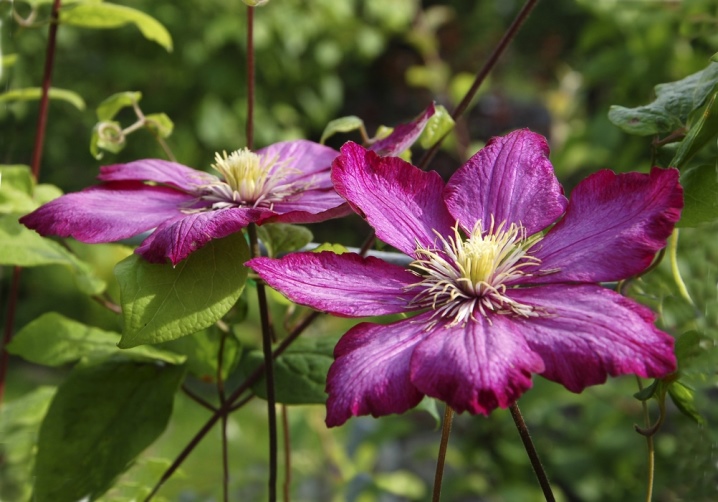

- forest;

- ligous-leaved;

- straight;

- gray;

- Tangut;

- texas;

- purple;

- whole-leaved;

- six-petal;

- Raeder.
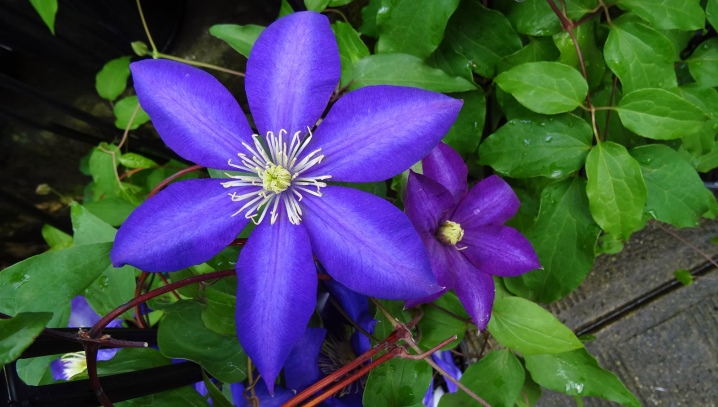

Curly compact hybrids from the Florida group with low frost resistance are more likely to be suitable for growing on a veranda or balcony. They hibernate in containers indoors at temperatures from 0 to +5. Paniculata clematis is used for landscaping in the south of Russia, where it grows up to 5 meters and longer, and is distinguished by abundant flowering. In the middle lane, this variety is less common and requires special care, since the plant is not winter-hardy and freezes over.

Seat selection
For large-flowered varieties of clematis, it is recommended to choose a cooler place. Coolness is obtained by shading the bush. For the full development of the bush, the sun needs about 6 hours a day. Many varieties of clematis from places where daylight hours are short. In latitude, where the sun is more frequent (the middle zone of Russia and to the north), an overabundance of light causes the active growth of the plant, which delays the appearance of flowers. The plant does not have time to prepare for winter.

In the non-black earth, it is better to plant clematis near the eastern wall of the house or fence, you can from the south or from the west. In the north, shade-tolerant varieties are planted (Alpine, mountain, Manchurian, Clematis Redera, "Lavson", "Nelly Moser", "Fargezioides"). Near a single support - a column, a tree - are planted from the north, so the underground part will be protected from overheating. In colder areas, the southern wall works best. Full shade is contraindicated for plants.

It is necessary to provide that clematis are protected from the wind: by a wall, fence or other plants. Strong gusts break the shoots and knock the flowers off the plant, such conditions can delay the appearance of the first leaves and flowers. If there is no protection from the wind, then clematis is planted near a low fence (veranda railing, gate).
Clematis do not tolerate transplanting well, so it is better to plant them immediately in a place where they will grow constantly. The soil for planting is preferable loose and well-permeable to water, fertile. Loamy or sandy loamy, slightly alkaline, neutral or slightly acidic, ordinary garden soil are suitable. Damp, clayey, heavy, very alkaline and acidic soils are contraindicated. They improve such soils by adding humus, peat, compost, coarse sand to them, loosening them. The same operations are carried out with sandy soil. Some clematis, for example, eastern, grow on dry, poor and saline soil.

Plant roots develop most actively in acidic soil, the best pH value is 5.5–6. More acidic soils above pH 7 must be alkalized: mulch with sand mixed with ash, or watered with lime.Large-flowered species and hybrids from the Viticella and Integrifolia groups prefer acidic soils. Alkaline is required for clematis of tangutica, orientale, montana, alpina, macro-metal and grape-leaved, Koreana and vitalba can grow on them.

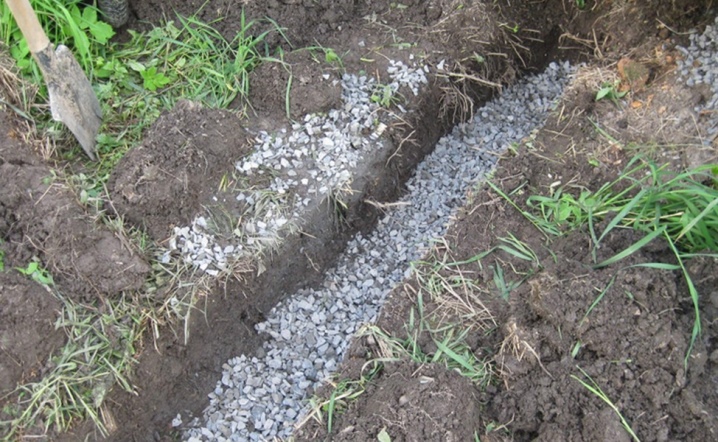
Nearby groundwater creates significant inconvenience for clematis and can lead to the death of the plant. It is necessary to lay drainage ditches, and plant the bush on an earthen embankment. The soil at the planting site needs to be well dug up and fertilized. It is important to take into account those components that are already present in the soil. Processing is carried out a month before the autumn planting and in the fall for the spring. You can plant small varieties in balcony containers or flowerpots filled with a mixture of earth, sand, humus and mineral fertilizers. Wood ash must be added.

Climate zone accounting
In areas with warm and mild winters, clematis are planted in autumn (late September - early November), in a more severe climate, planting dates are postponed to April - May, the soil should warm up well. In the southern regions, spring planting is carried out no later than March; in the northern regions, they are planted in late August - early September. Clematis is planted during the entire growing season, after planting in open ground, the plant is shaded for two weeks. For clematis, the temperature regime is important. Attention should be paid to the origin of the planted variety: large-flowered species, whose ancestors grow in the mountains of Asia, do not like heat and can hardly tolerate temperatures of +25 degrees, and those who arrived from America perfectly adapt to a temperature of +40.


From budding to autumn yellowing of foliage, clematis takes about 200 days, in the south this period is longer, and in northern latitudes it is shorter.
In March - April, clematis buds begin to open in the following order:
- brown;

- Manchurian;

- purple;
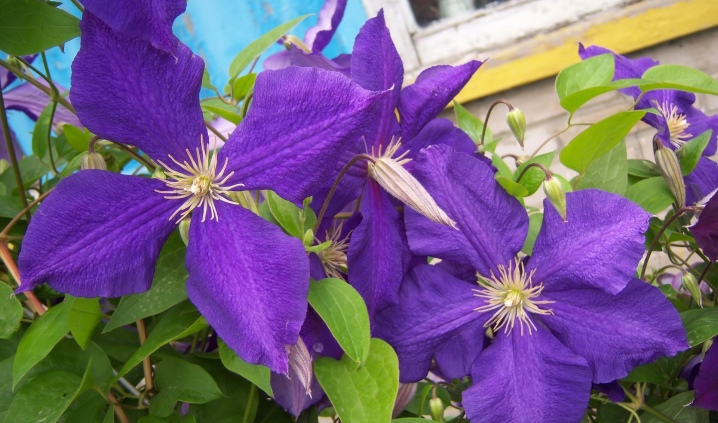

- Oriental;
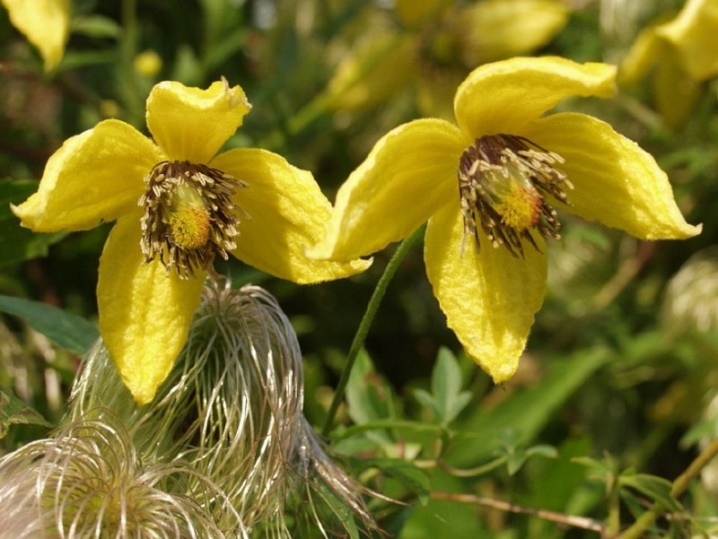

- mountain;
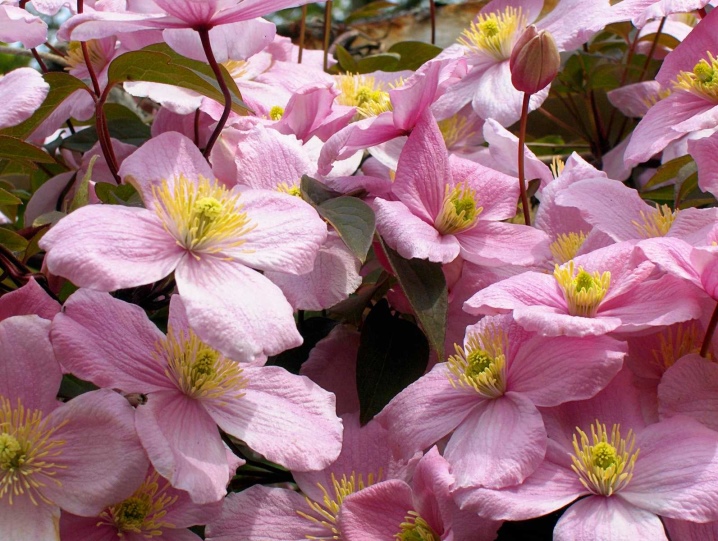

- straight;
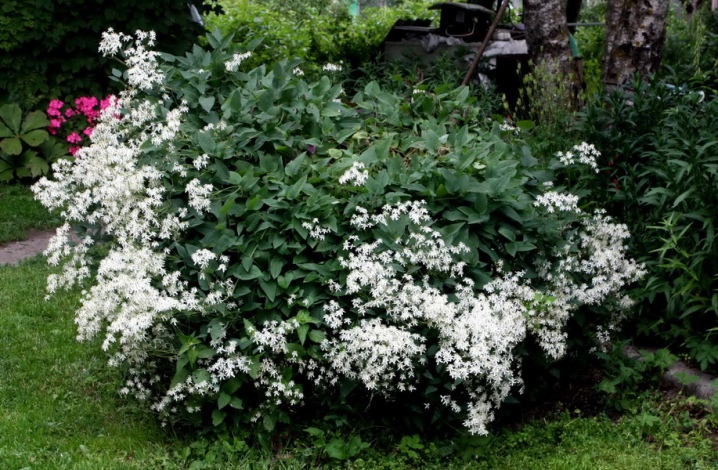

- Tangut;

- six-petal;

- whole-leaved;

- hogweed;

- grape-leaved;

- burning;

- shrub;

- gray;

- texas.
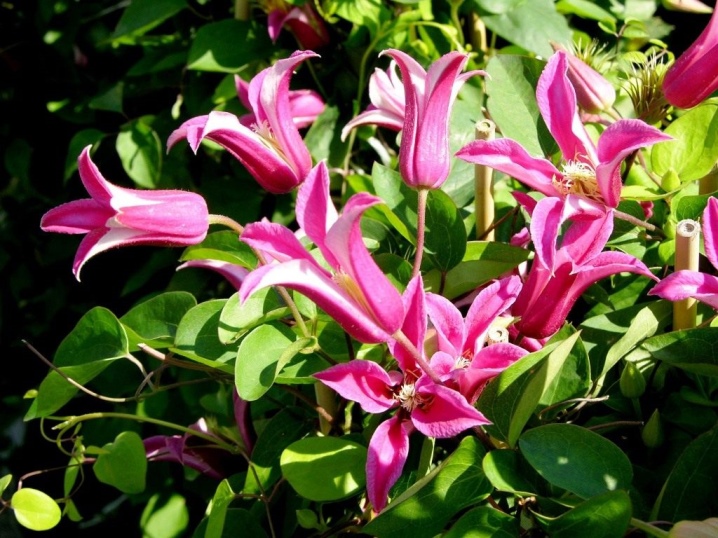

For areas with a mild climate, the growing season begins approximately at the specified time; in colder areas, the date may shift by a month. Flowers also open later. In colder years - late spring with frosts, rainy, cloudy summers - one should not expect record abundant flowering from clematis.
Clematis after pruning and wintering can bloom profusely on new regrown vines. This allows it to be grown in central Russia, Siberia, and the Far East. The root system of clematis can withstand frosts down to about -20 degrees. Alpine and Siberian princes - up to -35. The frost resistance of a particular species is taken into account when choosing a variety for the southern territories, the middle lane and the northern regions.
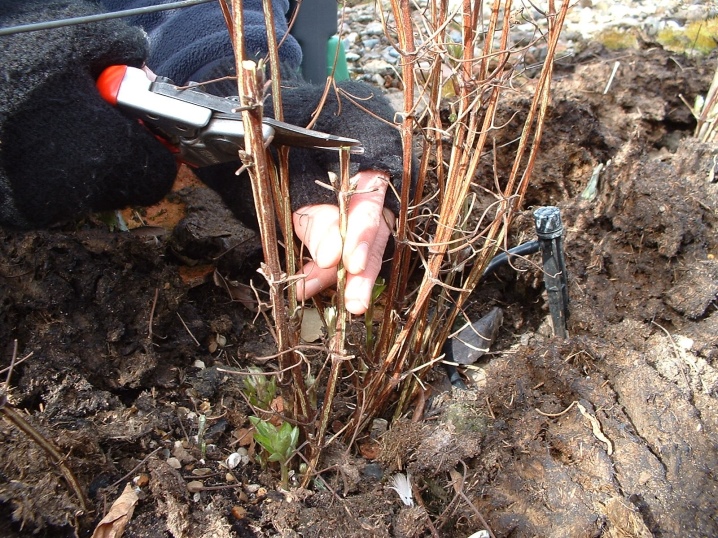

Installation of supports
All clematis grow very quickly, in spring the shoots lengthen by 10-15 cm per day, but the shoots do not have time to get stronger and need support. It is necessary to ensure that the vines do not intertwine, from this clematis form fewer buds. Overgrown and weak shoots are removed at the base of the stem.
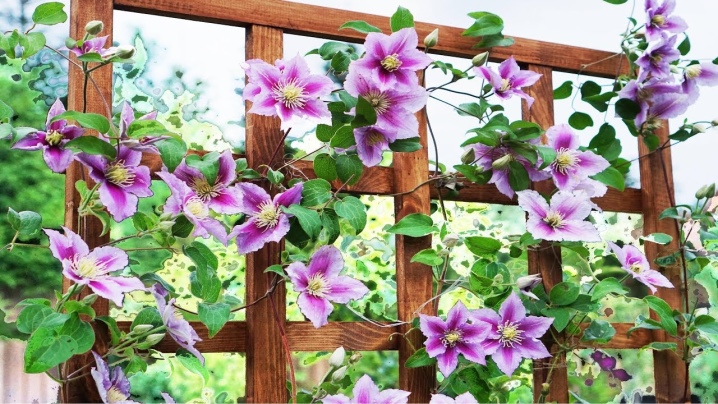

Types of supports:
- single support (wood, column);


- fence;
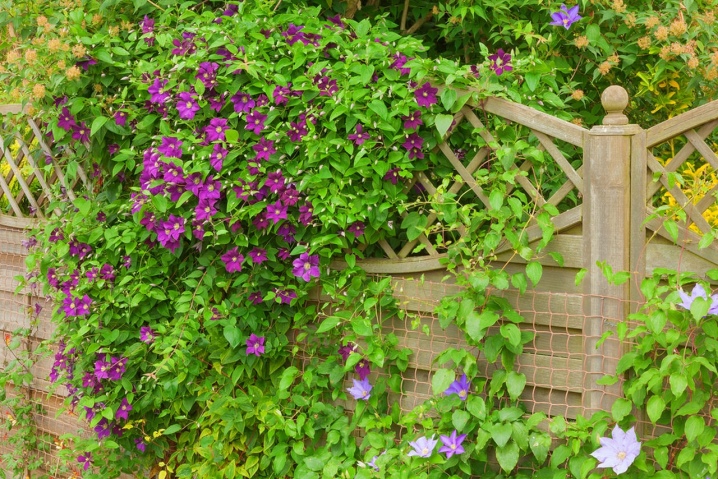

- arch;
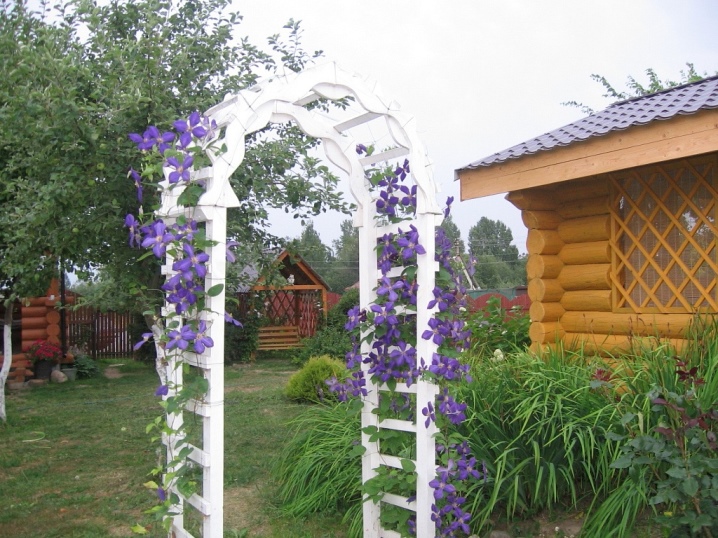

- lattice (pyramid, ball, trellis);


- pergola.
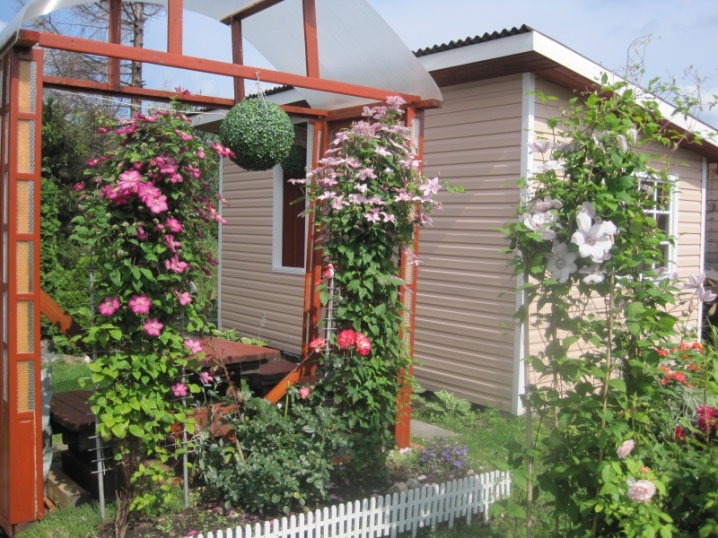

The most used type of support for clematis is a grating, installed separately or attached to the wall. The size between the squares is about 5x5 cm. The vines should pass freely between the grate. Supports can be wooden or metal. Aesthetically designed, they will create an additional composition and help shape a curly flowering liana. When placing the supports in a row, they are positioned from east to west to create the most suitable lighting. The height of the supports varies from half a meter to three.
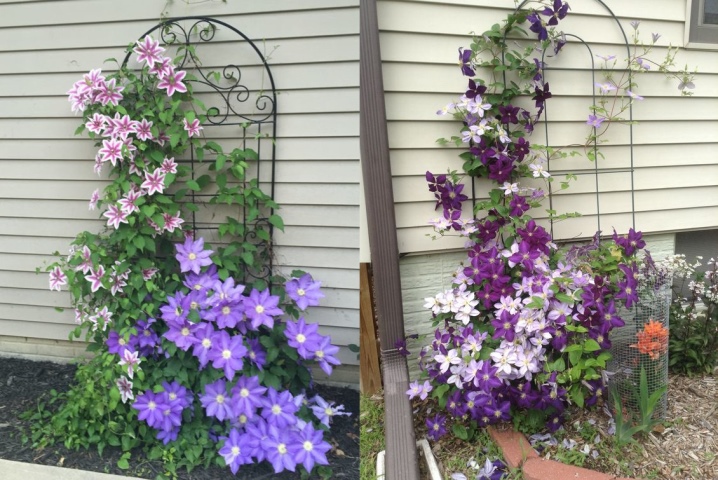

Reinforced concrete structures seem, at first glance, more practical. Vertical and transverse elements are made of thin rods - this way it is more convenient for the plant to climb and cling.Clematos are wrapped around them so tightly that in the fall you have to cut off each leaf, trying not to break the stems, which are covered for the winter. During installation, the supports must be carefully fixed, otherwise the plants may be damaged in heavy rain and wind if the grate falls.
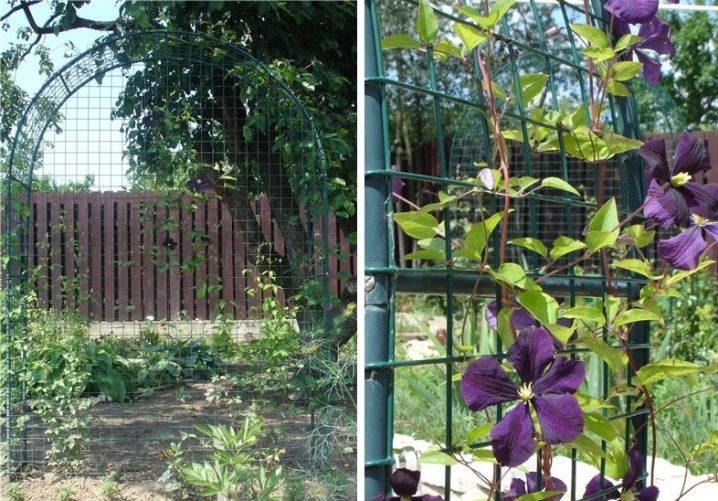

Some gardeners use fishing line for supports - this is an economical option in terms of cost and installation. Near a bush planted against a fence or wall, several hooks are stuck into the ground. The lower edges of the fishing line are tied to them, and the upper ones to the crossbar on the fence or wall. The shoots of the plant wrap around the fishing line well and do not fall off it. In the fall, the line is cut from above, and the bush is on the ground.
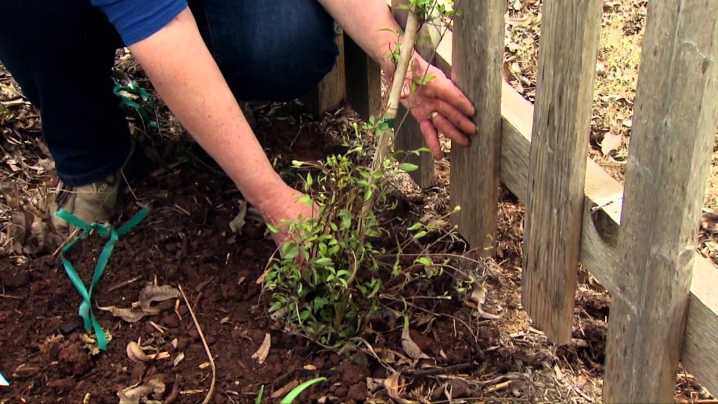
Landing features
Clematis do not tolerate transplanting well, so they choose a permanent place for them right away. Seedlings are placed at joint planting at intervals, and if the bush is single - from neighboring plants and supports. For different varieties and species, the distance is chosen individually, this is influenced by the length of the future vine and the volume of its ground part:
- Zhakmana, Vititsella, Integrifolia at a distance of 1–2 meters;
- Patens, Florida, Lanuginoza with an interval of 0.7 to 1 meter, if the bushes take cover for the winter, in the northern regions it is increased to 1.5 meters;
- small-flowered tall shrubs are placed at a distance of 2-4 meters.
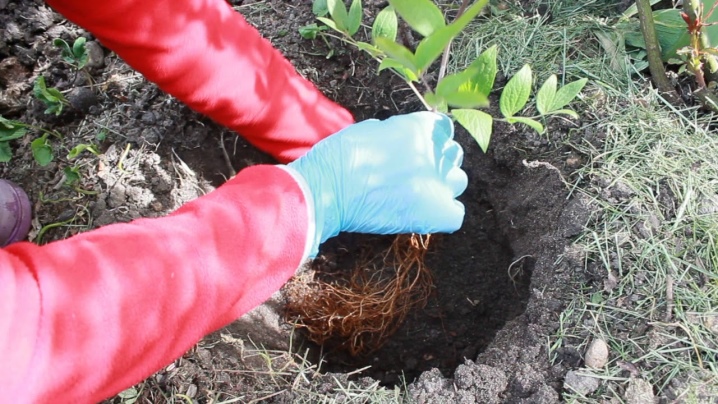

Clematis of different varieties, planted next to each other, do not over-pollinate, the proximity of different varieties does not affect the shape and color of flowers in any way. The roots of clematis go deep into the ground, and around them do not diverge more than a meter, do not drown out other plants. It is recommended to plant the plant no closer than 2 meters from a tree or shrub. The roots are insulated with a special partition made of slate or similar material. Clematis roots are removed from the wall of the house or the fence by half a meter. There are several opinions and recommendations on how to plant clematis correctly.
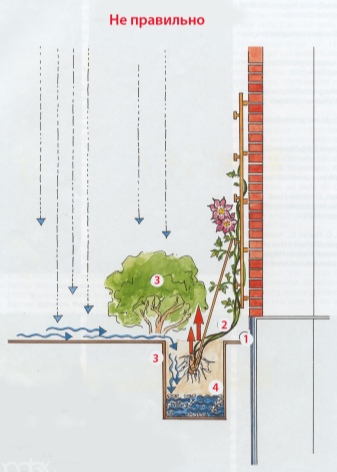
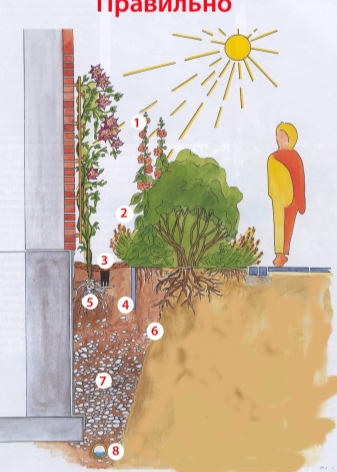
For fifteen hundred years it was believed that for such plants it is necessary to dig deep holes 60x60 cm, on the bottom of which a 15-cm layer of drainage should be laid (crushed stone or small stone), and on top an earthen mixture with humus, peat, compost, wood ash and mineral fertilizers (superphosphate , nitrophobic). Many specialized publications recommend planting this way. But this method is only suitable for light soils without groundwater.

Friedrich Manfred Westphal has been breeding clematis for most of his life, just like his father. In his opinion, clematis should not be planted in this way. If you dig a hole in heavy soil and fill it with lighter soil, then it will become a container in which water from the entire site will be collected. Drainage at the bottom will not help in such a situation. This is the wrong landing pattern.


The depth of the planting pit, according to the German clematis breeder, should be the same diameter as the container in which the seedling was transported, about 20 cm. The planting hole must be filled with the same soil that was dug. A drainage and a pipe for draining water are placed just below. The roots of a neighboring plant should be separated from clematis by a partition, which is deepened into the soil by 30-50 cm. This is the correct planting scheme.
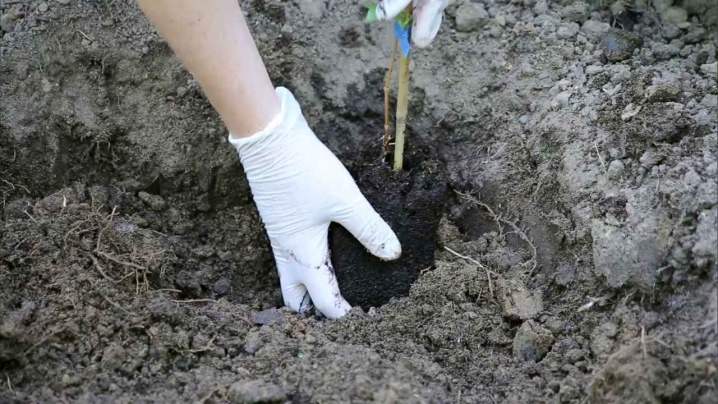

With a close location of groundwater, you can try to plant clematis on an embankment with deep grooves on the sides. Do not plant very close to a stone wall and fence, where the plant can overheat, the distance should be at least 30 cm.
Clematis are susceptible to root damage. The seedling can be planted in a hole in a purchased container by cutting off the bottom. Then the container can be removed. When planting without a container, they are planted at the same level at which the plant was in the container, 7–8 cm. The damaged root is cut and disinfected with a pink solution of potassium permanganate, the cut is sprinkled with crushed charcoal or ash. Lime is added to the landing hole. It is imperative to water it, you can use a solution of dolomite flour or natural chalk (15 liters + 3 pinches of dolomite).The diluted mixture should have the color of baked milk, this procedure is carried out 2-3 times over the summer, always after fertilization with organic matter.
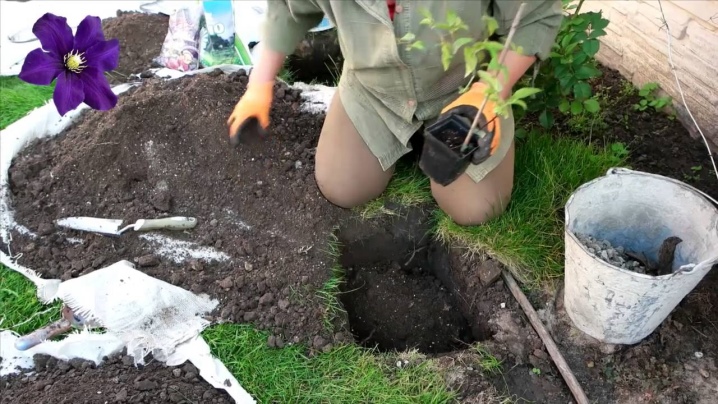

For planting, two-year, rarely annual, rooted cuttings, layering and clematis seedlings are used. Saplings obtained by grafting or budding must be planted 10 cm deeper than usual. Sand is poured onto the neck of the root to protect it from damage by a putrefactive fungus. Throughout the summer, a little fertile soil is poured into the hole until it is level with the soil level.

Care rules
Swampy soils are contraindicated for clematis; they are not planted near a wall under a roof without a drainage system. Otherwise, they will fall ill and die. Tall and spreading trees are not the best neighborhood for clematis, the powerful roots of the tree will prevent the liana from growing. The lush bushy part of clematis feels great in the sun, and the roots prefer shading. Growing secrets: for the southern regions, clematis are planted in partial shade, in the northern ones - in sunny areas. Low-growing plants - flowers or decorative species - will be a good solution. You can mulch the roots with sawdust, straw, needles.

Shrub and climbing types of clematis are suitable for growing in a flower bed in the garden and for single compositions. At the dacha, they are placed near the fence or near the gazebo to create abundant greenery and shade. When landing in flowerpots on a balcony or veranda, it is necessary to ensure that there is enough lighting, they must be looked after in the same way as for clematis in the open ground. With little light, the flowers will bloom pale or greenish. After the flowering of an adult bush, the peduncle is cut off.

Young plants in spring may not open their buds for a long time and not release shoots. The root system is not yet strong enough, and the plant is growing it. When the first leaves appear, the shoot will begin to grow rapidly. Liana is carefully lifted and tied to a support. According to the rules of agricultural technology, you can increase the number of shoots on a small bush by simply pinching the crown, but this will delay flowering by 10-14 days.

Plants need to be watered frequently in hot summer weather (2-3 times a week), but make sure that moisture does not stagnate in the soil. It should always be moist and loose. It is important to water correctly: do not pour on the bush in the center. A depression is made 15-30 cm from the base, the required volume of water is poured into it. An excess of moisture on the lower part of the vine can cause wilt disease. If the shoots wilt after watering, then the bush is pulled out and burned, and the soil is disinfected with a solution of copper sulfate.On heavy soils, the clematis growth point is deepened by 8 cm, it is recommended to loosen the soil more often, feed it and close it more carefully for the winter. With a shallower planting in the spring, the bushes will grow and bloom faster, which is very important for the northern regions, where the summer is shorter. On light soils, the base of the root is placed as deep as possible by 10-15 cm.

After planting for about a year, the buds are advised to be torn off so that clematis can build up the root system. It is not necessary to fertilize for the first two months so that the plant develops roots, and not green shoots.
Support
Most clematis are vines, and there are climbing shrubs among them. Both varieties need supports. Supports for different types require different. For lianas-leaf climbers, those are suitable for which it will be convenient to cling to the leaf stalks. These are single structures in the form of a pillar, column, lattice in different configurations. Other plants are also used as a support: trees, shrubs (chubushnik, weigela, forsythia). Climbing clematis practically do not cling, but they need to lean on a stand so as not to fall under their own weight. Near a fence or a gazebo, such clematis rely on buildings.
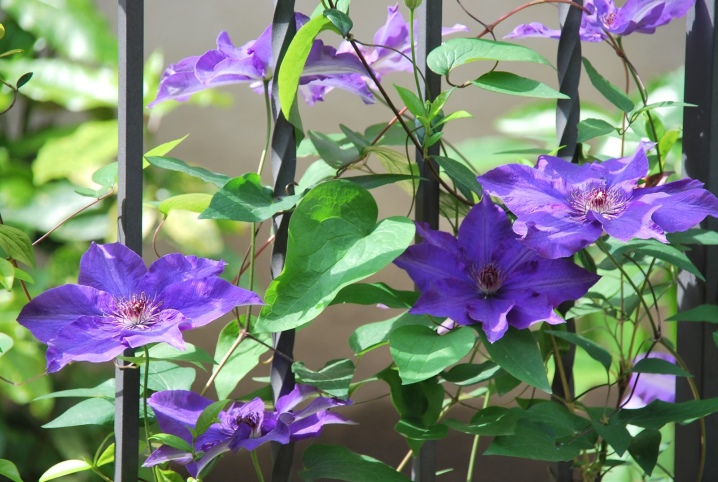

What should be the support for clematis:
- durable (should not break under the weight of a large plant);
- resistant (do not fall from wind and rain);
- convenient for pruning and covering plants for the winter;
- aesthetically pleasing or mobile (easy to install and assemble).
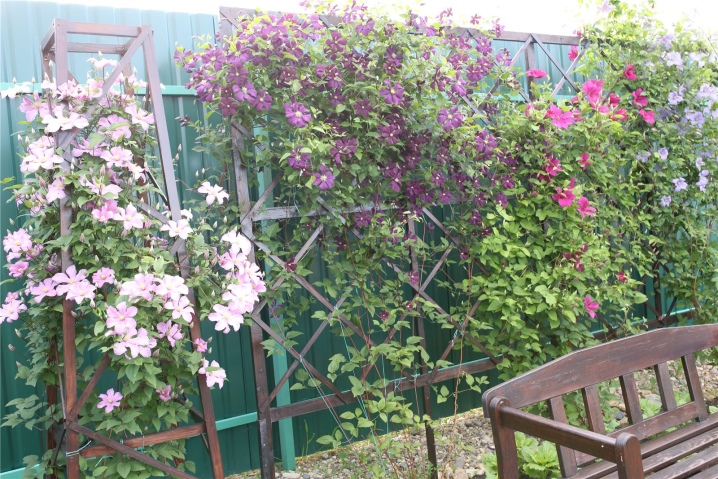

A trellis is fixed on the facade of a building or a blank fence, an arch-shaped structure is suitable for decorating a gazebo or a walkway, a pyramid-shaped support can be placed on a flowerbed or front garden in the center. Clematis will twine around the supports with flexible shoots, the thickness of the surface along which the plant winds should not be more than 2 cm. Clematis grow well on lattice and mesh surfaces, for example, on a regular mesh fence. The same net, stretched on the wall, will allow the plant to climb up, and twisted around the post - along the post.

Triangular structures (pyramid or obelisk) made of slats or planks are very popular with fans of clematis. They can be quickly made from improvised means and installed by sticking deep into the ground.
Watering
Clematis should be watered about once a week. Young plants need about 10–20 liters of water per watering, and adults - about 40. For container plants up to 5 liters, it is desirable that there are drainage holes in the container. It is watered not at the root, but in a depression (40–50 cm), located at a distance of an elbow from the base of the bush. After 2-3 days after watering around the clematis, it is necessary to loosen the soil, it should be moist and crumbly. Loose soil contains air necessary to feed the roots.
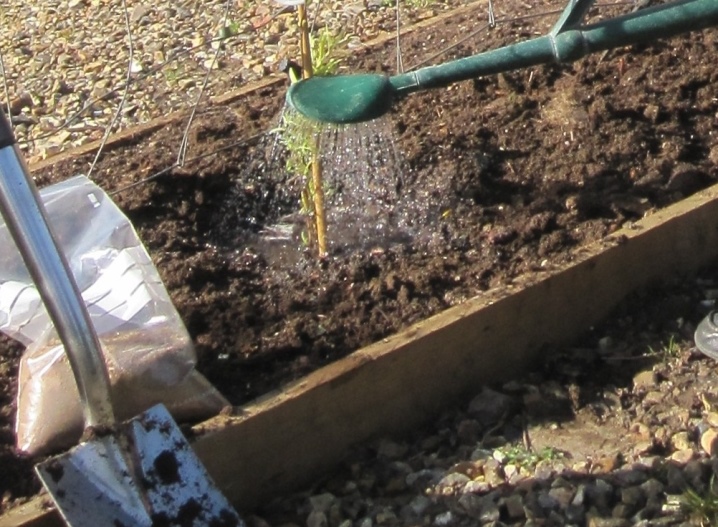

In a bush that grows for a long time in one place, the earth is compacted, and it is difficult for moisture to penetrate deep into the soil. In the hot season, up to 60 liters are poured under an adult liana. Regularity is important in watering clematis. Lack of water affects clematis: the greens turn pale and the flowers become smaller. The soil around the bush is gradually compacted so that the plant does not get sick from this, an underground watering method is recommended. To do this, dig in around the plant 3-4:
- perforated pipes;
- vertical filters filled with gravel or crushed stone, 10-15 cm in diameter;
- old pot or container.
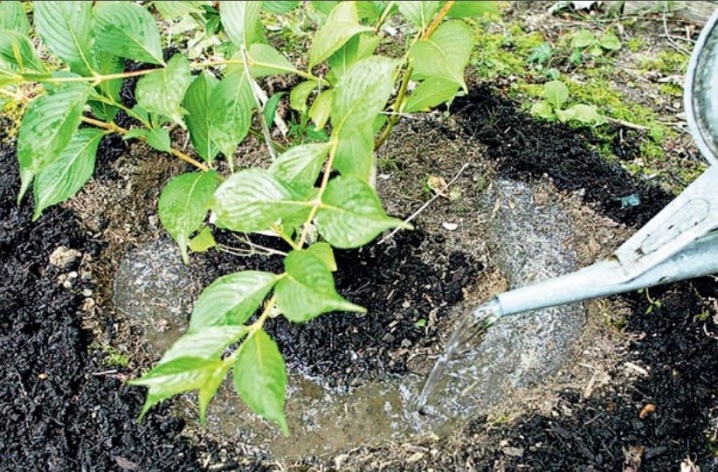

The devices are placed vertically in the ground and, when irrigated, are filled with water, which is gradually distributed around the bush, does not spread and penetrates deeply.
Top dressing
Clematis are fed about 5 times during the spring-autumn period. Fertilizers are used organic and inorganic. Usually, if the required amount of nutrients was introduced into the ground during planting, then at first they are not introduced. The lack of useful trace elements manifests itself in the appearance of plants: small leaves and flowers, few buds. Types of dressings.
- Mineral - nitrogen (stimulating the growth of stems and leaves), phosphorus and potassium (for the formation of buds). Fertilizers containing chlorine must not be used.
- Organic (urea, mullein infusion, chicken droppings).
It is not recommended to fertilize clematis with manure

Organic and mineral dressings are applied in turn. It is recommended to feed more often and in small doses, at a high concentration of substances, the roots are damaged, the plant may die. First feeding: late April or early May. Ammonium nitrate 2 g per 10 liters of water. Or scatter a handful or two near the bush. Ammonia (3 tablespoons per 10 liters) is suitable. Second feeding: after a week, organic fertilizers are applied in a ratio of 1: 10 (mullein), 1: 15 (chicken droppings), 10 g per 10 liters (urea). It is watered with milk of lime in May (100 g of slaked lime or chalk per 10 liters of water, you can use dolomite flour).

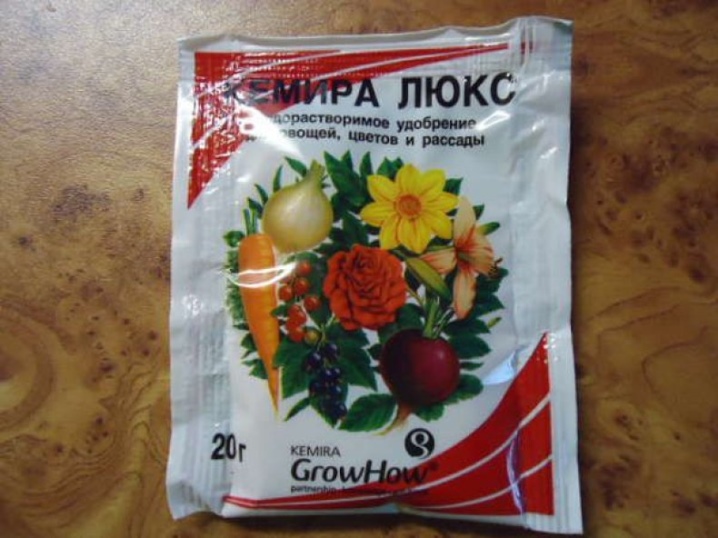
The third feeding: spend in a week or two with complex fertilizer, for example, "Kemira universal" 1 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water. Fourth feeding: before the formation of buds with phosphorus-potassium complexes. Flowering bushes do not feed, this shortens the flowering time. Fifth feeding: after pruning with complex fertilizer 1 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water. In August, 2-3 glasses of ash are brought under each bush.

Foliar treatments 3 times per season:
- urea solution (1 tbsp. l. per 20 l of water);
- a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- boric acid solution (1-2 g per 10 l).

In autumn, the roots of clematis are mulched with humus, sawdust, straw, poured with a solution of nitrogen fertilizers (50-60 g of urea or ammonium nitrate per 10 liters of water).
Cropping groups and rules
For the formation of a bush of an adult plant, an important stage is pruning. With proper pruning, clematis grow well and delight owners with abundant flowering. Different types of clematis are pruned in several ways: in some, only old and dry shoots, in others, vines are pruned, on which buds will not appear. There are three pruning groups.

1 group (A)
Pruning small, remove shoots that interfere with plant growth, old, broken, overgrown. They include clematis blooming on the shoots of the last season. After flowering, a part of the stem with a flower is cut off. There are few or no flowers on the flowers grown this year. Cover thoroughly in autumn.
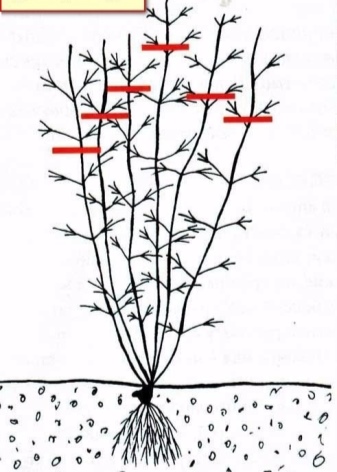

2 group (B)
Moderate pruning is carried out to evenly distribute the shoots. If necessary, remove the shoot completely. The second group includes varieties in which inflorescences appear on last year's shoots and the current year. On old flowers appear in May - June. It doesn't last long. On new ones, it blooms profusely in summer and continues until autumn. Pruned 2 times a year. After the disappearance of flowers in June, the stems with peduncles or part of the liana are cut off at a height of about a meter from the ground. The second pruning is carried out after the full end of flowering in the fall.
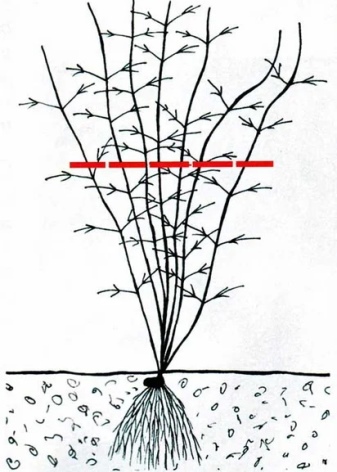

Group 3 (C)
Prune most of the plant intensively. Flowering occurs on young shoots. Bloom from July to September. Before shelter in the fall, cut off either to the first bud, or completely. The bush must be pinched for the density of the greenery, and so that the clematis branches well. Usually, the tops of young shoots are cut off or pinched off, after which two vines are formed in place of one vine. This method helps to form the decorative appearance of an adult plant.
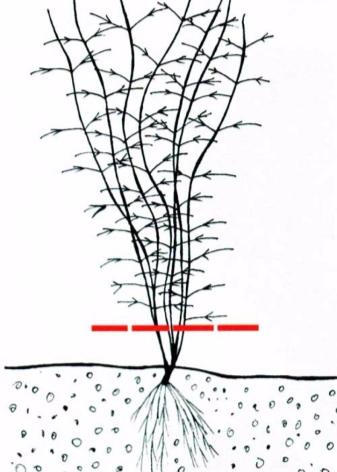

Reproduction methods
Breeding clematis in several ways:
- cuttings (green or woody);
- grafting (the cutting is implanted into the root);
- dividing the bush;
- layering;
- seeds.
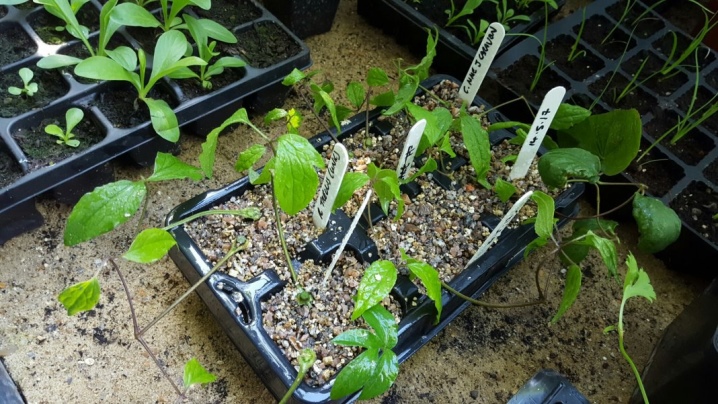

Large-flowered species can be bred vegetatively - hybrids do not produce seeds, and the resulting material does not inherit the features of varietal plants. Small-flowered and propagated by seeds. Pruning for propagation by cuttings is done in spring or June on a plant specially selected for this. Shoots are completely cut off, leaving 1–2 knots with buds from below. For the cuttings, the middle part of the shoot without buds is taken. The bush from which the cuttings were cut is fed with mineral fertilizers.


Cut shoots are cut into cuttings with one or two knots, removing the lower leaves. The upper cut is made above the knot 2 cm higher, the lower one is beveled. The rest of the leaves are cut by one third or half, if very large.
Mix for cuttings:
- coarse sand;
- vermiculite;
- perlite;
- non-acidic peat;
- sand;
- Earth.
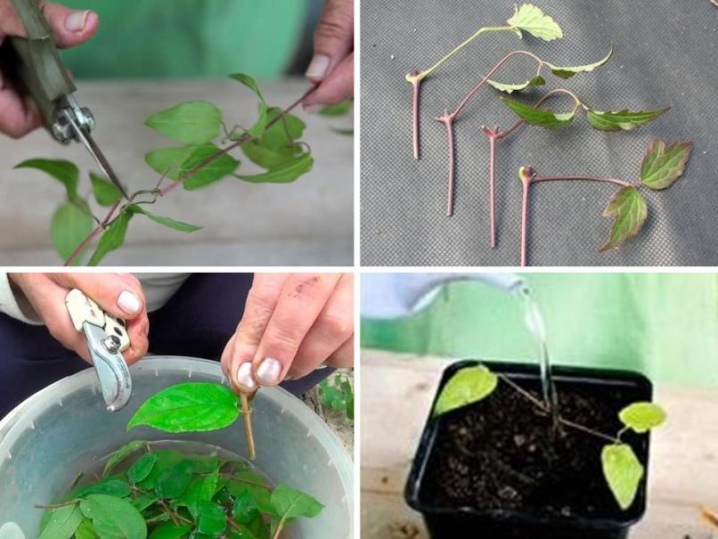

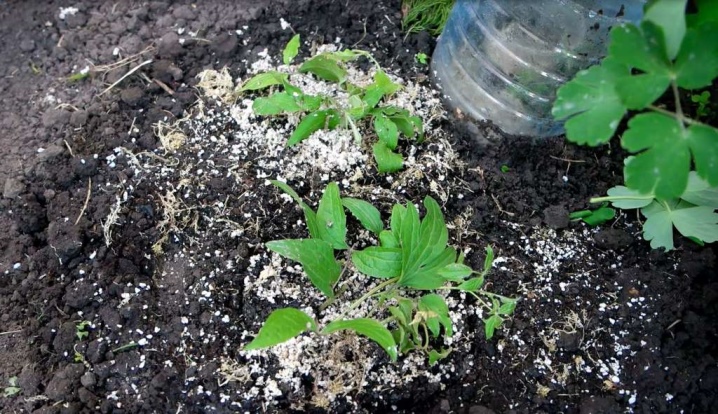
The mixture is thoroughly disinfected. Cuttings are planted straight or obliquely, leaving the buds at ground level or deepening by 2-3 mm. Recommended to be planted in a greenhouse or greenhouse. The cuttings are shaded, sprayed 2-3 times a day, ventilated, weeded, watered. The best temperature for rooting is + 18–22 C. After a month or two, rooting takes place. Shading is gradually removed. For rooting, watered with heteroauxin (1 tablet per 10 l), for the prevention of fungus "Fundazol" (1 tbsp. L. Per 8 l). In autumn, the seedlings are covered with sawdust or dry leaves, and on top with tar paper. In the spring, rooted plants are dug up and transplanted to the site.

Diseases and pests
Growing clematis, lovers of these vines are often faced with various diseases, which can be caused by fungi or pests. If a bush of an adult plant does not form buds, it is most likely sick. The most dangerous fungal diseases for clematis are wilt, gray rot, fusarium, powdery mildew, brown spot. Humidity becomes a favorable environment for the appearance.The plant is treated with fungicides in the spring-autumn period. The affected shoots are cut off, the stems, leaves and soil are treated with copper sulfate or diluted potassium permanganate.

Common aphid is considered one of the most dangerous pests. Examine young shoots, leaves on both sides, there you can find small clusters of insects. Until the aphid has filled the entire bush, it can be washed off with water or a sponge. You can plant ladybirds, lacewings, wasps on the plant for the prevention of aphids. Plant garlic and onions nearby to scare off pests with the smell.
Spraying with a vinegar solution with a spray bottle will help deal with aphid colonies. Use:
- table vinegar - 1 tsp. for 1 liter of water;
- apple - 1 tbsp. l. for 1 liter of water;
- vinegar essence - 1-2 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water.
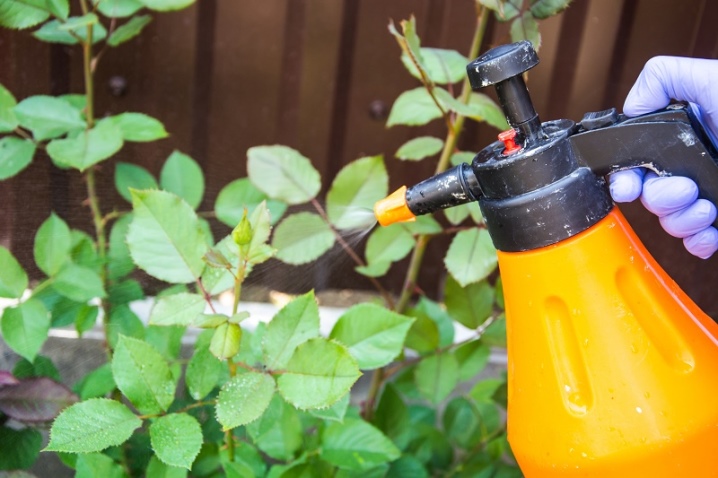

It is necessary to spray early in the morning or in the late afternoon. In case of mass distribution, the treatment for aphids is carried out with insecticides. Aphids are spread throughout the garden by ants: they transfer it from one plant to another and protect it from natural enemies. Ants are destroyed with boric acid, scattering it along the path of movement and near the anthill.
Possible problems
Clematis has light green leaves, buds have dropped, it wilted - the reasons may be different, but most likely the cause was a fungus, wilt disease. An annual fungicide treatment will help prevent this disease from occurring. In case of detection:
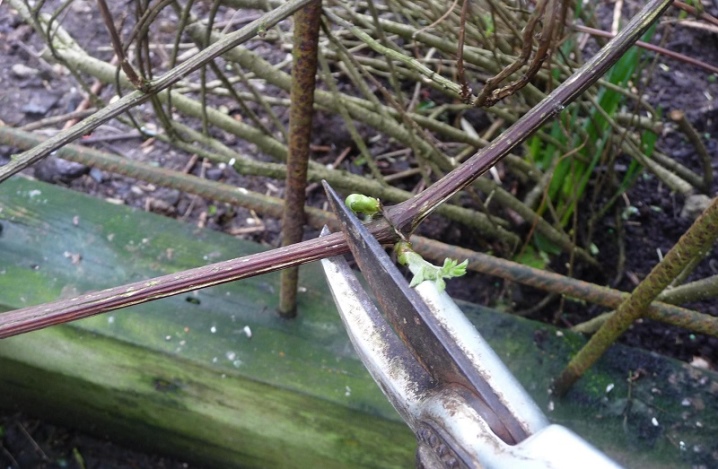
- cut off wilted stems to the root;
- the stem and the soil around it are treated with a solution of "Fundazol", a pink solution of potassium permanganate, a copper-soap solution (20 g of copper sulfate + 200 g of soap + 10 l of water).

Pale green leaves can appear from lack of sunlight if clematis grows next to trees or a fence. You should pay attention to how much time he spends in the sun, he needs at least 6 hours a day. Leaves curl on the clematis liana - most likely, this is a fungal disease ascochitosis or fusarium. The damaged parts of clematis are removed and treated: in case of ascochitis - a preparation containing copper is sprayed with "Fitosporin" or "Alirin-B" (1 tablet for 1 liter of water), in case of fusarium - "Previkur". Flowers and inflorescences curl up and dry out when clematis is affected by a fungus.


From the wind or through carelessness, the top of the creeper can break off. There are no reasons for concern, the broken off place is treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, sprinkled with crushed ash. The plant will soon begin to grow new shoots. It is not necessary to expect abundant flowering from young plants. It will come only in the third year after disembarkation. In order for clematis to bloom magnificently, it is necessary to increase the root system of the plant. The plant gains root volume well in warmed-up soil. Top dressing with a warm solution of fertilizers will well stimulate root growth in the spring.


Abundant and regular watering, feeding and pruning - all these steps will help clematis bloom profusely all summer.
How to save?
Clematis can withstand frosts down to -30 C. It is very important to properly close them in autumn and open them in spring in time. Before the shelter, the soil is dug up around the bushes so that the soil does not crack from frost, in milder climates this is done to maintain moisture. In the southern regions (where the winter temperature is above –18 C), clematis are not sheltered for the winter, they are cut off, the necessary fertilizing is applied and a layer of dry earth is earthed. In the middle lane - Central Chernozem, Non-Black Earth and further north - the plants are covered after the onset of frost in dry weather in late October - early November. Previously, they do not cover, the plants may die.
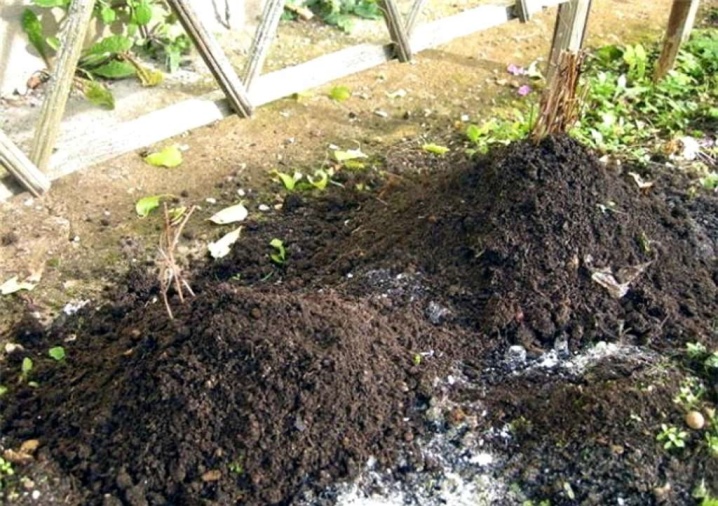

Clematis blooming on the shoots of this season, cut off to 2-4 pairs of buds, cover with a box or container (compact species), tar paper or roofing felt; dry soil, peat, humus, sand, sawdust, dry foliage are distributed on top (1-2 buckets per bush). After a snowfall, the top is covered with a layer of snow. A cover of 20–25 cm will help plants to endure frost down to –30 C and higher. Clematis vines, which bloom in spring on overwintered shoots, are carefully removed from the supports. Unviable ones are removed, and the rest are cut by a third. They are laid in a row or in a ring near a bush on brushwood or spruce branches. Cover with spruce branches or brushwood from above, and then with a material that does not allow water to pass through (boards, roofing felt, roofing felt, thick film). Sawdust, earth, peat or snow are poured on top.

Colds are not so terrible for clematis as excess waterlogging. Covering bushes for the winter, it is better not to do the flooring close to the ground. They put low arches or reinforcement structures above the bed. With the onset of the first spring thaws, holes are made for ventilation. They remove the shelter gradually: first, a layer of earth and sawdust, and then boards or roofing material. They do this when the night temperature ceases to fall below -5 C.

Tips for Beginners
When choosing clematis for the garden and having no experience in growing these plants, it is better to pay attention to the features of care: pruning group, frost resistance, flowering period. For beginner clematis growers, it is recommended to select varieties that almost do not require pruning, that is, the first group (A). Unpretentious varieties: "Ville de Lyon", Jacquemana, "Heigly Hybrid", "Justa", "Marmari".
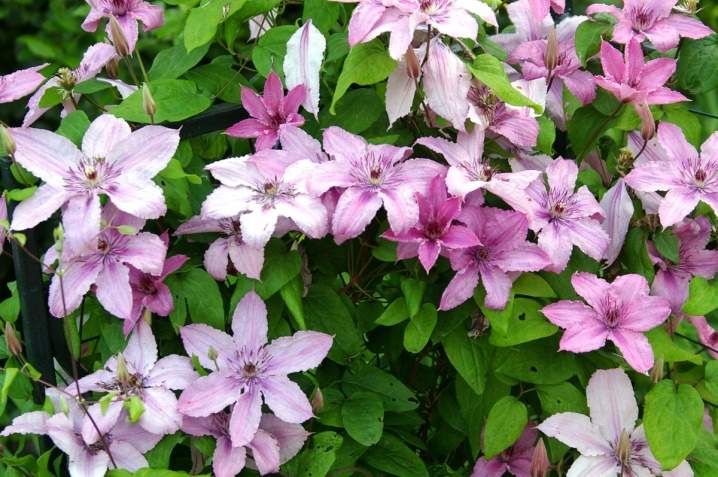

It is optimal to choose biennial plants with a closed root system (in a container). It is necessary to ensure that there is no rot on the roots and drooping foliage.
When buying a young plant in early spring, you will have to wait for a suitable time for planting. The container is placed on a sunny windowsill, the soil in the pot is disinfected with fungicides and insecticides. Spray with Epin solution. The roots are fed with vermicompost. They are planted after the end of frost only in warm soil. The plant is taken out to the site and left for several days in the shade for adaptation. Then they are planted in open ground.

Examples in landscape design
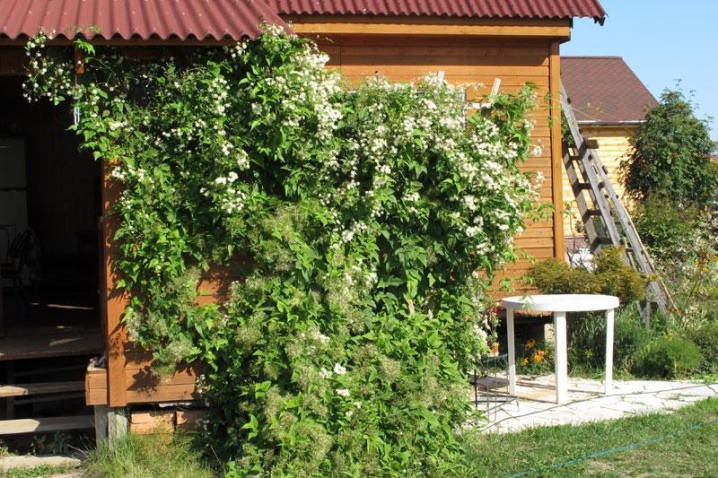
In a short time, clematis vines cover the walls and fences with a lush flowering cover.


Regular mesh fencing will turn into a hedge with vibrant colors.


The plot, entwined with a beautifully climbing plant, will be transformed and will amaze during the flowering period.



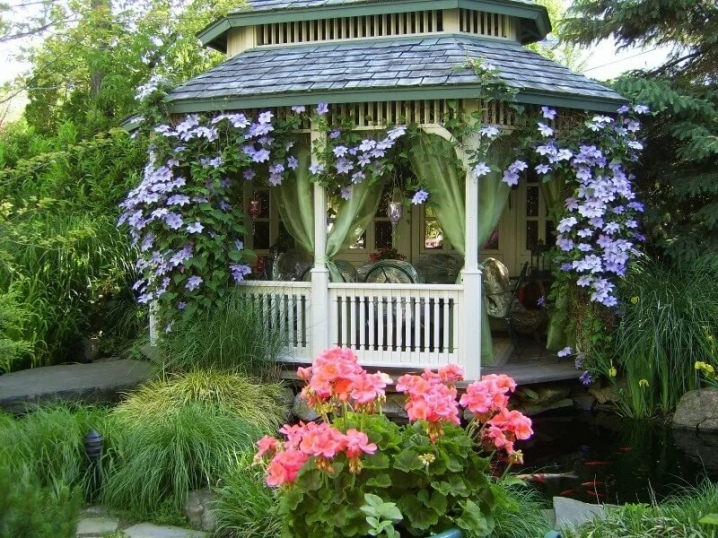
A porch or window decorated with clematis will turn the house into an extension of the garden.




On a hot afternoon, a gazebo or a veranda entwined with clematis will create a cool shade, and bright and fragrant flowers will become a magnificent decoration for more than one year.



It is recommended to plant from the north side, shading the roots with irises, marigolds, calendula, cinquefoil. In tandem with liliaceae, he creates amazing compositions.


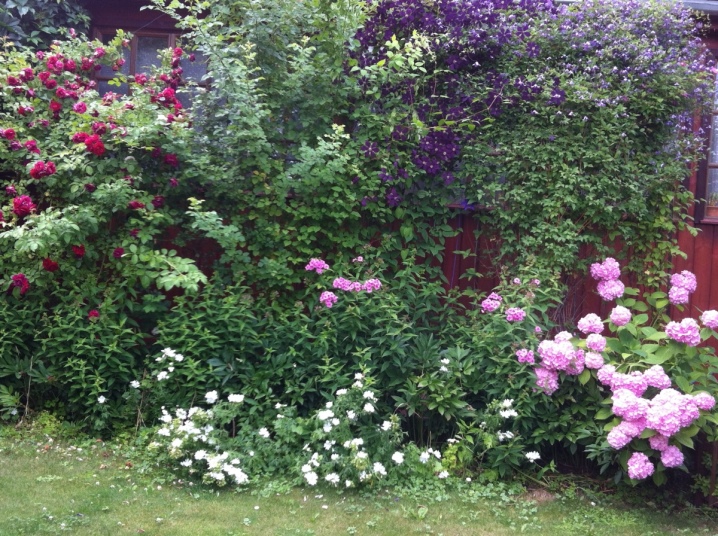
The combination of clematis and rose is considered traditional for the English front garden; clematis looks no less impressive next to the hydrangea.

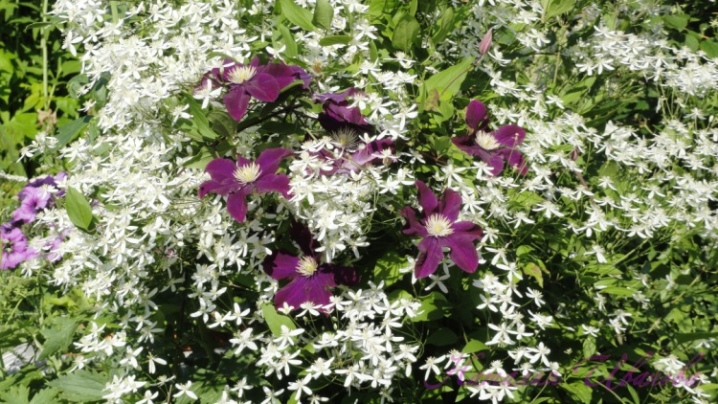
Small-flowered and large-flowered varieties of clematis grow well with each other.

For information on how to properly plant clematis with your own hands, see the next video.







































































































Thanks! It will come in handy!
The comment was sent successfully.