Planting and caring for clematis in the Urals

Decorating a garden with flowers is a useful activity. It gives spiritual satisfaction to the owner of the site. When you are surrounded by a variety of colors, then life becomes better. Plants such as clematis are able to enrich the world around us with indescribable beauty. There is no person who would not like the arch, where large and bright flowers make their way through the green foliage in lush color. This is how clematis grows.
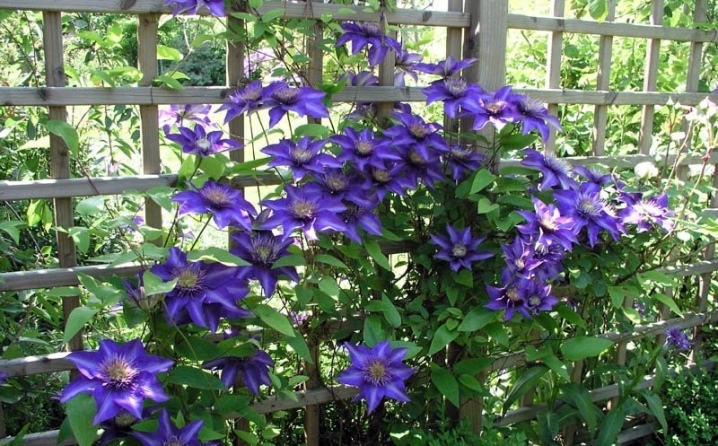

Features of growing in the Urals
Clematis is an attractive plant that is suitable for vertical garden landscaping. The twining branches perfectly highlight the beauty of roses and other flowering plants. The birthplace of clematis, or as it is also called in Latin Clematis, is Asia, Europe, North and South America, Australia. This plant belongs to the buttercup family.
About 300 varieties of clematis can take root in the garden of ordinary people. This type is used to decorate fences, gazebos, arches, etc. The rest of the varieties need careful care. They are botanical varieties. Among summer residents and owners of personal plots, hybrids with large flowers are very popular.
Clematis can bloom in spring, summer and fall. It all depends on the variety. Pruning of these plants is related to the flowering time. For example, autumn varieties require pruning in the spring, others in the fall. Absolutely all varieties of clematis grow like this: the root and root parts should be in the shade, and the rest in the sun.
Liana has stems (they grow stiff over time) and flexible shoots. There are bush forms (up to 1.5 m), and there are curly ones (over the summer they grow up to 3 m). The plant is perennial and is distinguished by trifoliate, ovate, linear-lanceolate, and also simple leaves. The length of the leaves ranges from 4 to 10 cm, depending on the species.



Flowers differ in different colors and large sizes. They can reach 20 cm. There are also small-flowered clematis. But they are less popular, since not all species take root well in a particular environment and have some high requirements for growing.
Based on general information, it becomes clear that clematis can grow well in the Urals, and even more so in the South Urals. It is necessary to discard the statements that clematis grow only in warm places. They perfectly tolerate low temperatures. To grow thermophilic flowers in harsh conditions, where there is uneven rainfall and there are sharp temperature changes, you just need to choose a variety that has been adapted by breeders to adverse weather conditions.
These should be winter-hardy hybrid varieties. These species must be properly planted and properly cared for. Then on your site, even after the longest and frosty winter, clematis will bloom and give you a good mood for the whole summer.


Which variety should you choose?
Of course, if you are determined to grow thermophilic and delicate plants in the Urals, you need to master all the information. Therefore, know that first, as a result of selection work in 1860, a large-flowered hybrid "Jacqueman" appeared. He combined 3 wild species at once. This is what gave impetus to the further emergence of other varieties. Now there are more than 2000 of them.
To successfully grow clematis in the Urals, take those hybrids that belong to the second and third pruning groups. However, these species require careful maintenance.In especially harsh winters, it is necessary to cover their roots with special material. So, let's consider what kind of plants can take root in very difficult conditions.
Easiest to grow in colder climates such varieties as Mrs Cholmondeley ("Mrs. Cholmondeli"), Blue Light ("Blue Light"), "Rouge Cardinal" (Rouge Cardinal). July is the month of abundant flowering varieties "Purpurea Plena Elegance"which has a second clipping group.




There is a special group of clematis - this varieties "Gray", "Vititsella", "Pilchatolistny", "Jackman", "Tunguska", "Virginsky", "Short-tail", "Woolly"that are resistant to -30 degrees. The most hardy is recognized Ville de Lyon variety ("Ville de Lyon")... This plant stands out with long shoots up to 4 m and an abundance of carmine flowers.




There are also those specimens that can overwinter in the Urals, or they may die. They grow and develop rather sluggishly due to negative factors. However, those who are not afraid of the difficulties of growing should try to get Japanese hybrids on their site - this is Kaen ("Kaen"), Little Mermaid, ("Little Mermaid"), Kakio ("Kakio")... There are varieties of clematis that do not lend themselves well to cultivation, and their flowering is very poor in the Urals - this is Alba Plena ("Alba Captivity"), Daniel Deronda ("Daniel Deronda"), Jeanne dArc ("Jeanne Dark).




These are shrubby clematis with a height of about 2.5 m. Whole-leaf clematis hybrids ("Integrifolia") acceptable for the Urals. This plant has 11-centimeter bell-shaped flowers in diameter. With the onset of frost, it requires pruning.


There are large-flowered vines (bush form). They have shoots up to 5 cm and attractive feather-shaped leaves. it Zhakman hybrids... The root system is well developed. That is why they do not need special costs and efforts for care. Usually their flowering is long-lasting and abundant. In order for the plant to winter well, the branches are eliminated.
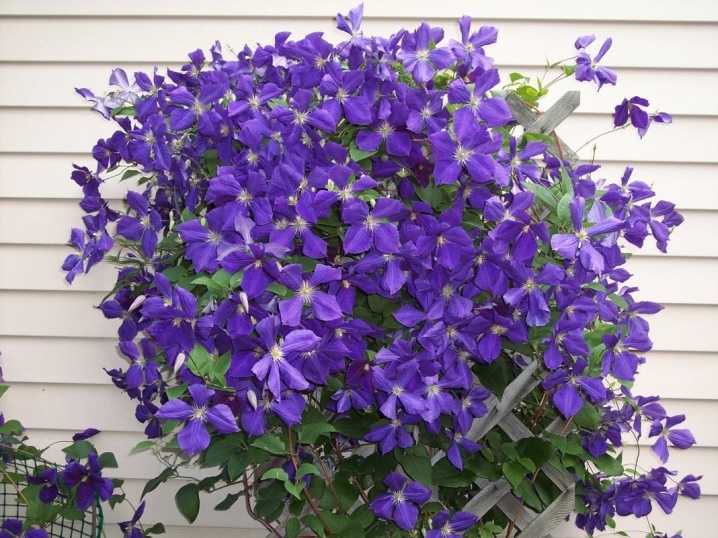

There are also such specimens, whose shoots are cut for the winter to the ground. They are adapted to the fourth climatic zone and give a good lush color in these parts. This category includes unpretentious representatives of clematis - these are Ernest Markham ("Ernest Markham"), "Prince Charles" (Prince Charles), Hagley Hybrid ("Hegley Hybrid").



- The bush-shaped climbing plants are hybrids of lilac clematis. They have shoots of about 3-4 m, the leaves are complex, the flowers are large, their diameter reaches 12 cm. Up to 100 flowers can form on one plant. Their color range is unusual. Mostly purples, pinks and reds predominate. Flowers are formed on the shoots, which are completely removed with the onset of cold weather.


Clematis differ from each other in a variety of shapes and colors. However, they are all divided into:
herbaceous perennials;
shrubs, semi-shrubs;
lianas.



If you like dwarf shrubs with clematis, know that they include whole-leaved and hogweed specimens. After winter, these clematis retain only a part of the shoots, which has become stiff, and the uppermost tender part dies off in winter.
Tree branches of the lobed and Tangut varieties winter well. The most beautiful species are vines. They need support. This includes a large group of species. As we already know, not everyone takes root well in the Urals.
In specimens such as herbaceous perennial clematis, the tops dry completely for the winter, but the roots remain. In spring, the plant recovers and sprouts green. Grape-leaved, pungent and straight - these varieties have a short dormancy. They will be able to survive twenty degrees of frost. If the temperature drops below, these specimens will not survive.
Not paying attention to this factor, store employees still offer them for sale, not considering that in some regions these plants will die.

Landing dates and rules
To plant the plant correctly, you need to prepare the hole in advance.Ideally, it should be about a meter in diameter. But if your soil is not fertile, then dig a hole wider so that you can also put organic fertilizers in it. It is this fertilizer that will protect the roots of young clematis from freezing in winter.
The ideal time for planting clematis in the Urals is spring. Store-bought seedlings require a special approach. These plants may not be adapted to your climate and therefore need help to thrive. At first, they must be protected from the wind and provided with sunlight and heat. To do this, choose seats for landing that will meet the above requirements.
The presence of groundwater in your garden suggests that drainage needs to be placed at the bottom of the pit. For this, broken brick or coarse gravel are suitable. If the soil is still heavy and acidic, then it is better to make a soil mixture, which subsequently needs to be sprinkled with a hole with roots. Distribute in equal proportions and then mix the sand and soil. Add a little lime and fertilizer to the mixture (mix humus and superphosphate). Plant the seedling about 8 cm deep and leave a hole around it.

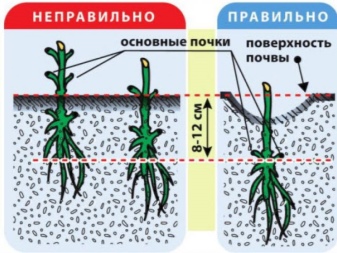


How to grow?
To ensure proper care, water the plant abundantly after planting outdoors (3 buckets per week). It is advisable to mulch the hole and protect your clematis from the burning sun. Make supports near it with a height of 2-3 m (they should be beautiful and strong). As soon as the young plant begins to release shoots, tie them up.
If you want a lush bloom, then provide the plant with feeding. Water clematis with water mixed with mineral fertilizers (35 g per 10 liters) once a week. Can be fed with mullein and wood ash. Please note that the roots will develop in the first 2 years. There will be few shoots, flowers too, they need to be cut off. The plant gains beauty for 5 years.


Diseases and pests
The plant is resistant to diseases. However, it must be remembered that it is better to prevent the disease than to cure it later. Therefore, loosen the soil in time, remove weeds, water and feed your clematis. Correct action in the spring prevents the development of diseases in plants and the appearance of parasites on them. What to do:
- The mulch layer is removed after winter. This composition may contain parasites.
- The most effective preventive method is Bordeaux mixture in 2% concentration. Spray the clematis before flowering.
- Apply nitrogen fertilizers in early spring no more than 2 times a month.
- Spraying with fertilizers (diluted in a double portion of water) is combined with soil dressings.

With the onset of an unfavorable season (rainy, cold summer), the plant can get sick. You need to be aware of this in order to take action in time. So, let's list the diseases of clematis.
The viral disease is a yellow mosaic. It occurs extremely rarely. Infection occurs from pests. Their destruction promotes healing.
Brown, brown spots are ascochitis (fungal disease). Against it, it is recommended to sprinkle ash around the plant and use other antifungal measures.
Microscopic fungus - verticellous wilting. Shoots wither, leaves darken. If an infection has occurred, urgently remove the dying shoots.
The disease begins in May. Rounded brown or yellow spots appear - this is Phomopsis wilting, very dangerous for hybrids. Treat the plant with Previkur.
If small orange bumps are found in the spring, this is rust. Her spores are airborne. The plant may die. Therefore, remove weeds, especially wheatgrass. Treatment must be carried out with fungicides: "Abiga-Peak", "Cumulus", "Poliram", "Strobi".
Powdery mildew is a white coating. Clematis is especially vulnerable in southern climates. Spray it with mustard or salicylic acid.




With a lack of light or during the rainy season, gray rot may develop on the plant. Brown spots lead to the death of leaves. Treatment is carried out with fungicides. Along with this, it is necessary to take preventive work throughout the site so that there is no contamination of other plants.
Some parts of clematis contain bitterness and even poisonous substances. Therefore, it is not very attractive to insects. However, this plant also has enemies.
Medvedki. They pose the greatest danger to young plants. The insect is able to plow the ground near the seedlings and destroy the roots. For adult plants, this threat is also terrible. Damaged roots can get sick. Therefore, it is necessary to fight the bear. Periodically pour soapy water into the holes or bury porridge with a special poison for bears in the ground.
There are worms that parasitize on the roots. These are nematodes (especially dangerous for clematis). Their appearance leads to thickening of the roots. This creates an obstacle to the nutrition of the plant. Clematis begin to develop poorly. There are no special methods for eliminating worms. Parts of the affected bush are removed and simply burned. The fight against this harmful phenomenon must take place during landing. Treat the hole with boiling water before planting clematis. Subsequently, continually mulch the soil around the plant. This method allows you to drive away not only worms, but also other pests.
A sticky web has appeared - this is a spider mite. After infection, shoots and leaves dry out. The plant becomes infected in dry and hot weather. To eliminate the pest, it is necessary to spray it with Aktellik, Akarin, Antiklesch insecticides. And remember that spraying with garlic can only be a preventive method.
From spring to autumn, snails are often disturbed by clematis. Therefore, remove weeds in the area on time. And the method of dealing with snails is ash or superphosphate. An effective measure is scattering of "Metaldehyde" or "Ferramol" granules.
Aphids harm all plants, and clematis too. Its larvae can hibernate in plants. You can identify the pest by sticky bloom.




To get rid of it, you need to treat the leaves with soapy water or dishwashing detergent mixed with water.
For planting and growing clematis, see the next video.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.