Clematis grape-leaved: description, planting and care, reproduction

Decorative grape-leaved clematis is often used for landscaping a garden or personal plot. Many are interested in how to care for it, plant and propagate it.
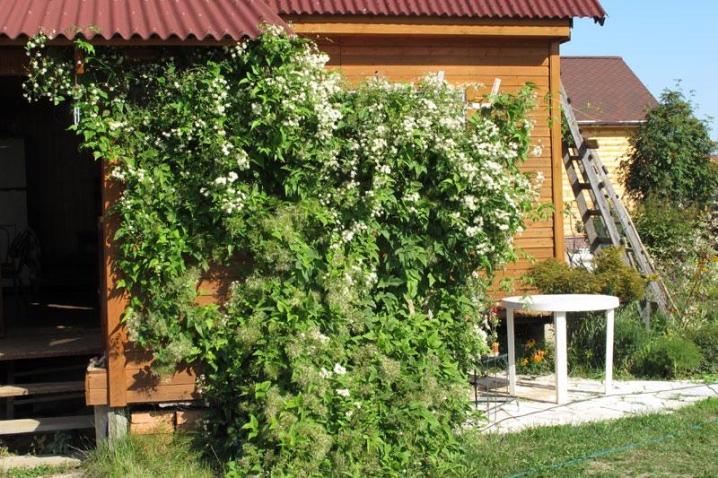

Description
Grape-leaved Clematis belongs to the genus Lomonos of the Buttercup family. The shrub resembles a liana. Elongated cuttings of ribbed leaves curl, helping the branches to grasp the base of any support and catch on to it. For its ability to curl, the plant received the definition "grape-leaved".
A climbing plant is used to decorate gazebos, terraces, and various fences. It perfectly hides various building flaws. The shrub provides additional shade, bringing coolness in hot, dry summers.
In nature, there are 2 forms of a wild plant: herbaceous and semi-handicraft clematis. Herbaceous shoots die off after the vegetative period, only the roots remain. The semi-artisan type tolerates wintering well.
The root system of a given culture is of two types:
thin rod;
branched fibrous.



The roots are located in the upper layers of the soil. A plant with the first type of root system does not like transplanting. The culture must be immediately placed in a permanent place.
The stems of the shrub are thin flexible twigs with dark brown cracked bark. Many young shoots appear on them every year. In one season, the bush can grow strongly.
Complicated pinnate leaves consist of five or three lobes. An egg-shaped dark green leaf with a rounded base and a sharp end resembles a heart. Large denticles are sometimes located along the edge. Smooth or slightly pubescent leaves can have a length of 3 to 10 cm, a width of 3 to 4.5 cm. Flowering begins 3 years after planting.
Buds are formed only on young shoots. The white flowers have a light aroma reminiscent of the delicate scent of almonds. Their diameter is usually 2 cm. Asexual flowers are collected in paniculate inflorescences on long legs, which sometimes reach 12 cm. Flowers have the appearance of an asterisk. The core is covered with numerous yellow stamens and surrounded by 5 or 6 petals. Flowering occurs in June-July and can last until the end of September.
At the end of flowering, fruits appear, collected in maned heads. Their edges are thickened, a feathery, pubescent nose can be 4 cm. Brown elongated seeds reach 7 mm in length and 4 mm in width. The fruits remain on the branches for a long time.



Landing
Of no small importance is the choice of a place for planting a plant. The intensity of flowering and the development of culture depend on this. A light-loving shrub requires the presence of a shade, otherwise the leaves in the sun burn and turn yellow. He needs to provide protection from drafts and winds. The culture tolerates gas pollution and smoke well.
You need to plant shoots in September-October. In areas with cold winters, it is best to plant seedlings in early spring.
First you need to prepare the soil. It must necessarily contain sand, peat, humus in equal proportions (about 20% each). The resulting mixture is poured into the dug soil (30%). Then chalk, ash and complex mineral fertilizer should be added. Crushed stone is used as drainage.
The prepared soil is placed in a pre-dug hole. Its length, width and depth are about half a meter. Saplings are placed at a distance of at least a meter from other bushes. They are dropped into a hole to a depth of 15 cm, then watered and mulched with a layer of sawdust. Cover the sprouts at low night temperatures.



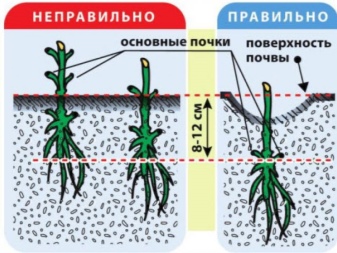
Care
An unpretentious shrub does not require much attention. He needs moist soil, but excess moisture is undesirable. Water it as needed. On hot and dry days, abundant watering is carried out every 3-5 days. Pour 2 buckets of water under the plant. The strong jet should not hit the center of the bush.
Annual plants and flowers planted nearby help to maintain moisture and coolness. The shrub adjoins beautifully with a climbing rose.
In order to avoid rotting in wet weather, it is necessary to inspect the lower part of the shrub. Putrefactive processes contribute to the death of culture. To eliminate rot after the soil has dried, antifungal agents are used. Then the soil is sprinkled with ash.
Top dressing is done in early spring with a solution of lime: 1 glass per bucket of water. This amount is enough to fertilize 3 bushes. Then carefully loosen the ground and sprinkle it with sawdust. In the spring, fertilize with chicken manure in combination with nitrogen agents.
From May to August, once a month, complex mineral fertilizers are alternated with organic means: manure mixed with water. Before the formation of buds, phosphorus and potash fertilizers are applied, then there will be a lot of lush inflorescences. In the fall, use humus and mullein.
It is recommended to prune the shrub 2 times a year. In the spring, the procedure is carried out before the appearance of the kidneys. Spring and autumn pruning gives the plant a neat appearance and a beautiful shape. Weeds are removed as needed.



Protection against diseases and pests
Despite resistance to various diseases, the crop can sometimes be exposed to rust, root rot and powdery mildew.
Rust is characterized by the appearance of spots on the leaves. The infection spreads quickly. In a short period of time, the entire bush becomes covered with spots. The treatment is carried out with copper sulfate. It is recommended to remove damaged branches.
Root rot is caused by too moist soil. It is necessary to thoroughly dry the ground, constantly loosen it and follow the rules of watering.
Powdery mildew can be recognized by a gray coating on the leaves, which is removed with Bordeaux liquid or soapy water.



Sometimes the bushes are overpowered by pests.
Aphids feed on the juice of young shoots and leaves, cover the culture with a specific sticky layer that provokes fungal diseases. It can be exterminated by spraying with soapy water.
A spider mite enmeshes the leaves and shoots with cobwebs, affecting the entire bush. The mite is recognized by the black dots on the foliage. The insect is destroyed with Fitoverm and Actellik preparations.


Reproduction
The plant reproduces in several ways.
The seeds are sown in early spring. First, they are soaked in warm water, then planted in a container with a nutrient mixture. After emergence, the seedlings are dived and transferred to the greenhouse. There she is left for a whole year. The seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place in the open ground next spring.
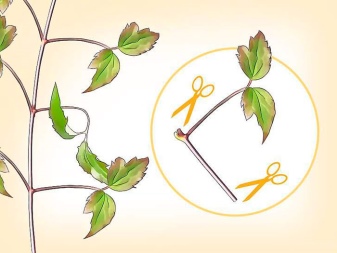
Clematis is propagated by cuttings 10-15 cm long in about July. First, the petioles are placed in a vessel with "Kornevin" for a day, then planted in a container with a nutrient mixture. A year later, they are planted in open ground.
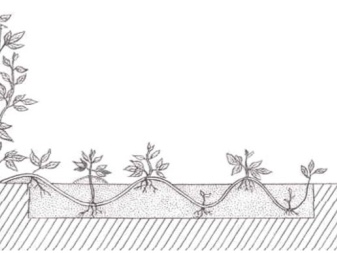
By layering, reproduction is carried out in the middle of summer. The shoot is tilted to the ground, fixed with something and left to germinate.
The division of the bush is carried out in late autumn or early spring. A part, together with the root, is separated from the adult mother bush with a sharp shovel. The damaged root segment is sprinkled with ash and treated with a solution of potassium permanganate. After planting in the soil, watering with warm water is necessary.


See below for more details.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.